一、C# 队列初相识
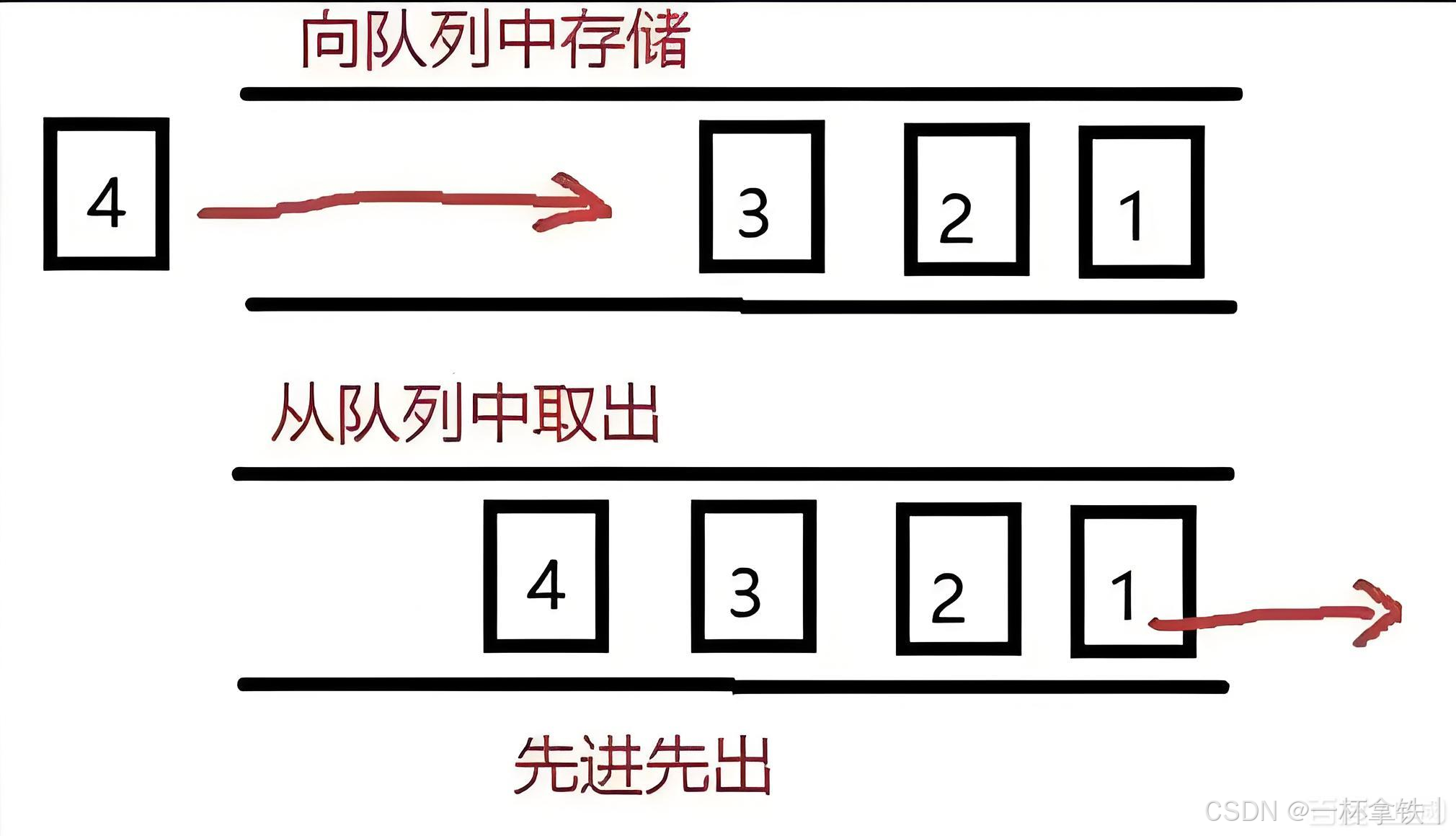
在 C# 的编程世界里,队列(Queue)是一种遵循先进先出(FIFO,First In First Out )原则的数据结构。简单来说,就像是我们日常生活中排队买票的场景,先到的人排在队伍前面,先接受服务;后来的人只能排在队尾等待,按照顺序依次接受服务 。
在 C# 中,我们可以使用System.Collections.Generic命名空间下的Queue<T>泛型类来轻松实现队列的各种操作。这里的T代表队列中元素的类型,它可以是任何类型,比如int、string、自定义类等等,这使得队列具有很强的通用性和灵活性。
二、Queue 基本操作实战
(一)队列创建
在 C# 中,创建队列非常简单。我们只需要引入System.Collections.Generic命名空间,然后实例化一个Queue<T>对象,这里的T代表队列中元素的类型。例如,创建一个整数队列和一个字符串队列:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建一个整型队列
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>();
// 创建一个字符串队列
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
}
}在上述代码中,Queue<int>表示这是一个存储整数的队列,Queue<string>则表示存储字符串的队列。通过这种方式,我们可以轻松创建出存储不同类型元素的队列 。
(二)入队操作(Enqueue)
入队操作是将元素添加到队列的尾部,在 C# 中,我们使用Enqueue方法来完成这个操作。以下是向前面创建的整数队列和字符串队列中添加元素的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建一个整型队列
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>();
// 向整型队列中添加元素
intQueue.Enqueue(10);
intQueue.Enqueue(20);
intQueue.Enqueue(30);
// 创建一个字符串队列
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
// 向字符串队列中添加元素
stringQueue.Enqueue("apple");
stringQueue.Enqueue("banana");
stringQueue.Enqueue("cherry");
Console.WriteLine("整型队列元素个数: " + intQueue.Count);
Console.WriteLine("字符串队列元素个数: " + stringQueue.Count);
}
}上述代码中,我们分别向intQueue和stringQueue中添加了三个元素,并且使用Count属性来获取队列中当前元素的数量 。可以看到,Enqueue方法使得元素按照我们添加的顺序依次排列在队列中,符合先进先出的原则。
(三)出队操作(Dequeue)
出队操作是从队列的头部移除并返回一个元素,C# 中使用Dequeue方法来实现。还是以上面的队列为例,来看一下出队操作的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建一个整型队列
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>();
intQueue.Enqueue(10);
intQueue.Enqueue(20);
intQueue.Enqueue(30);
// 出队操作
int firstElement = intQueue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine("出队的整数元素: " + firstElement);
Console.WriteLine("出队后整型队列元素个数: " + intQueue.Count);
// 创建一个字符串队列
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
stringQueue.Enqueue("apple");
stringQueue.Enqueue("banana");
stringQueue.Enqueue("cherry");
// 出队操作
string firstString = stringQueue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine("出队的字符串元素: " + firstString);
Console.WriteLine("出队后字符串队列元素个数: " + stringQueue.Count);
}
}在这个示例中,我们从intQueue和stringQueue中分别进行了出队操作。Dequeue方法会返回队列头部的元素,并将其从队列中移除,同时队列的元素个数也会相应减少 。
(四)查看队头元素(Peek)
有时候我们只是想查看队列头部的元素,而不想移除它,这时就可以使用Peek方法。下面是使用Peek方法查看队头元素的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建一个整型队列
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>();
