文章目录
资料快车
1、Android GUI系统之SurfaceFlinger介绍
https://blog.csdn.net/vviccc/article/details/104860616
2、Android 重学系列 SurfaceFlinger 的初始化(Android 9.0)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/9dac91bbb9c9
1、SF的功能职责
1)管理显存的分配;
2)监听HWC发送的Vsync信号并分发给app;
3)合成所有图层;
2、基本数据结构
1、BE : back end 后端的缩写,
SurfaceFlingerBE:处理硬件底层相关
2、Flattenable<...>。这是 Android 为 Binder IPC 设计的序列化/反序列化协议
3、
GraphicBuffer : 代表一个Buffer内存
DisplayDevice : 代表显示设备(主屏、副屏、虚拟设备等)
dirty : 脏了,表示有数据更新了,需要进一步处理(重新合成、渲染等)
dirty机制:它的高效执行(依赖脏区域机制)是保证 Android UI 流畅响应,同时避免不必要计算和功耗的关键。
Renderer 渲染,代表使用硬件GPU进行工作
4、native window
/android/frameworks/native/libs/nativewindow/include/android/native_window.h
/android/frameworks/native/libs/nativewindow/include/system/window.hBuffer相关
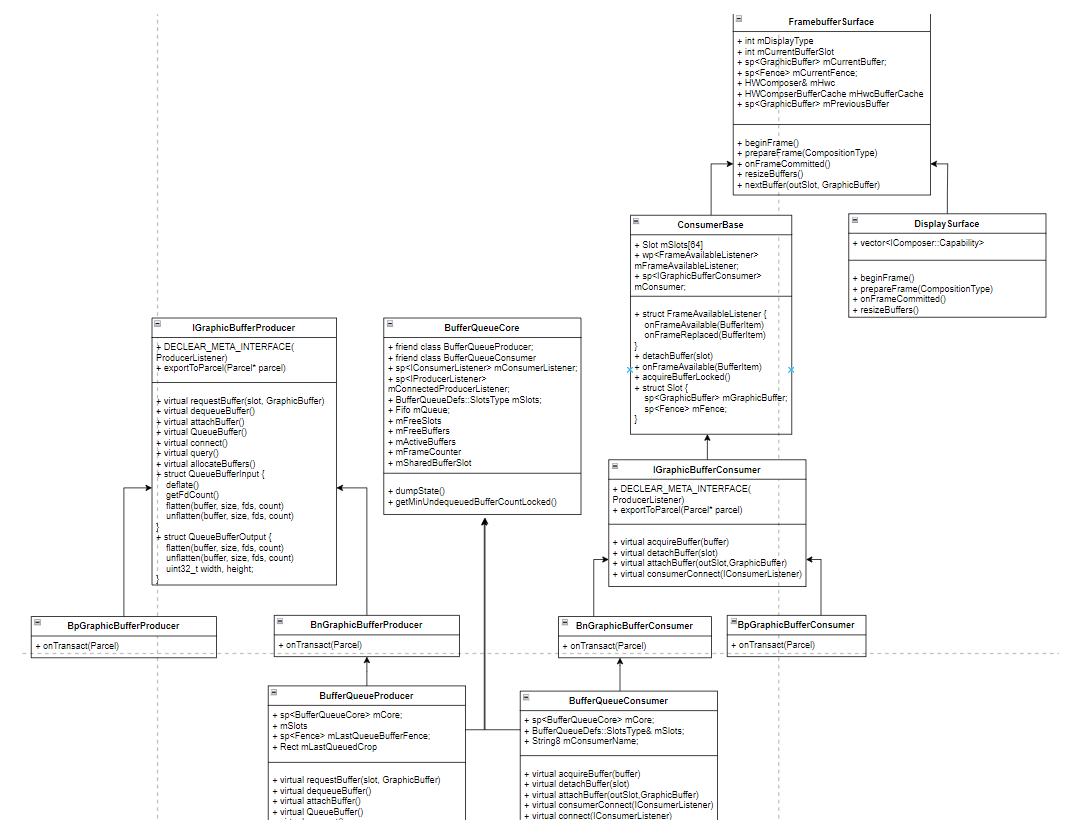
Layer相关
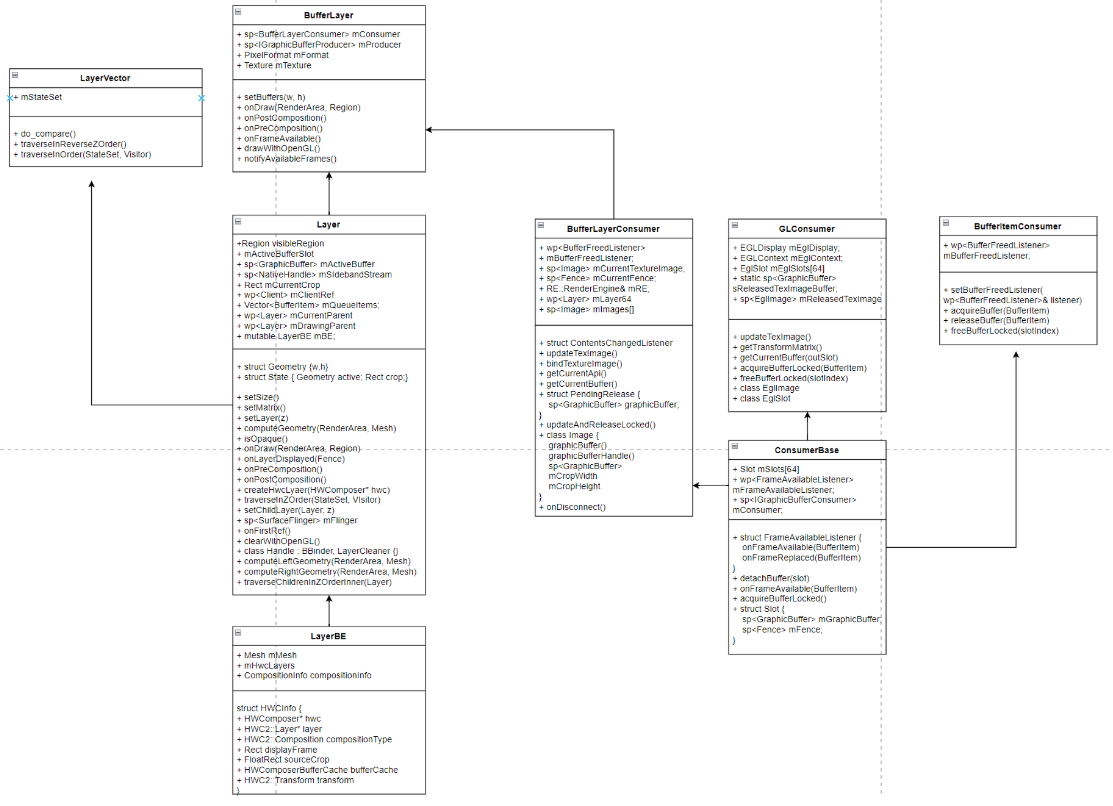
Surface相关
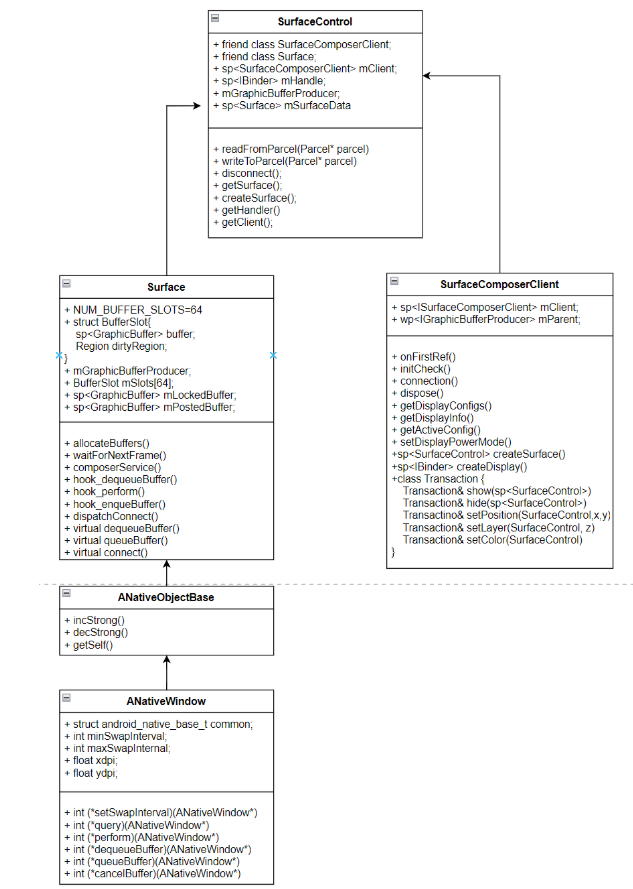
3、OpenGL-ES本地窗口
1)本地窗口产生的原因?
