文章目录
- 原型模式是什么?
- 传统方式硬编码的弊端
- 原型模式主要适用于以下场景:
- [一个简单的原型模式 Demo](#一个简单的原型模式 Demo)
- [使用 JDK 接口实现方式](#使用 JDK 接口实现方式)
- 使用序列化实现深度克隆
- 克隆破坏单例模式
- 原型模式在源码中的应用
- 原型模式的优缺点
原型模式是什么?
原型模式(Prototype Pattern)是指原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象
- 调用者不需要知道任何创建细节,不调用构造方法
- 属于创建型模式
官方原文: Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance,and create new objects by copying this prototype.
原型模式的核心在于拷贝原型对象。以系统中已存在的一个对象为原型,直接基于内存二进制流进行拷,无需再经历耗时的对象初始化过程(不调用构造函数),性能提升许多。当对象的构建过程比较耗时时,可以利用当前系统中已存在的对象作为原型,对其进行克隆(一般是基于二进制流的复制),躲避初始化过程,使得新对象的创建时间大大减少。
通俗点讲就是复制,将复制的过程封装起来,使调用者不再需要通过构造函数去创建对象,下面,不妨让我们来看看一个简单原型模式类结构图:
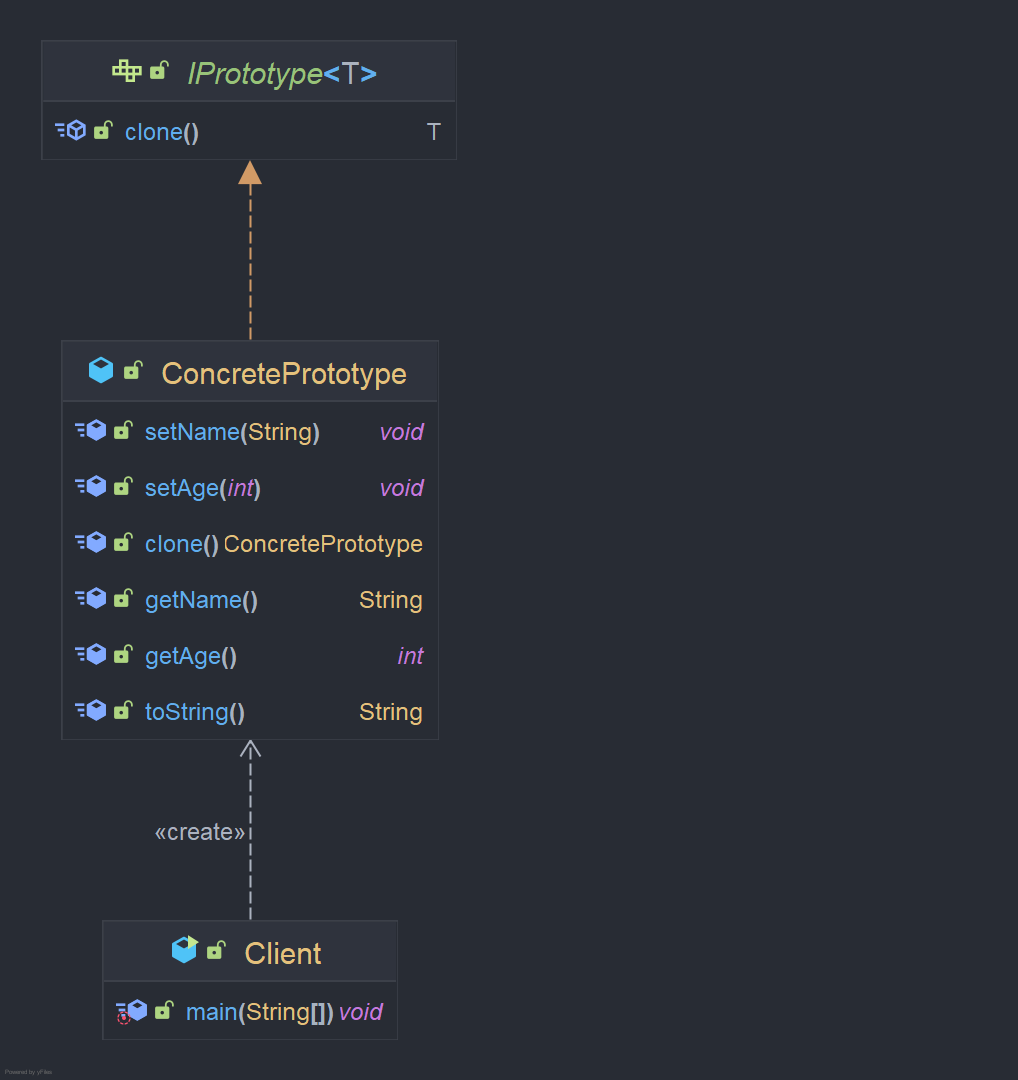
从UML图中,我们可以看到,原型模式主要包含三个角色:
- 客户(Client):客户类提出创建对象的请求。
- 抽象原型(IPrototype):规定拷贝接口。
- 具体原型(Concrete Prototype):被拷贝的对象。
注:对不通过new关键字,而是通过对象拷贝来实现创建对象的模式就称作原型模式。
传统方式硬编码的弊端
你一定遇到过大篇幅getter,setter赋值的场景。例如这样的代码:
java
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class ExamPaper {
//省略属性....
