一、MyBatis整体架构与设计模式
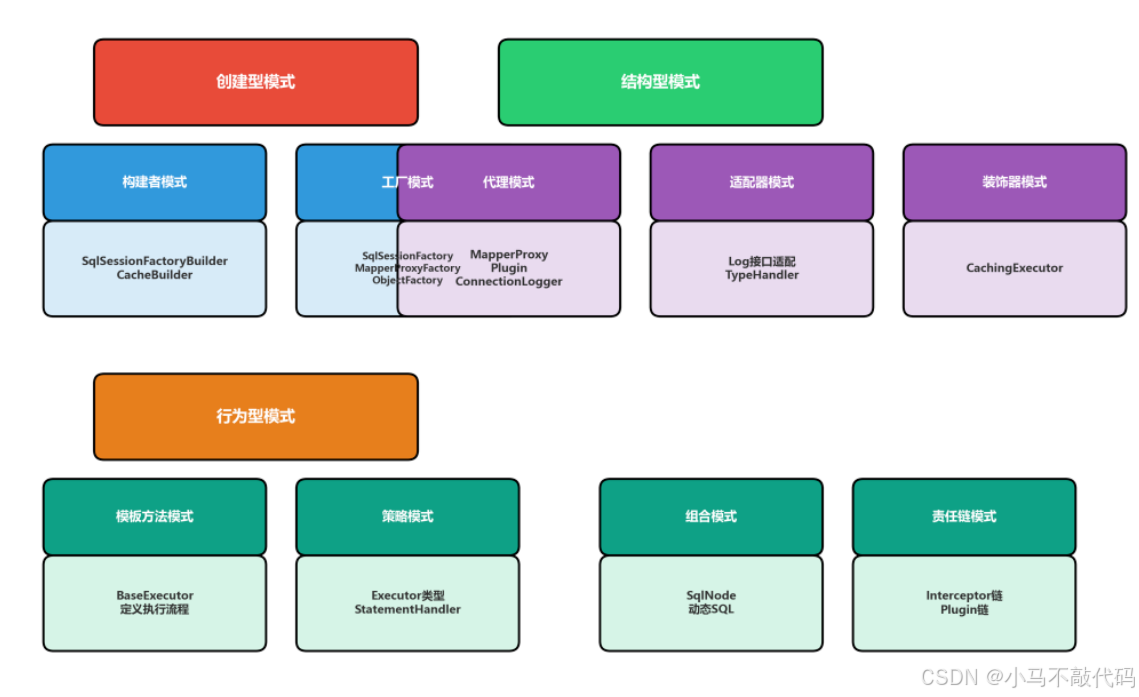
MyBatis作为一款优秀的持久层框架,其代码中运用了多种经典的设计模式。这些设计模式的应用,使得MyBatis具有良好的扩展性、灵活性和可维护性。
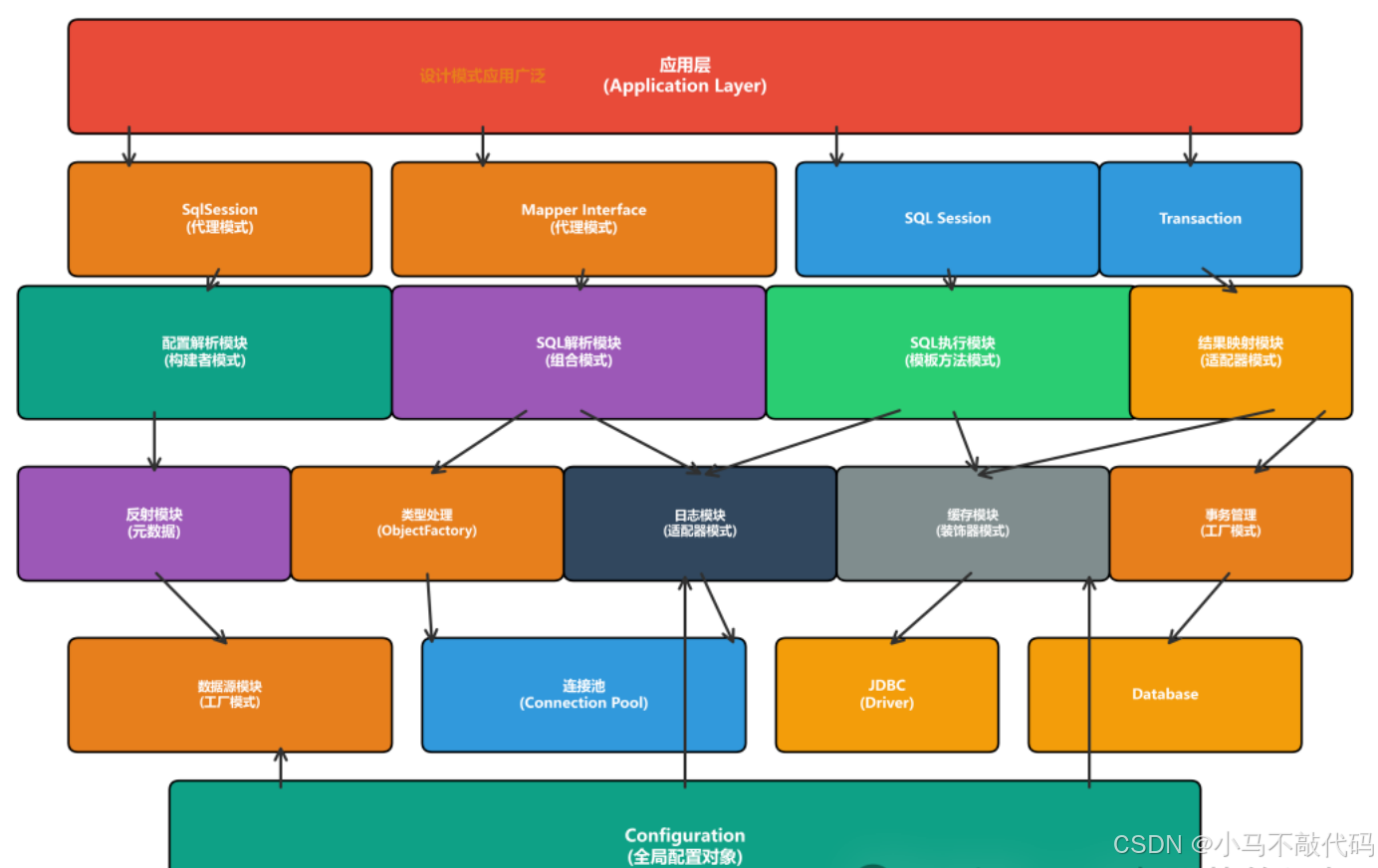
1.1 MyBatis整体架构
MyBatis采用了分层架构设计,从上到下主要包括:
应用层:用户应用程序
接口层:SqlSession、Mapper接口
核心处理层:SQL解析、执行、结果映射
基础支撑层:反射、类型处理、日志、缓存、事务等
数据层:数据源、连接池、JDBC驱动
在这些层次中,设计模式被广泛应用,贯穿整个框架。
1.2 MyBatis中的主要设计模式
MyBatis中使用的设计模式包括:
构建者模式(Builder Pattern):SqlSessionFactoryBuilder、CacheBuilder、ParameterExpression等
工厂模式(Factory Pattern):SqlSessionFactory、MapperProxyFactory、ObjectFactory、DataSourceFactory等
代理模式(Proxy Pattern):MapperProxy、Plugin、ConnectionLogger、PreparedStatementLogger等
组合模式(Composite Pattern):SqlNode、DynamicContext等
模板方法模式(Template Method Pattern):BaseExecutor、SimpleExecutor、BatchExecutor等
适配器模式(Adapter Pattern):Log接口及其适配器
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern):CachingExecutor、Executor的包装
策略模式(Strategy Pattern):RoutingStatementHandler、ResultSetHandler等
迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern):PropertyTokenizer、DefaultCursor等
责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility):Interceptor链、Plugin链
本文将重点讲解构建者模式、工厂模式和代理模式在MyBatis中的应用。
二、构建者模式(Builder Pattern)
构建者模式是一种创建型设计模式,它允许你分步骤创建复杂对象。该模式使你可以使用相同的创建代码生成不同类型和形式的对象。
2.1 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder是MyBatis中最典型的构建者模式应用。它负责从XML配置文件或Configuration对象构建SqlSessionFactory。
2.1.1 基本用法
java
// 从XML文件构建
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 从Configuration对象构建
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.addMapper(UserMapper.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(config);2.1.2 源码分析
java
publicclassSqlSessionFactoryBuilder{
// 从InputStream构建
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream){
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment){
return build(inputStream, environment, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, Properties properties){
return build(inputStream, null, properties);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties){
try {
// 1. 解析XML配置文件,创建XMLConfigBuilder
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// 2. 解析配置并构建Configuration对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
// 从Configuration构建