intQueue.Enqueue(10);
intQueue.Enqueue(20);
intQueue.Enqueue(30);
// 查看队头元素
int peekElement = intQueue.Peek();
Console.WriteLine("整型队列的队头元素: " + peekElement);
Console.WriteLine("查看队头元素后整型队列元素个数: " + intQueue.Count);
// 创建一个字符串队列
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
stringQueue.Enqueue("apple");
stringQueue.Enqueue("banana");
stringQueue.Enqueue("cherry");
// 查看队头元素
string peekString = stringQueue.Peek();
Console.WriteLine("字符串队列的队头元素: " + peekString);
Console.WriteLine("查看队头元素后字符串队列元素个数: " + stringQueue.Count);
}
}从代码执行结果可以看出,Peek方法成功返回了队列头部的元素,并且队列的元素个数并没有改变,因为它只是查看队头元素,而不会对队列进行修改 。
(五)判断元素是否存在(Contains)
如果我们想要判断队列中是否包含某个特定的元素,可以使用Contains方法。以下是示例代码:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建一个整型队列
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>();
intQueue.Enqueue(10);
intQueue.Enqueue(20);
intQueue.Enqueue(30);
// 判断队列中是否包含元素20
bool containsTwenty = intQueue.Contains(20);
Console.WriteLine("整型队列中是否包含20: " + containsTwenty);
// 创建一个字符串队列
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
stringQueue.Enqueue("apple");
stringQueue.Enqueue("banana");
stringQueue.Enqueue("cherry");
// 判断队列中是否包含元素"banana"
bool containsBanana = stringQueue.Contains("banana");
Console.WriteLine("字符串队列中是否包含banana: " + containsBanana);
}
}在上述代码中,Contains方法根据队列中是否存在指定元素,返回true或false ,方便我们在编程过程中根据元素是否存在来执行不同的逻辑 。
(六)清空队列(Clear)
当我们需要清空整个队列时,可以使用Clear方法。示例如下:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建一个整型队列
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>();
intQueue.Enqueue(10);
intQueue.Enqueue(20);
intQueue.Enqueue(30);
Console.WriteLine("清空之前整型队列元素个数: " + intQueue.Count);
// 清空队列
intQueue.Clear();
Console.WriteLine("清空之后整型队列元素个数: " + intQueue.Count);
// 创建一个字符串队列
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
stringQueue.Enqueue("apple");
stringQueue.Enqueue("banana");
stringQueue.Enqueue("cherry");
Console.WriteLine("清空之前字符串队列元素个数: " + stringQueue.Count);
// 清空队列
stringQueue.Clear();
Console.WriteLine("清空之后字符串队列元素个数: " + stringQueue.Count);
}
}执行Clear方法后,队列中的所有元素都会被移除,队列的元素个数变为 0 。在实际应用中,比如当我们处理完一批任务,不再需要队列中的数据时,就可以使用Clear方法清空队列,以便释放资源,为下一次使用做好准备 。
三、C# 队列遍历之道
(一)foreach 循环遍历
foreach循环是遍历队列最常用的方法之一,它简单直观,代码简洁。通过foreach循环,我们可以按先进先出的顺序依次访问队列中的每个元素,并且在遍历过程中不会改变队列的状态。以下是使用foreach循环遍历整数队列的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Queue<int> numberQueue = new Queue<int>();
numberQueue.Enqueue(1);
numberQueue.Enqueue(2);
numberQueue.Enqueue(3);
Console.WriteLine("使用foreach循环遍历队列:");
