引言
内存问题是Android应用最常见的性能瓶颈之一。一个看似正常运行的应用,可能因为内存泄漏在后台悄悄积累问题,最终在用户使用高峰期突然崩溃。根据Google Play统计数据,OOM(Out Of Memory)是Android应用崩溃的首要原因之一,占比超过30%。
为什么内存问题如此普遍?主要原因包括:
- 移动设备资源有限: 即使是高端手机,每个应用可用的堆内存也受到严格限制(通常256MB-512MB)
- 生命周期复杂: Activity/Fragment的生命周期管理不当容易导致泄漏
- 异步机制: Handler、AsyncTask等异步组件持有外部引用
- 图片资源: Bitmap占用大量内存,管理不当直接OOM
- 第三方库: 依赖库的内存问题难以察觉
本文将从原理到实战,系统讲解Android内存优化的完整方法论:
- 第一部分: Android内存管理机制 - 掌握底层原理
- 第二部分: 内存分析工具全解 - 熟练使用Memory Profiler、MAT、LeakCanary
- 第三部分: 常见内存泄漏场景 - 识别并解决典型问题
- 第四部分: OOM问题优化 - Bitmap、缓存、资源释放最佳实践
- 第五部分: 实战案例 - 图片浏览OOM优化从85%到3%
- 第六部分: 监控体系 - 建立内存预警机制
Android内存管理机制
要解决内存问题,首先要理解Android如何管理内存。Android的内存管理涉及进程内存模型、GC垃圾回收、LMK低内存杀手三个核心机制。
2.1 进程内存模型
每个Android进程的内存由多个区域组成,理解这些区域的用途是优化的基础。

Java堆 (Java Heap)
Java堆是存储Java对象的内存区域,由ART虚拟机管理。每个应用的Java堆大小受到系统限制:
bash
# 查看堆内存限制
adb shell getprop dalvik.vm.heapgrowthlimit # 普通应用堆限制 (如192m)
adb shell getprop dalvik.vm.heapsize # large heap限制 (如512m)关键概念:
- heapgrowthlimit: 默认堆限制,普通应用不能超过此值
- heapsize : 通过
android:largeHeap="true"可以申请的最大堆 - Pss (Proportional Set Size): 实际物理内存占用,计算共享内存的比例
- Uss (Unique Set Size): 进程独占内存,最准确反映实际占用
- Rss (Resident Set Size): 驻留内存,包含共享库
查看应用内存占用:
bash
# 详细内存信息
adb shell dumpsys meminfo com.example.app
# 关键指标解读
# Java Heap: Java对象占用
# Native Heap: Native代码分配 (JNI、NDK、so库)
# Code: 代码段 (dex、so、oat)
# Stack: 线程栈
# Graphics: GPU内存 (纹理、buffer)
# Private Other: 其他私有内存实际案例输出:
App Summary
Pss(KB)
------
Java Heap: 38436 # Java对象占用38MB
Native Heap: 12584 # Native分配12MB
Code: 15220 # 代码段15MB
Stack: 1036 # 栈1MB
Graphics: 25688 # GPU内存25MB
Private Other: 8432
System: 4256
Unknown: 0
TOTAL: 105652 # 总共105MBNative堆 (Native Heap)
Native堆存储通过JNI/NDK分配的内存,不受Java堆限制但计入进程总内存。常见使用场景:
- Bitmap像素数据 (Android 8.0+迁移到Native堆)
- Native库 (如WebView、OpenGL、第三方so)
- JNI对象分配
Native内存泄漏更难发现,因为Java GC无法回收这些对象。
栈和方法区
- 栈 (Stack): 每个线程都有独立栈空间,存储局部变量和方法调用。默认1MB,过深递归会导致StackOverflowError
- 方法区 (Method Area): 存储类信息、常量池、静态变量、JIT编译代码
图形内存 (Graphics Memory)
GPU使用的纹理、缓冲区等内存,在dumpsys meminfo的Graphics项显示。大量图片显示或复杂UI会占用大量图形内存。
2.2 垃圾回收机制 (GC)
Android的ART虚拟机使用自动垃圾回收管理Java堆内存。理解GC机制有助于优化内存分配和避免卡顿。
GC算法
ART使用了多种GC算法的组合:
- 标记-清除 (Mark-Sweep): 标记存活对象,清除未标记对象,会产生内存碎片
- 复制算法 (Copying): 将存活对象复制到另一块内存,适用于新生代
- 标记-整理 (Mark-Compact): 标记后整理内存,消除碎片,适用于老年代
GC类型
在logcat中可以看到不同类型的GC日志:
# 并发GC (Concurrent GC)
I/art: Background concurrent mark sweep GC freed 2MB, 15% free, 32MB/38MB, paused 1.203ms total 23.567ms
# 显式GC (Explicit GC)
I/art: Explicit concurrent mark sweep GC freed 156KB, 12% free, 38MB/43MB, paused 987us total 21.345ms
# 分配失败GC (Alloc Failed GC)
I/art: Alloc partial concurrent mark sweep GC freed 1MB, 24% free, 28MB/37MB, paused 2.456ms total 45.678ms关键指标解读:
- freed: 回收了多少内存
- free: 当前堆空闲比例
- paused: GC暂停时间 (影响UI流畅度)
- total: GC总耗时
GC Root对象
GC从GC Root对象开始标记存活对象。常见的GC Root包括:
- 虚拟机栈中引用的对象 (局部变量)
- 方法区中静态属性引用的对象
- 方法区中常量引用的对象
- Native方法引用的对象
- 活跃线程
内存泄漏的本质: 无用对象被GC Root直接或间接引用,导致GC无法回收。
对象引用类型
Java提供了四种引用类型来控制对象的生命周期:
kotlin
// 强引用 (Strong Reference) - 永远不会被GC回收
val strongRef: Object = Object()
// 软引用 (Soft Reference) - 内存不足时回收
val softRef: SoftReference<Bitmap> = SoftReference(bitmap)
// 弱引用 (Weak Reference) - 下次GC时回收
val weakRef: WeakReference<Activity> = WeakReference(activity)
// 虚引用 (Phantom Reference) - 用于对象回收监控
val phantomRef: PhantomReference<Object> = PhantomReference(obj, queue)最佳实践:
- 缓存图片使用
SoftReference或WeakReference - 避免在静态变量中持有Activity的强引用
- 异步回调使用
WeakReference持有外部对象
2.3 低内存杀手 (LMK)
当系统内存不足时,Android会通过LMK (Low Memory Killer)杀死进程释放内存。理解LMK机制有助于优化应用的生存优先级。
LMK工作原理
LMK是Linux OOM Killer的定制版本,根据进程的oom_adj值决定杀死顺序:
- 内核监测系统内存压力 (通过
/proc/meminfo) - 当可用内存低于阈值,触发LMK机制
- 根据
oom_adj值从高到低杀进程 (值越大越先被杀) - 释放的内存分配给前台进程
查看进程的oom_adj值:
bash
# 查看所有进程的oom_adj
adb shell ps -A -o NAME,PID,USER,%MEM,OOM_ADJ | grep com.example
# 输出示例
com.example.app 12345 u0_a123 8.5% 0 # 前台进程
com.example.app 12346 u0_a123 2.3% 6 # 可见进程oom_adj优先级
| 级别 | adj值 | 进程类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 前台进程 | 0 | FOREGROUND_APP | 用户正在交互的Activity |
| 可见进程 | 1-2 | VISIBLE_APP | 可见但非前台的Activity |
| 服务进程 | 3-6 | SERVICE | 后台Service |
| 缓存进程 | 7-15 | CACHED_APP | 已退出的Activity (保留在后台) |
| 空进程 | 16+ | EMPTY | 无活动组件的进程 |
优化建议:
- 避免在后台占用过多内存
- 及时释放不用的资源降低内存占用
- 关键Service使用
startForeground()提升优先级 - 监听
onTrimMemory()回调释放缓存
onTrimMemory回调
系统在内存不足时会回调onTrimMemory(),应用应该根据级别释放资源:
kotlin
override fun onTrimMemory(level: Int) {
super.onTrimMemory(level)
when (level) {
// UI隐藏,可以释放UI相关资源
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_UI_HIDDEN -> {
Log.d("Memory", "UI hidden, release UI resources")
releaseUIResources()
}
// 进程在后台LRU列表头部,可能被杀死
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_BACKGROUND -> {
Log.d("Memory", "Background, release some cache")
imageCache.evictSome()
}
// 内存严重不足,进程即将被杀死
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_COMPLETE -> {
Log.d("Memory", "Critical memory, release all cache")
imageCache.evictAll()
clearAllCache()
}
// 前台应用内存不足
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_LOW,
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_CRITICAL -> {
Log.d("Memory", "Low memory, shrink cache")
imageCache.trimToSize(imageCache.size() / 2)
}
}
}AOSP源码位置:
- LMK实现:
system/core/lmkd/lmkd.c - oom_adj管理:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ProcessList.java - 内存监控:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
内存分析工具全解
工欲善其事,必先利其器。Android提供了丰富的内存分析工具,掌握这些工具是解决内存问题的关键。

3.1 Memory Profiler (Android Studio自带)
Memory Profiler是Android Studio内置的实时内存监控工具,适合快速定位内存增长和泄漏。
基本使用
-
打开Memory Profiler:
- Android Studio → View → Tool Windows → Profiler
- 选择设备和应用进程
- 点击Memory行展开详细视图
-
实时内存图表:
- Java: Java堆内存
- Native: Native堆内存
- Graphics: 图形内存
- Stack: 栈内存
- Code: 代码段
- Others: 其他内存
-
操作功能:
- Force GC: 手动触发垃圾回收
- Dump Java Heap: 捕获堆快照
- Record Allocations: 记录对象分配
检测内存泄漏
典型流程:
- 建立基准: 在初始状态Dump堆快照
- 执行操作: 打开Activity → 返回 (重复多次)
- 触发GC: 点击"Force GC"按钮
- 对比快照: Dump第二次快照,对比对象数量
案例: 检测Activity泄漏
kotlin
// 操作步骤
1. 打开ProfileActivity → Dump Heap (快照1)
2. 返回 → 再次打开ProfileActivity → 返回 (重复5次)
3. Force GC
4. Dump Heap (快照2)
// 在快照2中搜索ProfileActivity
// 正常: 应该只有0-1个实例
// 泄漏: 如果有5+个实例,说明Activity没被回收在Heap Dump视图中:
- 按Class Name排序,搜索Activity类名
- 查看Shallow Size (对象自身大小) 和 Retained Size (对象及其引用树总大小)
- 点击实例查看引用链,找到GC Root
Allocation Tracking
记录对象分配可以找到内存增长的源头:
- 点击"Record"按钮开始记录
- 执行导致内存增长的操作
- 点击"Stop"停止记录
- 查看分配表格,按Allocations或Shallow Size排序
案例: 查找图片加载内存增长
操作: 滑动RecyclerView加载100张图片
分析结果:
Class Name Allocations Shallow Size
------------------------------------------------------
android.graphics.Bitmap 120 156 MB # 图片对象
byte[] 2340 78 MB # Bitmap像素数据
Glide$Request 120 0.5 MB # Glide请求可以看出Bitmap及其像素数据占用了主要内存,需要优化图片加载策略。
3.2 MAT (Memory Analyzer Tool)
MAT是Eclipse出品的强大Heap分析工具,适合深度分析复杂内存问题。
生成Heap Dump
bash
# 方式1: 通过adb命令
adb shell am dumpheap <pid> /data/local/tmp/heap.hprof
adb pull /data/local/tmp/heap.hprof
# 方式2: 通过Memory Profiler导出
# Memory Profiler → Dump Heap → 右键 → Export to file
# 转换格式 (Android hprof需要转换为标准格式)
hprof-conv heap.hprof heap-converted.hprofMAT分析流程
- 打开hprof文件: File → Open Heap Dump
- 查看概览: 自动生成Leak Suspects报告
- 分析内存占用: Histogram视图查看所有类的实例数量和内存
- 查找泄漏: Dominator Tree查看最大对象及其引用
关键视图
Histogram (直方图):
- 显示所有类的实例数量和Shallow/Retained Heap
- 按Retained Heap排序找到占用内存最多的类
- 右键 → List objects → with incoming references 查看引用链
Dominator Tree (支配树):
- 显示对象的支配关系 (对象A支配对象B意味着到B的所有路径都经过A)
- 直观展示哪些对象占用了最多内存
- 删除某对象能释放多少内存 (Retained Heap)
OQL查询:
sql
-- 查找所有Activity实例
SELECT * FROM INSTANCEOF android.app.Activity
-- 查找Bitmap占用超过1MB的对象
SELECT * FROM android.graphics.Bitmap WHERE retainedHeapSize > 1048576
-- 查找静态字段持有的对象
SELECT * FROM java.lang.Object s WHERE s.@GCRoot案例: 定位Activity泄漏
假设通过Memory Profiler发现有3个MainActivity实例:
-
Histogram查找 : 搜索
MainActivity,显示3个实例 -
查看引用链: 右键 → Merge Shortest Paths to GC Roots → exclude weak/soft references
-
分析引用链:
MainActivity @ 0x12a45000
← mContext in MyApplication
← sInstance in MyApplication (static)
← class MyApplication
← system class loader
结论: MyApplication的静态单例持有了MainActivity的引用,导致泄漏。
解决方案:
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 静态单例持有Activity
class MyApplication : Application() {
companion object {
var sInstance: MyApplication? = null
}
fun init(context: Context) {
sInstance = this // 持有Activity会导致泄漏
}
}
// ✅ Good: 使用ApplicationContext
class MyApplication : Application() {
companion object {
lateinit var sInstance: Application
}
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
sInstance = this // Application不会泄漏
}
}
// 或者使用弱引用
companion object {
var contextRef: WeakReference<Context>? = null
}3.3 LeakCanary (自动化泄漏检测)
LeakCanary是Square开源的自动内存泄漏检测库,能在开发和测试阶段自动发现泄漏。
集成LeakCanary
kotlin
// build.gradle.kts
dependencies {
// 仅在debug构建中启用
debugImplementation("com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:2.12")
}
// 无需其他配置,Application启动时自动初始化工作原理
- 监听生命周期: 自动监听Activity、Fragment、ViewModel等组件销毁
- 弱引用观察: 组件销毁后创建WeakReference引用
- 触发GC: 延迟5秒后触发GC
- 检测泄漏: GC后检查WeakReference是否被清除
- Dump分析: 发现泄漏时Dump堆快照分析引用链
- 通知展示: 在通知栏显示泄漏报告
查看泄漏报告
LeakCanary检测到泄漏后会显示详细报告:
┬───
│ GC Root: System class
│
├─ android.app.ActivityThread class
│ Leaking: NO (Android system class)
│ ↓ static ActivityThread.sCurrentActivityThread
│
├─ android.app.ActivityThread instance
│ Leaking: NO (ActivityThread is always reachable)
│ ↓ ActivityThread.mActivities
│
├─ android.util.ArrayMap instance
│ Leaking: NO (Application is still reachable)
│ ↓ ArrayMap[0]
│
├─ android.app.ActivityThread$ActivityClientRecord instance
│ Leaking: UNKNOWN
│ ↓ ActivityThread$ActivityClientRecord.activity
│
╰→ com.example.MainActivity instance
Leaking: YES (RefWatcher was watching this and MainActivity#onDestroy() was called)
key = 8a2b3c4d-5e6f-7a8b-9c0d-1e2f3a4b5c6d
retainedSize = 1.2 MB报告解读:
- GC Root: 泄漏的根源 (此例为ActivityThread静态字段)
- Leaking: YES: 确认发生泄漏
- retainedSize: 泄漏导致无法回收的内存大小
自定义监听
监听自定义对象:
kotlin
class MyService : Service() {
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// 通知LeakCanary监听此Service
AppWatcher.objectWatcher.watch(
watchedObject = this,
description = "MyService received onDestroy callback"
)
}
}生产环境禁用
LeakCanary仅应在debug构建中使用,发布版本会自动禁用:
kotlin
// 确保仅debug依赖
debugImplementation("com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:2.12")
// releaseImplementation不添加依赖3.4 命令行工具
除了图形化工具,命令行工具在CI/CD和自动化测试中更实用。
dumpsys meminfo
查看进程内存详情:
bash
# 查看指定应用
adb shell dumpsys meminfo com.example.app
# 查看所有应用内存排序
adb shell dumpsys meminfo --oom