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config){
// 3. 创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory
returnnew DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
// 从Reader构建
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader){
return build(reader, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment){
return build(reader, environment, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties properties){
return build(reader, null, properties);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties){
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
}2.1.3 构建过程分析
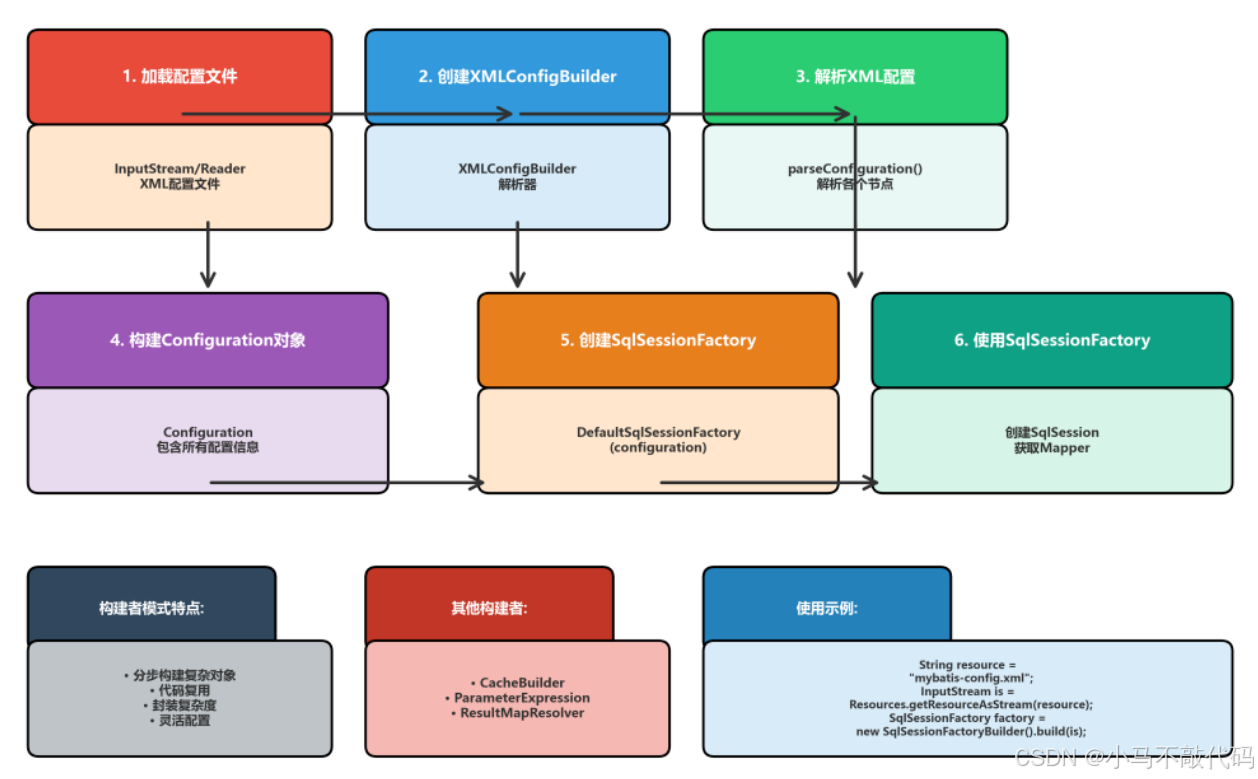
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的构建过程可以分为以下几个步骤:
加载配置文件:从InputStream或Reader加载XML配置文件
创建解析器:创建XMLConfigBuilder解析XML配置
解析配置:解析XML配置文件,构建Configuration对象
创建工厂:使用Configuration对象创建SqlSessionFactory
2.2 XMLConfigBuilder
XMLConfigBuilder是实际的构建者,负责解析XML配置文件并构建Configuration对象。
java
publicclassXMLConfigBuilderextendsBaseBuilder{
privateboolean parsed;
privatefinal XPathParser parser;
private String environment;
publicXMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props){
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
// 解析配置
public Configuration parse(){
if (parsed) {
thrownew BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 解析configuration节点
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
privatevoidparseConfiguration(XNode root){
try {
// 解析各个配置项
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginsElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory"));
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
thrownew BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}2.3 构建者模式的优势
分步构建:将复杂对象的构建过程分解为多个步骤
代码复用:相同的构建代码可以创建不同的对象
封装复杂度:隐藏对象创建的复杂细节
灵活配置:支持多种不同的配置方式
2.4 其他构建者模式应用
除了SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,MyBatis中还有其他构建者模式的应用:
2.4.1 CacheBuilder
java
publicclassCacheBuilder{
privatefinal String id;
private Class<? extends Cache> implementation;
private List<Class<? extends Cache>> decorators;
private Integer size;
private Long clearInterval;
privateboolean readWrite;
private Properties properties;
public Cache build(){
// 设置默认实现
setDefaultImplementations();