public ExamPaper copy() {
ExamPaper examPaper = new ExamPaper();
//剩余时间
examPaper.setLeavTime(this.getLeavTime());
//单位主键
examPaper.setOrganizationId(this.getOrganizationId());
//考试主键
examPaper.setId(this.getId());
//用户主键
examPaper.setUserId(this.getUserId());
//专业
examPaper.setSpecialtyCode(this.getSpecialtyCode());
//岗位
examPaper.setPostionCode(this.getPostionCode());
//等级
examPaper.setGradeCode(this.getGradeCode());
//考试开始时间
examPaper.setExamStartTime(this.getExamStartTime());
//考试结束时间
examPaper.setExamEndTime(this.getExamEndTime());
//单选题重要数量
examPaper.setSingleSelectionImpCount(this.getSingleSelectionImpCount());
//多选题重要数量
examPaper.setMultiSelectionImpCount(this.getMultiSelectionImpCount());
//判断题重要数量
examPaper.setJudgementImpCount(this.getJudgementImpCount());
//考试时间
examPaper.setExamTime(this.getExamTime());
//总分
examPaper.setFullScore(this.getFullScore());
//及格分
examPaper.setPassScore(this.getPassScore());
//学员姓名
examPaper.setUserName(this.getUserName());
//分数
examPaper.setScore(this.getScore());
//单选答对数量
examPaper.setSingleOkCount(this.getSingleOkCount());
//多选答对数量
examPaper.setMultiOkCount(this.getMultiOkCount());
//判断答对数量
examPaper.setJudgementOkCount(this.getJudgementOkCount());
return examPaper;
}
}代码非常工整,命名非常规范,注释也写的很全面,其实这就是原型模式的需求场景。但是,大家觉得这样的代码优雅吗?我认为,这样的代码属于纯体力劳动。那原型模式,能帮助我们解决这样的问题。
原型模式主要适用于以下场景:
1、类初始化消耗资源较多。
2、new产生的一个对象需要非常繁琐的过程(数据准备、访问权限等)
3、构造函数比较复杂。
4、循环体中生产大量对象时。
在Spring中,原型模式应用得非常广泛。例如scope="prototype",在我们经常用的JSON.parseObject()也是一种原型模式。
一个简单的原型模式 Demo
一个标准的原型模式代码,应该是这样设计的。
- 定义原型接口
java
public interface IPrototype<T> {
T clone();
}- 创建具体需要克隆的对象ConcretePrototype
java
public class ConcretePrototype implements IPrototype {
private int age;
private String name;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public ConcretePrototype clone() {
ConcretePrototype concretePrototype = new ConcretePrototype();
