示例
张三给李四转钱:必须同时执行两个sql
1.查询张三的账户余额,余额充足可以转钱
2.将张三的钱转给李四
李四买一本书
1.查询数据是否还有库存
2.库存充足,将数据加载到购物车
当多条sql语句进行增删改操作时,需要添加事务,因为事务是能保证多条sql语句不出错的关键
事务的四大特征
1.原子性
事务当中包含多条sql语句,这些sql语句是不可再分的,要么同时成功,要么同时失败
2.隔离性
多个事务之间的执行不能相互影响
事物的隔离级别:读未提交、读已提交、可重复读、串行化
3.持久性
事务一旦提交,不可再更改
4.一致性
事务能够回滚为原来的状态
案例
不加事务、无异常
表t_account
sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_account`;
CREATE TABLE `t_account` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin DEFAULT NULL,
`balance` double DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_bin ROW_FORMAT = Compact;
INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (1, '张三', 1000);
INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (2, '淘宝', 0);
INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (3, '京东', 0);实体类Account
java
package com.qcby.springbootdemo.model;
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double balance;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
}AccountDao接口
java
package com.qcby.springbootdemo.dao;
import com.qcby.springbootdemo.model.Account;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 更新账户余额
* 无论扣款还是入账,都是更新余额
* @param account 账户对象
* @return
*/
int update(Account account);
/**
* 根据id查询账户
* 转账都要查询余额
* @param id
* @return
*/
Account findById(Integer id);
}AccountMapper.xml
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.qcby.springbootdemo.dao.AccountDao"> <!--对谁进行操作就写谁-->
<update id="update" parameterType="account">
update t_account set balance = #{balance} where id = #{id}
</update>
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="account">