// 创建缓存
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);
// 应用装饰器
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
return cache;
}
}2.4.2 ParameterExpression
java
publicclassParameterExpressionimplementsIterator<ParameterExpression> {
// 构建者模式用于解析参数表达式
publicParameterExpression(String expression){
parseExpression(expression);
}
privatevoidparseExpression(String expression){
// 解析属性表达式
}
}三、工厂模式(Factory Pattern)
工厂模式是一种创建型设计模式,它提供了创建对象的最佳方式。在工厂模式中,我们在创建对象时不会对客户端暴露创建逻辑,并且是通过使用一个共同的接口来指向新创建的对象。
3.1 SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory是MyBatis中最核心的工厂接口,负责创建SqlSession对象。
3.1.1 接口定义
java
publicinterfaceSqlSessionFactory{
// 创建SqlSession的各种方法
SqlSession openSession();
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection);
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
Configuration getConfiguration();
}3.1.2 DefaultSqlSessionFactory
java
publicclassDefaultSqlSessionFactoryimplementsSqlSessionFactory{
privatefinal Configuration configuration;
publicDefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration){
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(){
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit){
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, autoCommit);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType){
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, false);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level){
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), level, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType,
TransactionIsolationLevel level,
boolean autoCommit){
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 1. 获取环境配置
Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 2. 获取事务工厂
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 3. 创建事务对象
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 4. 创建执行器
Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 5. 创建SqlSession
returnnew DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}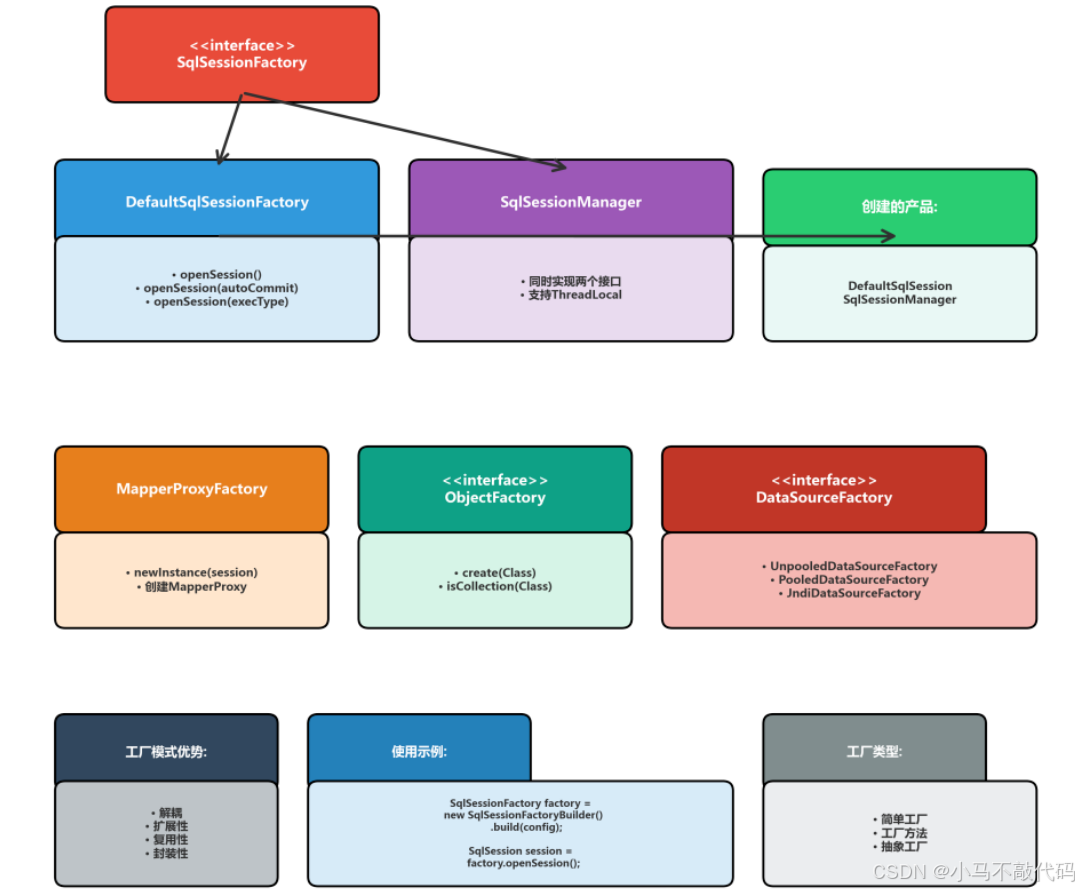
3.2 MapperProxyFactory
MapperProxyFactory负责创建Mapper接口的代理对象。
3.2.1 源码分析
java
publicclassMapperProxyFactory<T> {
privatefinal Class<T> mapperInterface;
