IO是 Input与Output
输入输出:针对终端而言的
键盘,鼠标用来输入数据的
显示数据时,在屏幕(显示器)
磁盘 存储数据
unix哲学:一切皆文件 抽象成文件描述符
IO流
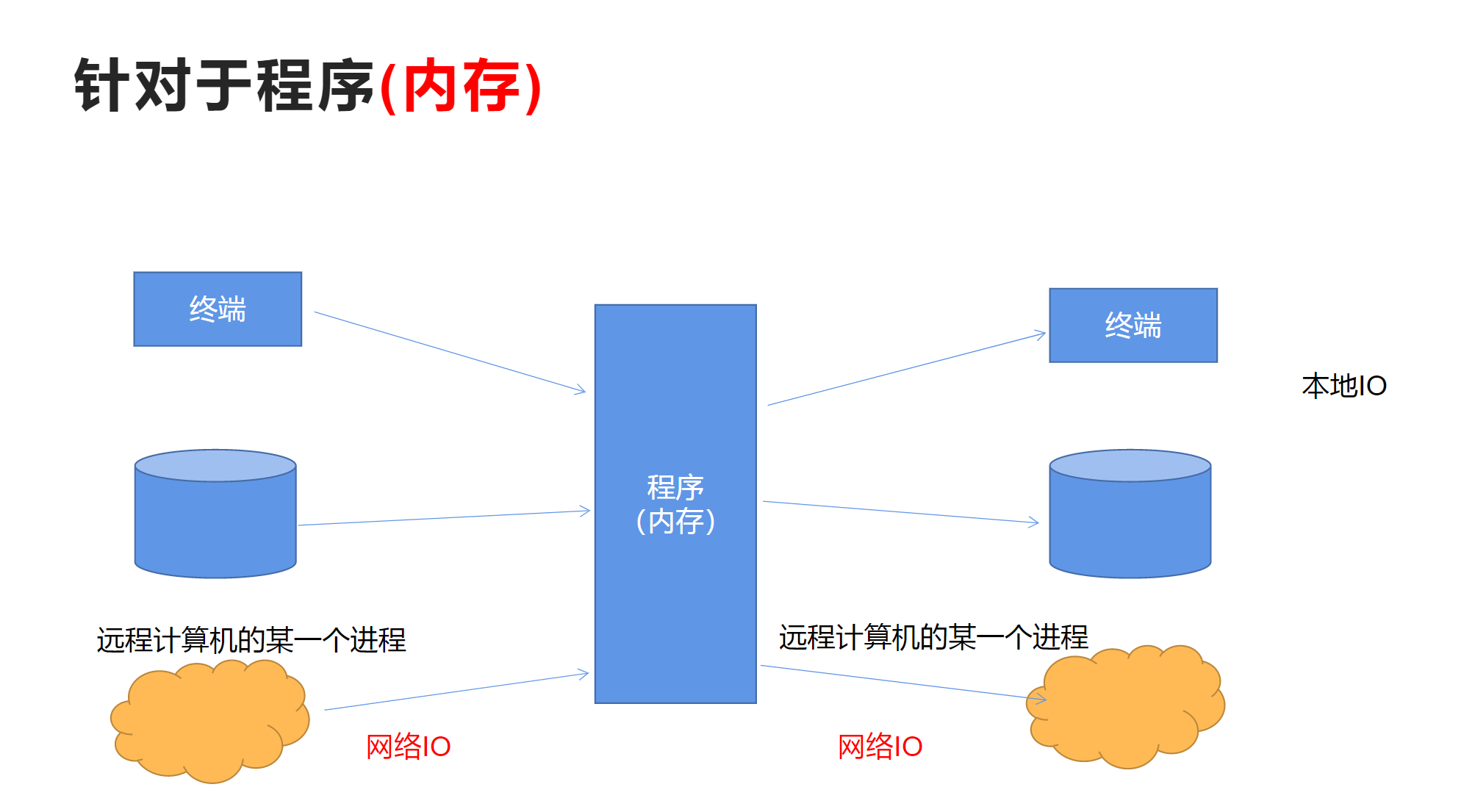
输入输出流针对于程序而言,针对于内存
数据从其他地方保存到内存中,称为输入流
数据从内存保存到其他地方,成为输出流

流的状态
流都有四种状态:
1.goodbit 有效状态
2 .badbit 系统级别的错误,不可恢复
3.failbit 可以恢复的错误
4.eofbit 到了流的末尾
当流处于有效状态时,才可以正常使用
bool good() const;
bool bad()const;
bool fail()const;
bool eof()const;
标准输入输出流:
Code:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::istream;//通用输入流
void printStreamStatus(istream &is)
{
cout << "it's goodbit: " << is.good() << endl;
cout << "it's badbit: " << is.bad() << endl;
cout << "it's eofbit: " << is.eof() << endl;
cout << "it's failbit: " << is.fail() << endl;
}
void test0()
{
int number = 0;
printStreamStatus(cin);
cin >> number;
cout << "number: " << number << endl;
printStreamStatus(cin);
//流的状态异常,会导致无法输入
cin.clear();//恢复流的状态
//清空缓冲区
cin.ignore(1024, '\n');
string line;
cin >> line;
cout << "line: " << line << endl;
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}对于cin这个istrem对象,在输入时,我们可以检测cin对象是否异常来判断输入是否正确,然后恢复状态,清空缓冲区。
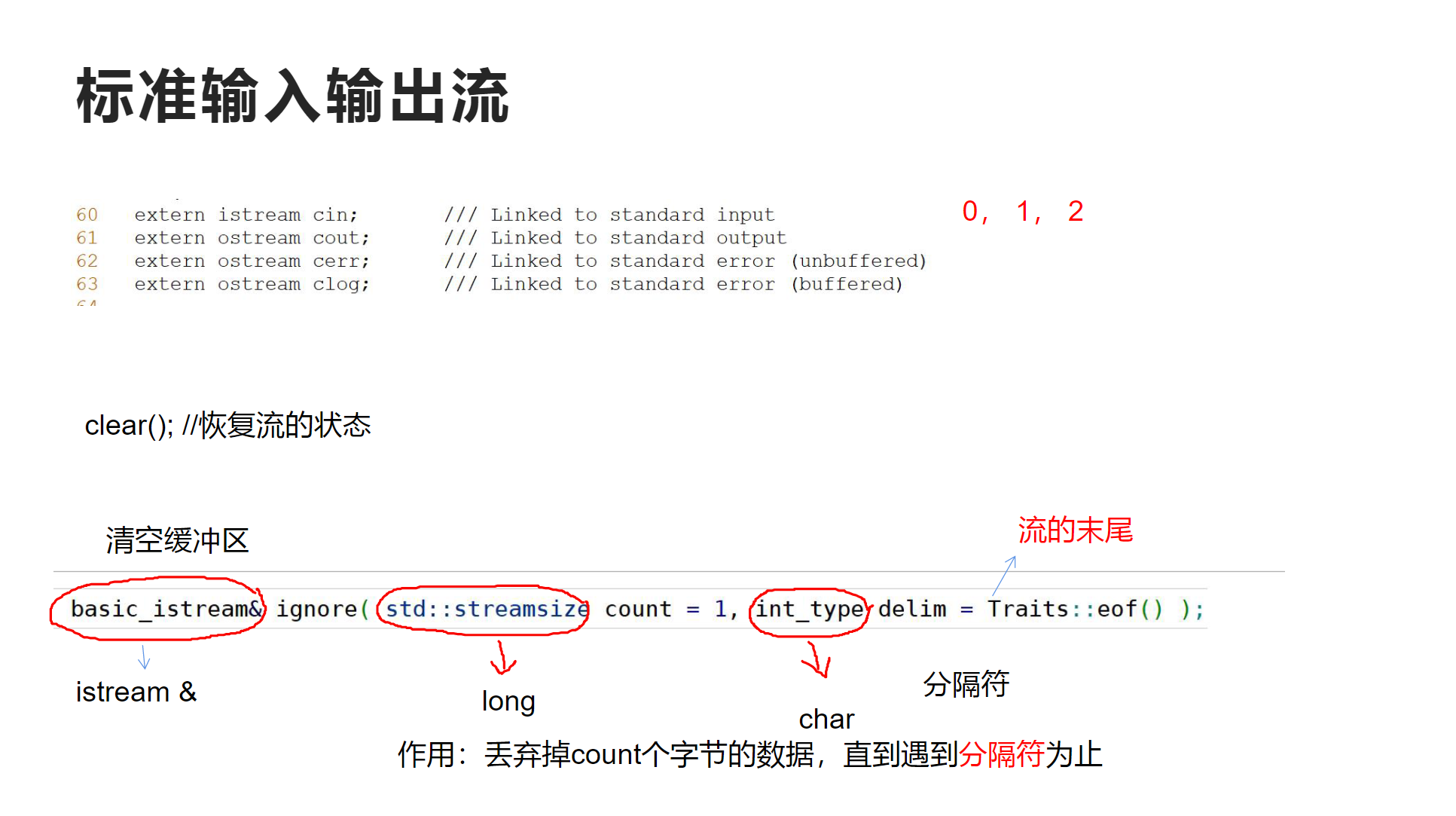
关于ignore函数的声明:
basic_istream& ignore(std::streamsize count=1,int_type delim=Traits::eof());
返回值时一个istream的引用,第一个参数是要舍弃的字节数,第二个是分隔符,默认值是流的末尾
作用就是:作用:丢弃掉count个字节的数据,直到遇到分隔符为止
示例:健壮的读取一个整形
Code:
cpp
void ReadInteger(istream &is,int &number)
{
cout << "Please input a interger: " << endl;
while (is >> number, !is.eof())
{
if (is.bad())
{
cout << "istream has broken!" << endl;
return;
}
else if (is.fail())
{
is.clear();
is.ignore(std::numeric_limits<std::streamsize>::max(), '\n');
cout << "Please input a interger: " << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "number: " << number << endl;
break;
}
}
}缓冲区是什么?
缓冲区(Buffer)是内存中的一块临时存储区域,用于暂存数据,减少频繁的I/O操作。
// 比喻:缓冲区就像快递的中转站
// 发送方(程序) -> 中转站(缓冲区) -> 接收方(屏幕/键盘)2. cout的缓冲区 vs cin的缓冲区
cout的缓冲区(输出缓冲区)
cpp
// 程序输出数据时:
程序数据 → cout缓冲区 → 操作系统 → 屏幕控制台
// 示例:
cout << "Hello"; // 数据先进入输出缓冲区
// 此时屏幕上可能还看不到"Hello"cin的缓冲区(输入缓冲区)
// 用户输入数据时:
键盘输入 → 操作系统 → cin缓冲区 → 程序读取
// 示例:
int num;
cin >> num; // 从输入缓冲区读取数据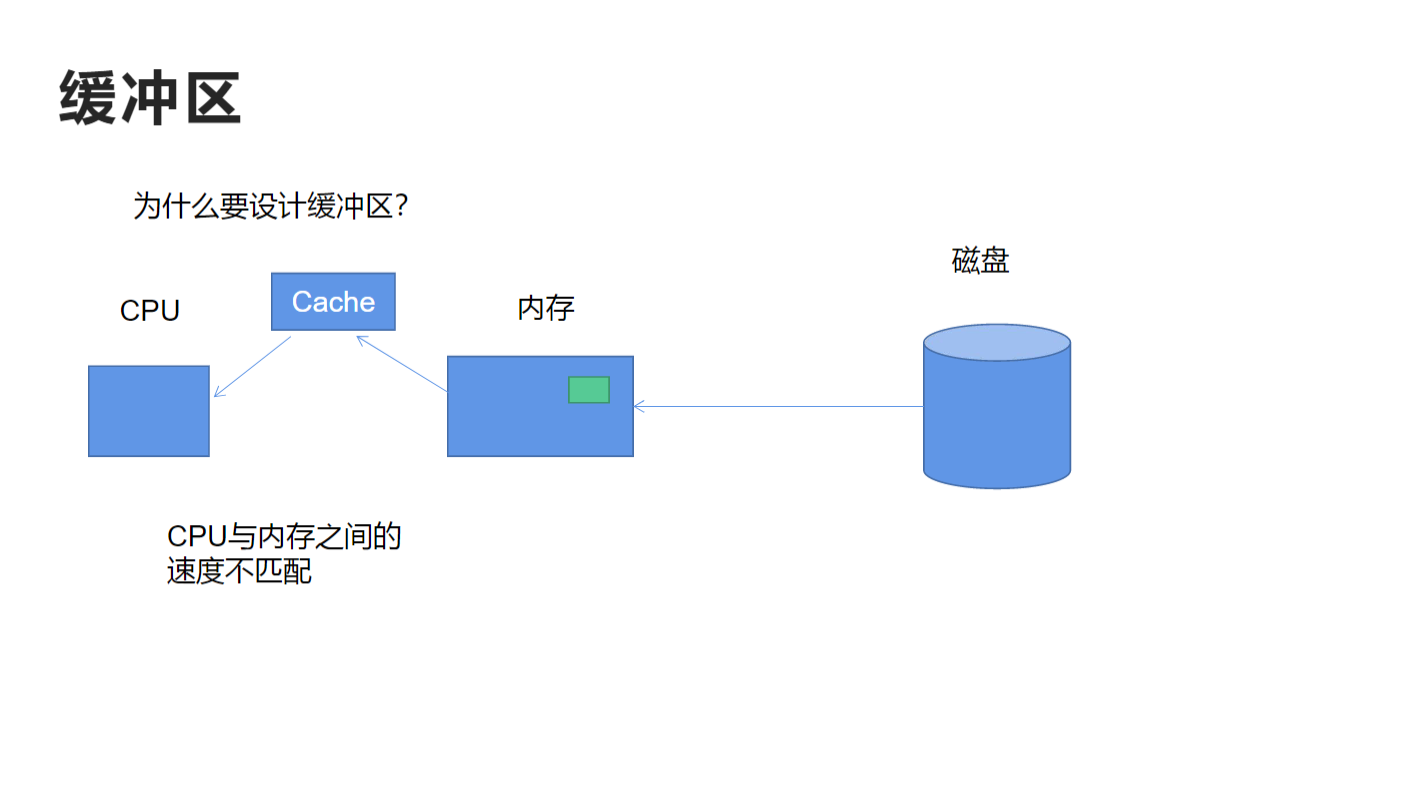


Code:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<Windows.h>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::istream;//通用输入流
void test0()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4097; i++)
{
cout << 'a';
}
Sleep(3000);
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}成因介绍:
详细的执行过程分析
第1-4096个字符:
-
循环输出第1到第4096个字符'a'
-
每个字符占用1字节,共4096字节
-
当输出第4096个字符时,缓冲区正好填满
-
缓冲区满触发自动刷新
-
结果:您看到屏幕上立即显示出4096个'a'
第4097个字符:
-
当程序试图输出第4097个字符时,发现缓冲区已满
-
系统自动执行:
-
刷新当前缓冲区(4096个'a'已显示)
-
清空缓冲区
-
将第4097个字符'a'放入现在空了的缓冲区
-
-
结果:第4097个字符进入缓冲区,但未显示
Sleep(3000):
-
程序暂停3秒
-
此时缓冲区中只有1个字符'a'
-
缓冲区未满(只有1/4096),不会触发自动刷新
-
结果:屏幕上没有新输出,保持4096个'a'的显示状态
程序结束(return 0):
-
main()函数返回 -
程序正常退出
-
退出前自动刷新所有标准流的缓冲区
-
结果:缓冲区中仅存的1个字符'a'被刷新显示到屏幕

可用cerr输出用于调试,输出内容不会到缓冲区,而是直接输出。
文件IO

文件输入流 ifstream
std::basic_ifstream<CharT,Traits>::basic_ifstream
几种构造函数:
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----|-----------|
| basic_ifstream(); | (1) | |
| explicit basic_ifstream( const char* filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::in ); | (2) | |
| explicit basic_ifstream( const std::filesystem::path::value_type* filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::in ); | (3) | (C++17 起) |
| explicit basic_ifstream( const std::string& filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::in ); | (4) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class FsPath > explicit basic_ifstream( const FsPath& filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::in ); | (5) | (C++17 起) |
| basic_ifstream( basic_ifstream&& other ); | (6) | (C++11 起) |
| basic_ifstream( const basic_ifstream& rhs ) = delete; |
explicit basic_ifstream( const char* filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode= std::ios_base::in );
第一个参数是文件名,第二个操作是文件的打开模式
指定可用的文件打开标志。它是一个 BitmaskType,定义了以下常量
|-----------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 常量 | 解释 |
| app | 每次写入前定位到流的末尾 |
| 二进制 | 以 二进制模式 打开 |