select * from t_account where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>AccountService接口
事务是一个简单的业务(业务:真是解决的问题),所以要有service层
java
package com.qcby.springbootdemo.service;
public interface AccountService {
int transferMoney(int fromId, int toId, double money);
}AccountServiceImpl实现类
java
package com.qcby.springbootdemo.service.impl;
import com.qcby.springbootdemo.dao.AccountDao;
import com.qcby.springbootdemo.model.Account;
import com.qcby.springbootdemo.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
/**
* 转账
* @param fromId 付款人id
* @param toId 收款人id
* @param money
* @return
*/
@Override
public int transferMoney(int fromId, int toId, double money) {
/**
* 转账业务步骤:
* 1. 查询付款人账户余额,判断余额是否充足
* 2.从转出账户(付款人)扣除转账金额,并更新转出账户余额(转出账户余额-转账金额)
* 3.查询收款人账户余额
* 4.向转入账户(收款人)转入转账金额,并更新转入账户余额(转入账户余额+转账金额)
*/
//1.查询付款人账户余额,判断余额是否充足
Account fromAccount = accountDao.findById(fromId);
if (fromAccount.getBalance() < money) {
System.out.println("余额不足,转账失败");
return 0;
}
//2.从转出账户(付款人)扣除转账金额,并更新转出账户余额(转出账户余额-转账金额)
fromAccount.setBalance(fromAccount.getBalance() - money);
accountDao.update(fromAccount);
//3.查询收款人账户余额
Account toAccount = accountDao.findById(toId);
//4.向转入账户(收款人)转入转账金额,并更新转入账户余额(转入账户余额+转账金额)
toAccount.setBalance(toAccount.getBalance() + money);
accountDao.update(toAccount);
return 1;
}
}AccountController
java
package com.qcby.springbootdemo.controller;
import com.qcby.springbootdemo.model.ResponseResult;
import com.qcby.springbootdemo.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/account")
