目录
[operator bool](#operator bool)
[C++ IO 流](#C++ IO 流)
[C++ 文件 IO 流](#C++ 文件 IO 流)
[C++ 字符串流](#C++ 字符串流)
前置知识:
operator bool
我们在刷算法题时经常会碰到输入多组测试用例的情况,一般写法如下:
cpp
string s;
while (cin >> s)
{
}由于 s 是自定义类型对象,因此 >> 会去调用 s 的 >>运算符重载函数,返回值是 cin 本身,也就是 istream 类型的对象,但是 istream 类型对象为啥能作为 while 的判断条件呢??while / if 的判断条件必须是 bool(true / false),或者是 int(0 / 1),或者是是指针(nullptr / !nullptr),这就说明 istream 类型的对象可以隐式类型转换成 bool 类型

cpp
string s;
//while(operator>>(cin, s)) 本质是调用 operator>>
while (cin >> s)
{
}正常情况下自定义类型是无法转换为内置类型的
cpp
class A
{};
int main()
{
A aa;
int i = aa; //err
return 0;
}但是如果我们在类中提供了 "operator 内置类型" 函数,那么该类型就可以转换为"内置类型"
cpp
class A
{
public:
operator int()
{
return 0;
}
};
int main()
{
A aa;
int i = aa; //√
return 0;
}因此自定义类型的对象能够充当 if / while 的条件判断部分,也是因为提供了 operator int / operator bool /operator void* 函数
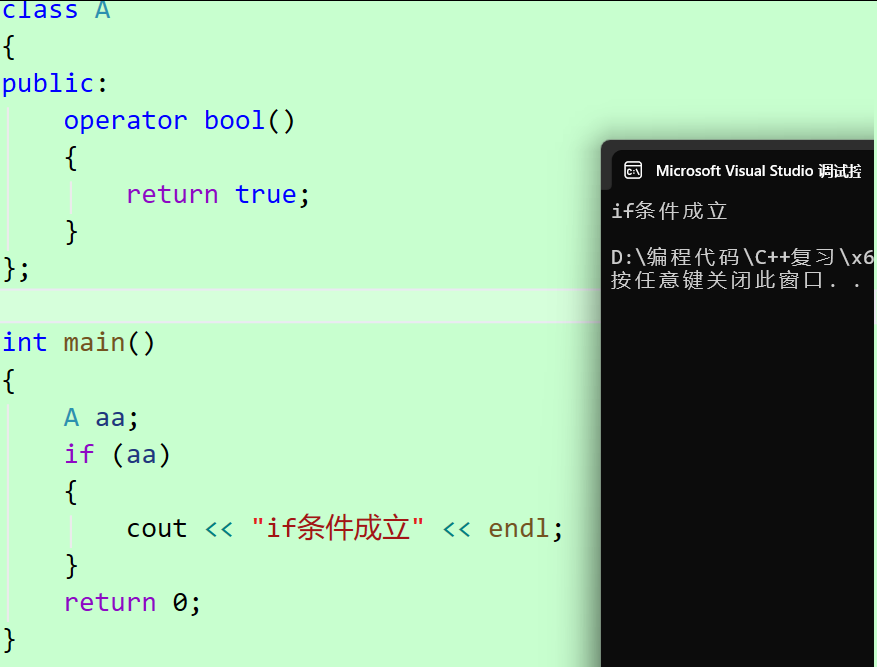
库中的 istream 对象也是提供了 operator void* 函数,简单理解,当键盘输入 ctrl + z + 回车 / ctrl + c 时,cin >> s 的返回值就会隐式类型转换为 nullptr,就会结束输入;输入其余字符串返回值会隐式类型转换为 true,就可以继续输入了!