由于图形库OpenGL-ES是开源软件,会适应到各种系统(Windows/Android等),图形库产生的数据如何写到特定系统的内存块中呢,OpenGL-ES使用ANativeWindow本地窗口来对接各种平台,Android要使用OpenGL-ES,需要按照OpenGL-ES规范来设计,比如Android Surface需要继承ANativeWindow,实现对应的接口;
2)两种场合需要用到OpenGL-ES写内存
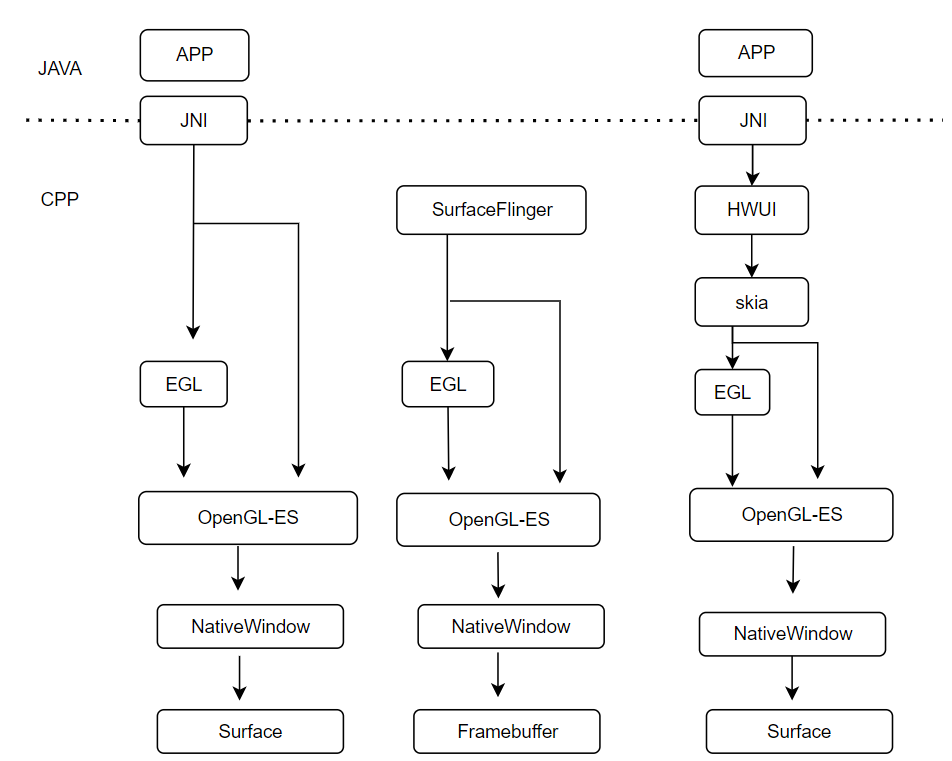
1、APP使用GL库构造UI数据放到Surface中(生产者);
2、SF使用GL库进行合成(处理HWC不能合成的需求),结果放到Framebuffer中(消费者);
3)Surface与ANativeWindow
1、APP向Surface写数据流程:APP->EGL->OpenGL-ES->ANativeWindow ->Surface
2、数据结构
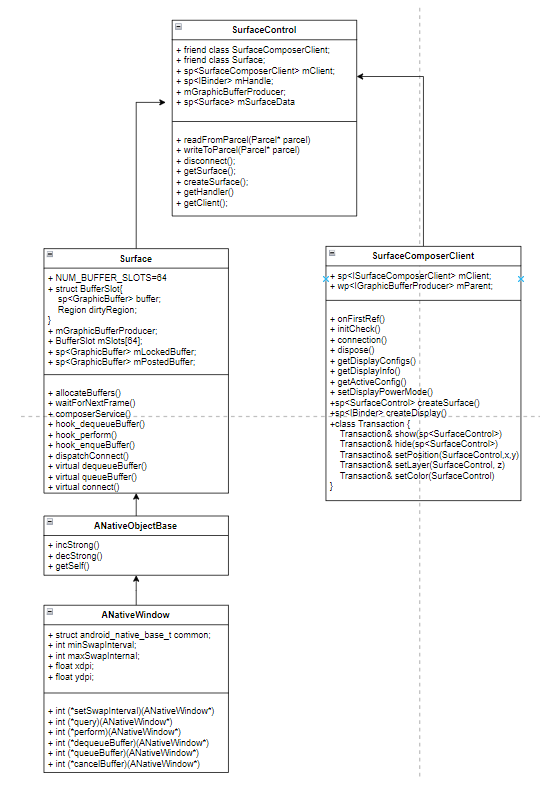
3、Surface的初始化
Surface::Surface(const sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>& bufferProducer, bool controlledByApp)
{
ANativeWindow::setSwapInterval = hook_setSwapInterval;
ANativeWindow::dequeueBuffer = hook_dequeueBuffer;
ANativeWindow::queueBuffer = hook_queueBuffer;
}4、Client架构与初始化
1)测试程序-Android5上的例子
/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/tests/resize/resize.cpp
main()
sp<SurfaceComposerClient> client = new SurfaceComposerClient()
sp<SurfaceControl> surfaceControl = client->createSurface(String8("resize"))
sp<Surface> surface = surfaceControl->getSurface()
SurfaceComposerClient::openGlobalTransaction();
surfaceControl->setLayer(100000); //设置Z值,Z值越大,越靠前
SurfaceComposerClient::closeGlobalTransaction();
ANativeWindow_Buffer outBuffer;
surface->lock(&outBuffer, NULL);
ssize_t bpr = outBuffer.stride * bytesPerPixel(outBuffer.format);
android_memset16((uint16_t*)outBuffer.bits, 0xF800, bpr*outBuffer.height);
surface->unlockAndPost();
surface->lock(&outBuffer);
android_memset16((uint16_t*)outBuffer.bits, 0x07E0, bpr*outBuffer.height);
surface->unlockAndPost();
SurfaceComposerClient::openGlobalTransaction();
surfaceControl->setSize(320, 240);
SurfaceComposerClient::closeGlobalTransaction();5、client<->lib<->service
用到的lib
1、libgui
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.cpp
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp
2、libui
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/6、Service架构和初始化
1、surfaceflinger
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger
2.
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/main_surfaceflinger.cpp
main()
--sp<SurfaceFlinger> flinger = new SurfaceFlinger();
--flinger->init()
--startDisplayService()
--flinger->run()7、APP创建SurfaceFlinger客户端Client过程
1、client创建过程
1)
sp<SurfaceComposerClient> client = new SurfaceComposerClient()
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/SurfaceComposerClient.cpp
--onFirstRef()
----sp<ISurfaceComposer> sf(ComposerService::getComposerService());