privatefinal Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
publicMapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface){
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface(){
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache(){
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy){
// 使用JDK动态代理创建代理对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { mapperInterface },
mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession){
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}3.2.2 使用示例
java
// MapperRegistry中注册Mapper
public <T> voidaddMapper(Class<T> type){
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
thrownew BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 创建MapperProxyFactory并注册
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// 解析注解
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
// 获取Mapper实例
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession){
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
thrownew BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通过工厂创建Mapper代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
thrownew BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}3.3 ObjectFactory
ObjectFactory是MyBatis的对象工厂,负责创建对象实例。
3.3.1 接口定义
java
publicinterfaceObjectFactory{
// 创建对象
<T> T create(Class<T> type);
// 有参构造创建对象
<T> T create(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs);
// 判断是否是集合类型
<T> booleanisCollection(Class<T> type);
}3.3.2 DefaultObjectFactory
java
publicclassDefaultObjectFactoryimplementsObjectFactory{
@Override
public <T> T create(Class<T> type){
return create(type, null, null);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <T> T create(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs){
// 1. 解析集合类型
Class<?> classToCreate = resolveInterface(type);
// 2. 使用构造器创建实例
return (T) instantiateClass(classToCreate, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs);
}
private <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes,
List<Object> constructorArgs){
try {
Constructor<T> constructor;
// 有参构造
if (constructorArgTypes == null || constructorArgs == null) {
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor();
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