concretePrototype.setAge(this.age);
concretePrototype.setName(this.name);
return concretePrototype;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConcretePrototype{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}- 测试代码
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建原型对象
ConcretePrototype prototype = new ConcretePrototype();
prototype.setAge(26);
prototype.setName("Cheese");
System.out.println(prototype);
//拷贝原型对象
ConcretePrototype cloneType = prototype.clone();
System.out.println(cloneType);
}- 运行结果
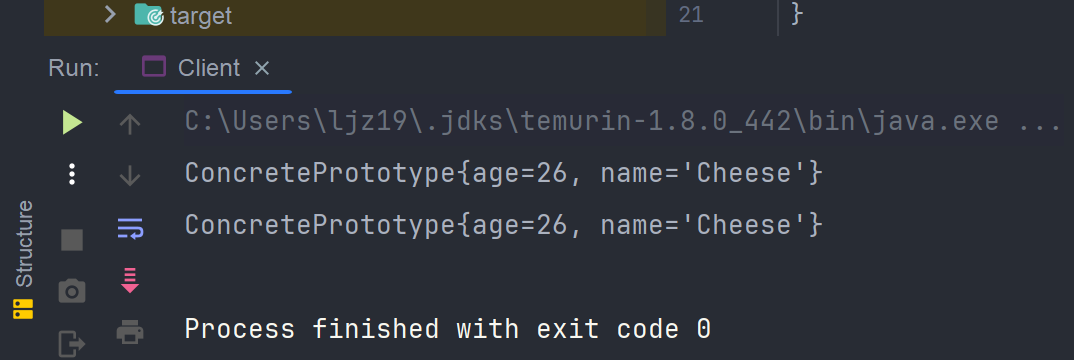
这时候,有小伙伴就问了,原型模式就这么简单吗?对,就是这么简单。在这个简单的场景之下,看上去操作好像变复杂了。但如果有几百个属性需要复制,那我们就可以一劳永逸。
使用 JDK 接口实现方式
上面的复制过程是我们自己完成的,在实际编码中,我们一般不会浪费这样的体力劳动,JDK已经帮我们实现了一个现成的API,我们只需要实现Cloneable接口即可。来改造一下代码,修改ConcretePrototype类:
java
@Data
public class ConcretePrototype implements Cloneable {
private int age;
private String name;
@Override
public ConcretePrototype clone() {
try {
return (ConcretePrototype)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConcretePrototype{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name +
'}';
}
}重新运行,也会得到同样的结果。有了JDK的支持再多的属性复制我们也能轻而易举地搞定了。下面我们再来做一个测试,给ConcretePrototype增加一个个人爱好的属性hobbies:
java
@Data
public class ConcretePrototype implements Cloneable {
private int age;
private String name;
private List<String> hobbies;
.....
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConcretePrototype{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name +
'\'' + ", hobbies=" + hobbies +
'}';
}
}- 修改测试方法
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建原型对象
ConcretePrototype prototype = new ConcretePrototype();
prototype.setAge(26);
prototype.setName("Cheese");
List<String> hobbies = new ArrayList<String>();
hobbies.add("Coffee");
hobbies.add("Coding");
prototype.setHobbies(hobbies);
//拷贝原型对象
ConcretePrototype cloneType = prototype.clone();
cloneType.getHobbies().add("技术控");