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
----sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> sf->createConnection();
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Client.cpp
------new Client(this)
2)
sp<SurfaceControl> surfaceControl = client->createSurface(String8("resize"))
--flinger->createLayer(name, &client, *gbp, ...) //获取GraphicBufferProducer gdp
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
----createBufferLayer()
------sp<BufferLayer> layer = new BufferLayer(this, client, name, w, h, flags);
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/BufferLayer.cpp
--------BufferLayer()
----------Layer()
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Layer.cpp
----------flinger->getHwComposer()
--------onFirstRef() //创建生产者,消费者
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueue.cpp
----------BufferQueue::createBufferQueue(&producer, &consumer, true);
------------sp<BufferQueueCore> core(new BufferQueueCore());
------------sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> producer(new BufferQueueProducer(core, consumerIsSurfaceFlinger));
------------sp<IGraphicBufferConsumer> consumer(new BufferQueueConsumer(core));
----------mProducer = new MonitoredProducer(producer, mFlinger, this); //对Producer、Consumer封装一层
----------mConsumer = new BufferLayerConsumer(consumer,mFlinger->getRenderEngine(), mTextureName, this);
----------mConsumer->setContentsChangedListener(this);
----------sp<const DisplayDevice> hw(mFlinger->getDefaultDisplayDevice()); //使用默认的显示器
----*gdp = layer->getProducer();
----addClientLayer(client, *gbp)
------mGraphicBufferProducerList.insert(IInterface::asBinder(gbc).get()); //插入全局List,等待使用
3)
sp<Surface> surface = surfaceControl->getSurface()
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/SurfaceControl.cpp
--generateSurfaceLocked();
----new Surface(mGraphicBufferProducer, false); // mGraphicBufferProducer=gdp8、APP申请(lock)buffer过程
1、lock过程
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp
surface->lock(&outBuffer, NULL);
--Surface::connect(NATIVE_WINDOW_API_CPU) //获取dispalydevice信息
----mGraphicBufferProducer->connect(listener, api, mProducerControlledByApp, &output);
--dequeueBuffer(&out, &fenceFd);
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/IGraphicBufferProducer.cpp
----onTransact()
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueProducer.cpp
----mGraphicBufferProducer->dequeueBuffer(&buf, &fence, ...)
