目录
- 一、负载均衡的应用场景
-
- [1.1 问题引入](#1.1 问题引入)
- [1.2 解决方法](#1.2 解决方法)
- 二、负载均衡介绍
-
- [2.1 服务器负载均衡](#2.1 服务器负载均衡)
- [2.2 客户端负载均衡](#2.2 客户端负载均衡)
- [三、Spring Cloud LoadBalancer](#三、Spring Cloud LoadBalancer)
-
- [3.1 快速使用](#3.1 快速使用)
- [3.2 负载均衡策略](#3.2 负载均衡策略)
- [3.3 原理](#3.3 原理)

一、负载均衡的应用场景
1.1 问题引入
这是我们原来获取服务的方式:
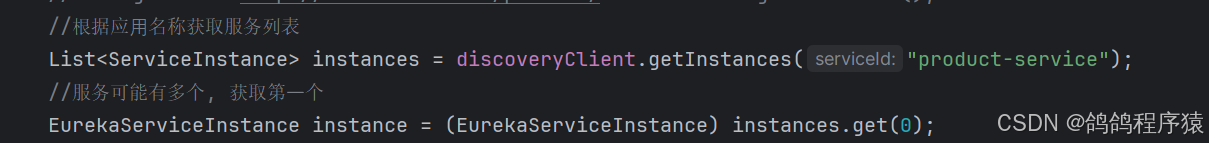
但是这样⼀个服务对应多个实例呢? 流量是否可以合理的分配到多个实例呢?
在启动两个商品服务: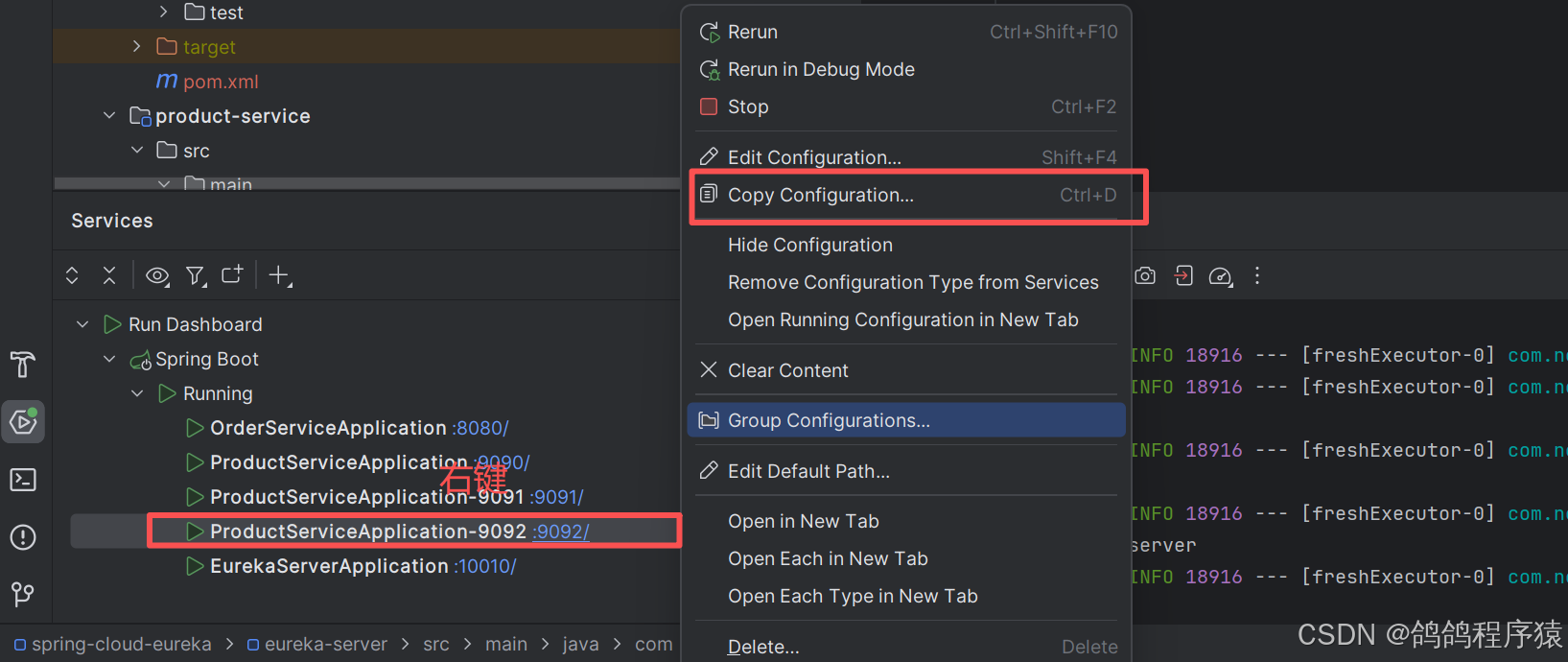
配置端口:
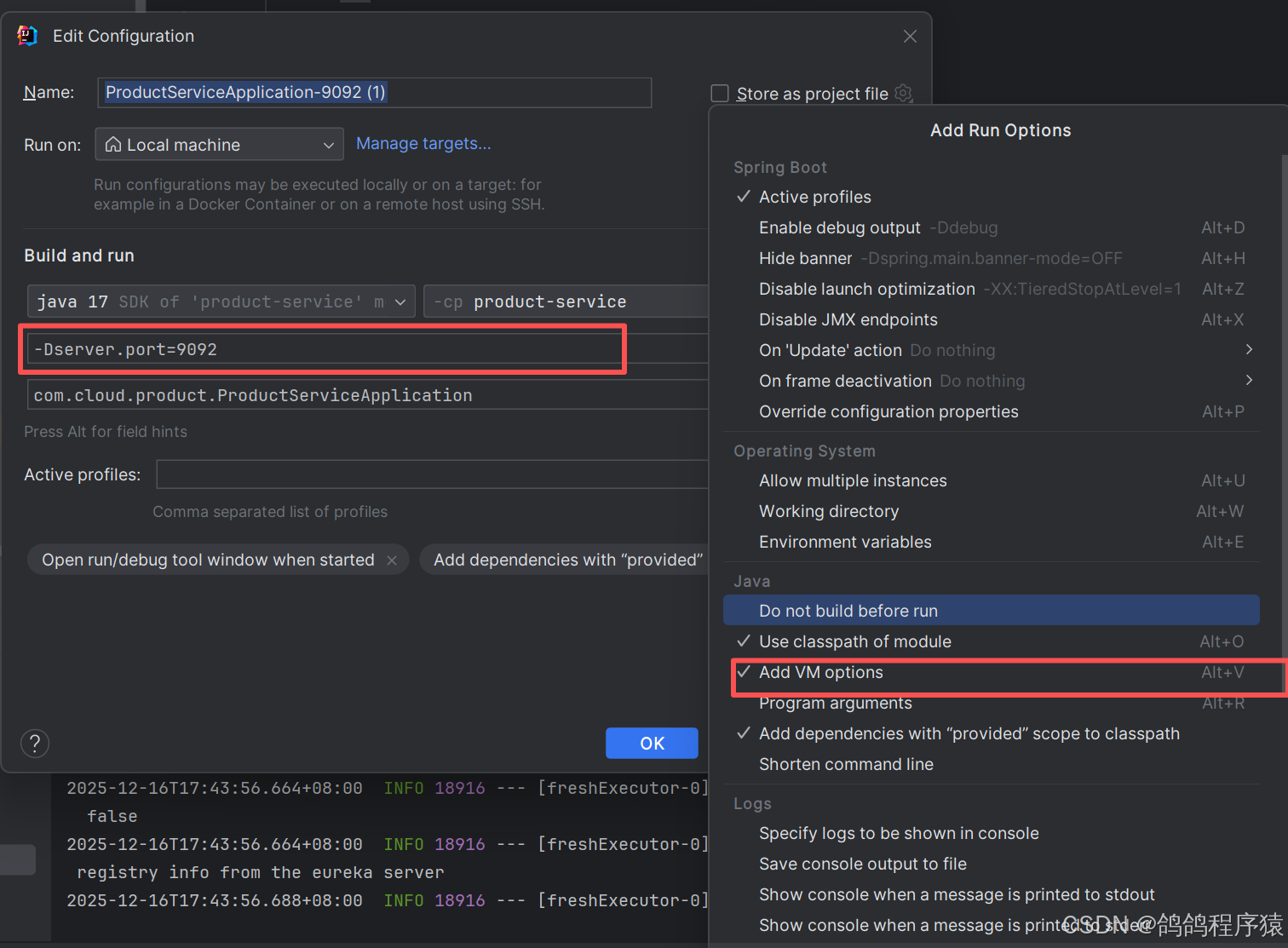
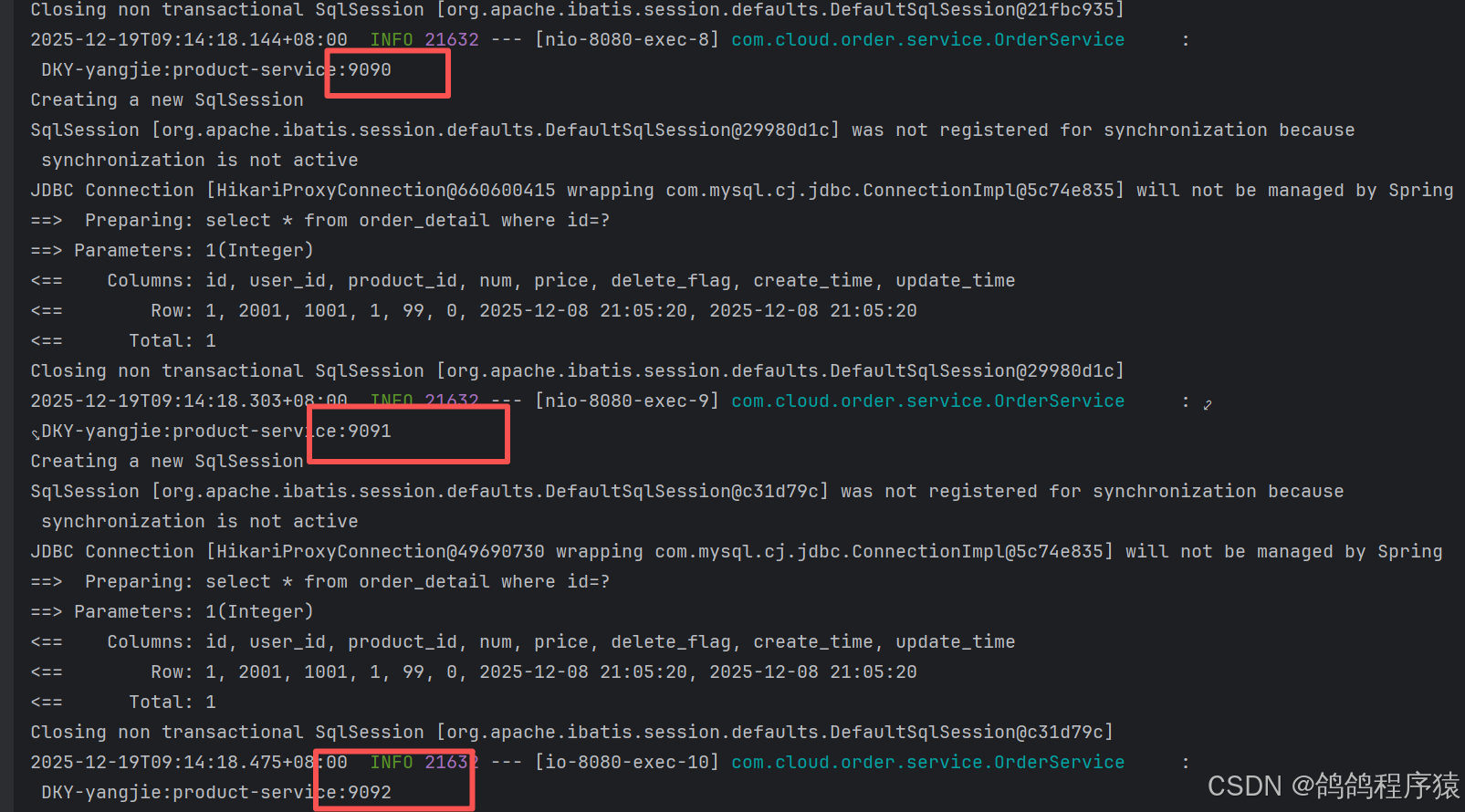
后端多次访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/order/1,端口大部分都是9090,可以看到流量分配是不均匀的。
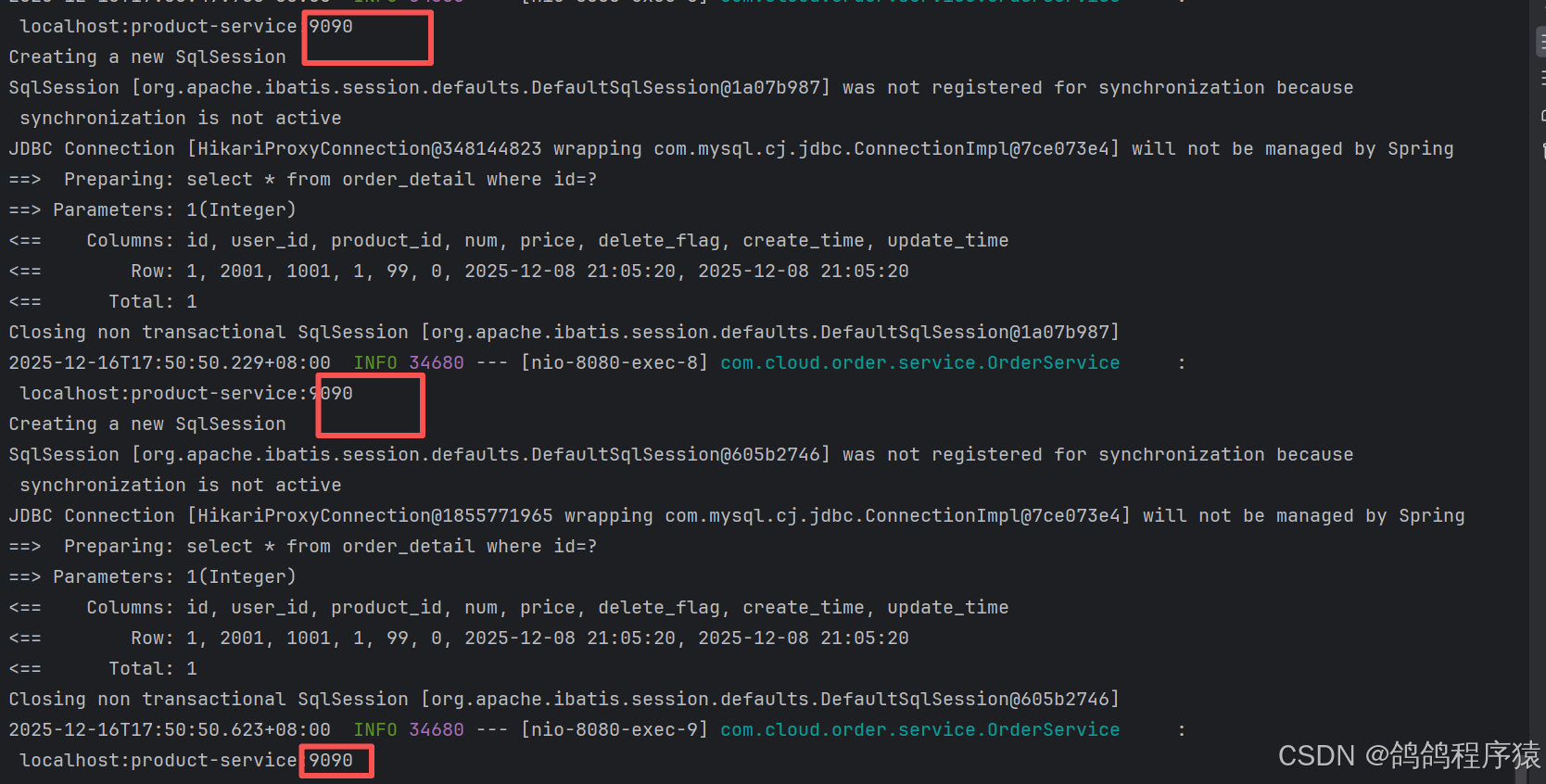
1.2 解决方法
引入计数器:
- 需要引入线程安全的计数器
- 需要将获取服务列表放在类中,不能因为方法的调用而重新创建。
java
package com.cloud.order.service;
import com.cloud.order.mapper.OrderMapper;
import com.cloud.order.model.OrderInfo;
import com.cloud.order.model.ProductInfo;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Resource
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
