Abs Function - Derivatives and Gradients {导数和梯度}
- [1. Abs (Absolute Value) Function](#1. Abs (Absolute Value) Function)
-
- [1.1. Parameters](#1.1. Parameters)
- [1.2. Keyword Arguments](#1.2. Keyword Arguments)
- [2. Abs Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)](#2. Abs Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度))
-
- [2.1. PyTorch `torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor`](#2.1. PyTorch
torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor) - [2.2. PyTorch `torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor`](#2.2. PyTorch
torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor) - [2.3. Python Abs Function](#2.3. Python Abs Function)
- [2.4. Python Abs Function](#2.4. Python Abs Function)
- [2.1. PyTorch `torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor`](#2.1. PyTorch
- References
1. Abs (Absolute Value) Function
torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.abs.html
torch.absolute(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.absolute.html
Alias for torch.abs().
Computes the absolute value of each element in input.
The absolute value of a number is the number without a sign.
sign [saɪn]
v. 签名;签署;叹息;预示
n. 符号;信号;表示;招牌The definition of the Abs function:
out i = ∣ input i ∣ \text{out}{i} = |\text{input}{i}| outi=∣inputi∣
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x x x, denoted ∣ x ∣ |x| ∣x∣, is the non-negative value of x x x without regard to its sign. Namely, ∣ x ∣ = x {\displaystyle |x|=x} ∣x∣=x if x {\displaystyle x} x is a positive number, and ∣ x ∣ = − x {\displaystyle |x|=-x} ∣x∣=−x if x {\displaystyle x} x is negative (in which case negating x {\displaystyle x} x makes − x {\displaystyle -x} −x positive), and ∣ 0 ∣ = 0 {\displaystyle |0|=0} ∣0∣=0.
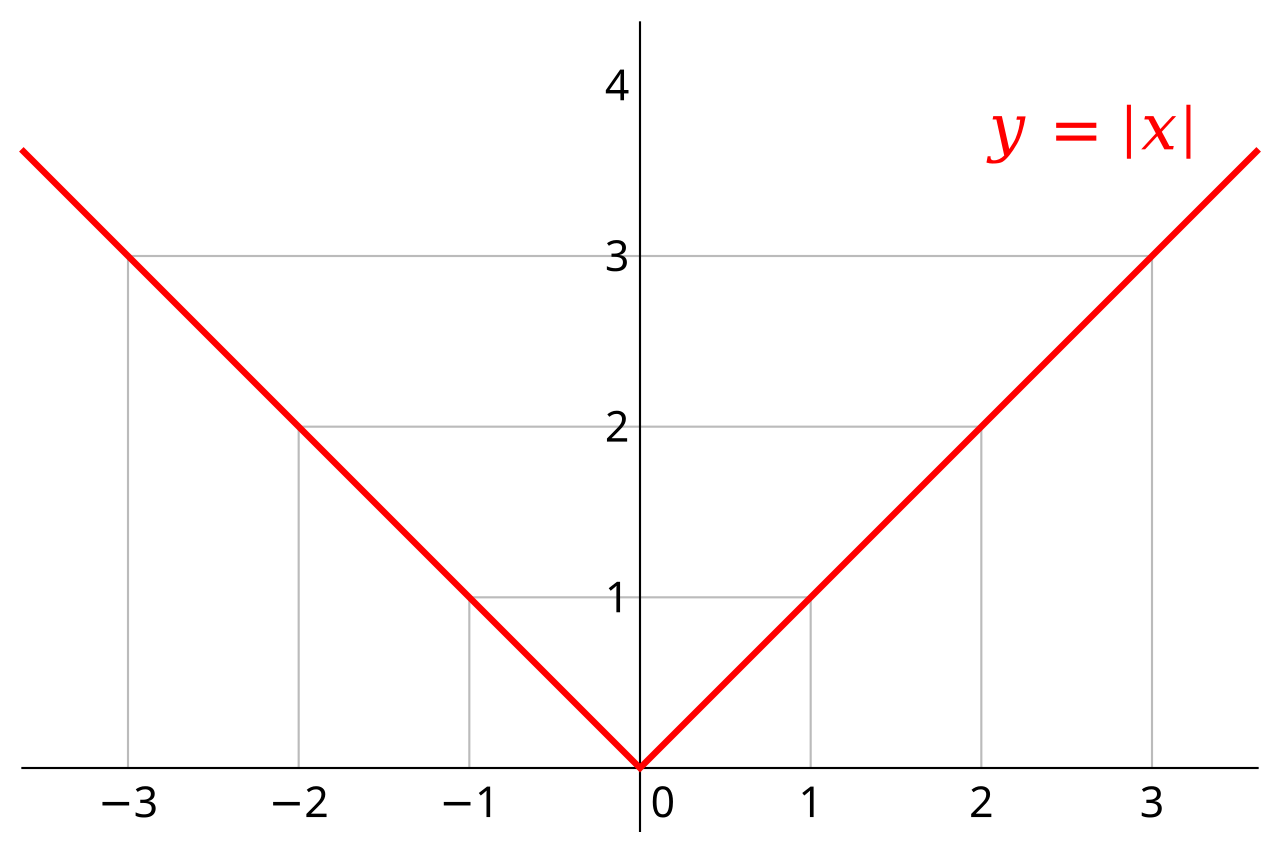