------*outSlot = found; //在mSlots[]数组中找到可用的Slot,把下标返回,否则需要让Gralloc分配新的buffer
----sp<GraphicBuffer>& gbuf(mSlots[buf].buffer);
----mGraphicBufferProducer->requestBuffer(buf, &gbuf); //拿出刚分配好的buffer
------*buf = mSlots[slot].mGraphicBuffer;
--sp<GraphicBuffer> backBuffer(GraphicBuffer::getSelf(out)); //表示准备显示的buffer内容,即当前构造的layer
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/GraphicBufferMapper.cpp
--backBuffer->lockAsync(&vaddr) //获取vaddr 虚拟地址
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/Gralloc2.cpp
----mMapper->lock()
/android/hardware/libhardware/modules/gralloc/mapper.cpp
------gralloc_lock(gralloc_module_t, buffer_handle_t, vaddr)
--------private_handle_t* hnd = (private_handle_t*)handle;
--------*vaddr = (void*)hnd->base;
--outBuffer->bits = vaddr; //传给APP使用
2、向Gralloc分配内存的过程
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueProducer.cpp
mGraphicBufferProducer->dequeueBuffer(&buf, &fence, ...)
--waitForFreeSlotThenRelock() //如果限制不能分配新的buffer,则等待空闲的Slot,然后锁定
--sp<GraphicBuffer> graphicBuffer = new GraphicBuffer()
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/GraphicBuffer.cpp
----initWithSize()
------GraphicBufferAllocator& allocator = GraphicBufferAllocator::get();
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/Gralloc2.cpp
------allocator.allocate() //使用Gralloc模块分配内存
--------mAllocator->allocate()
/android/hardware/libhardware/modules/gralloc/gralloc.cpp
----------gralloc_alloc()
------------gralloc_alloc_buffer(dev, size, usage, pHandle);
--------------ashmem_create_region("gralloc-buffer", size); //向匿名共享内存分配
----------------private_handle_t* hnd = new private_handle_t(fd, size, 0);
----------------mapBuffer(module, hnd); //虚拟地址供给SF使用
/android/hardware/libhardware/modules/gralloc/mapper.cpp
------------------gralloc_map(module, hnd);
------mBufferMapper.getTransportSize()
--graphicBuffer->initCheck();
3、远程传输数据使用 flatten/unflatten
GraphicBuffer::flatten(void*& buffer, size_t& size, int*& fds, size_t& count)
/android/frameworks/native/libs/binder/Parcel.cpp9、APP提交(unlockAndPost)buffer过程
1、数据构造
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueConsumer.cpp
BufferQueueConsumer::BufferQueueConsumer(const sp<BufferQueueCore>& core) :
--mCore(core),
--mSlots(core->mSlots),
2、unlockAndPost
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp
surface->unlockAndPost();
--mLockedBuffer->unlockAsync(&fd);
--queueBuffer(mLockedBuffer.get(), fd);
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/IGraphicBufferProducer.cpp
----onTransact()
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueProducer.cpp