foreach (int number in numberQueue)
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
}
}在上述代码中,foreach (int number in numberQueue) 语句会依次从 numberQueue 中取出每个元素,并将其赋值给 number 变量,然后在循环体中我们可以对 number 进行相应的操作,这里只是简单地将其输出到控制台 。这种方式非常适合在不需要修改队列元素,只需要读取队列数据的场景中使用。
(二)迭代器遍历
除了foreach循环,我们还可以使用迭代器来遍历队列。通过调用队列的GetEnumerator方法,我们可以获取一个迭代器对象,然后使用迭代器的MoveNext方法来移动到下一个元素,并通过Current属性获取当前元素的值。这种方式相比foreach循环更加底层和灵活,我们可以更精细地控制遍历的过程 。下面是使用迭代器遍历字符串队列的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
stringQueue.Enqueue("apple");
stringQueue.Enqueue("banana");
stringQueue.Enqueue("cherry");
Console.WriteLine("使用迭代器遍历队列:");
IEnumerator<string> iterator = stringQueue.GetEnumerator();
while (iterator.MoveNext())
{
string currentString = iterator.Current;
Console.WriteLine(currentString);
}
}
}在这段代码中,首先通过stringQueue.GetEnumerator()获取迭代器iterator,然后在while循环中,使用iterator.MoveNext()判断是否存在下一个元素,如果存在,则通过iterator.Current获取当前元素并输出 。使用迭代器遍历队列时,我们可以在遍历过程中根据需要灵活地控制循环的流程,比如在满足某些条件时提前结束遍历等 。
(三)创建临时副本遍历
当我们需要对队列进行一些复杂的操作,同时又不想影响原始队列时,可以先创建一个队列的临时副本,然后对副本进行遍历和操作。对于普通的Queue<T>,我们可以直接在创建新队列时传入原始队列作为参数,这样新队列就会包含原始队列的所有元素 。以下是创建临时副本遍历整数队列的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Queue<int> originalQueue = new Queue<int>();
originalQueue.Enqueue(1);
originalQueue.Enqueue(2);
originalQueue.Enqueue(3);
Console.WriteLine("创建临时副本遍历队列:");
Queue<int> tempQueue = new Queue<int>(originalQueue);
while (tempQueue.Count > 0)
{
int currentNumber = tempQueue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine(currentNumber);
}
Console.WriteLine("原始队列元素个数: " + originalQueue.Count);
}
}在上述代码中,Queue<int> tempQueue = new Queue<int>(originalQueue); 创建了 originalQueue 的临时副本 tempQueue 。然后我们对 tempQueue 进行遍历,通过 Dequeue 方法逐个取出元素并输出 。最后输出原始队列的元素个数,可以看到原始队列并没有受到影响 。
如果是线程安全的ConcurrentQueue<T>,创建副本的方式类似,只是需要使用ConcurrentQueue<T>的构造函数来创建副本 。示例如下:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
ConcurrentQueue<int> originalConcurrentQueue = new ConcurrentQueue<int>();
originalConcurrentQueue.Enqueue(1);
originalConcurrentQueue.Enqueue(2);
originalConcurrentQueue.Enqueue(3);
Console.WriteLine("创建临时副本遍历线程安全队列:");
ConcurrentQueue<int> tempConcurrentQueue = new ConcurrentQueue<int>(originalConcurrentQueue);
int result;
while (tempConcurrentQueue.TryDequeue(out result))
{
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
Console.WriteLine("原始线程安全队列元素个数: " + originalConcurrentQueue.Count);
}