# 只显示关键摘要
adb shell dumpsys meminfo com.example.app --summaryprocrank
查看所有进程内存排序 (需要root):
bash
adb shell procrank
# 输出示例
PID Vss Rss Pss Uss cmdline
1234 580M 85M 42M 35M com.example.app
5678 420M 65M 28M 22M com.android.systemuishowmap
查看进程内存映射 (需要root):
bash
adb shell showmap <pid>
# 显示各个so库、dex文件的内存占用脚本自动化
将内存监控集成到CI流程:
bash
#!/bin/bash
# memory_monitor.sh
PACKAGE="com.example.app"
THRESHOLD_MB=200
while true; do
PSS=$(adb shell dumpsys meminfo $PACKAGE | grep "TOTAL PSS" | awk '{print $3}')
echo "$(date): PSS = ${PSS}KB"
PSS_MB=$((PSS / 1024))
if [ $PSS_MB -gt $THRESHOLD_MB ]; then
echo "WARNING: Memory exceeded threshold ${THRESHOLD_MB}MB"
adb shell am dumpheap $(adb shell pidof $PACKAGE) /data/local/tmp/heap.hprof
echo "Heap dump saved"
break
fi
sleep 5
done常见内存泄漏场景与解决
内存泄漏是Android开发中最常见的问题。掌握典型场景和解决方案,可以避免90%的内存问题。

4.1 静态变量持有Activity
这是最常见的泄漏场景,因为静态变量的生命周期是整个应用进程。
错误示例1: 静态变量直接持有Activity
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 静态变量持有Activity引用
class DataManager {
companion object {
var sContext: Context? = null
}
fun init(context: Context) {
sContext = context // 如果传入Activity,会导致泄漏
}
fun doSomething() {
val text = sContext?.getString(R.string.app_name)
}
}
// MainActivity中初始化
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
DataManager().init(this) // ⚠️ 传入Activity引用
}
}泄漏原因 : sContext是静态变量,持有MainActivity引用,MainActivity即使销毁也无法被GC回收。
解决方案: 使用ApplicationContext
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用ApplicationContext
class DataManager {
companion object {
lateinit var sAppContext: Context
}
fun init(context: Context) {
// 转换为ApplicationContext
sAppContext = context.applicationContext
}
}
// 或者在Application中初始化
class MyApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
DataManager.sAppContext = this
}
}核心原则: 静态变量只能持有ApplicationContext,永远不要持有Activity、Service、View等短生命周期对象。
错误示例2: 静态内部类持有外部引用
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 单例持有Activity
class ImageLoader private constructor() {
companion object {
val instance: ImageLoader by lazy { ImageLoader() }
}
private var context: Context? = null
fun init(context: Context) {
this.context = context // 持有Activity会泄漏
}
fun loadImage(url: String, imageView: ImageView) {
// 使用context加载图片
}
}解决方案: 使用弱引用或ApplicationContext
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用WeakReference
class ImageLoader private constructor() {
companion object {
val instance: ImageLoader by lazy { ImageLoader() }
}
private var contextRef: WeakReference<Context>? = null
fun init(context: Context) {
contextRef = WeakReference(context.applicationContext)
}
fun loadImage(url: String, imageView: ImageView) {
contextRef?.get()?.let { context ->
// 使用context加载图片
}
}
}4.2 非静态内部类持有外部类
内部类、匿名类默认持有外部类引用,如果生命周期不一致会导致泄漏。
错误示例1: Handler内部类泄漏
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: Handler内部类持有Activity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val handler = object : Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
override fun handleMessage(msg: Message) {
// 这个匿名内部类持有MainActivity引用
updateUI()
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
// 发送延迟消息
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 60000) // 1分钟后处理
// 如果用户在1分钟内退出Activity,Activity无法被回收
}
private fun updateUI() {
// 更新界面
}
}泄漏原因:
- Handler匿名内部类持有MainActivity引用
- Handler的Message被放入MessageQueue,持有Handler引用
- MessageQueue在1分钟内一直持有Message
- MainActivity → Handler → Message → MessageQueue,导致MainActivity无法回收
解决方案: 静态内部类 + 弱引用
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 静态Handler + 弱引用
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val handler = MyHandler(this)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 60000)
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// 清理Handler消息
handler.removeCallbacksAndMessages(null)
}
private fun updateUI() {
// 更新界面
}
// 静态内部类不持有外部类引用
private class MyHandler(activity: MainActivity) : Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
// 使用弱引用持有Activity
private val activityRef = WeakReference(activity)
override fun handleMessage(msg: Message) {
// 获取Activity,可能为null
val activity = activityRef.get()
if (activity == null || activity.isFinishing) {
return // Activity已销毁,直接返回
}
activity.updateUI()
}
}
}核心原则:
- Handler使用静态内部类或独立类
- 通过WeakReference持有外部对象
- onDestroy中移除所有消息:
handler.removeCallbacksAndMessages(null)
错误示例2: Thread/Runnable匿名类泄漏
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: Thread匿名类持有Activity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
Thread {
// 长时间任务
Thread.sleep(60000)
// 访问Activity成员
runOnUiThread {
updateUI()
}
}.start()
// Thread持有Activity引用,即使Activity销毁Thread仍在运行
}
}解决方案: 使用静态类或协程
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用Kotlin协程
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val scope = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main + Job())
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
scope.launch {
withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
// 后台任务
delay(60000)
}
// 回到主线程更新UI
updateUI()
}
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// 取消所有协程
scope.cancel()
}
}4.3 单例模式持有Context
单例的生命周期是整个应用,如果持有Activity引用会导致严重泄漏。
错误示例: 单例持有Activity