----mGraphicBufferProducer->queueBuffer(i, input, &output);
------sp<IConsumerListener> frameReplacedListener=mCore->mConsumerListener;
------BufferItem item; //构造item
------item.mAcquireCalled = mSlots[slot].mAcquireCalled;
------item.mGraphicBuffer = mSlots[slot].mGraphicBuffer;
------mCore->mQueue.push_back(item); //加到mQueue中
------frameAvailableListener=mCore->mConsumerListener;
------frameAvailableListener->onFrameAvailable(item);
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueue.cpp
--------ConsumerListener->onFrameAvailable() //onFrameAvailable是通知入口,注意这个函数存在很多地方
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/ConsumerBase.cpp
----------FrameAvailableListener->onFrameAvailable(item);
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/BufferLayer.cpp
------------mFlinger->signalLayerUpdate();
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
--------------mEventQueue->invalidate(); //通知SF线程队列干活 - 涉及VSync10、DisplayDevice
1)DisplayDevice代表一个实际的显示屏,在高版本上已经不再使用,这里了解即可
2)DisplayDevice初始化
1. 初始化
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
init()
--processDisplayHotplugEventsLocked();
----processDisplayChangesLocked(); //显示屏的增减变化处理
--getBE().mHwc->isConnected(HWC_DISPLAY_PRIMARY) //绑定主显示器
--getDefaultDisplayDeviceLocked()->makeCurrent();
--initializeDisplays();
2.新增一个显示屏
processDisplayChangesLocked
// find displays that were added,新增显示屏处理
--sp<DisplaySurface> dispSurface;
--sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> producer;
--sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> bqProducer;
--sp<IGraphicBufferConsumer> bqConsumer;
--mCreateBufferQueue(&bqProducer, &bqConsumer, false);
--dispSurface=new FramebufferSurface(*getBE().mHwc, hwcId, bqConsumer);
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/DisplayHardware/FramebufferSurface.cpp
----mConsumer->setConsumerUsageBits(GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_FB | GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_RENDER | GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_COMPOSER) //表明向FrameBuffer申请内存
--producer = bqProducer;
//初始化displayDevice,并加入到mDisplays Vector中
--mDisplays.add(display,setupNewDisplayDeviceInternal(display, hwcId, state, dispSurface,producer));
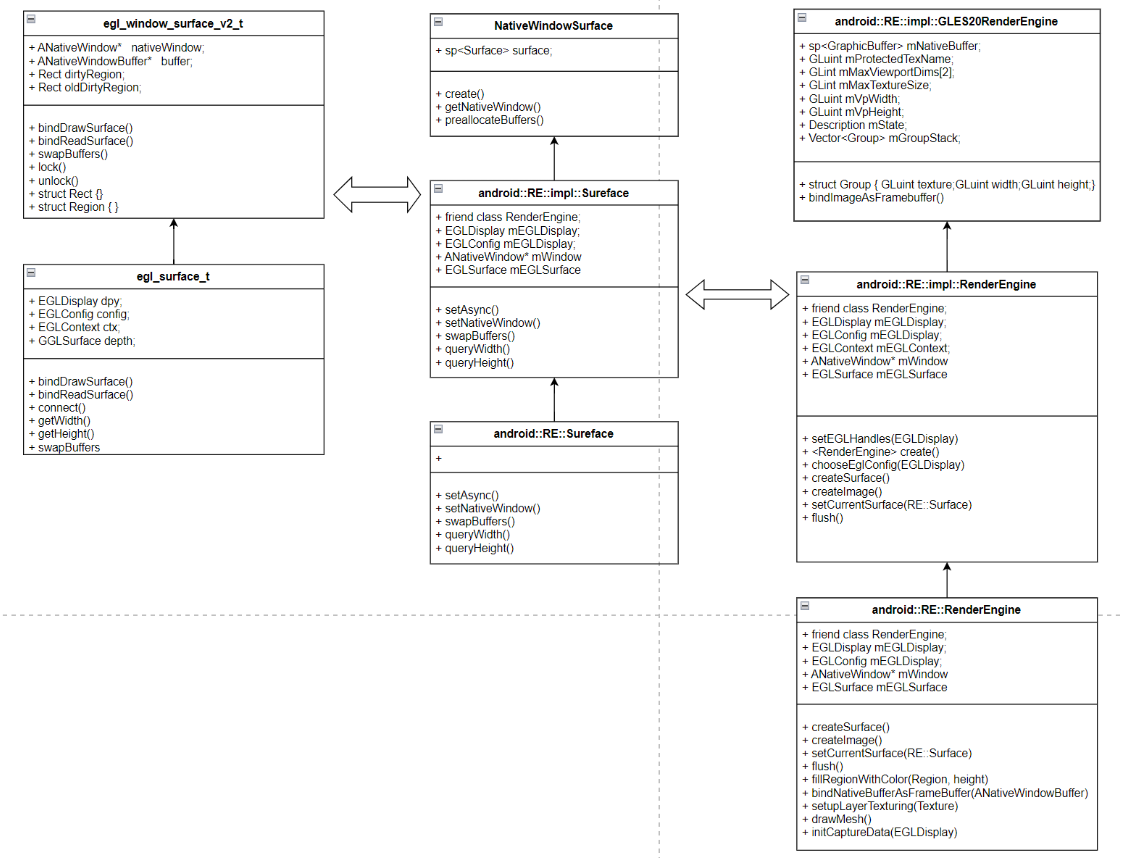
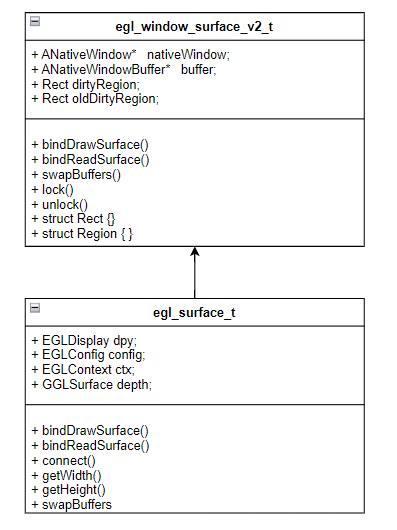
----RE::Surface renderSurface = getRenderEngine().createSurface();
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/RenderEngine/RenderEngine.cpp
------EGLDisplay display = eglGetDisplay(EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
----renderSurface->setNativeWindow(nativeWindow.get());