}这里使用 ConcurrentQueue<int> tempConcurrentQueue = new ConcurrentQueue<int>(originalConcurrentQueue); 创建了线程安全队列的副本,然后通过 TryDequeue 方法从副本中取出元素并输出 ,同样原始队列不受影响 。
(四)结合 LINQ 查询遍历
LINQ(Language Integrated Query)是 C# 中强大的数据查询和处理工具,结合 LINQ,我们可以对队列中的数据进行筛选、排序等操作,然后再进行遍历输出。这在需要对队列数据进行复杂处理时非常有用 。以下是结合 LINQ 对整数队列进行排序后遍历输出的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Queue<int> numberQueue = new Queue<int>();
numberQueue.Enqueue(5);
numberQueue.Enqueue(3);
numberQueue.Enqueue(8);
Console.WriteLine("结合LINQ查询遍历队列:");
var sortedNumbers = numberQueue.OrderBy(n => n).ToList();
foreach (int number in sortedNumbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
}
}在这段代码中,numberQueue.OrderBy(n => n).ToList() 使用 LINQ 的OrderBy方法对numberQueue中的元素进行升序排序,并将结果转换为List<int> 。然后通过foreach循环遍历排序后的列表,输出排序后的元素 。通过这种方式,我们可以方便地对队列数据进行各种复杂的数据处理操作,然后再按照我们需要的顺序进行遍历 。
(五)逐个取出元素遍历
逐个取出元素遍历是一种比较直接的遍历方式,它从队列的头部逐一移除元素,直到队列被清空。这种方式会直接修改队列,遍历完成后,原队列将为空 。在一些不需要保存队列状态,只需要处理队列中元素的场景下,这种遍历方式非常适用 。以下是逐个取出元素遍历字符串队列的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Queue<string> stringQueue = new Queue<string>();
stringQueue.Enqueue("First Item");
stringQueue.Enqueue("Second Item");
Console.WriteLine("逐个取出元素遍历队列:");
while (stringQueue.Count > 0)
{
string currentString = stringQueue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine(currentString);
}
Console.WriteLine("遍历后队列元素个数: " + stringQueue.Count);
}
}在上述代码中,while (stringQueue.Count > 0) 循环条件判断队列是否为空,只要队列不为空,就通过 stringQueue.Dequeue() 方法取出队列头部的元素,并将其赋值给 currentString 变量,然后输出 。当循环结束时,队列中的所有元素都被取出,队列变为空,通过输出队列元素个数可以验证这一点 。
四、C# 队列性能剖析
在实际应用中,了解队列的性能特点对于我们选择合适的数据结构至关重要。队列的插入(Enqueue)和删除(Dequeue)操作具有非常高的效率,它们的时间复杂度均为 O (1) 。这是因为插入操作总是在队列的尾部进行,而删除操作总是在队列的头部进行,不需要进行复杂的查找或移动元素的操作 ,就如同在一条一端进一端出的通道中,进和出的操作都非常直接和迅速 。
然而,队列的查找(Contains)操作效率相对较低,时间复杂度为 O (n) 。这是因为队列需要从头部开始,逐个遍历队列中的元素,直到找到目标元素或者遍历完整个队列 。就好像在一条长长的队伍中寻找某个人,必须从队伍的开头一个一个地看过去 。所以当队列中的元素数量较多时,查找操作的耗时会明显增加 。
此外,队列不支持直接索引访问,这意味着我们不能像访问数组或列表那样,通过索引快速获取队列中指定位置的元素 。如果需要访问队列中特定位置的元素,只能通过逐个出队的方式,直到找到目标元素,这无疑会耗费大量的时间和资源 。所以,如果在程序中需要频繁查找或索引访问元素,队列并不是一个理想的选择,我们应考虑使用列表(List)或字典(Dictionary)等数据结构,它们在查找和索引访问方面具有更高的效率 。
五、C# 队列线程安全策略
在多线程编程中,线程安全是一个至关重要的问题。默认情况下,C# 中的Queue<T>并不是线程安全的 。当多个线程同时对Queue<T>进行读写操作时,可能会出现数据不一致、丢失数据或者抛出异常等问题 。比如在一个任务调度系统中,如果多个线程同时向任务队列中添加任务或者取出任务,就可能导致任务的处理顺序混乱,甚至出现任务丢失的情况 。
为了解决多线程环境下队列的线程安全问题,我们可以采取以下两种常见的策略 :
(一)手动加锁
手动加锁是一种较为基础的线程安全解决方案。我们可以使用lock关键字来对队列的操作进行同步,确保在同一时刻只有一个线程能够访问队列 。下面是一个使用lock关键字实现线程安全的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
class ThreadSafeQueueExample
{
