这一节主要了解一下MutableStateFlow,在Jetpack Compose开发中,MutableStateFlow是协程库提供的一个可变状态流,用于在协程环境中以响应式方式管理UI状态。它结合了状态持有和冷流的特性,适合与Compose集成,实现高效、安全的状态驱动UI更新。
API
MutableStateFlow:创建一个可变的StateFlow实例,用于初始化一个可被修改的状态容器,初始值为value;
asStateFlow():将 MutableStateFlow 转换为只读的StateFlow,暴露给外部使用时隐藏写权限,保证封装性;
collectAsStateWithLifecycle():在Compose中订阅StateFlow,并自动处理生命周期;
一般场景:
1 UI表单状态管理
2 加载状态与数据展示
栗子:
Kotlin
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Arrangement
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Spacer
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height
import androidx.compose.material3.Button
import androidx.compose.material3.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.sp
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.compose.collectAsStateWithLifecycle
import androidx.lifecycle.viewmodel.compose.viewModel
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.StateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.asStateFlow
class CounterViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val _count = MutableStateFlow(0)
val count: StateFlow<Int> = _count.asStateFlow()
fun increment() {
_count.value++
}
}
@Composable
fun CounterScreenDemo(viewModel: CounterViewModel = viewModel()) {
val count by viewModel.count.collectAsStateWithLifecycle()
Column(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text(text = "Count: $count", fontSize = 24.sp)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(16.dp))
Button(onClick = { viewModel.increment() }) {
Text("Increment")
}
}
}
Kotlin
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Spacer
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.wrapContentHeight
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.wrapContentSize
import androidx.compose.material3.Button
import androidx.compose.material3.Checkbox
import androidx.compose.material3.CircularProgressIndicator
import androidx.compose.material3.Text
import androidx.compose.material3.TextField
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.text.input.PasswordVisualTransformation
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.compose.collectAsStateWithLifecycle
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.SharingStarted
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.StateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.asStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.map
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.stateIn
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
data class LoginFormState(
val username: String = "",
val password: String = "",
val agreeTerms: Boolean = false,
val isLoading: Boolean = false,
val loginResult: String? = null
)
class LoginViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val _formState = MutableStateFlow(LoginFormState())
val formState: StateFlow<LoginFormState> = _formState.asStateFlow()
val canSubmit: StateFlow<Boolean> = _formState
.map { state ->
state.username.isNotBlank() &&
state.password.length >= 6 &&
state.agreeTerms &&
!state.isLoading
}
.stateIn(
scope = viewModelScope,
started = SharingStarted.WhileSubscribed(5000),
initialValue = false
)
fun updateUsername(username: String) {
_formState.value = _formState.value.copy(username = username)
}
fun updatePassword(password: String) {
_formState.value = _formState.value.copy(password = password)
}
fun toggleAgreeTerms() {
_formState.value = _formState.value.copy(
agreeTerms = !_formState.value.agreeTerms
)
}
fun performLogin() {
if (!canSubmit.value) return
_formState.value = _formState.value.copy(
isLoading = true,
loginResult = null
)
viewModelScope.launch {
delay(2000)
val success = _formState.value.username == "test" && _formState.value.password == "123456"
_formState.value = _formState.value.copy(
isLoading = false,
loginResult = if (success) "登录成功!" else "用户名或密码错误"
)
}
}
}