return constructor.newInstance();
} else {
// 查找匹配的构造器
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor(constructorArgTypes.toArray(new Class[0]));
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[0]));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常
}
}
@Override
public <T> booleanisCollection(Class<T> type){
return Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(type);
}
}3.4 工厂模式的优势
解耦:调用者不需要知道对象创建的细节
扩展性:新增产品类时不需要修改现有代码
复用性:工厂类可以被多个客户端复用
封装性:封装了对象创建的复杂逻辑
四、代理模式(Proxy Pattern)
代理模式是一种结构型设计模式,它允许你提供对象的替代品或占位符。代理控制着对原对象的访问,并允许在将请求提交给对象前后进行一些处理。
4.1 MapperProxy
MapperProxy是MyBatis中最核心的代理模式应用,它为Mapper接口创建代理对象,拦截方法调用并执行相应的SQL操作。
4.1.1 源码分析
java
publicclassMapperProxy<T> implementsInvocationHandler{
privatefinal SqlSession sqlSession;
privatefinal Class<T> mapperInterface;
privatefinal Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
publicMapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache){
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws Throwable {
// 1. 如果是Object类的方法,直接执行
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
// 2. 获取MapperMethod
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 3. 执行Mapper方法
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method){
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method,
k -> new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
}4.1.2 MapperMethod
java
publicclassMapperMethod{
privatefinal SqlCommand command;
privatefinal MethodSignature method;
publicMapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config){
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args){
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} elseif (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} elseif (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} elseif (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
thrownew BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
thrownew BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
}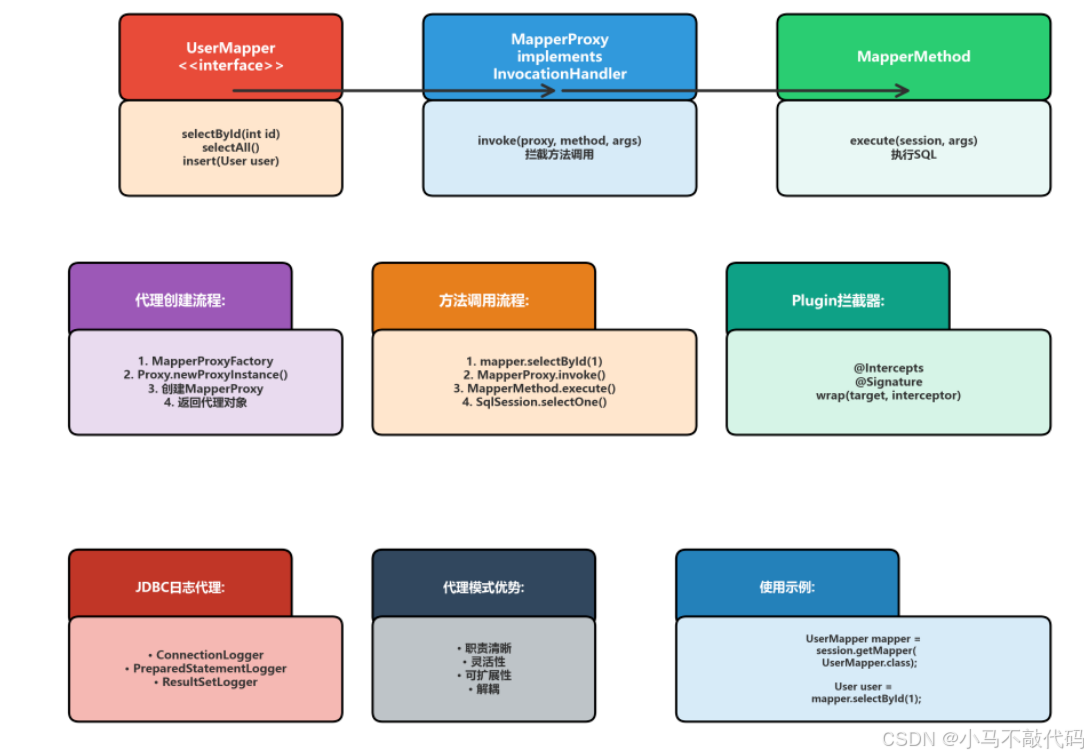
4.2 Plugin拦截器
Plugin是MyBatis的插件机制的核心,它通过动态代理实现对目标对象的拦截。
4.2.1 Interceptor接口
java
publicinterfaceInterceptor{
// 拦截方法
Object intercept(Invocation invocation)throws Throwable;
// 创建代理对象