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 单例持有Activity
class LocationManager private constructor(private val context: Context) {
companion object {
@Volatile
private var instance: LocationManager? = null
fun getInstance(context: Context): LocationManager {
return instance ?: synchronized(this) {
instance ?: LocationManager(context).also { instance = it }
}
}
}
fun startLocationUpdates() {
// 使用context注册监听器
}
}
// Activity中使用
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// ⚠️ 传入Activity,导致单例持有Activity引用
val locationManager = LocationManager.getInstance(this)
}
}解决方案: 使用ApplicationContext
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 单例使用ApplicationContext
class LocationManager private constructor(context: Context) {
// 转换为ApplicationContext
private val appContext: Context = context.applicationContext
companion object {
@Volatile
private var instance: LocationManager? = null
fun getInstance(context: Context): LocationManager {
return instance ?: synchronized(this) {
instance ?: LocationManager(context.applicationContext).also { instance = it }
}
}
}
fun startLocationUpdates() {
// 使用appContext注册监听器
}
}最佳实践: 所有单例涉及Context时,统一在Application中初始化:
kotlin
class MyApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
// 统一初始化单例
LocationManager.getInstance(this)
DatabaseHelper.init(this)
ImageLoader.init(this)
}
}4.4 未取消的监听器和回调
注册的监听器、回调如果未及时取消,会持有对象引用导致泄漏。
错误示例1: 未注销BroadcastReceiver
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 注册Receiver未注销
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val receiver = object : BroadcastReceiver() {
override fun onReceive(context: Context?, intent: Intent?) {
updateUI()
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// 动态注册Receiver
val filter = IntentFilter("com.example.ACTION")
registerReceiver(receiver, filter)
// ⚠️ 忘记在onDestroy中注销
}
// 缺少onDestroy注销
}解决方案: 配对注册和注销
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 配对注册和注销
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val receiver = object : BroadcastReceiver() {
override fun onReceive(context: Context?, intent: Intent?) {
updateUI()
}
}
private var isReceiverRegistered = false
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
val filter = IntentFilter("com.example.ACTION")
registerReceiver(receiver, filter)
isReceiverRegistered = true
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// 注销Receiver
if (isReceiverRegistered) {
unregisterReceiver(receiver)
isReceiverRegistered = false
}
}
}错误示例2: 未移除Listener
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 添加Listener未移除
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val scrollListener = object : RecyclerView.OnScrollListener() {
override fun onScrolled(recyclerView: RecyclerView, dx: Int, dy: Int) {
updateHeader()
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
recyclerView.addOnScrollListener(scrollListener)
// ⚠️ 忘记移除Listener
}
}解决方案: onDestroy中移除
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 移除Listener
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val scrollListener = object : RecyclerView.OnScrollListener() {
override fun onScrolled(recyclerView: RecyclerView, dx: Int, dy: Int) {
updateHeader()
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
recyclerView.addOnScrollListener(scrollListener)
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// 移除Listener
recyclerView.removeOnScrollListener(scrollListener)
}
}常见需要注销的组件
| 组件 | 注册方法 | 注销方法 | 注销时机 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BroadcastReceiver | registerReceiver() | unregisterReceiver() | onDestroy |
| EventBus | EventBus.register() | EventBus.unregister() | onDestroy |
| RxJava | subscribe() | dispose() | onDestroy |
| LiveData | observe() | removeObserver() | 自动管理(lifecycle-aware) |
| Animation | start() | cancel() | onPause/onDestroy |
| Handler Message | sendMessage() | removeCallbacksAndMessages(null) | onDestroy |
最佳实践: 使用Lifecycle感知组件自动管理生命周期:
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用LiveData自动管理
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val viewModel: MyViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// LiveData会自动在onDestroy时移除观察者
viewModel.data.observe(this) { data ->
updateUI(data)
}
}
// 无需手动注销
}4.5 资源未关闭
File、Cursor、Stream等资源使用后必须关闭,否则会导致文件描述符泄漏。
错误示例: 文件未关闭
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 文件未关闭
fun readFile(path: String): String {
val inputStream = FileInputStream(path)
val reader = BufferedReader(InputStreamReader(inputStream))
return reader.readText()
// ⚠️ 忘记关闭stream,导致文件描述符泄漏
}解决方案: 使用use()自动关闭
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用use自动关闭
fun readFile(path: String): String {
return File(path).inputStream().use { inputStream ->
BufferedReader(InputStreamReader(inputStream)).use { reader ->
reader.readText()
}
}
}
// 或者简化为
fun readFile(path: String): String {
return File(path).readText()
}核心原则 : 所有Closeable资源都应该用use()包裹,确保自动关闭。
OOM问题分析与优化
OOM(Out Of Memory)是Android应用崩溃的首要原因。理解OOM类型和优化策略是每个Android开发者的必备技能。
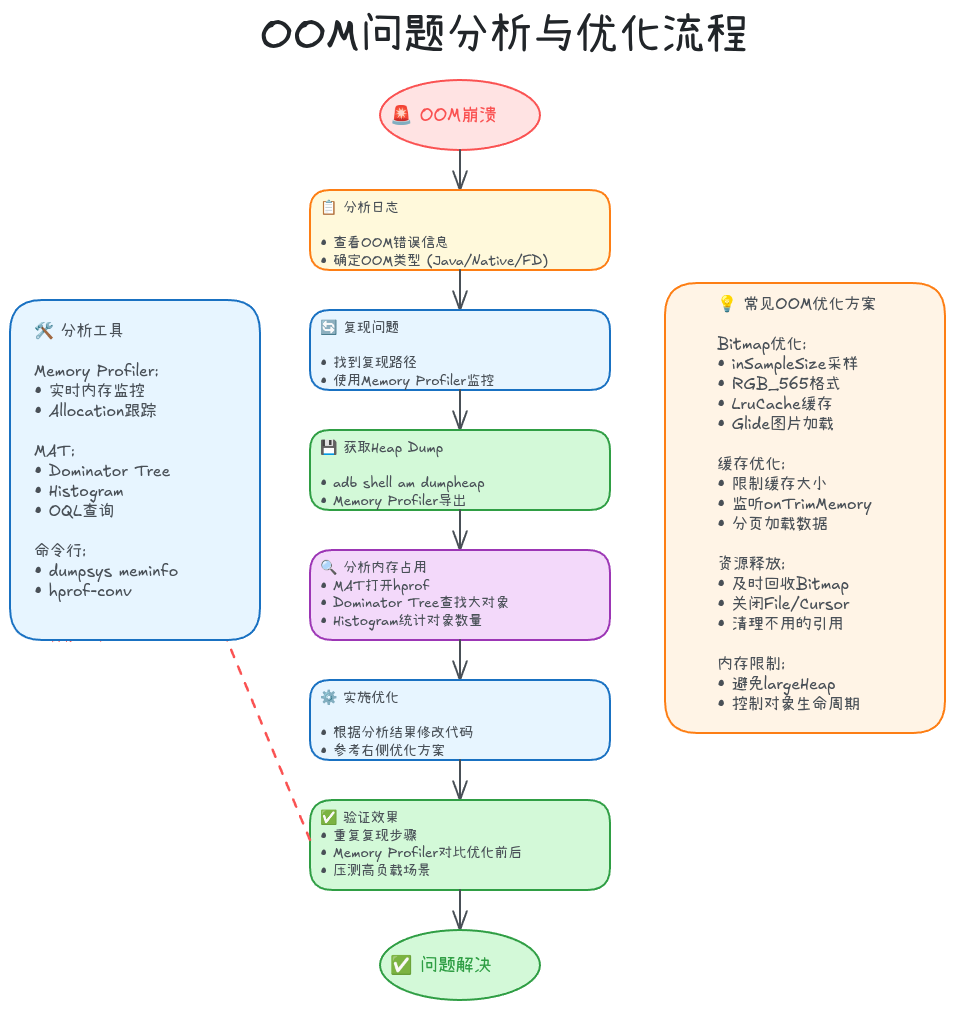
5.1 OOM类型分类
Android OOM有多种类型,需要针对性分析。
Java堆OOM
最常见的OOM,Java对象分配超过堆限制:
Fatal Exception: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Failed to allocate a 4194316 byte allocation with 2097152 free bytes and 2MB until OOM特征:
- 错误信息:
OutOfMemoryError: Failed to allocate - 原因: Bitmap、大数组、对象泄漏
Native堆OOM
Native代码分配内存失败:
Fatal signal 11 (SIGSEGV), code 1, fault addr 0x0 in tid 12345特征:
- 错误信息:
pthread_create failed: couldn't allocate或 SIGSEGV - 原因: JNI内存泄漏、第三方so库问题、Bitmap像素数据(Android 8.0+)
FD(文件描述符)耗尽
打开文件/Socket过多:
java.io.IOException: Could not open file: /data/xxx.db: Too many open files特征:
- 错误信息:
Too many open files - 原因: 文件/Cursor/Stream未关闭
线程数超限
创建线程过多:
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: pthread_create (1040KB stack) failed: Try again特征:
- 错误信息:
pthread_create failed - 原因: 线程泄漏、线程池配置不当
查看当前线程数:
bash
adb shell ps -T <pid> | wc -l5.2 Bitmap内存优化
Bitmap是OOM的主要元凶,优化Bitmap加载是解决OOM的关键。
问题: 加载大图导致OOM
kotlin
// ❌ Bad: 直接加载大图
fun loadLargeImage(path: String): Bitmap {
return BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path)
// 4K图片(4096x2160 ARGB_8888)占用: 4096*2160*4 = 35MB
// 可能直接OOM
}优化1: 采样压缩 (inSampleSize)
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 按需采样加载
fun decodeSampledBitmapFromFile(
path: String,
reqWidth: Int, // 需要的宽度
reqHeight: Int // 需要的高度
): Bitmap {
return BitmapFactory.Options().run {
// 第一次解码: 只获取图片尺寸
inJustDecodeBounds = true
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path, this)
val (actualWidth, actualHeight) = outWidth to outHeight
// 计算采样率
inSampleSize = calculateInSampleSize(actualWidth, actualHeight, reqWidth, reqHeight)
// 第二次解码: 实际加载图片
inJustDecodeBounds = false
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path, this)
}
}
fun calculateInSampleSize(
actualWidth: Int,
actualHeight: Int,
reqWidth: Int,
reqHeight: Int
): Int {
var inSampleSize = 1
if (actualHeight > reqHeight || actualWidth > reqWidth) {
val halfHeight = actualHeight / 2
val halfWidth = actualWidth / 2
// 计算最大的inSampleSize(2的幂次),保证缩放后尺寸仍大于需要的尺寸
while ((halfHeight / inSampleSize) >= reqHeight &&
(halfWidth / inSampleSize) >= reqWidth) {
inSampleSize *= 2
}
}
return inSampleSize
}
// 使用: 加载到ImageView (1080x1920屏幕)
val bitmap = decodeSampledBitmapFromFile(
path = "/sdcard/large_image.jpg",
reqWidth = 1080,
reqHeight = 1920
)
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap)
// 4K图片采样后: 4096/4 x 2160/4 x 4 = 2.2MB (节省93%内存)核心原理:
inJustDecodeBounds = true: 只解析图片头部获取尺寸,不分配内存inSampleSize: 采样率,必须是2的幂次 (2, 4, 8, 16...)inSampleSize=4: 宽高各缩小4倍,内存占用减少16倍
优化2: 使用RGB_565格式
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用RGB_565减少内存
fun loadBitmapRGB565(path: String): Bitmap {
return BitmapFactory.Options().run {
inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565 // 2字节/像素
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path, this)
}
}
// ARGB_8888: 4字节/像素 (透明度+RGB各1字节)
// RGB_565: 2字节/像素 (R5位+G6位+B5位,无透明度)
// 内存节省50%,适合不需要透明度的场景优化3: Bitmap复用 (inBitmap)
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 复用Bitmap内存
class BitmapPool {
private val reusableBitmaps = mutableSetOf<SoftReference<Bitmap>>()
fun addBitmapToPool(bitmap: Bitmap) {
reusableBitmaps.add(SoftReference(bitmap))
}
fun getBitmapFromPool(options: BitmapFactory.Options): Bitmap? {
var bitmap: Bitmap? = null
if (reusableBitmaps.isNotEmpty()) {
val iterator = reusableBitmaps.iterator()
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
val item = iterator.next().get()
if (item != null && item.isMutable) {
// 检查尺寸是否匹配
if (canUseForInBitmap(item, options)) {
bitmap = item
iterator.remove()
break
}
} else {
iterator.remove()
}
}
}
return bitmap
}
private fun canUseForInBitmap(
candidate: Bitmap,
targetOptions: BitmapFactory.Options
): Boolean {
val width = targetOptions.outWidth / targetOptions.inSampleSize
val height = targetOptions.outHeight / targetOptions.inSampleSize
val byteCount = width * height * getBytesPerPixel(candidate.config)
return byteCount <= candidate.allocationByteCount
}
private fun getBytesPerPixel(config: Bitmap.Config): Int {
return when (config) {
Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888 -> 4
Bitmap.Config.RGB_565 -> 2
Bitmap.Config.ARGB_4444 -> 2
Bitmap.Config.ALPHA_8 -> 1
else -> 1
}
}
}
// 使用复用池
val pool = BitmapPool()
fun loadBitmapWithReuse(path: String): Bitmap {
return BitmapFactory.Options().run {
inMutable = true
inBitmap = pool.getBitmapFromPool(this) // 尝试复用
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path, this)
}
}核心原理 : 设置inBitmap后,BitmapFactory会尝试复用该Bitmap的内存,避免重新分配。
优化4: 及时回收Bitmap
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 不用时及时回收
imageView.setImageBitmap(null) // 清除ImageView引用
bitmap.recycle() // 回收Bitmap内存
// 注意: recycle()后Bitmap不可再使用5.3 LruCache缓存优化
使用LruCache管理内存缓存,自动淘汰旧数据。
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用LruCache管理图片缓存
class ImageCache {
private val maxMemory = (Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() / 1024).toInt() // KB
private val cacheSize = maxMemory / 8 // 使用1/8堆内存作为缓存
private val memoryCache = object : LruCache<String, Bitmap>(cacheSize) {
// 计算每个Bitmap的大小(KB)
override fun sizeOf(key: String, bitmap: Bitmap): Int {
return bitmap.byteCount / 1024
}
// 移除时回收Bitmap
override fun entryRemoved(
evicted: Boolean,
key: String?,
oldValue: Bitmap?,
newValue: Bitmap?