@Composable
fun LoginFormDemo() {
val viewModel = remember { LoginViewModel() }
val formState by viewModel.formState.collectAsStateWithLifecycle()
val canSubmit by viewModel.canSubmit.collectAsStateWithLifecycle()
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.wrapContentSize()
.padding(20.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
TextField(
value = formState.username,
onValueChange = { viewModel.updateUsername(it) },
label = { Text("用户名") },
modifier = Modifier.wrapContentHeight().fillMaxWidth()
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(10.dp))
TextField(
value = formState.password,
onValueChange = { viewModel.updatePassword(it) },
label = { Text("密码(至少6位)") },
modifier = Modifier.wrapContentHeight().fillMaxWidth(),
visualTransformation = PasswordVisualTransformation()
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(10.dp))
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Checkbox(
checked = formState.agreeTerms,
onCheckedChange = { viewModel.toggleAgreeTerms() }
)
Text("同意用户协议和隐私政策")
}
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(20.dp))
if (formState.isLoading) {
CircularProgressIndicator()
} else {
Button(
onClick = { viewModel.performLogin() },
enabled = canSubmit,
modifier = Modifier.wrapContentSize()
) {
Text("登录")
}
}
formState.loginResult?.let {
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(20.dp))
Text(
text = it,
color = if (it.contains("成功")) androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color.Green
else androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color.Red
)
}
}
}效果:
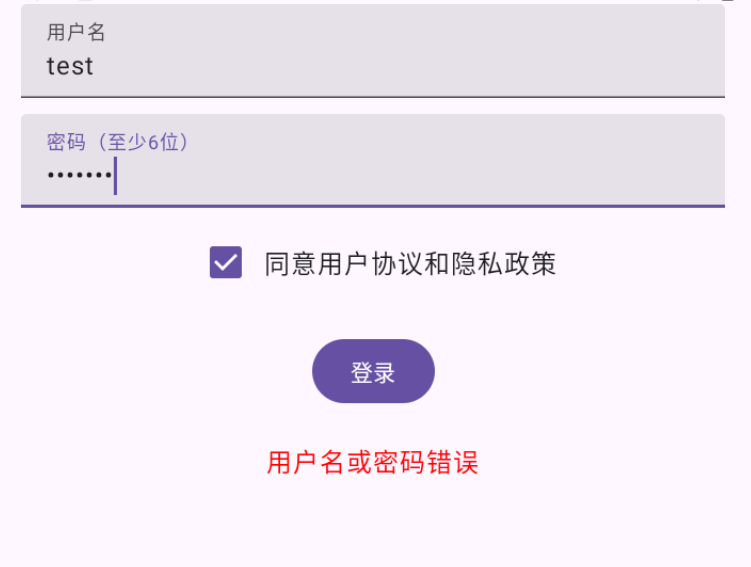
注意:
1 避免在Composable中直接修改MutableStateFlow
2 避免在Flow操作符中阻塞主线程
3 避免过度使用StateFlow替代remember
源码:
Kotlin
public fun <T> MutableStateFlow(value: T): MutableStateFlow<T> = StateFlowImpl(value ?: NULL)说明:使用NULL来统一表示null值,避免泛型擦除下无法区分T=null和未初始化。实际创建的是StateFlowImpl实例,它是MutableStateFlow的默认实现。
Kotlin
private class StateFlowImpl<T>(
initialState: Any // T | NULL
) : ... {
private val _state = atomic(initialState)
private var sequence = 0
}说明:
_state是一个原子引用,保证多线程读写安全。
sequence是一个状态机标志:
偶数:表示当前没有正在进行的值更新。
奇数:表示有更新正在处理中。
这种设计避免了在高并发下重复触发通知。
Kotlin
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
public override var value: T
get() = NULL.unbox(_state.value)
set(value) { updateState(null, value ?: NULL) }说明:
getter:通过NULL.unbox()将内部NULL对象还原为Kotlin的null。
setter:调用updateState(null, newValue),表示"无条件更新"。
Kotlin
synchronized(this) {
val oldState = _state.value
if (expectedState != null && oldState != expectedState) return false
if (oldState == newState) return true
_state.value = newState说明:
1.如果expectedState!= null,说明是compareAndSet调用,需校验
2.去重:新旧值相等(==),直接返回true
3.更新 _state
Kotlin
curSequence = sequence
if (curSequence and 1 == 0) {
curSequence++
sequence = curSequence
} else {
sequence = curSequence + 2
return true
}
curSlots = slots
}说明:
如果当前是偶数 则变成奇数,表示"更新开始",
如果当前不是偶数 已有更新在进行,只需递增sequence,通知合并
然后获取当前所有订阅者槽位
Kotlin
while (true) {
curSlots?.forEach { it?.makePending() }
synchronized(this) {
if (sequence == curSequence) {
sequence = curSequence + 1
return true
}
curSequence = sequence
curSlots = slots
}
}说明:
标记每个订阅者"有新值待处理",轻量操作,只是设置一个标志位
synchronized{}中如果没有新更新发生,变回偶数,结束更新;如果有新更新,重新读取slots和sequence继续循环
Kotlin
override suspend fun collect(collector: FlowCollector<T>): Nothing {
val slot = allocateSlot()
try {
var oldState: Any? = null
while (true) {
val newState = _state.value
if (oldState == null || oldState != newState) {
collector.emit(NULL.unbox(newState))
oldState = newState
}
if (!slot.takePending()) {
slot.awaitPending()
}
}
} finally {
freeSlot(slot)
}
}说明:collect订阅者如何接收值:
1 注册订阅者
2 首次或值变化时 emit
3 快速路径:检查是否有pending更新
4 最后 取消订阅
简单总结:
1 原子状态存储:state+atomic保证线程安全。
2 智能去重:old==new则跳过通知。
3 无锁通知:通过sequence状态机+makePending/awaitPending实现高效、合并式广播。
4 热流语义:新订阅者立即收到当前值。
5 协程友好:collect挂起点精准,不阻塞发射端。