default Object plugin(Object target){
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
// 设置属性
defaultvoidsetProperties(Properties properties){
// NOP
}
}4.2.2 Plugin类
java
publicclassPluginimplementsInvocationHandler{
privatefinal Object target;
privatefinal Interceptor interceptor;
privatefinal Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
privatePlugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap){
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
publicstatic Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor){
// 1. 获取拦截的类和方法签名
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 2. 获取所有需要拦截的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
// 3. 如果有需要拦截的接口,创建代理对象
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws Throwable {
try {
// 4. 检查当前方法是否需要被拦截
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 5. 调用拦截器的intercept方法
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 6. 不需要拦截,直接调用目标方法
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error: " + e, e);
}
}
privatestatic Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取@Intercepts注解
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
thrownew PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.computeIfAbsent(sig.type(), k -> new HashSet<>());
try {
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
thrownew PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
privatestatic Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[0]);
}
}4.2.3 插件使用示例
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method= "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}),
@Signature(type= Executor.class,
method= "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
publicclassMyPluginimplementsInterceptor{
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation)throws Throwable {
// 前置处理
System.out.println("Before: " + invocation.getMethod().getName());
// 执行目标方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// 后置处理
System.out.println("After: " + invocation.getMethod().getName());
return result;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target){
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
publicvoidsetProperties(Properties properties){
// 读取配置