) {
if (evicted && oldValue != null && !oldValue.isRecycled) {
oldValue.recycle()
}
}
}
fun getBitmap(key: String): Bitmap? {
return memoryCache.get(key)
}
fun putBitmap(key: String, bitmap: Bitmap) {
if (getBitmap(key) == null) {
memoryCache.put(key, bitmap)
}
}
fun evictAll() {
memoryCache.evictAll()
}
fun trimToSize(size: Int) {
memoryCache.trimToSize(size)
}
}
// 使用
val imageCache = ImageCache()
fun loadImageWithCache(url: String, imageView: ImageView) {
val cached = imageCache.getBitmap(url)
if (cached != null) {
imageView.setImageBitmap(cached)
return
}
// 从网络/磁盘加载
loadImageAsync(url) { bitmap ->
imageCache.putBitmap(url, bitmap)
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap)
}
}LruCache原理:
- LRU (Least Recently Used): 最近最少使用算法
- 缓存满时自动淘汰最久未使用的项
- 通过
sizeOf()计算每项大小 trimToSize()可手动缩减缓存
5.4 集成Glide优化图片加载
推荐使用Glide等成熟图片加载库,已内置大量优化:
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 使用Glide加载图片
dependencies {
implementation("com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.15.1")
}
// 基本使用
Glide.with(context)
.load(imageUrl)
.placeholder(R.drawable.placeholder) // 占位图
.error(R.drawable.error) // 错误图
.into(imageView)
// 指定尺寸(自动采样)
Glide.with(context)
.load(imageUrl)
.override(800, 600) // 指定目标尺寸
.into(imageView)
// 使用缩略图
Glide.with(context)
.load(imageUrl)
.thumbnail(0.1f) // 先加载10%尺寸的缩略图
.into(imageView)
// 监听内存警告
override fun onTrimMemory(level: Int) {
super.onTrimMemory(level)
if (level >= ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_MODERATE) {
Glide.get(this).clearMemory() // 清空内存缓存
}
}Glide内置优化:
- 自动采样和缩放
- 三级缓存 (内存/磁盘/网络)
- Bitmap复用池
- 生命周期感知 (自动取消请求)
- 格式转换 (WebP/JPEG优化)
5.5 大对象缓存优化
除了图片,其他大对象也需要合理缓存。
分页加载
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 分页加载大数据
class DataRepository {
private val pageSize = 50
private val cache = LruCache<Int, List<Data>>(20) // 缓存20页
suspend fun loadPage(page: Int): List<Data> {
// 先查缓存
cache.get(page)?.let { return it }
// 从数据库/网络加载
val data = database.queryPage(page, pageSize)
cache.put(page, data)
return data
}
}及时释放资源
kotlin
// ✅ Good: 监听内存警告
override fun onTrimMemory(level: Int) {
super.onTrimMemory(level)
when (level) {
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_UI_HIDDEN -> {
// UI隐藏,释放UI资源
releaseUIResources()
}
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_BACKGROUND -> {
// 进入后台,释放部分缓存
imageCache.trimToSize(imageCache.size() / 2)
}
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_COMPLETE -> {
// 内存严重不足,清空所有缓存
imageCache.evictAll()
dataCache.clear()
}
}
}实战案例: 图片浏览OOM优化
通过一个真实案例,展示完整的OOM问题分析和优化过程。
6.1 问题现象
场景: 图片浏览应用,用户快速滑动浏览大量高清图片时频繁OOM崩溃。
统计数据 (优化前):
- OOM崩溃率: 85次/万次启动
- 平均内存占用: 420MB (接近512MB堆限制)
- 内存峰值: 498MB (触发OOM)
- 用户反馈: 浏览50+张图片必然崩溃
6.2 问题分析
步骤1: 复现问题
kotlin
// 原始代码 (存在问题的版本)
class GalleryActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val images = mutableListOf<Bitmap>()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// 加载图片列表
val imagePaths = getImagePaths()
imagePaths.forEach { path ->
val bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path) // ❌ 直接加载大图
images.add(bitmap) // ❌ 全部保存在内存
}
setupRecyclerView(images)
}
}步骤2: Memory Profiler分析
-
打开Memory Profiler监控内存
-
滑动浏览50张图片
-
观察内存曲线:
内存占用变化:
0s: 80MB (启动)
10s: 180MB (加载10张)
20s: 320MB (加载30张)
30s: 450MB (加载48张)
32s: 498MB → OOM崩溃 -
Dump Heap分析:
- Bitmap及byte[]占用: 385MB
- 单张4K图片: 35MB (4096x2160x4)
- 问题根源: 全量加载+未压缩+未复用
步骤3: 定位代码问题
通过MAT分析Heap Dump:
Dominator Tree:
├─ GalleryActivity @ 0x12a45000 Retained: 485MB
├─ images: ArrayList @ 0x12a46000 Retained: 385MB
│ ├─ [0] Bitmap @ 0x12b00000 Retained: 35MB
│ ├─ [1] Bitmap @ 0x12b50000 Retained: 35MB
│ ├─ [2] Bitmap @ 0x12c00000 Retained: 35MB
│ ... (48 Bitmaps)问题点:
- 直接加载原图,未采样压缩
- ArrayList持有所有Bitmap引用
- RecyclerView未复用Bitmap
- 未使用缓存机制
6.3 优化方案
优化1: 采样加载
kotlin
// ✅ 优化: 按需采样加载
fun loadSampledBitmap(path: String, targetWidth: Int = 1080): Bitmap {
return BitmapFactory.Options().run {
inJustDecodeBounds = true
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path, this)
// 计算采样率
inSampleSize = calculateInSampleSize(outWidth, outHeight, targetWidth, targetWidth * 16 / 9)
inJustDecodeBounds = false
inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565 // 使用RGB_565
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path, this)
}
}
// 内存占用: 35MB → 2.2MB (节省93%)优化2: 使用Glide + LruCache
kotlin
// ✅ 优化: 集成Glide
class GalleryActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
val imagePaths = getImagePaths()
// 使用RecyclerView + Glide
recyclerView.adapter = GalleryAdapter(imagePaths)
}
}
class GalleryAdapter(private val imagePaths: List<String>) :
RecyclerView.Adapter<GalleryAdapter.ViewHolder>() {
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int) {
val path = imagePaths[position]
// Glide自动管理内存
Glide.with(holder.itemView.context)
.load(path)
.override(1080, 1920) // 指定目标尺寸
.placeholder(R.drawable.placeholder)
.into(holder.imageView)
}
class ViewHolder(view: View) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(view) {
val imageView: ImageView = view.findViewById(R.id.imageView)