private List<ServiceInstance> instances;
@PostConstruct
private void init() { //根据应⽤名称获取服务列表
instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("product-service");
}
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
public OrderInfo selectOrderById(Integer orderId) {
OrderInfo orderInfo = orderMapper.selectOrderById(orderId);
//String url = "http://127.0.0.1:9090/product/"+ orderInfo.getProductId();
//服务可能有多个, 获取第index个
int index = counter.getAndIncrement() % instances.size();
EurekaServiceInstance instance = (EurekaServiceInstance) instances.get(index);
log.info(instance.getInstanceId());
//拼接url
String url = instance.getUri()+"/product/"+ orderInfo.getProductId();
ProductInfo productInfo = restTemplate.getForObject(url, ProductInfo.class);
orderInfo.setProductInfo(productInfo);
return orderInfo;
}
}这样分配之后,服务的调用就均匀一些了:
二、负载均衡介绍
负载均衡(Load Balance,简称 LB) :是⾼并发,⾼可⽤系统必不可少的关键组件。当服务流量增⼤时,通常会采⽤增加机器的⽅式进⾏扩容,负载均衡就是⽤来在多个机器或者其他资源中,按照**⼀定的规则**合理分配负载。
2.1 服务器负载均衡
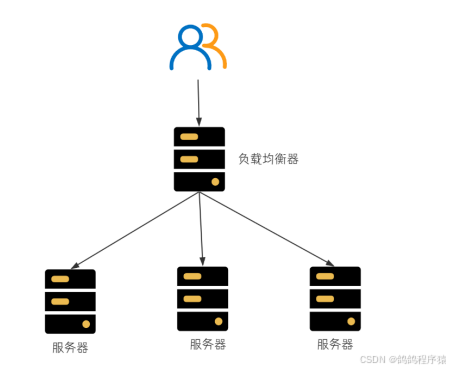
在服务端进⾏负载均衡的算法分配。
⽐较有名的服务端负载均衡器是Nginx。请求先到达Nginx负载均衡器,然后通过负载均衡算法,在多个服务器之间选择⼀个进⾏访问。
2.2 客户端负载均衡
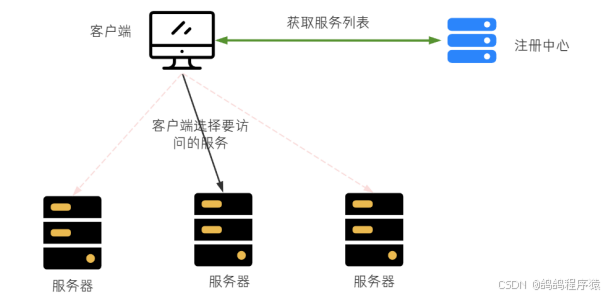
在客⼾端进⾏负载均衡的算法分配。
把负载均衡的功能以库的⽅式集成到客⼾端,⽽不再是由⼀台指定的负载均衡设备集中提供。
⽐如Spring Cloud的Ribbon,请求发送到客⼾端,客⼾端从注册中⼼(⽐如Eureka)获取服务列表,在发送请求前通过负载均衡算法选择⼀个服务器,然后进⾏访问。
Ribbon是Spring Cloud早期的默认实现,由于不维护了,所以最新版本的Spring Cloud负载均衡集成的是Spring Cloud LoadBalancer(Spring Cloud官⽅维护)。
客⼾端负载均衡和服务端负载均衡最⼤的区别在于服务清单所存储的位置
服务器负载均衡是在负载均衡器,客户端负载均衡是在客户端。
三、Spring Cloud LoadBalancer
3.1 快速使用
SpringCloud 从 2020.0.1 版本开始,移除了Ribbon 组件,使⽤Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 组件来代替 Ribbon 实现客⼾端负载均衡。
- 给 RestTemplate 这个Bean添加 @LoadBalanced 注解就可以
java
package com.cloud.order.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}- 修改IP 和 端⼝号为服务名称
java
package com.cloud.order.service;
import com.cloud.order.mapper.OrderMapper;
import com.cloud.order.model.OrderInfo;
import com.cloud.order.model.ProductInfo;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