C++ IO 流
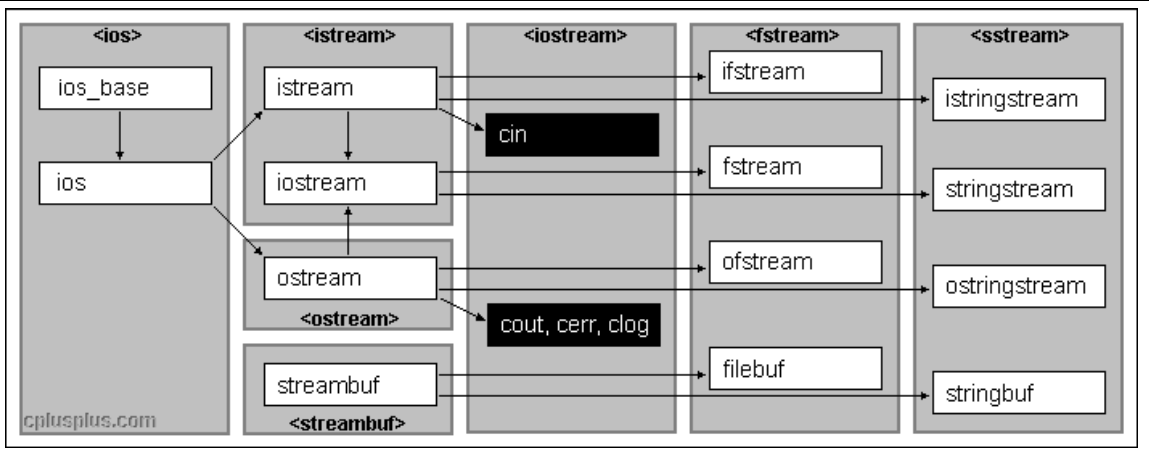
C++系统实现了一个庞大的类库,其中ios为基类,其他类都是直接或间接派生自 ios 类
C++ 文件 IO 流
C++ 文件分为二进制文件和文本文件,采用文件流对象操作文件的一般步骤:
- 定义一个文件流对象
ifstream ifile(只输入用),ofstream ofile(只输出用),fstream iofile(既输入又输出用)
-
使用文件流对象的成员函数打开一个磁盘文件,使得文件流对象和磁盘文件之间建立联系
-
使用提取和插入运算符对文件进行读写操作,或使用成员函数进行读写
-
关闭文件
二进制读写
二进制读写指的是 将内存中的数据 原封不动的写入文件中,内存解析数据的方式和磁盘是不一样的,因此二进制写入文件后,直接打开就是乱码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
//out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day<<"日";
//out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day;
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day;
return out;
}
struct ServerInfo
{
char _address[100];
double _x;
Date _date;
};
class BinIO
{
public:
BinIO(const char* filename = "info.bin")
:_filename(filename)
{}
void Write(const ServerInfo& winfo)
{
ofstream ofs(_filename, ofstream::out | ofstream::binary);