Abs ( x ) = ∣ x ∣ = { x , x ≥ 0 − x , x < 0 \begin{aligned} \text{Abs}(x) &= |x| \\ &= \begin{cases} x, & x \geq 0\\ -x, & x < 0\\ \end{cases} \\ \end{aligned} Abs(x)=∣x∣={x,−x,x≥0x<0
The absolute value of x {\displaystyle x} x is thus always either a positive number or zero, but never negative. When x {\displaystyle x} x itself is negative ( x < 0 {\displaystyle x<0} x<0), then its absolute value is necessarily positive ( ∣ x ∣ = − x > 0 {\displaystyle |x|=-x>0} ∣x∣=−x>0).
The absolute value function of a real number returns its value irrespective of its sign, whereas the sign (or signum) function returns a number's sign irrespective of its value.
实数的绝对值函数返回该数的数值,而不考虑其正负号;而符号函数或正负号函数返回该数的正负号,而不考虑其数值大小。
The following equations show the relationship between these two functions:
∣ x ∣ = x sgn ( x ) , {\displaystyle |x|=x\operatorname {sgn} (x),} ∣x∣=xsgn(x),
or
∣ x ∣ sgn ( x ) = x , {\displaystyle |x|\operatorname {sgn} (x)=x,} ∣x∣sgn(x)=x,
and for x ≠ 0 x \neq 0 x=0,
sgn ( x ) = ∣ x ∣ x = x ∣ x ∣ . {\displaystyle \operatorname {sgn} (x)={\frac {|x|}{x}}={\frac {x}{|x|}}.} sgn(x)=x∣x∣=∣x∣x.
The derivative of the Abs function:
d y d x = f ′ ( x ) = d ( { x , x ≥ 0 − x , x < 0 ) d x = { 1 , x > 0 0 ( common convention ) , x = 0 − 1 , x < 0 \begin{aligned} \frac{dy}{dx} &= f'(x) \\ &= \frac{d \left( \begin{cases} x, & x \geq 0\\ -x, & x < 0\\ \end{cases} \right) }{dx} \\ &= \begin{cases} 1, & x > 0\\ 0 \ (\text{common convention}), & x = 0\\ -1, & x < 0\\ \end{cases} \\ \end{aligned} dxdy=f′(x)=dxd({x,−x,x≥0x<0)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧1,0 (common convention),−1,x>0x=0x<0
The derivative is undefined at x = 0 x=0 x=0. In practice, deep learning frameworks like PyTorch or TensorFlow return 0 0 0 at this point.
The derivative is the sign function. At x = 0 x=0 x=0, the derivative is technically undefined, but frameworks typically default to 0 0 0.