private static Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
private static readonly object lockObject = new object();
static void Main()
{
// 创建多个线程向队列中添加元素
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() =>
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lock (lockObject)
{
queue.Enqueue(i);
Console.WriteLine($"线程1添加元素: {i}");
}
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() =>
{
for (int i = 10; i < 20; i++)
{
lock (lockObject)
{
queue.Enqueue(i);
Console.WriteLine($"线程2添加元素: {i}");
}
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
});
// 启动线程
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
// 等待线程执行完毕
thread1.Join();
thread2.Join();
// 输出队列中的元素
lock (lockObject)
{
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
int item = queue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine($"取出元素: {item}");
}
}
}
}在上述代码中,我们定义了一个静态的Queue<int>和一个静态的lockObject对象 。在向队列中添加元素和从队列中取出元素的操作时,都使用lock (lockObject)语句块对队列操作进行了加锁,这样就保证了在同一时刻只有一个线程能够对队列进行操作,从而避免了多线程访问队列时可能出现的线程安全问题 。
(二)使用线程安全的 ConcurrentQueue
ConcurrentQueue<T>是System.Collections.Concurrent命名空间下提供的一个线程安全的队列实现 。它采用了无锁算法来实现线程安全,相比手动加锁,ConcurrentQueue<T>在高并发场景下具有更好的性能和可扩展性 。下面是使用ConcurrentQueue<T>的示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Threading;
class ConcurrentQueueExample
{
private static ConcurrentQueue<int> concurrentQueue = new ConcurrentQueue<int>();
static void Main()
{
// 创建多个线程向队列中添加元素
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() =>
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
concurrentQueue.Enqueue(i);
Console.WriteLine($"线程1添加元素: {i}");
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() =>
{
for (int i = 10; i < 20; i++)
{
concurrentQueue.Enqueue(i);
Console.WriteLine($"线程2添加元素: {i}");
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
});
// 启动线程
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
// 等待线程执行完毕
thread1.Join();
thread2.Join();
// 输出队列中的元素
while (concurrentQueue.TryDequeue(out int item))
{
Console.WriteLine($"取出元素: {item}");
}
}
}在这个示例中,我们使用ConcurrentQueue<int>来替代普通的Queue<int> 。ConcurrentQueue<int>的Enqueue和TryDequeue等方法都是线程安全的,多个线程可以同时调用这些方法,而无需手动加锁 。这使得代码更加简洁,并且在高并发场景下能够提供更好的性能表现 。
(三)策略选择
手动加锁的方式虽然简单直观,但是在高并发场景下,频繁的加锁和解锁操作会带来一定的性能开销,可能会导致线程的阻塞和等待,从而影响程序的整体性能 。因此,手动加锁适用于并发程度较低、对性能要求不是特别高的场景 。
而ConcurrentQueue<T>由于采用了无锁算法,能够更好地支持多线程并发访问,在高并发场景下具有明显的性能优势 。所以,在多线程环境中,如果需要频繁地对队列进行读写操作,优先考虑使用ConcurrentQueue<T>来保证线程安全和提高程序性能 。
六、C# 队列应用实战
(一)打印任务队列
