1 概述
本文会介绍LFU和LRU缓存两道题目的思路和实现。
2 LRU缓存
2.1 原题

2.2 思路
LRU是最近最少使用缓存,实现时需要基于哈希表+双向链表实现。
基于哈希表是因为题目要求的O(1)平均时间复杂度,而使用双向链表是什么原因呢?
LRU的核心操作有:
- 访问
key并调整key位置 - 插入新
key - 容量满时删除最久未使用的
key
而使用双向链表能完美地支持上面三个核心操作:
- 访问
key调整key位置:通过哈希表定位到链表节点,并从链表中删除该节点,移动到链头,这样能做到O(1)的时间 - 插入新
key:直接插入到链头即可,O(1) - 容量满时删除最久未使用的
key:如果访问key和插入新key按照上面的描述操作,那么需要删除的key就自然位于链尾,直接从链尾删除即可,能做到O(1)
而其他数据结构,都无法O(1)内做到这三种操作,例如:
- 栈:插入
O(1),但是只允许一端操作,无法做到动态调整 - 队列:无法处理中间被访问的情况,中间元素被访问的话无法调整
- 双端队列:也无法处理中间被访问的情况
- 单向链表:无法做到
O(1)删除
所以实现方式就是哈希表配合双向链表实现:
- 哈希表里面的
key是参数传过来的key - 哈希表里面的
value是这个存储这个key的双向链表的节点
实现细节1:实现双向链表的时候,可以利用哨兵节点,可以避免处理链头链尾的特殊情况。
对于get操作:
- 如果没有包含该
key,直接返回 - 如果有包含,从双向链表中删除该
key对应的节点,并移动到链头
对于put操作:
- 如果包含该
key,覆盖旧value,从双向链表中删除该key对应的节点,并移动到链头 - 如果不包含该
key,创建该key对应的节点并插入到链头,如果大于容量,删除链尾对应的节点
实现细节2:由于删除节点和移动到链头是常用操作,可以用一个函数封装起来,避免每次手动操作出错。
2.3 动图演示
动态参数如下:
- 容量为3
- 操作路径为
put(1),put(2),put(3),get(1),put(4)(由于动图大小限制,只能容下这么多操作)
HEAD和TAIL是两个哨兵,表示链头和链尾哨兵。LRU是指最近最少使用,MRU是指最近使用,实际上,MRU就是链头,LRU就是链尾。