| in | 为读取而打开 |
| out | 为写入而打开 |
| trunc | 打开时丢弃流的内容 |
| ate | 打开后立即定位到流的末尾 |
| noreplace (C++23) | 以独占模式打开 |
app针对文件输出流,ate针对输入流
basic_ifstream( const basic_ifstream& rhs ) = delete;
表明拷贝构造被删除,文件输入流的拷贝构造被删除
几种成员函数:
成员函数
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------|
| (构造函数) | 构造文件流 (public member function) |
| (析构函数) [virtual](隐式声明) | 销毁 basic_ifstream 和关联的缓冲区,关闭文件 (virtual public member function) |
| operator= (C++11) | 移动文件流 (public member function) |
| swap (C++11) | 交换两个文件流 (public member function) |
| rdbuf | 返回底层原始文件设备对象 (public member function) |
| native_handle (C++26) | 返回底层实现定义的句柄 (public member function) |
| ###### 文件操作 ||
| is_open | 检查流是否关联了文件 (public member function) |
| open | 打开文件并将其与流关联 (public member function) |
| close | 关闭关联的文件 (public member function) |
读取一行
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----|---|
| basic_istream& getline( char_type* s, std::streamsize count ); | (1) | |
| basic_istream& getline( char_type* s, std::streamsize count, char_type delim ); | (2) |
标准库里的getline
template< class CharT, class Traits, class Allocator >
std::basic_istream<CharT, Traits>&
getline( std::basic_istream<CharT, Traits>& input,
std::basic_string<CharT, Traits, Allocator>& str, CharT delim );
第一个参数是流对象,第二个是字符串,第三个是分隔符

Code:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<vector>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::cerr;
using std::string;
using std::istream;//通用输入流
using std::ifstream;
void test0()
{
//文件输入流要求文件必须存在
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("ifstream.txt");
if (!ifs.good())
{
cout << "iftream open file error!" << endl;
return;
}
//string word;
////>>输入流运算符以空格\t \n作为分格符
//while (ifs >> word)
//{
// cout << word;
//}
//每次读取一行数据
//成员函数方式
//char buff[1024] = { 0 };
//while (ifs.getline(buff, 1024))
//{
// cout << buff << endl;
//}
//std标准库方式
std::vector<string>file;
file.reserve(20);
string line;
while (std::getline(ifs, line))
{
cout << line << endl;
file.push_back(line);
}