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/RenderEngine/Surface.cpp
------mEGLSurface=eglCreateWindowSurface(mEGLDisplay, mEGLConfig, mWindow);
/android/frameworks/native/opengl/libagl/egl.cpp
--------createWindowSurface()
----------new egl_window_surface_v2_t(dpy, config,...)
创建一个DisplayDevice
----sp<DisplayDevice> hw=new DisplayDevice(this, state.type, hwcId, state.isSecure, display, nativeWindow,
dispSurface, std::move(renderSurface),..)
------mNativeWindow(nativeWindow)
------mSurface{std::move(renderSurface)}, //指向renderSurface,即Surface
------mLayerStack(NO_LAYER_STACK),
3.后续有新屏接入流程处理,会有消息发出,在SurfaceFlinger消息队列中处理
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
handleTransaction(transactionFlags);
--handleTransactionLocked()
--processDisplayChangesLocked()
----setupNewDisplayDeviceInternal()
------sp<DisplayDevice> hw= new DisplayDevice(wp<IBinder>, surface)
4.setDisplaySize的实现
void DisplayDevice::setDisplaySize(const int newWidth, const int newHeight) {
dirtyRegion.set(getBounds());
mSurface->setNativeWindow(nullptr);
mDisplaySurface->resizeBuffers(newWidth, newHeight);
ANativeWindow* const window = mNativeWindow.get();
mSurface->setNativeWindow(window);
mDisplayWidth = mSurface->queryWidth();
mDisplayHeight = mSurface->queryHeight();
}
5.送显流程
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/DisplayDevice.cpp
displayDevice->swapBuffers(getHwComposer()) //送显
/android/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/RenderEngine/Surface.cpp
--mSurface->swapBuffers();
/android/frameworks/native/opengl/libagl/egl.cpp
----eglSwapBuffers(mEGLDisplay, mEGLSurface)
------d->swapBuffers();
/android/frameworks/native/libs/nativewindow/ANativeWindow.cpp
--------nativeWindow->queueBuffer(nativeWindow, buffer, -1);
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp
----------hook_queueBuffer()
------------queueBuffer()
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueProducer.cpp
--------------mGraphicBufferProducer->queueBuffer()
----------------frameAvailableListener->onFrameAvailable(item); //最终导致poset给硬件
6.申请内存
--------nativeWindow->dequeueBuffer(); //获取新的buffer供下次使用
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp
----------hook_dequeueBuffer()
------------dequeueBuffer()
/android/frameworks/native/libs/gui/BufferQueueProducer.cpp
--------------mGraphicBufferProducer->dequeueBuffer()
----------------usage |= mCore->mConsumerUsageBits; //根据usage决定给APP使用还是DisplayDevice
------------------sp<GraphicBuffer> graphicBuffer = new GraphicBuffer()11、Gralloc模块
1、gralloc模块
1) client
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/Gralloc2.cpp