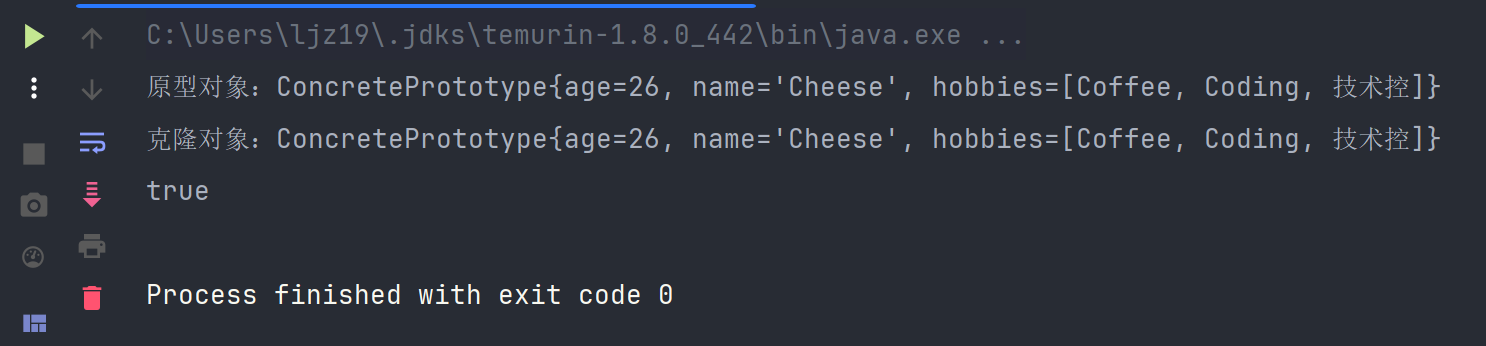
System.out.println("原型对象:" + prototype);
System.out.println("克隆对象:" + cloneType);
System.out.println(prototype == cloneType);
}- 测试结果
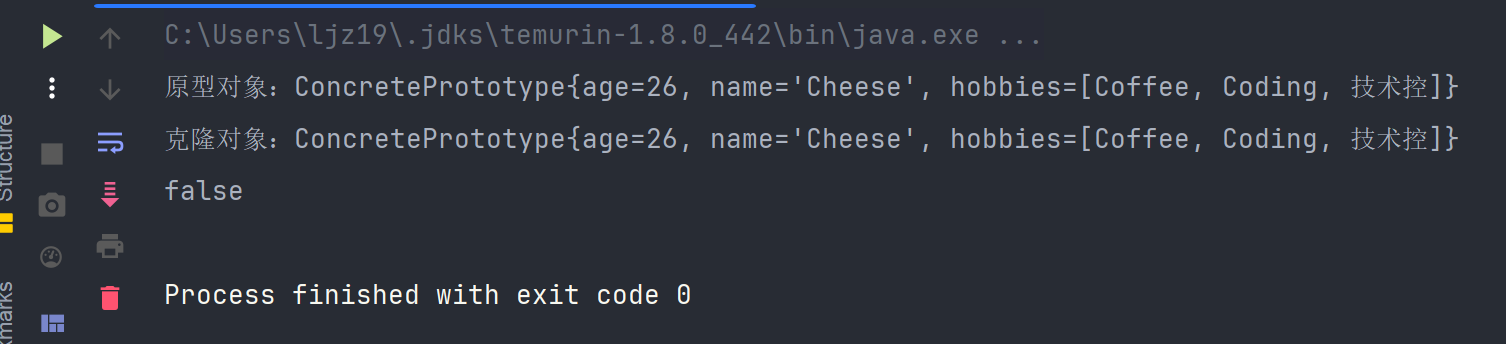
我们给,复制后的克隆对象新增一项爱好,发现原型对象也发生了变化,这显然不符合我们的预期。
因为我们希望克隆出来的对象应该和原型对象是两个独立的对象,不应该再有联系了。从测试结果分析来看,应该是hobbies共用了一个内存地址,意味着复制的不是值,而是引用的地址。
这样的话,如果我们修改任意一个对象中的属性值,prototype和 cloneType的hobbies值都会改变。这就是我们常说的浅克隆。只是完整复制了值类型数据,没有赋值引用对象。换言之,所有的引用对象仍然指向原来的对象,显然不是我们想要的结果。那如何解决这个问题呢?下面我们来看深度克隆继续改造。
使用序列化实现深度克隆
在上面的基础上我们继续改造,来看代码,增加一个deepClone0方法:
java
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Cheese.
*/
@Data
public class ConcretePrototype implements Cloneable,Serializable {
private int age;
private String name;
private List<String> hobbies;
@Override
public ConcretePrototype clone() {
try {
return (ConcretePrototype)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public ConcretePrototype deepClone(){
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
return (ConcretePrototype)ois.readObject();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ConcretePrototype{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", hobbies=" + hobbies +
'}';
}
}- 测试代码调用
deepClone方法创建克隆对象
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
....
//拷贝原型对象
ConcretePrototype cloneType = prototype.deepClone();
....
}- 重新运行原测试代码,我们发现得到了我们期望的结果:
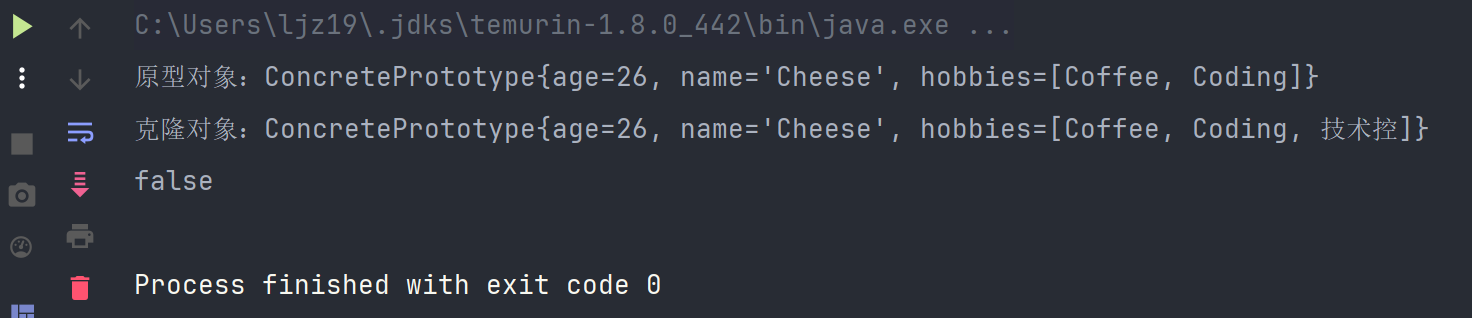
克隆破坏单例模式
如果我们克隆的目标的对象是单例对象,那意味着,克隆就会破坏单例。实际上防止克隆破坏单例解决思路非常简单,禁止克隆便可。要么你我们的单例类不实现Cloneable接口;要么我们重写clone0方法,在clone方法中返回单例对象即可,具体代码如下:
java
@Override
public ConcretePrototype clone() {
return instance;
}- 运行测试代码,我们看到原型对象和克隆对象都是同一 实例
原型模式在源码中的应用
先来JDK中Cloneable接口:
java
public interface Cloneable {
}接口定义还是很简单的,我们找源码其实只需要找到看哪些接口实现了Cloneable即可。来看ArrayList类的实现。
java
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance. (The
* elements themselves are not copied.)