private static final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
public OrderInfo selectOrderById(Integer orderId) {
OrderInfo orderInfo = orderMapper.selectOrderById(orderId);
String url = "http://product-service/product/"+ orderInfo.getProductId();
ProductInfo productInfo = restTemplate.getForObject(url, ProductInfo.class);
orderInfo.setProductInfo(productInfo);
return orderInfo;
}
}3.2 负载均衡策略
Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 默认负载均衡策略是 轮询策略,实现是 RoundRobinLoadBalancer,如果服务的消费者如果想采⽤随机的负载均衡策略,也⾮常简单。
- 定义随机算法对象,通过@Bean 将其加载到 Spring 容器中(参考官网https://docs.spring.io/spring-cloud-commons/reference/spring-cloud-commons/loadbalancer.html)
这个类必须满足:
- 不⽤ @Configuration 注释
- 在组件扫描范围内
java
package com.cloud.order.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.RandomLoadBalancer;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ReactorLoadBalancer;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ServiceInstanceListSupplier;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.support.LoadBalancerClientFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
public class LoadBalancerConfig {
@Bean
ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> randomLoadBalancer(Environment environment,
LoadBalancerClientFactory loadBalancerClientFactory) {
String name = environment.getProperty(LoadBalancerClientFactory.PROPERTY_NAME);
System.out.println("=============="+name);
return new RandomLoadBalancer(loadBalancerClientFactory.getLazyProvider(name,ServiceInstanceListSupplier.class),
name);
}
}- 使⽤ @LoadBalancerClient 或者 @LoadBalancerClients 注解
在 RestTemplate 配置类上⽅,使⽤ @LoadBalancerClient 或 @LoadBalancerClients 注解,可以对不同的服务提供⽅配置不同的客⼾端负载均衡算法策略。
- name: 该负载均衡策略对哪个服务⽣效(服务提供⽅)
- configuration : 该负载均衡策略 ⽤哪个负载均衡策略实现
java
package com.cloud.order.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.annotation.LoadBalancerClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