}
}优化3: 预加载与复用
kotlin
// ✅ 优化: RecyclerView预加载
recyclerView.apply {
// 设置RecycledViewPool
setRecycledViewPool(RecyclerView.RecycledViewPool().apply {
setMaxRecycledViews(0, 20) // 缓存20个ViewHolder
})
// 设置预加载
layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(context).apply {
isItemPrefetchEnabled = true
initialPrefetchItemCount = 4
}
}
// Glide预加载
fun preloadNextImages(startPosition: Int, count: Int) {
for (i in startPosition until min(startPosition + count, imagePaths.size)) {
Glide.with(this)
.load(imagePaths[i])
.preload(1080, 1920)
}
}优化4: 监听内存警告
kotlin
// ✅ 优化: 响应内存警告
override fun onTrimMemory(level: Int) {
super.onTrimMemory(level)
when (level) {
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_LOW,
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_CRITICAL -> {
// 清空Glide内存缓存
Glide.get(this).clearMemory()
}
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_UI_HIDDEN -> {
// UI隐藏,清空部分缓存
Glide.get(this).trimMemory(level)
}
}
}6.4 优化效果

| 指标 | 优化前 | 优化后 | 改善幅度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| OOM崩溃率 | 85次/万次启动 | 3次/万次启动 | ↓ 96.5% |
| 平均内存占用 | 420MB | 95MB | ↓ 77% |
| 内存峰值 | 498MB | 156MB | ↓ 69% |
| 浏览体验 | 50张必崩溃 | 500+张流畅 | ↑ 10倍 |
优化措施贡献度:
- 采样加载 + RGB_565: 60% (35MB → 2.2MB/张)
- Glide LruCache自动管理: 25% (限制缓存大小)
- RecyclerView复用: 10% (减少对象创建)
- 内存警告响应: 5% (及时释放缓存)
6.5 验证与监控
自动化测试
kotlin
@Test
fun testImageLoadingMemory() {
// 启动应用
val scenario = ActivityScenario.launch(GalleryActivity::class.java)
// 获取初始内存
val initialMemory = getMemoryUsage()
// 滑动加载100张图片
onView(withId(R.id.recyclerView))
.perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollToPosition(100))
// 触发GC
Runtime.getRuntime().gc()
Thread.sleep(1000)
// 检查内存增长
val currentMemory = getMemoryUsage()
val memoryIncrease = currentMemory - initialMemory
// 断言: 内存增长不超过200MB
assert(memoryIncrease < 200 * 1024 * 1024) {
"Memory increase exceeded 200MB: ${memoryIncrease / 1024 / 1024}MB"
}
}
fun getMemoryUsage(): Long {
val runtime = Runtime.getRuntime()
return runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory()
}线上监控
kotlin
// 集成Firebase Crashlytics监控OOM
class MyApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
// 监听内存警告
registerComponentCallbacks(object : ComponentCallbacks2 {
override fun onTrimMemory(level: Int) {
val memoryInfo = getMemoryInfo()
// 记录到Crashlytics
FirebaseCrashlytics.getInstance().log(
"onTrimMemory: level=$level, availMem=${memoryInfo.availMem / 1024 / 1024}MB"
)
if (level >= ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_CRITICAL) {
// 上报内存危机事件
FirebaseCrashlytics.getInstance().recordException(
Exception("Critical memory warning")
)
}
}
override fun onConfigurationChanged(newConfig: Configuration) {}
override fun onLowMemory() {}
})
}
private fun getMemoryInfo(): ActivityManager.MemoryInfo {
val activityManager = getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE) as ActivityManager
return ActivityManager.MemoryInfo().also {
activityManager.getMemoryInfo(it)
}
}
}内存监控与预警
建立完善的内存监控体系,可以在问题发生前预警和干预。
7.1 Runtime API监控
在应用运行时实时监控内存状态:
kotlin
class MemoryMonitor {
fun getMemoryInfo(): MemoryInfo {
val runtime = Runtime.getRuntime()
val activityManager = context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE) as ActivityManager
val memInfo = ActivityManager.MemoryInfo()
activityManager.getMemoryInfo(memInfo)
return MemoryInfo(
maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory(), // 最大堆内存
totalMemory = runtime.totalMemory(), // 已分配堆内存
freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory(), // 堆中空闲内存
usedMemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory(), // 已使用内存
systemAvailMem = memInfo.availMem, // 系统可用内存
systemTotalMem = memInfo.totalMem, // 系统总内存
systemLowMemory = memInfo.lowMemory // 系统是否低内存
)
}
fun getMemoryUsagePercent(): Float {
val runtime = Runtime.getRuntime()
val used = (runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory()).toFloat()
val max = runtime.maxMemory().toFloat()
return (used / max) * 100
}
fun isMemoryWarning(): Boolean {
return getMemoryUsagePercent() > 80 // 超过80%触发警告
}
}
data class MemoryInfo(
val maxMemory: Long,
val totalMemory: Long,
val freeMemory: Long,
val usedMemory: Long,
val systemAvailMem: Long,
val systemTotalMem: Long,
val systemLowMemory: Boolean
)7.2 定期检测与告警
kotlin
class MemoryWatchdog(private val context: Context) {
private val handler = Handler(Looper.getMainLooper())
private val monitor = MemoryMonitor()
private val checkInterval = 5000L // 5秒检测一次
private val checkRunnable = object : Runnable {
override fun run() {
checkMemory()
handler.postDelayed(this, checkInterval)
}
}
fun start() {
handler.post(checkRunnable)
}
fun stop() {
handler.removeCallbacks(checkRunnable)
}
private fun checkMemory() {
val info = monitor.getMemoryInfo()
val usagePercent = monitor.getMemoryUsagePercent()
Log.d("MemoryWatchdog", "Memory usage: ${usagePercent.toInt()}%")
// 内存预警
when {
usagePercent > 90 -> {
Log.e("MemoryWatchdog", "CRITICAL: Memory usage ${usagePercent.toInt()}%")