}
}4.3 代理模式的优势
职责清晰:将日志、事务等横切关注点与业务逻辑分离
灵活性:可以在不修改原始对象的情况下增加功能
可扩展性:通过插件机制轻松扩展框架功能
解耦:调用者不需要知道代理的存在
五、设计模式的协同应用
在MyBatis中,多种设计模式往往协同工作,共同完成复杂的功能。
5.1 创建SqlSession的完整流程
创建SqlSession的过程涉及多个设计模式的协同:
构建者模式:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构建Configuration
工厂模式:SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
代理模式:MapperProxy创建Mapper代理对象
java
// 1. 构建者模式:构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
java
// 2. 工厂模式:创建SqlSession
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
java
// 3. 代理模式:获取Mapper代理对象
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);5.2 执行SQL的完整流程
执行SQL的过程也涉及多个设计模式的协同:
代理模式:MapperProxy拦截方法调用
工厂模式:SqlSession创建Statement
模板方法模式:BaseExecutor定义执行流程
策略模式:不同的Executor使用不同的执行策略
六、最佳实践
6.1 使用构建者模式
当你需要创建复杂对象时,可以考虑使用构建者模式:
java
publicclassComplexObjectBuilder{
private ComplexObject object = new ComplexObject();
public ComplexObjectBuilder withProperty1(String value){
object.setProperty1(value);
returnthis;
}
public ComplexObjectBuilder withProperty2(int value){
object.setProperty2(value);
returnthis;
}
public ComplexObject build(){
return object;
}
}
// 使用
ComplexObject obj = new ComplexObjectBuilder()
.withProperty1("value1")
.withProperty2(100)
.build();6.2 使用工厂模式
当对象的创建逻辑复杂或需要根据配置创建不同实现时,使用工厂模式:
java
publicinterfaceServiceFactory{
Service createService();
}
publicclassServiceFactoryAimplementsServiceFactory{
@Override
public Service createService(){
returnnew ServiceA();
}
}
publicclassServiceFactoryBimplementsServiceFactory{
@Override
public Service createService(){
returnnew ServiceB();
}
}6.3 使用代理模式
当你需要在不修改原始对象的情况下添加功能时,使用代理模式:
java
publicclassServiceProxyimplementsInvocationHandler{
private Object target;
publicServiceProxy(Object target){
this.target = target;
}
publicstatic <T> T createProxy(T target){
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new ServiceProxy(target));
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws Throwable {
// 前置处理
System.out.println("Before: " + method.getName());
// 执行目标方法
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
// 后置处理
System.out.println("After: " + method.getName());
return result;
}
}七、总结
MyBatis作为一款优秀的持久层框架,其代码中大量运用了经典的设计模式。这些设计模式的应用,使得MyBatis具有良好的架构设计和可扩展性。