//for (auto& line : file)cout << line << endl;
ifs.close();//切记关闭流对象
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}读取整个文件

std::basic_istream<CharT,Traits>::read
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---|---|
| basic_istream& read( char_type* s, std::streamsize count ); | | |
| | | |
从流中提取字符。
行为类似于 UnformattedInputFunction。构造并检查哨兵对象后,提取字符并将其存储到字符数组的连续位置,该字符数组的第一个元素由 s 指向。字符的提取和存储会一直持续到满足以下任一条件:
- count 个字符已被提取和存储。
- 输入序列上发生文件尾条件(在这种情况下,调用 setstate(failbit|eofbit))。可以使用 gcount() 查询成功提取的字符数。
std::basic_istream<CharT,Traits>::seekg
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----|---|
| basic_istream& seekg( pos_type pos ); | (1) | |
| basic_istream& seekg( off_type off, std::ios_base::seekdir dir ); | (2) | |
| | | |
设置当前关联的 streambuf 对象的输入位置指示器。
|-----------------------------------|-----------|
| 在执行任何其他操作之前,seekg 会清除 eofbit。 | (C++11 起) |
seekg 的行为类似于 非格式化输入函数,除了 gcount() 不受影响。在构造并检查哨兵对象后,
-
如果 fail() != true,将输入位置指示器设置为绝对值(相对于文件开头)pos。具体来说,执行 rdbuf()->pubseekpos(pos, std::ios_base::in)(pubseekpos 又会调用特定缓冲区的 seekpos,例如 basic_filebuf::seekpos、basic_stringbuf::seekpos 或 strstreambuf::seekpos)。如果失败,则调用 setstate(std::ios_base::failbit)。
-
如果 fail() != true,将输入位置指示器设置为相对于 dir 定义的位置的 off 位置。具体来说,执行 rdbuf()->pubseekoff(off, dir, std::ios_base::in)。如果失败,则调用 setstate(std::ios_base::failbit)。
参数
|-----|---|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| pos | - | 要设置输入位置指示器的绝对位置 |
| off | - | 要设置输入位置指示器的相对位置(正或负) |
| dir | - | 定义应用相对偏移量的基本位置。它可以是以下常量之一 |----------------------------------------------------------------|-------------| | 常量 | 解释 | | beg | 流的开始 | | end | 流的结束 | | cur | 流位置指示器的当前位置 | |
std::basic_istream<CharT,Traits>::tellg
|-------------------|---|---|
| pos_type tellg(); | | |
| | | |
返回当前关联的 streambuf 对象的输入位置指示符。
行为类似于 UnformattedInputFunction,除了 gcount() 不受影响。构造并检查守卫对象后,如果 fail() == true,则返回 pos_type(-1)。否则,返回 rdbuf()->pubseekoff(0, std::ios_base::cur, std::ios_base::in)。
Code:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<vector>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::cerr;