在日常办公中,我们经常会遇到多个打印任务需要依次执行的情况。以打印机后台服务为例,队列在这里就发挥着重要的作用 。下面是使用队列管理打印任务的代码示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class PrintTask
{
public string DocumentName { get; set; }
public int PageCount { get; set; }
public PrintTask(string name, int pages)
{
DocumentName = name;
PageCount = pages;
}
}
class PrintQueue
{
private Queue<PrintTask> taskQueue = new Queue<PrintTask>();
public void AddTask(PrintTask task)
{
taskQueue.Enqueue(task);
Console.WriteLine($"任务 {task.DocumentName} 已加入打印队列。");
}
public void PrintTasks()
{
while (taskQueue.Count > 0)
{
PrintTask currentTask = taskQueue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine($"正在打印 {currentTask.DocumentName},共 {currentTask.PageCount} 页...");
// 模拟打印操作
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine($"{currentTask.DocumentName} 打印完成。");
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
PrintQueue printQueue = new PrintQueue();
PrintTask task1 = new PrintTask("报告.docx", 10);
PrintTask task2 = new PrintTask("简历.pdf", 5);
PrintTask task3 = new PrintTask("合同.txt", 3);
printQueue.AddTask(task1);
printQueue.AddTask(task2);
printQueue.AddTask(task3);
printQueue.PrintTasks();
}
}在上述代码中,我们定义了一个PrintTask类来表示打印任务,包含文档名称和页数两个属性 。PrintQueue类中使用Queue<PrintTask>来管理打印任务队列 。AddTask方法用于将打印任务添加到队列中,PrintTasks方法则从队列中依次取出任务并进行打印 。这里通过队列的 FIFO 特性,保证了打印任务按照添加的顺序依次执行,避免了打印顺序混乱的问题 。
(二)任务调度系统
在多线程或异步编程中,我们常常需要处理大量的待处理请求或任务,这时队列就成为了一个非常实用的数据结构 。以下是一个简单的任务调度系统代码示例,展示了如何使用队列存放待处理任务,并实现任务的添加和处理:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
class TaskItem
{
public int TaskId { get; set; }
public string TaskName { get; set; }
public TaskItem(int id, string name)
{
TaskId = id;
TaskName = name;
}
}
class TaskScheduler
{
private Queue<TaskItem> taskQueue = new Queue<TaskItem>();
private Thread processingThread;
public TaskScheduler()
{
// 创建并启动任务处理线程
processingThread = new Thread(ProcessTasks);
processingThread.Start();
}
public void AddTask(TaskItem task)
{
lock (taskQueue)
{
taskQueue.Enqueue(task);
Console.WriteLine($"任务 {task.TaskName} 已加入任务队列。");
}
}
private void ProcessTasks()
{
while (true)
{
TaskItem currentTask = null;
lock (taskQueue)
{
if (taskQueue.Count > 0)
{
currentTask = taskQueue.Dequeue();
}
}
if (currentTask != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"正在处理任务 {currentTask.TaskName}...");
// 模拟任务处理操作
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine($"任务 {currentTask.TaskName} 处理完成。");
}
else
{
// 队列中没有任务时,线程等待一段时间