public class AccountController {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@RequestMapping("/transfer")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseResult transfer(int fromId, int toId, double money) {
int result = accountService.transferMoney(fromId, toId, money);
if (result == 1){
return new ResponseResult(200, "转账成功");
}else {
return new ResponseResult(999, "转账失败");
}
}
}运行
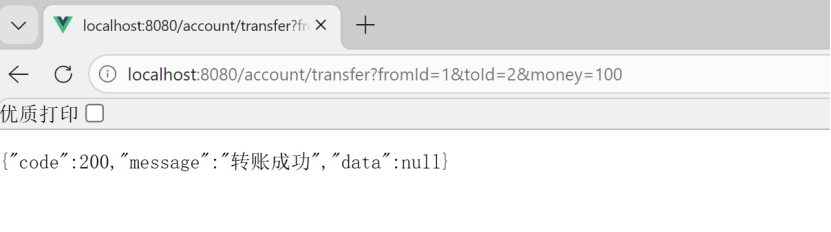
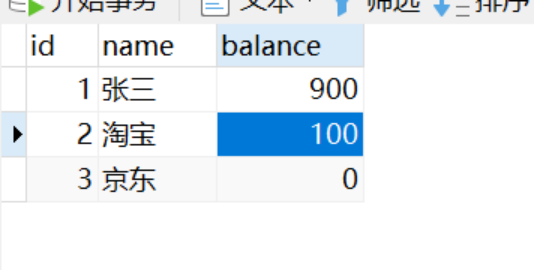
不加事务,模拟异常
先把数据库的数据还原,然后在业务层模拟异常
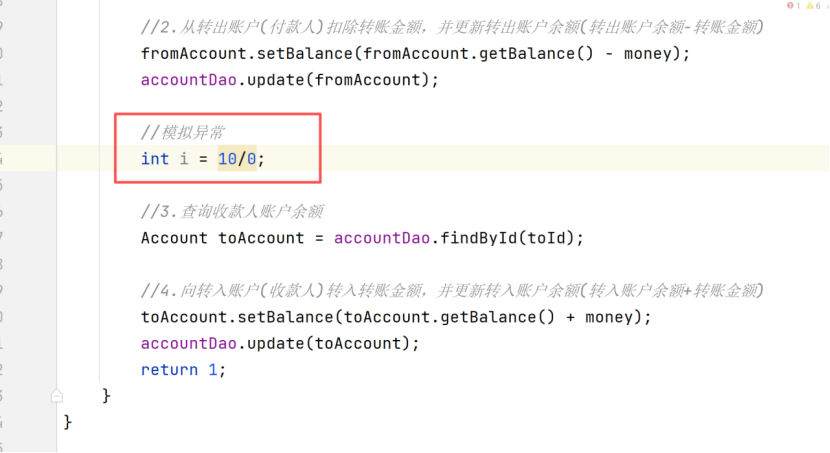
再运行
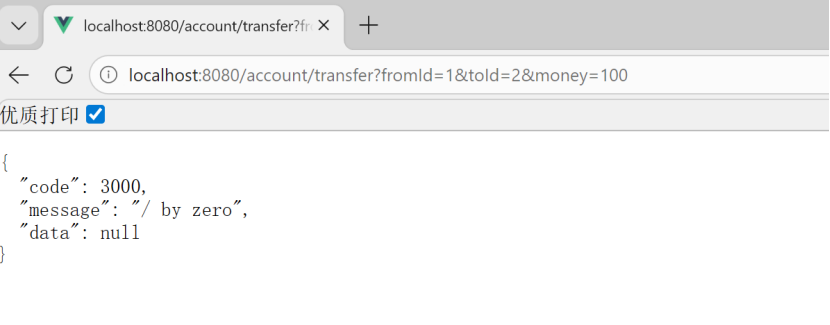
这里是因为我做了异常处理
张三转过去了,但是淘宝没有收到,所以需要事务
加上事务、模拟异常
回到原始状态,加上事务,只需要加一个@Transactional注解即可
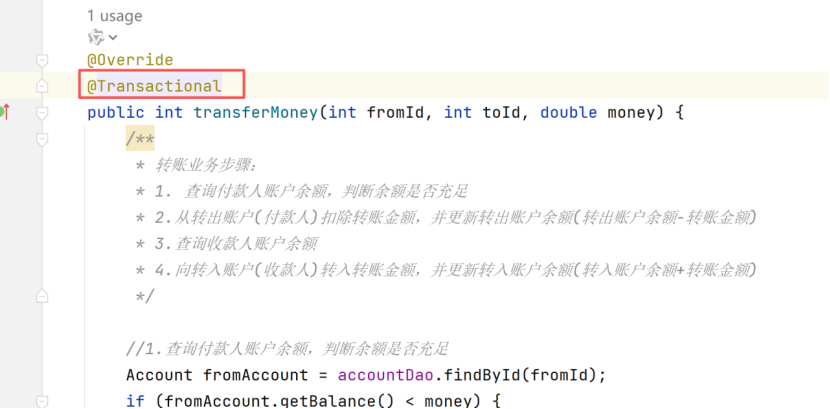
再运行:
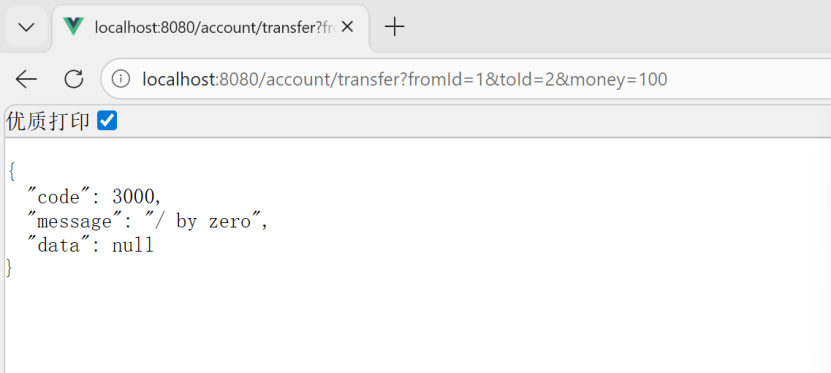
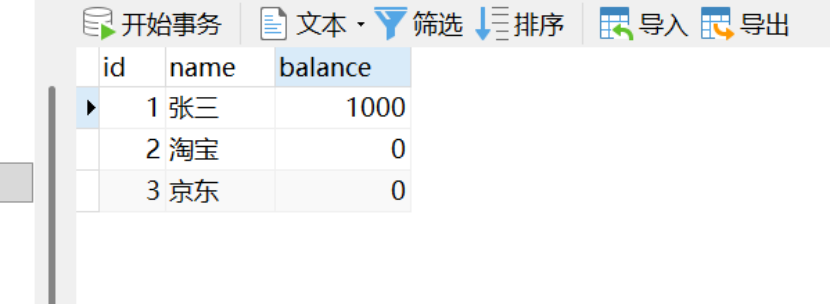
钱没转过去,事务回滚了
@Transactional注解
可以设置属性
propagation
用于设置事务的传播行为,指一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法应该如何运行
Spring定义了7种传播行为:
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Propagation.REQUIRED | 默认传播行为,如果有事务运行,当前方法就在这个事务运行;没有就启动一个新事务,并在自己事务内运行 |
| Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW | 当前方法必须启动新事务,并在自己事务内运行;若有事务正在运行,将他挂起 |
| Propagation.SUPPORTS | 有事务运行,当前方法就在这个事务内运行;没有就不运行在事务中 |
| Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED | 当前方法不运行在事务中,若有运行的事务,将他挂起 |
| Propagation.MANDATORY | 当前方法必须运行在事务内,如果没有正在运行的事务,抛出异常 |
| Propagation.NEVER | 当前方法不应该运行在事务内,若有运行的事务,抛出异常 |
| Propagation.NESTED | 如果有事务在运行,当前方法应在这个事务的嵌套事务内运行;否则启动一个新事务,并在自己事务内运行 |
isolation
用于设置事务的隔离级别,默认值为:Isolation.DEFAULT
理论上说,事务之间应彼此完全隔离,以避免并发事务所导致的问题,但这样会对性能产生极大的影响,因为事务必须按顺序运行,所以实际开发中,为了提高性能,事务会以较低的隔离级别运行