Allocator::Allocator(const Mapper& mapper) //构造函数
--IAllocator::getService();
2)service
/android/hardware/libhardware/modules/gralloc/gralloc.cpp
static struct hw_module_methods_t gralloc_module_methods = {
.open = gralloc_device_open
};
struct private_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.base = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
},
.registerBuffer = gralloc_register_buffer,
.unregisterBuffer = gralloc_unregister_buffer,
.lock = gralloc_lock,
.unlock = gralloc_unlock,
},
};
/android/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/fb.h
#define GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0 "fb0"
/android/hardware/libhardware/modules/gralloc/framebuffer.cpp
fb_device_open(hw_module_t *module)
--mapFrameBuffer()
----mapFrameBufferLocked()
------fd = open("fb0", O_RDWR, 0);
------ioctl(fd, FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO, &info)
fb_post(struct framebuffer_device_t* dev, buffer_handle_t buffer) //提交buffer12、Fence机制
1)资料快车
1、Fence机制导读: https://blog.csdn.net/vviccc/article/details/104757947
2、Fence-Framework实现:https://juejin.cn/post/7474077946542981174
3、Fence-kernel实现:https://blog.csdn.net/ear5cm/article/details/45093807
4、Android 重学系列Fence原理(基于drm_hwcomposer):https://www.jianshu.com/p/dca7c4d9495c
5、Fence个人理解:https://blog.csdn.net/bruce_zhang123/article/details/124848001
2)Fence框架
Android 4.4引入的Fence机制,用于GPU、CPU、HWC器件之间的buffer数据同步;
BUFFER两种状态, Fence(buffer不可用)和no_Fence(buffer可用);
Fence是纯软件实现?硬件实现(闭源),也可以由软件模拟Fence(/external/drm_hwcomposer)
1、经典架构
1)Framework源码实现
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/Fence.cpp
/android/frameworks/native/libs/ui/FenceTime.cpp
Fence : 对libsync的c++ 封装,mFenceFd的封装,再调用libsync实现api
FenceTime :对Fence的封装,提供简单的API:isValid getSignalTime
2)lib-open/read/write Fence驱动,可以是软件,也可以是硬件
/android/system/core/libsync
1、sync_timeline的初始化
sw_sync_timeline_create(void)
--open("/sys/kernel/debug/sync/sw_sync", O_RDWR);
--open("/dev/sw_sync", O_RDWR);
2、sw_sync_timeline_inc
--ioctl(fd, SW_SYNC_IOC_INC, &arg);
3、sync_wait
/android/system/core/libsync/sync.c
3)Kernel驱动实现(软件模拟实现的Fence驱动)
/android/kernel/fusion/4.19/drivers/dma-buf
2、基于DRM的hwc开源实现
/android/external/drm_hwcomposer/hwcomposer.cpp
在drm框架中集成了Fence的功能,更加方便统一管理和使用Fence时间轴设计(按顺序唤醒)
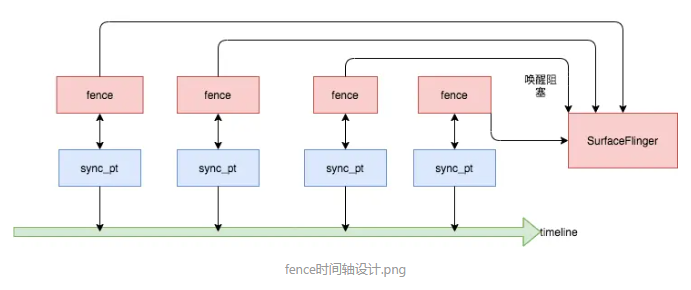
3)Fence与VSYnc的区别?
https://www.oryoy.com/news/jie-mi-android-fence-yu-vsync-xing-neng-ti-sheng-hai-shi-shi-jue-xian-jing-a13347758.html
1)Fence是一种硬件级别的同步机制(类似锁机制),保证UI显示的三个步骤顺序执行,渲染->(no Fence)->合成->(no Fence)->显示
2)VSYNC是一种同步信号(类似硬件的时钟信号),保证各个阶段的处理速度移植,比如帧率和GPU渲染同步;