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
TaskScheduler scheduler = new TaskScheduler();
TaskItem task1 = new TaskItem(1, "任务1");
TaskItem task2 = new TaskItem(2, "任务2");
TaskItem task3 = new TaskItem(3, "任务3");
scheduler.AddTask(task1);
scheduler.AddTask(task2);
scheduler.AddTask(task3);
// 主线程等待一段时间,确保任务处理线程有足够时间处理任务
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}在这个示例中,TaskItem类表示一个任务,包含任务 ID 和任务名称 。TaskScheduler类使用Queue<TaskItem>来存储任务队列,并创建了一个专门的线程processingThread来处理任务 。AddTask方法用于将任务添加到队列中,并且使用lock关键字来保证线程安全 。ProcessTasks方法在任务处理线程中不断运行,从队列中取出任务并进行处理 。如果队列中没有任务,线程会等待一段时间,避免资源浪费 。通过这种方式,我们实现了一个简单的任务调度系统,能够有效地管理和处理多个任务 。
(三)消息队列与事件总线
在构建复杂的系统时,解耦系统模块是提高系统可维护性和可扩展性的关键。队列作为消息队列或事件总线,可以在不同模块之间传递消息和事件,实现模块之间的解耦 。以微服务架构中订单服务和库存服务解耦为例,当用户下单时,订单服务需要通知库存服务扣减库存,通过消息队列可以实现这一过程的异步解耦 。以下是一个简单的代码示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
class Order
{
public int OrderId { get; set; }
public string CustomerName { get; set; }
public List<string> Products { get; set; }
public Order(int id, string customer, List<string> products)
{
OrderId = id;
CustomerName = customer;
Products = products;
}
}
class MessageQueue
{
private Queue<Order> messageQueue = new Queue<Order>();
public void SendMessage(Order order)
{
lock (messageQueue)
{
messageQueue.Enqueue(order);
Console.WriteLine($"订单 {order.OrderId} 消息已发送到队列。");
}
}
public Order ReceiveMessage()
{
lock (messageQueue)
{
if (messageQueue.Count > 0)
{
return messageQueue.Dequeue();
}
return null;
}
}
}
class InventoryService
{
private MessageQueue messageQueue;
public InventoryService(MessageQueue queue)
{
messageQueue = queue;
// 启动一个线程来处理库存更新
Thread thread = new Thread(ProcessMessages);
thread.Start();
}
private void ProcessMessages()
{
while (true)
{
Order order = messageQueue.ReceiveMessage();
if (order != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"库存服务接收到订单 {order.OrderId},正在扣减库存...");
// 模拟库存扣减操作
Thread.Sleep(1500);
Console.WriteLine($"订单 {order.OrderId} 库存扣减完成。");
}
else
{
// 没有消息时,线程等待一段时间
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
}
}
}
class OrderService
{
private MessageQueue messageQueue;
public OrderService(MessageQueue queue)
{
messageQueue = queue;
}
public void PlaceOrder(Order order)
{
Console.WriteLine($"订单 {order.OrderId} 已创建,发送消息到库存服务...");
messageQueue.SendMessage(order);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
MessageQueue messageQueue = new MessageQueue();
OrderService orderService = new OrderService(messageQueue);