using std::string;
using std::istream;//通用输入流
using std::ifstream;
void test0()
{
//文件输入流要求文件必须存在
ifstream ifs("ifstream.txt",std::ios::binary);
ifs.seekg(0, std::ios::end);
long len = ifs.tellg();
cout << "length: " << len << endl;
char* pbuff = new char[len + 1];
//读取整个文件的内容
ifs.seekg(0);
ifs.read(pbuff, len);
pbuff[len] = '\0';
cout << pbuff << endl;
delete[] pbuff;
ifs.close();//切记关闭流对象
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}输出流:
std::basic_ofstream
std::basic_ofstream
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---|---|
| 定义于头文件 <fstream> | | |
| template< class CharT, class Traits = std::char_traits<CharT> > class basic_ofstream : public std::basic_ostream<CharT, Traits> | |
std::basic_ofstream<CharT,Traits>::basic_ofstream
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----|-----------|
| basic_ofstream(); | (1) | |
| explicit basic_ofstream( const char* filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::out ); | (2) | |
| explicit basic_ofstream( const std::filesystem::path::value_type* filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::out ); | (3) | (C++17 起) |
| explicit basic_ofstream( const std::string& filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::out ); | (4) | (C++11 起) |
| template< class FsPath > explicit basic_ofstream( const FsPath& filename, std::ios_base::openmode mode = std::ios_base::out ); | (5) | (C++17 起) |
| basic_ofstream( basic_ofstream&& other ); | (6) | (C++11 起) |
| basic_ofstream( const basic_ofstream& rhs ) = delete; | (7) | (C++11 起) |
| | | |
构造新的文件流。
- 默认构造函数:构造一个未关联文件的流:默认构造 std::basic_filebuf,并使用指向此默认构造的 std::basic_filebuf 成员的指针构造基类。
2,3) 首先,执行与默认构造函数相同的步骤,然后通过调用 rdbuf()->open(filename, mode | std::ios_base::out) 将流与文件关联(有关该调用的效果的详细信息,请参阅 std::basic_filebuf::open)。如果 open() 调用返回空指针,则设置 setstate(failbit)。重载 (3) 仅在 std::filesystem::path::value_type 不是 char 时提供。(C++17 起)