onMemoryCritical()
}
usagePercent > 80 -> {
Log.w("MemoryWatchdog", "WARNING: Memory usage ${usagePercent.toInt()}%")
onMemoryWarning()
}
}
// 上报监控数据
reportMemoryMetrics(info, usagePercent)
}
private fun onMemoryWarning() {
// 清理部分缓存
context.applicationContext.apply {
if (this is Application) {
(this as? ComponentCallbacks2)?.onTrimMemory(
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_LOW
)
}
}
}
private fun onMemoryCritical() {
// 紧急清理所有缓存
Glide.get(context).clearMemory()
// 通知所有Activity
context.applicationContext.apply {
if (this is Application) {
(this as? ComponentCallbacks2)?.onTrimMemory(
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_CRITICAL
)
}
}
// 触发GC
Runtime.getRuntime().gc()
}
private fun reportMemoryMetrics(info: MemoryInfo, usagePercent: Float) {
// 上报到监控平台
FirebaseAnalytics.getInstance(context).logEvent("memory_usage") {
param("usage_percent", usagePercent.toLong())
param("used_mb", (info.usedMemory / 1024 / 1024).toInt().toLong())
param("max_mb", (info.maxMemory / 1024 / 1024).toInt().toLong())
}
}
}
// Application中启动
class MyApplication : Application() {
private lateinit var memoryWatchdog: MemoryWatchdog
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
memoryWatchdog = MemoryWatchdog(this)
memoryWatchdog.start()
}
}7.3 内存泄漏自动检测
集成LeakCanary在开发阶段自动检测:
kotlin
// build.gradle.kts
dependencies {
debugImplementation("com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:2.12")
}
// 自定义LeakCanary配置
class MyApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
// 自定义LeakCanary配置 (可选)
LeakCanary.config = LeakCanary.config.copy(
dumpHeap = true, // 发现泄漏时Dump堆
retainedVisibleThreshold = 3 // 保留3个对象未回收时告警
)
}
}7.4 线上OOM监控
通过Firebase Crashlytics监控线上OOM:
kotlin
class CrashReportingTree : Timber.Tree() {
override fun log(priority: Int, tag: String?, message: String, t: Throwable?) {
if (priority < Log.WARN) return
val crashlytics = FirebaseCrashlytics.getInstance()
crashlytics.log("$tag: $message")
t?.let {
if (it is OutOfMemoryError) {
// OOM特殊处理
val memoryInfo = getMemorySnapshot()
crashlytics.setCustomKey("oom_heap_used", memoryInfo.usedMemory)
crashlytics.setCustomKey("oom_heap_max", memoryInfo.maxMemory)
}
crashlytics.recordException(it)
}
}
private fun getMemorySnapshot(): MemoryInfo {
return MemoryMonitor().getMemoryInfo()
}
}
// Application中初始化
Timber.plant(CrashReportingTree())总结与最佳实践
8.1 核心要点回顾
内存管理机制:
- Java堆受heapgrowthlimit限制,普通应用通常192-256MB
- GC无法回收被GC Root直接或间接引用的对象
- LMK根据oom_adj值从高到低杀进程释放内存
- 监听onTrimMemory()及时释放缓存
内存分析工具:
- Memory Profiler: 实时监控,快速定位内存增长
- MAT: 深度分析Heap Dump,查找泄漏根源
- LeakCanary: 自动化泄漏检测,开发必备
- 命令行工具: dumpsys meminfo用于脚本监控
常见泄漏场景:
- 静态变量持有Activity → 使用ApplicationContext
- Handler内部类持有Activity → 静态类+弱引用
- 单例持有Context → 转换为ApplicationContext
- 未注销Listener/Receiver → onDestroy中配对注销
- 资源未关闭 → 使用use()自动关闭
OOM优化:
- Bitmap采样加载: inSampleSize降低内存
- 使用RGB_565格式节省50%内存
- LruCache管理缓存,自动淘汰旧数据
- 集成Glide简化图片加载和内存管理
- 监听onTrimMemory()及时释放资源
8.2 最佳实践清单
开发阶段:
- ✅ 所有Activity销毁后检查LeakCanary报告
- ✅ 使用Memory Profiler监控内存曲线
- ✅ Bitmap加载必须采样,禁止直接BitmapFactory.decodeFile()
- ✅ 长生命周期对象(单例/静态)不持有短生命周期对象(Activity/View)
- ✅ Handler/Thread/Runnable使用静态类+弱引用
- ✅ 所有Closeable资源用use()包裹
测试阶段:
- ✅ 编写自动化测试验证内存增长
- ✅ 使用Monkey测试长时间运行稳定性
- ✅ 分析MAT Heap Dump检查大对象
- ✅ 压测高负载场景 (快速滑动/频繁切换)
生产阶段:
- ✅ 集成Crashlytics监控OOM崩溃率
- ✅ 定期分析线上OOM堆栈
- ✅ 监控关键页面内存指标
- ✅ A/B测试内存优化效果
代码规范:
kotlin
// ✅ DO: 正确的内存管理
class GoodActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// 使用ViewModel管理数据
private val viewModel: MyViewModel by viewModels()
// 静态Handler + 弱引用
private val handler = MyHandler(this)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// 使用Glide加载图片
Glide.with(this)
.load(url)
.override(800, 600)
.into(imageView)
// LiveData自动管理生命周期
viewModel.data.observe(this) { data ->
updateUI(data)
}
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// 清理Handler消息
handler.removeCallbacksAndMessages(null)
}
private class MyHandler(activity: GoodActivity) : Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
private val activityRef = WeakReference(activity)
override fun handleMessage(msg: Message) {
activityRef.get()?.let { activity ->
if (!activity.isFinishing) {
// 安全使用Activity
}
}
}
}
}
// ❌ DON'T: 错误的内存管理
class BadActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
companion object {
var sContext: Context? = null // ❌ 静态变量持有Context
}
private val handler = object : Handler() { // ❌ 匿名内部类持有Activity
override fun handleMessage(msg: Message) {
updateUI()
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
sContext = this // ❌ 存储Activity到静态变量
val bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path) // ❌ 直接加载大图
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap)
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 60000) // ❌ 长时间持有Activity
}
// ❌ 缺少onDestroy清理
}8.3 延伸阅读
AOSP源码:
- ART GC实现:
art/runtime/gc/ - LMK机制:
system/core/lmkd/lmkd.c - ActivityManager内存管理:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/
工具文档:
系列文章:
作者简介: 多年Android系统开发经验,专注于系统稳定性与性能优化领域。欢迎关注本系列,一起深入Android系统的精彩世界!