1.1. Parameters
- input (Tensor) - the input tensor.
1.2. Keyword Arguments
-
out (Tensor, optional) - the output tensor.
!/usr/bin/env python
coding=utf-8
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as pltdef plot(X, Y=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=[], xlim=None, ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear',
fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), figsize=(3.5, 2.5), axes=None):
"""
https://github.com/d2l-ai/d2l-en/blob/master/d2l/torch.py
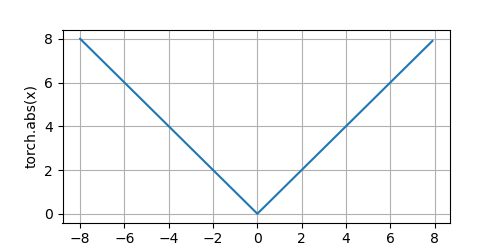
"""def has_one_axis(X): # True if X (tensor or list) has 1 axis return ((hasattr(X, "ndim") and (X.ndim == 1)) or (isinstance(X, list) and (not hasattr(X[0], "__len__")))) if has_one_axis(X): X = [X] if Y is None: X, Y = [[]] * len(X), X elif has_one_axis(Y): Y = [Y] if len(X) != len(Y): X = X * len(Y) # Set the default width and height of figures globally, in inches. plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = figsize if axes is None: axes = plt.gca() # Get the current Axes # Clear the Axes axes.cla() for x, y, fmt in zip(X, Y, fmts): axes.plot(x, y, fmt) if len(x) else axes.plot(y, fmt) axes.set_xlabel(xlabel), axes.set_ylabel(ylabel) # Set the label for the x/y-axis axes.set_xscale(xscale), axes.set_yscale(yscale) # Set the x/y-axis scale axes.set_xlim(xlim), axes.set_ylim(ylim) # Set the x/y-axis view limits if legend: axes.legend(legend) # Place a legend on the Axes # Configure the grid lines axes.grid() plt.show() plt.savefig("yongqiang.png", transparent=True) # Save the current figurex = torch.arange(-8.0, 8.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.abs(x)
plot(x.detach(), y.detach(), 'x', 'torch.abs(x)', figsize=(5, 2.5))Clear out previous gradients
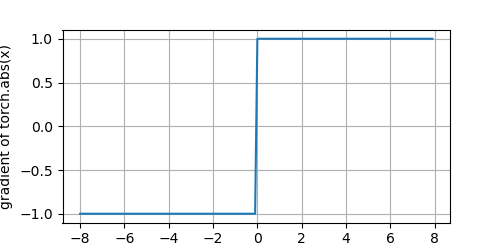
x.grad.data.zero_()
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x), retain_graph=True)
plot(x.detach(), x.grad, 'x', 'gradient of torch.abs(x)', figsize=(5, 2.5))
The Abs function:
The derivative of the Abs function:
2. Abs Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)
Notes
- Element-wise Multiplication (Hadamard Product) (
*operator ornumpy.multiply()): Multiplies corresponding elements of two arrays that must have the same shape (or be broadcastable to a common shape). - Matrix Multiplication (Dot Product) (
@operator ornumpy.matmul()ornumpy.dot()): Performs the standard linear algebra operation that requires specific dimension compatibility rules. (e.g., the number of columns in the first array must match the number of rows in the second).
2.1. PyTorch torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6)
input = torch.tensor([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
print(f"input.requires_grad: {input.requires_grad}, input.shape: {input.shape}")
forward_output = torch.abs(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
forward_output.backward(torch.ones_like(input), retain_graph=True)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {input.grad.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{input.grad}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/abs.py
input.requires_grad: True, input.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
forward_output.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
Forward Pass Output:
tensor([[1.500000, 0.000000, 1.500000],
[0.500000, 2.000000, 3.000000]], grad_fn=<AbsBackward0>)
backward_output.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
Backward Pass Output:
tensor([[-1., 0., 1.],
[ 1., -1., 1.]])