4,5) 与 basic_ofstream(filename.c_str(), mode) 相同。(5) 仅当 FsPath 为 std::filesystem::path 时才参与重载决议。(C++17 起) 注意,尽管默认模式是 out,但效果与 std::filebuf::open 中描述的 out | trunc 的效果相同。
-
移动构造函数。首先,从 other 移动构造基类(不影响 rdbuf() 指针),然后移动构造 std::basic_filebuf 成员,然后调用 this->set_rdbuf() 以将新的
basic_filebuf安装为基类中的 rdbuf() 指针。 -
复制构造函数被删除:此类不可复制

Code:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<vector>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::cerr;
using std::string;
using std::istream;//通用输入流
using std::ifstream;
using std::ofstream;
string file;
void test0()
{
//文件输入流要求文件必须存在
ifstream ifs("ifstream.txt",std::ios::binary);
ifs.seekg(0, std::ios::end);
long len = ifs.tellg();
cout << "length: " << len << endl;
char* pbuff = new char[len + 1];
//读取整个文件的内容
ifs.seekg(0);
ifs.read(pbuff, len);
pbuff[len] = '\0';
file = pbuff;
delete[] pbuff;
ifs.close();//切记关闭流对象
}
void test1()
{
///string filename("ofstream.txt");
//文件输出流没有文件直接创建一个新文件
//ofstream ofs(filename);
////默认out模式,当文件存在时直接清空内容
//if (!ofs)
//{
// cout << "ofstream open file error" << endl;
// return;
//}
////ofs << file;
//在文件末尾追加
ofstream ofs("ifstream.txt", std::ios::app);
string text = "\n你好\n";
ofs << text;
ofs.close();
}
int main()
{
test0();
test1();
return 0;
}
fstream
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<fstream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::istream;//通用输入流
using std::fstream;
void test0()
{
//文件输入输出流要求文件必须存在
fstream fs("fstream.txt");
if (!fs)
{
cout << "fstream open file error!" << endl;
return;
}
int number = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cin >> number;
fs << number << " ";
}
//要想正确读取,必须偏移位置
fs.seekg(0);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
fs >> number;
cout << number << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}字符串的输入输出流
作用:在字符串与其他类型之间做类型(格式)转换
三种类型
istringstream
ostringstream
stringstream
std::basic_istringstream
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---|---|
| 定义于头文件 <sstream> | | |
| template< class CharT, class Traits = std::char_traits<CharT>, class Allocator = std::allocator<CharT> > class basic_istringstream : public basic_istream<CharT, Traits>; | | |