*
* @return a clone of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}源码对改方法的描述
返回此<tt>ArrayList</tt>实例的浅拷贝。(元素本身不会被复制。)
我们发现方法中只是将List中的元素循环遍历了一遍。这个时候我们再思考一下,是不是这种形式就是深克隆呢?其实用代码验证一下就知道了,继续修改ConcretePrototype类,增加一个deepCloneHobbies0方法:
java
@Data
public class ConcretePrototype implements Cloneable,Serializable {
....
public ConcretePrototype deepCloneHobbies(){
try {
ConcretePrototype result = (ConcretePrototype)super.clone();
result.hobbies = (List)((ArrayList)result.hobbies).clone();
return result;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
....
}- 修改测试代码调用
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
....
//拷贝原型对象
ConcretePrototype cloneType = prototype.deepCloneHobbies();
....
}- 查看测试结果
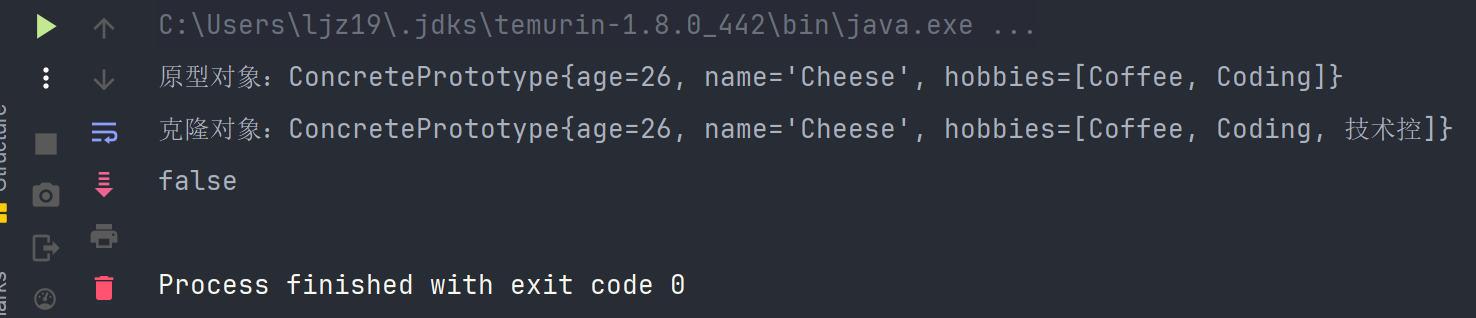
运行也能得到期望的结果。但是这样的代码,其实是硬编码,如果在对象中声明了各种集合类型,那每种情况都需要单独处理。因此,深克隆的写法,一般会直接用序列化来操作。
原型模式的优缺点
优点
1、性能优良,Java自带的原型模式是基于内存二进制流的拷,比直接new一个对象性能上提升了许多。
2、可以使用深克隆方式保存对象的状态,使用原型模式将对象复制一份并将其状态保存起来,简化了创建对象的过程,以便在需要的时候使用(例如恢复到历史某一状态),可辅助实现撤销操作。
缺点
1、需要为每一个类配置一个克隆方法。
2、克隆方法位于类的内部,当对已有类进行改造的时候,需要修改代码,违反了开闭原则。
3、在实现深克隆时需要编写较为复杂的代码,而且当对象之间存在多重嵌套引用时,为了实现深克隆,每一层对象对应的类都必须支持深克隆,实现起来会比较麻烦。因此,深拷贝、浅拷贝需要运用得