ofs.write((char*)&winfo, sizeof(winfo));
}
void Read(ServerInfo& rinfo)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename, ofstream::in | ofstream::binary);
ifs.read((char*)&rinfo, sizeof(rinfo));
}
private:
string _filename;
};
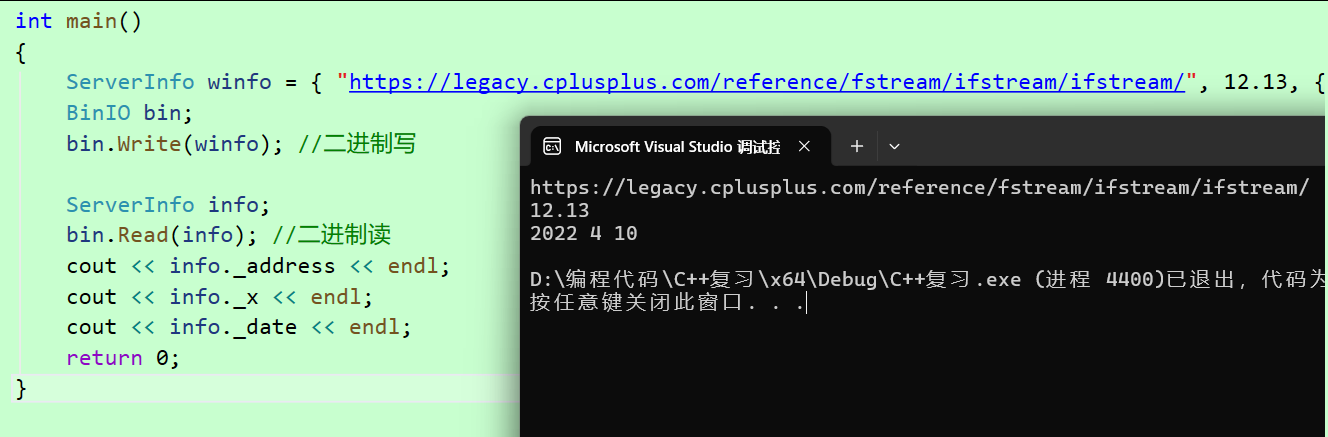
int main()
{
ServerInfo winfo = { "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/fstream/ifstream/ifstream/", 12.13, { 2022, 4, 10 } };
BinIO bin;
bin.Write(winfo); //二进制写
ServerInfo info;
bin.Read(info); //二进制读
cout << info._address << endl;
cout << info._x << endl;
cout << info._date << endl;
return 0;
}
当我们将 char 数组 改为 string 类型,发现程序运行之后崩溃了
cpp
struct ServerInfo
{
//char _address[100];
string _address;
double _x;
Date _date;
};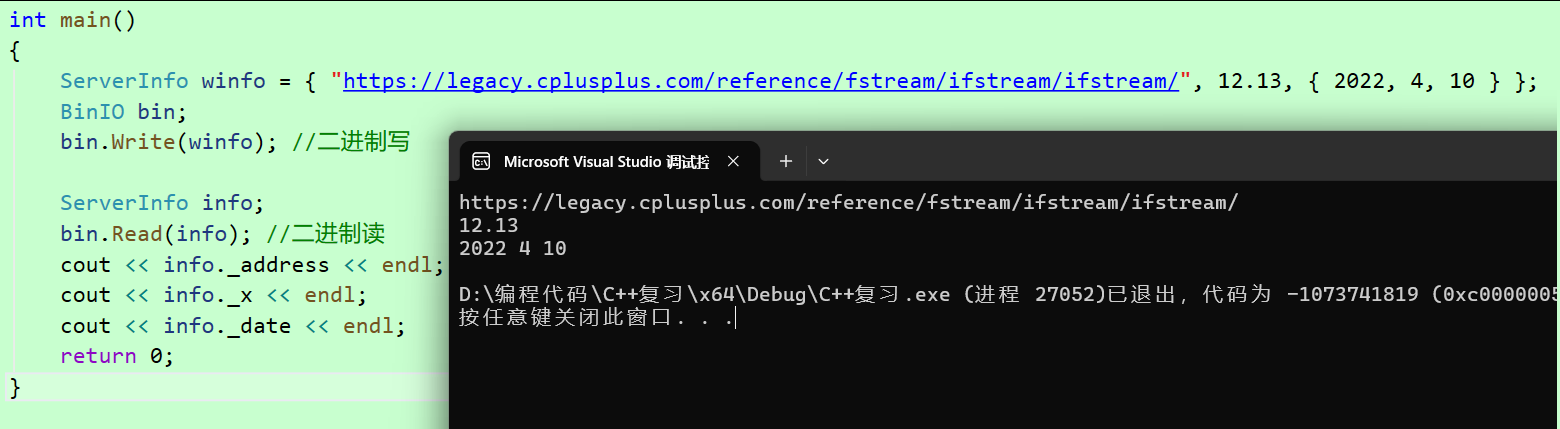
因为 string 对象的成员是三个指针变量,写文件时我们定义了 winfo 对象,内部的 _str 指针指向一段堆区空间,读文件时我们定义了 info 对象,将_str内容读到了 info对象的 _str中,这就导致了浅拷贝问题,两个指针指向同一块内存空间,会有析构两次的问题!