| | | |
类模板 std::basic_istringstream 对基于字符串的流实现输入操作。它有效地存储 std::basic_string 的实例并对其执行输入操作。
在底层,该类实际上将 std::basic_stringbuf 的原始字符串设备实现封装到 std::basic_istream 的高级接口中。提供了 std::basic_stringbuf 唯一成员的完整接口。
常见构造:
explicit basic_istringstream
( const std::basic_string<CharT, Traits, Allocator>& str,
std::ios_base::openmode mode =
std::basic_ostringstream
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---|---|
| 定义于头文件 <sstream> | | |
| template< class CharT, class Traits = std::char_traits<CharT>, class Allocator = std::allocator<CharT> > class basic_ostringstream : public basic_ostream<CharT, Traits>; | | |
| | | |
类模板 std::basic_ostringstream 实现基于字符串流的输出操作。它有效地存储 std::basic_string 的实例并对其执行输出操作。
在底层,该类主要将 std::basic_stringbuf 的原始字符串设备实现封装到 std::basic_ostream 的高级接口中。提供了指向独有 std::basic_stringbuf 成员的完整接口。
常见构造:
explicit basic_ostringstream
( const std::basic_string<CharT, Traits, Allocator>& str,
std::ios_base::openmode mode =
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using std::istream;//通用输入流
using std::fstream;
using std::istringstream;
using std::ostringstream;
using std::ifstream;
void test0()
{
//将其它类型转换为字符串
int num1 = 512;
int num2 = 1024;
ostringstream oss;
oss << "num1= " << num1 << " num2= " << num2;
//cout << oss.str() << endl;
string str = oss.str();
cout << str << endl;
//将字符串类型转换为其他类型
string key;
int number;
istringstream iss(str);
//输入流运算符是以\t \n为分隔符
while (iss >> key >> number)
{
cout << key << " " << number << endl;
}
}
//将整形转换为字符串
string int2str(int number)
{
ostringstream oss;
oss << number;
return oss.str();
}
//读取配置文件
void readConfigruation(const string& filename)
{
ifstream ifs(filename);
if (!ifs)
{
cout << "ifstream open file " << filename << " error" << endl;
return;
}
string line;
string key, val;
while (std::getline(ifs, line))
{
istringstream iss(line);
iss >> key >> val;
cout << key << " -> " << val << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test0();
return 0;
}