一、概述:
方法内部自己调用自己
二、分类:
1.直接递归
public static void method(){
method()
}
2.间接递归:
A(){
B()
}
B(){
C()
}
C(){
A()
}
3.注意:
(1)递归必须要有出口,否则会出现"栈内存溢出"
(2)递归即使有出口,次数也不要太多。
三、练习:
1.输出3,2,1
java
public class a_Recursion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method(3);
}
public static void method(int n){
if (n == 1){
System.out.println(n);
return;
}
System.out.println(n);
n--;
method(n);
}
}内存运行:
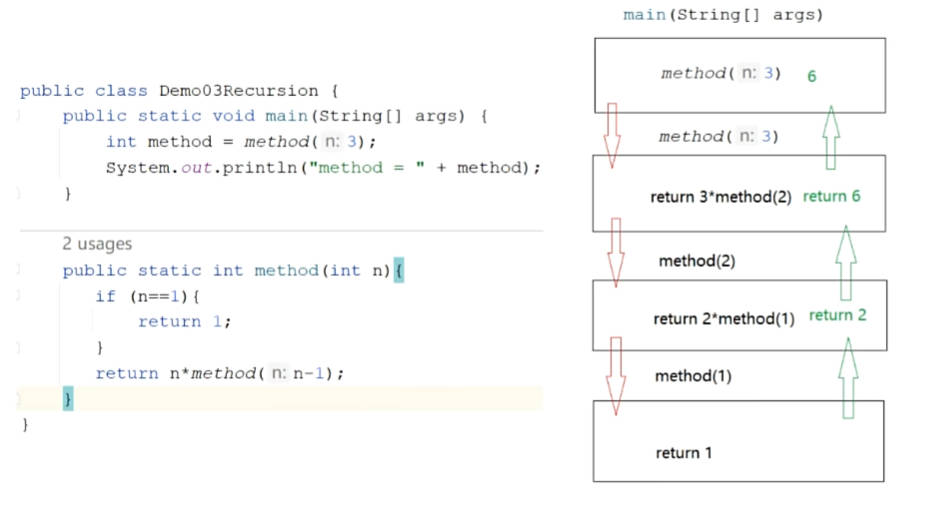
2.实现5的阶乘:
method(1) 1
method(2) 2*1 = 2*method(1)
method(3) 3*2*1 = 3*method(2)
method(n) = n*method(n-1)
java
public class a_Recursion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = method(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int method(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return n * method(n-1);
}
}
3.斐波那契数列:
即:1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89,144....
java
public class a_Recursion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = method(12);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int method(int n) {
if (n == 1 || n == 2) {
return 1;
}
return method(n-1) + method(n-2);
}
}