cpp
//先读文件
int main()
{
ServerInfo winfo = { "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/fstream/ifstream/ifstream/", 12.13, { 2022, 4, 10 } };
BinIO bin;
bin.Write(winfo); //二进制写
return 0;
}
//再写文件
int main()
{
ServerInfo info;
BinIO bin;
bin.Read(info); //二进制读
cout << info._address << endl;
cout << info._x << endl;
cout << info._date << endl;
return 0;
}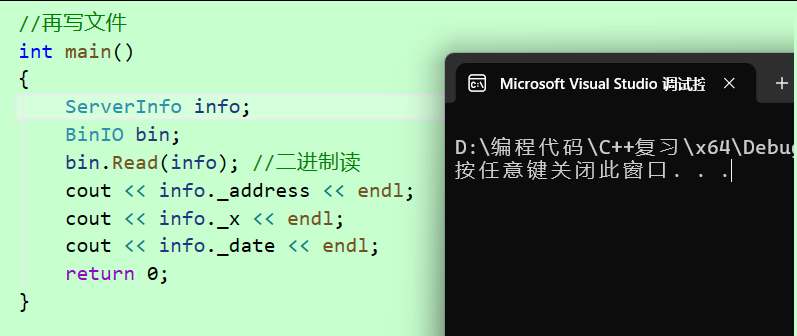
发现我们什么都读不进来,并且程序会崩溃,因为写完文件之后,程序退出,堆区上的内存就会被
回收,那么读文件后 info 中的 _str 就是野指针,指向了已经归还给OS的堆区空间,因此什么都读不到并且程序崩溃了!
文本读写
文本读写的用法比较简单,创建文件流对象时不需要指定 out/in,也不需要指明是文本方式读写,默认就是文本读写,读写时也不需要调用 write / read 接口,直接使用 << 以及 >> 即可写入和读取
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
//out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day<<"日";
//out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day;
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day;
return out;
}
struct ServerInfo
{
char _address[100];
double _x;
Date _date;
};
class TextIO
{
public:
TextIO(const char* filename = "info.text")
:_filename(filename)
{
}
void Write(const ServerInfo& winfo)
{
ofstream ofs(_filename);
ofs << winfo._address << endl;
ofs << winfo._x << endl;
ofs << winfo._date << endl;
}
void Read(ServerInfo& rinfo)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename);
ifs >> rinfo._address;
ifs >> rinfo._x;
ifs >> rinfo._date;
}
private:
string _filename;
};
int main()
{
ServerInfo winfo = { "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/fstream/ifstream/ifstream/", 12.13, { 2022, 4, 10 } };
TextIO bin;
bin.Write(winfo); //文本方式写
ServerInfo info;
bin.Read(info); //文本方式读
cout << info._address << endl;
cout << info._x << endl;
cout << info._date << endl;
return 0;
}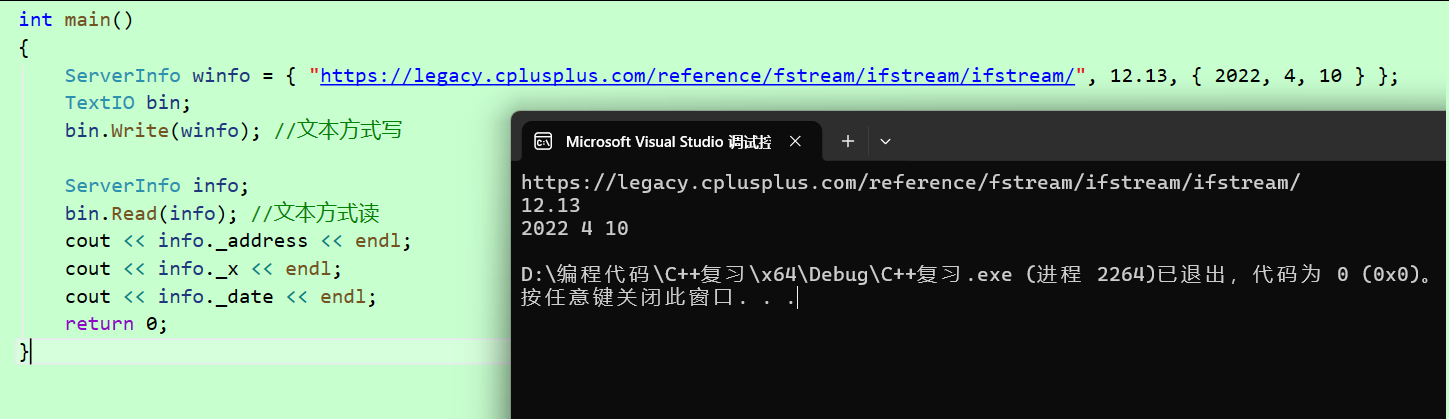
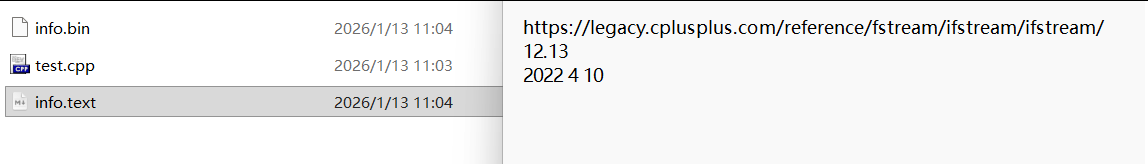
文本方式写入文件后我们打开文件就可以直接看到,不再是乱码了!