@LoadBalancerClient(name = "product-service", configuration = LoadBalancerConfig.class)
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}3.3 原理
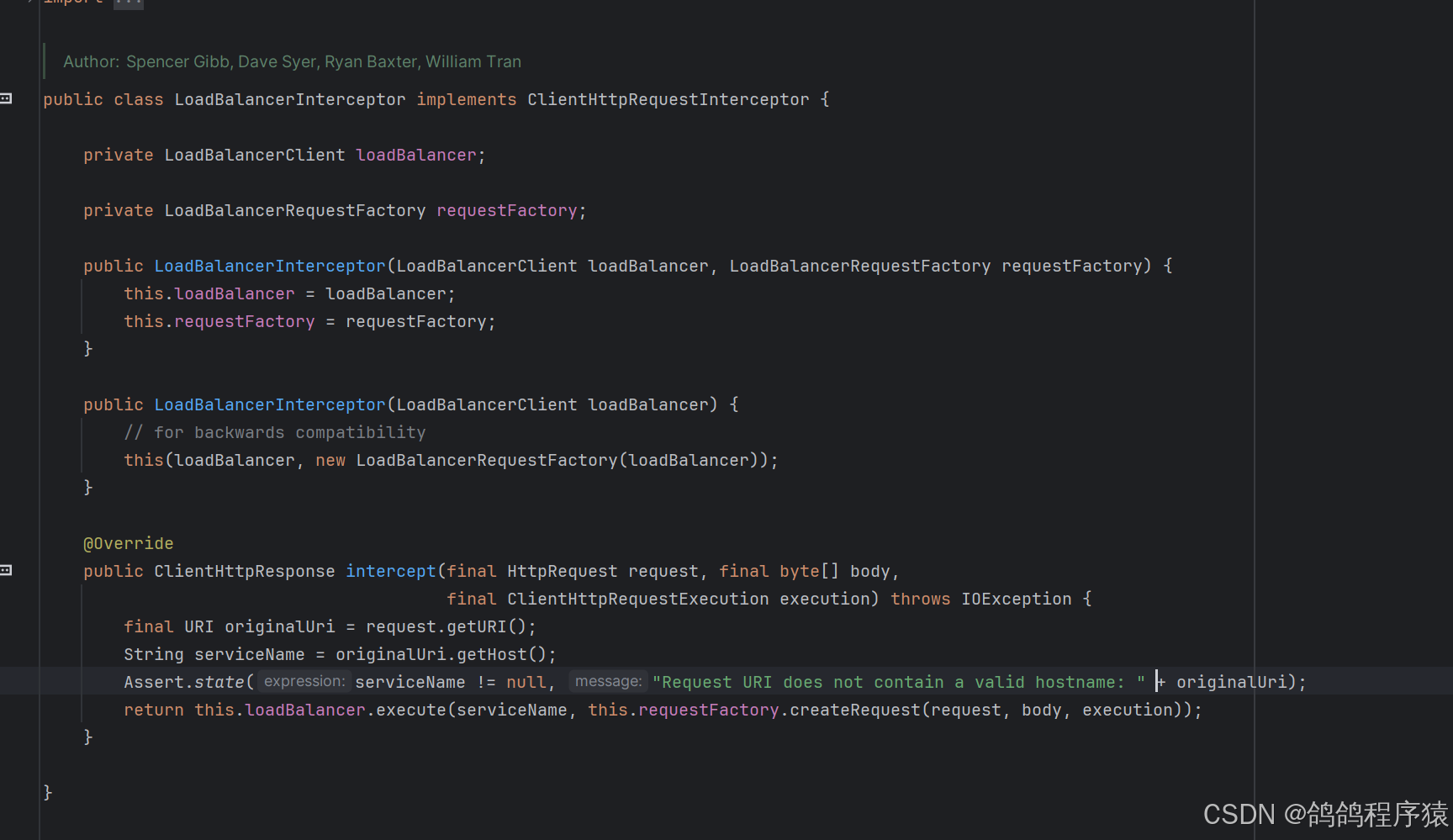
LoadBalancer 的实现,主要是 LoadBalancerInterceptor ,这个类会对 RestTemplate 的请求进⾏拦截,然后从Eureka根据服务id获取服务列表,随后利⽤负载均衡算法得到真实的服务地址信息,替换服务id。
下一步实现轮询策略,跟我们前面的计数器逻辑差不多:
java
/*
* Copyright 2012-2020 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.blocking.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.Set;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.CompletionContext;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.DefaultRequest;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.DefaultRequestContext;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.DefaultResponse;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.EmptyResponse;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.HttpRequestLoadBalancerRequest;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerLifecycle;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerLifecycleValidator;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerRequest;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerRequestAdapter;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerUriTools;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.Request;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.RequestData;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.RequestDataContext;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.Response;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.ResponseData;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.TimedRequestContext;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.reactive.ReactiveLoadBalancer;
import org.springframework.http.HttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import static org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.reactive.ReactiveLoadBalancer.REQUEST;
/**
* The default {@link LoadBalancerClient} implementation.