Process finished with exit code 02.2. PyTorch torch.abs(input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]) -> Tensor
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6)
input = torch.tensor([-1.5, 0.0, 1.5, 0.5, -2.0, 3.0], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
print(f"input.requires_grad: {input.requires_grad}, input.shape: {input.shape}")
forward_output = torch.abs(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
forward_output.backward(torch.ones_like(input), retain_graph=True)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {input.grad.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{input.grad}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/abs.py
input.requires_grad: True, input.shape: torch.Size([6])
forward_output.shape: torch.Size([6])
Forward Pass Output:
tensor([1.500000, 0.000000, 1.500000, 0.500000, 2.000000, 3.000000],
grad_fn=<AbsBackward0>)
backward_output.shape: torch.Size([6])
Backward Pass Output:
tensor([-1., 0., 1., 1., -1., 1.])
Process finished with exit code 02.3. Python Abs Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class AbsLayer:
"""
A class to represent the Abs layer for a neural network.
"""
def __init__(self):
# Cache the input for the backward pass
self.input = None
def forward(self, input):
"""
Forward Pass: f(x) = abs(x)
Computes the element-wise absolute value
"""
self.input = input
output = np.abs(input)
return output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
Backward Pass (Backpropagation): f'(x) = -1 if x < 0, 0 if x == 0, 1 if x > 0
The derivative of |x| is the sign function, np.sign(0) returns 0 by default in NumPy
The total gradient is the element-wise product of the upstream
gradient and the derivative of the Log.
"""
abs_derivative = np.sign(self.input)
print(f"abs_derivative.shape: {abs_derivative.shape}")
print(f"Abs Derivative:\n{abs_derivative}")
# upstream_gradient: the gradient of the loss with respect to the output
# Computes the gradient of the loss with respect to the input (dL/dx)
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
# dL/dx = dL/dy * dy/dx = upstream_gradient * f'(x)
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * abs_derivative
return downstream_gradient
layer = AbsLayer()
input = np.array([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/abs.py
forward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Forward Pass Output:
[[1.5 0. 1.5]
[0.5 2. 3. ]]
abs_derivative.shape: (2, 3)
Abs Derivative:
[[-1. 0. 1.]
[ 1. -1. 1.]]
backward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Backward Pass Output:
[[-0.1 0. 0.1]
[ 0.1 -0.1 0.1]]
Process finished with exit code 02.4. Python Abs Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class AbsLayer:
"""
A class to represent the Abs layer for a neural network.
"""
def __init__(self):
# Cache the input for the backward pass
self.input = None
def forward(self, input):
"""
Forward Pass: f(x) = abs(x)
Computes the element-wise absolute value
"""
self.input = input
output = np.abs(input)
return output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
Backward Pass (Backpropagation): f'(x) = -1 if x < 0, 0 if x == 0, 1 if x > 0
The derivative of |x| is the sign function, np.sign(0) returns 0 by default in NumPy
The total gradient is the element-wise product of the upstream
gradient and the derivative of the Log.
"""
abs_derivative = np.sign(self.input)
print(f"abs_derivative.shape: {abs_derivative.shape}")
print(f"Abs Derivative:\n{abs_derivative}")
# upstream_gradient: the gradient of the loss with respect to the output
# Computes the gradient of the loss with respect to the input (dL/dx)
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
# dL/dx = dL/dy * dy/dx = upstream_gradient * f'(x)
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * abs_derivative
return downstream_gradient
layer = AbsLayer()
input = np.array([-1.5, 0.0, 1.5, 0.5, -2.0, 3.0], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/abs.py
forward_output.shape: (6,)
Forward Pass Output:
[1.5 0. 1.5 0.5 2. 3. ]
abs_derivative.shape: (6,)
Abs Derivative:
[-1. 0. 1. 1. -1. 1.]
backward_output.shape: (6,)
Backward Pass Output:
[-0.1 0. 0.1 0.1 -0.1 0.1]
Process finished with exit code 0References
1\] Yongqiang Cheng (程永强),