C++ 字符串流
在很多场景下,我们经常会将各种类型的数据格式化为字符串类型,比如网络传输中的序列化和反序列化,C语言中我们可以使用 sprintf / scanf,C++ 中提供了字符串流对象
ostringstream 是 C++ 标准库中的一个类,用于将数据格式化为字符串,继承自 ostream,因此可以使用所有标准输出操作(如 << 操作符)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
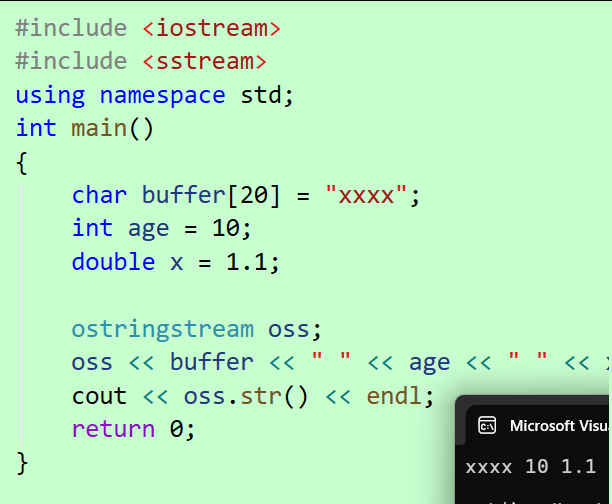
int main()
{
char buffer[20] = "xxxx";
int age = 10;
double x = 1.1;
ostringstream oss;
oss << buffer << " " << age << " " << x;
cout << oss.str() << endl;
return 0;
}
自定义类型对象也可以格式化成字符串,前提是重载了operator << 函数
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
//out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day<<"日";
//out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day;
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day;
return out;
}
int main()
{
ostringstream oss;
Date d(2026, 1, 13);
oss << d;
cout << oss.str() << endl;
return 0;
}
istringstream 是 C++ 标准库中的一个类,用于从字符串中读取数据。istringstream 位于 <sstream> 头文件中,继承自 istream,因此可以使用所有标准输入操作(如 >> 操作符)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
//out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day<<"日";
//out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day;
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day;
return out;
}
struct ChatInfo
{
string _name; // 名字
int _id; // id
Date _date; // 时间
string _msg; // 聊天信息
};
int main()
{
ChatInfo winfo = { "张三", 135246, { 2022, 4, 10 }, "晚上一起看电影吧" };
ostringstream oss;
//序列化, 方便网络传输
oss << winfo._name << endl;
oss << winfo._id << endl;
oss << winfo._date << endl;
oss << winfo._msg << endl;
//收到消息后解析成结构化数据
ChatInfo rinfo;
istringstream iss(oss.str());
iss >> rinfo._name;
iss >> rinfo._id;
iss >> rinfo._date;
iss >> rinfo._msg;
cout << rinfo._name << endl;
cout << rinfo._id << endl;
cout << rinfo._date << endl;
cout << rinfo._msg << endl;
return 0;
}