*
* @author Olga Maciaszek-Sharma
* @since 2.2.0
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public class BlockingLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient {
private final ReactiveLoadBalancer.Factory<ServiceInstance> loadBalancerClientFactory;
public BlockingLoadBalancerClient(ReactiveLoadBalancer.Factory<ServiceInstance> loadBalancerClientFactory) {
this.loadBalancerClientFactory = loadBalancerClientFactory;
}
@Override
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException {
String hint = getHint(serviceId);
LoadBalancerRequestAdapter<T, TimedRequestContext> lbRequest = new LoadBalancerRequestAdapter<>(request,
buildRequestContext(request, hint));
Set<LoadBalancerLifecycle> supportedLifecycleProcessors = getSupportedLifecycleProcessors(serviceId);
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onStart(lbRequest));
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = choose(serviceId, lbRequest);
if (serviceInstance == null) {
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onComplete(
new CompletionContext<>(CompletionContext.Status.DISCARD, lbRequest, new EmptyResponse())));
throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId);
}
return execute(serviceId, serviceInstance, lbRequest);
}
private <T> TimedRequestContext buildRequestContext(LoadBalancerRequest<T> delegate, String hint) {
if (delegate instanceof HttpRequestLoadBalancerRequest) {
HttpRequest request = ((HttpRequestLoadBalancerRequest) delegate).getHttpRequest();
if (request != null) {
RequestData requestData = new RequestData(request);
return new RequestDataContext(requestData, hint);
}
}
return new DefaultRequestContext(delegate, hint);
}
@Override
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request)
throws IOException {
if (serviceInstance == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Service Instance cannot be null");
}
DefaultResponse defaultResponse = new DefaultResponse(serviceInstance);
Set<LoadBalancerLifecycle> supportedLifecycleProcessors = getSupportedLifecycleProcessors(serviceId);
Request lbRequest = request instanceof Request ? (Request) request : new DefaultRequest<>();
supportedLifecycleProcessors
.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onStartRequest(lbRequest, new DefaultResponse(serviceInstance)));
try {
T response = request.apply(serviceInstance);
Object clientResponse = getClientResponse(response);
supportedLifecycleProcessors
.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onComplete(new CompletionContext<>(CompletionContext.Status.SUCCESS,
lbRequest, defaultResponse, clientResponse)));
return response;
}
catch (IOException iOException) {
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onComplete(
new CompletionContext<>(CompletionContext.Status.FAILED, iOException, lbRequest, defaultResponse)));
throw iOException;
}
catch (Exception exception) {
supportedLifecycleProcessors.forEach(lifecycle -> lifecycle.onComplete(
new CompletionContext<>(CompletionContext.Status.FAILED, exception, lbRequest, defaultResponse)));
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception);
}
return null;
}
private <T> Object getClientResponse(T response) {
ClientHttpResponse clientHttpResponse = null;
if (response instanceof ClientHttpResponse) {
clientHttpResponse = (ClientHttpResponse) response;
}
if (clientHttpResponse != null) {
try {
return new ResponseData(clientHttpResponse, null);
}
catch (IOException ignored) {
}
}
return response;
}
private Set<LoadBalancerLifecycle> getSupportedLifecycleProcessors(String serviceId) {
return LoadBalancerLifecycleValidator.getSupportedLifecycleProcessors(
loadBalancerClientFactory.getInstances(serviceId, LoadBalancerLifecycle.class),
DefaultRequestContext.class, Object.class, ServiceInstance.class);
}
@Override
public URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance serviceInstance, URI original) {
return LoadBalancerUriTools.reconstructURI(serviceInstance, original);
}
@Override
public ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId) {
return choose(serviceId, REQUEST);
}
@Override
public <T> ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId, Request<T> request) {
ReactiveLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> loadBalancer = loadBalancerClientFactory.getInstance(serviceId);
if (loadBalancer == null) {
return null;
}
Response<ServiceInstance> loadBalancerResponse = Mono.from(loadBalancer.choose(request)).block();
if (loadBalancerResponse == null) {
return null;
}
return loadBalancerResponse.getServer();
}
private String getHint(String serviceId) {
LoadBalancerProperties properties = loadBalancerClientFactory.getProperties(serviceId);
String defaultHint = properties.getHint().getOrDefault("default", "default");
String hintPropertyValue = properties.getHint().get(serviceId);
return hintPropertyValue != null ? hintPropertyValue : defaultHint;
}
}