InventoryService inventoryService = new InventoryService(messageQueue);
Order order = new Order(1, "张三", new List<string> { "商品1", "商品2" });
orderService.PlaceOrder(order);
// 主线程等待一段时间,确保消息处理完成
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}在上述代码中,Order类表示订单信息 。MessageQueue类实现了一个简单的消息队列,用于存储订单消息 。OrderService负责创建订单并将订单消息发送到消息队列中 。InventoryService通过一个单独的线程从消息队列中接收订单消息,并进行库存扣减操作 。通过这种方式,订单服务和库存服务之间通过消息队列进行解耦,它们不需要直接相互依赖,提高了系统的灵活性和可维护性 。
(四)广度优先搜索(BFS)算法
在图或树的遍历算法中,广度优先搜索(BFS)是一种非常重要的算法,而队列是实现 BFS 算法的核心结构 。BFS 算法从起始节点开始,逐层地向外扩展搜索,直到找到目标节点或者遍历完所有节点 。以下是使用队列实现 BFS 算法遍历简单图结构的代码示例:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GraphNode
{
public int NodeId { get; set; }
public List<GraphNode> Neighbors { get; set; }
public GraphNode(int id)
{
NodeId = id;
Neighbors = new List<GraphNode>();
}
}
class Graph
{
private List<GraphNode> nodes;
public Graph()
{
nodes = new List<GraphNode>();
}
public void AddNode(GraphNode node)
{
nodes.Add(node);
}
public void AddEdge(GraphNode node1, GraphNode node2)
{
node1.Neighbors.Add(node2);
node2.Neighbors.Add(node1);
}
public void BFS(GraphNode startNode)
{
Queue<GraphNode> queue = new Queue<GraphNode>();
HashSet<GraphNode> visited = new HashSet<GraphNode>();
queue.Enqueue(startNode);
visited.Add(startNode);
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
GraphNode currentNode = queue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine($"访问节点: {currentNode.NodeId}");
foreach (GraphNode neighbor in currentNode.Neighbors)
{
if (!visited.Contains(neighbor))
{
queue.Enqueue(neighbor);
visited.Add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Graph graph = new Graph();
GraphNode node1 = new GraphNode(1);
GraphNode node2 = new GraphNode(2);
GraphNode node3 = new GraphNode(3);
GraphNode node4 = new GraphNode(4);
graph.AddNode(node1);
graph.AddNode(node2);
graph.AddNode(node3);
graph.AddNode(node4);
graph.AddEdge(node1, node2);
graph.AddEdge(node1, node3);
graph.AddEdge(node2, node4);
graph.AddEdge(node3, node4);
graph.BFS(node1);
}
}在这段代码中,GraphNode类表示图中的节点,每个节点包含一个节点 ID 和一个邻居节点列表 。Graph类用于管理图的节点和边,并实现了 BFS 算法 。在 BFS 方法中,我们使用一个队列queue来存储待访问的节点,使用一个哈希集合visited来记录已经访问过的节点 。从起始节点开始,将其加入队列和访问集合,然后不断从队列中取出节点进行访问,并将其未访问过的邻居节点加入队列和访问集合,直到队列为空,这样就完成了对图的广度优先搜索遍历 。
七、总结
在性能方面,队列的插入和删除操作具有高效性,但查找操作相对较慢且不支持直接索引访问,这使得我们在选择数据结构时需要根据实际需求进行权衡 。在多线程环境中,我们学习了如何通过手动加锁和使用ConcurrentQueue来保证队列的线程安全,并且了解了这两种方式在不同并发场景下的适用性 。
从应用场景来看,队列在打印任务队列、任务调度系统、消息队列与事件总线以及广度优先搜索算法等实际项目中都发挥着关键作用,能够帮助我们解决很多实际问题 。