2.4 完整代码
完整代码如下:
cpp
// 双向链表节点
struct Node {
// 前驱
Node *pre;
// 后继
Node *next;
// key
int key;
// value
int val;
};
class LRUCache {
// 数量
int cnt_;
// 容量
int capacity_;
// 哨兵
Node *head_;
Node *tail_;
// 哈希表
unordered_map<int, Node *> m_;
// 将node移动到链头
void move_to_head(Node *node) {
node->pre = head_;
node->next = head_->next;
head_->next->pre = node;
head_->next = node;
}
// 将node从链中移除
void remove_node(const Node *node) {
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
}
public:
explicit LRUCache(const int capacity): cnt_(0), capacity_(capacity), head_(new Node()), tail_(new Node()) {
// 初始化,让head和tail链接
head_->next = tail_;
tail_->pre = head_;
}
int get(const int key) {
// 判断有没有key,没有直接返回key
if (!m_.contains(key)) {
return -1;
}
// 获取当前key对应的node
const auto node = m_[key];
// 从链中移除这个node并移动到链头,符合题目定义
remove_node(node);
move_to_head(node);
return node->val;
}
void put(const int key, const int value) {
// 如果包含该key
if (m_.contains(key)) {
// 取出对应的node
const auto node = m_[key];
// 覆盖旧值
node->val = value;
// 类似get操作,从链中移除node并移动node到链头
remove_node(node);
move_to_head(node);
} else {
// 如果不包含,需要新增一个node
const auto node = new Node();
node->key = key;
node->val = value;
// 新的node需要移动到链头
move_to_head(node);
// 哈希表存储
m_[key] = node;
// 如果容量未满,容量+1,返回
if (cnt_ < capacity_) {
++cnt_;
return;
}
// 否则容量满了,删除最近最少使用的节点,也就是链尾节点
// 从哈希表中移除
m_.erase(tail_->pre->key);
// 从链中移除
remove_node(tail_->pre);
}
}
};这样能通过题目但是还有一个潜在的问题就是内存泄漏,因为从链中删除节点之后,没有手动释放节点对应的内存。另一方面,析构的时候也没有释放内存,所以一个更符合实际的版本应该加上内存释放,如下所示:
cpp
// 双向链表节点
struct Node {
// 前驱
Node *pre;
// 后继
Node *next;
// key
int key;
// value
int val;
};
class LRUCache {
// 数量
int cnt_;
// 容量
int capacity_;
// 哨兵
Node *head_;
Node *tail_;
// 哈希表
unordered_map<int, Node *> m_;
// 将node移动到链头
void move_to_head(Node *node) {
node->pre = head_;
node->next = head_->next;
head_->next->pre = node;
head_->next = node;
}
// 将node从链中移除
void remove_node(const Node *node) {
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
}
public:
explicit LRUCache(const int capacity): cnt_(0), capacity_(capacity), head_(new Node()), tail_(new Node()) {
// 初始化,让head和tail链接
head_->next = tail_;
tail_->pre = head_;
}
~LRUCache() {
// 析构的时候删除整条链
while (head_->next != tail_) {
const auto node = head_->next;
head_->next = node->next;
delete node;
}
// 删除两个哨兵
delete head_;
delete tail_;
}
int get(const int key) {
// 判断有没有key,没有直接返回key
if (!m_.contains(key)) {
return -1;
}
// 获取当前key对应的node
const auto node = m_[key];
// 从链中移除这个node并移动到链头,符合题目定义
remove_node(node);
move_to_head(node);
return node->val;
}
void put(const int key, const int value) {
// 如果包含该key
if (m_.contains(key)) {
// 取出对应的node
const auto node = m_[key];
// 覆盖旧值
node->val = value;
// 类似get操作,从链中移除node并移动node到链头
remove_node(node);
move_to_head(node);
} else {
// 如果不包含,需要新增一个node
const auto node = new Node();
node->key = key;
node->val = value;
// 新的node需要移动到链头
move_to_head(node);
// 哈希表存储
m_[key] = node;
// 如果容量未满,容量+1,返回
if (cnt_ < capacity_) {
++cnt_;
return;
}
// 否则容量满了,删除最近最少使用的节点,也就是链尾节点
// 从哈希表中移除
m_.erase(tail_->pre->key);
// 使用变量存储,因为remove_node()之后tail->pre就变了
const auto tail_pre = tail_->pre;
// 从链中移除
remove_node(tail_->pre);
// 释放内存
delete tail_pre;
}
}
};2.5 Java版本
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class Node {
public Node pre;
public Node next;
int key;
int val;
}
public class LRUCache {
private int cnt = 0;
private final int capacity;
private final Node head;
private final Node tail;
private final Map<Integer, Node> m = new HashMap<>();
private void moveToHead(Node node) {
node.pre = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.pre = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(Node node) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
Node node = m.get(key);
if(node == null){
return -1;
}
removeNode(node);
moveToHead(node);
return node.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node node = m.get(key);
if(node != null){
node.val = value;
removeNode(node);
moveToHead(node);
}else{
node = new Node();
node.key = key;
node.val = value;
moveToHead(node);
m.put(key,node);
if(cnt < capacity){
++cnt;
return;
}
m.remove(tail.pre.key);
removeNode(tail.pre);
}
}
}2.6 Go版本
go
var m map[int]*Node
var head *Node
var tail *Node
var capacity int
var cnt int
type Node struct {
Key int
Val int
Pre *Node
Next *Node
}
type LRUCache struct {
}
func removeNode(node *Node) {
pre, next := node.Pre, node.Next
pre.Next, next.Pre = next, pre
}
func moveToHead(node *Node) {
next := head.Next
node.Next = next
next.Pre = node
head.Next = node
node.Pre = head
}
func Constructor(cap int) LRUCache {
capacity, cnt = cap, 0
head, tail = &Node{-1, -1, nil, nil}, &Node{-1, -1, nil, nil}
head.Next, tail.Pre = tail, head
m = make(map[int]*Node)
return LRUCache{}
}
func (this *LRUCache) Get(key int) int {
node, exist := m[key]
if !exist {
return -1
}
removeNode(node)
moveToHead(node)
return node.Val
}
func (this *LRUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
node, exist := m[key]
if exist {
node.Val = value
removeNode(node)
moveToHead(node)
} else {
node = &Node{key, value, nil, nil}
moveToHead(node)
m[key] = node
if cnt < capacity {
cnt++
return
}
delete(m, tail.Pre.Key)
removeNode(tail.Pre)
}
}3 LFU缓存
3.1 原题

3.2 思路
LFU实际上是在LRU的基础上增加了一个频率的限制:
- 当需要移除缓存时,优先移除频率最低的数据
- 当频率最低的数据有多个时,采用
LRU的规则,移除最近最少使用数据
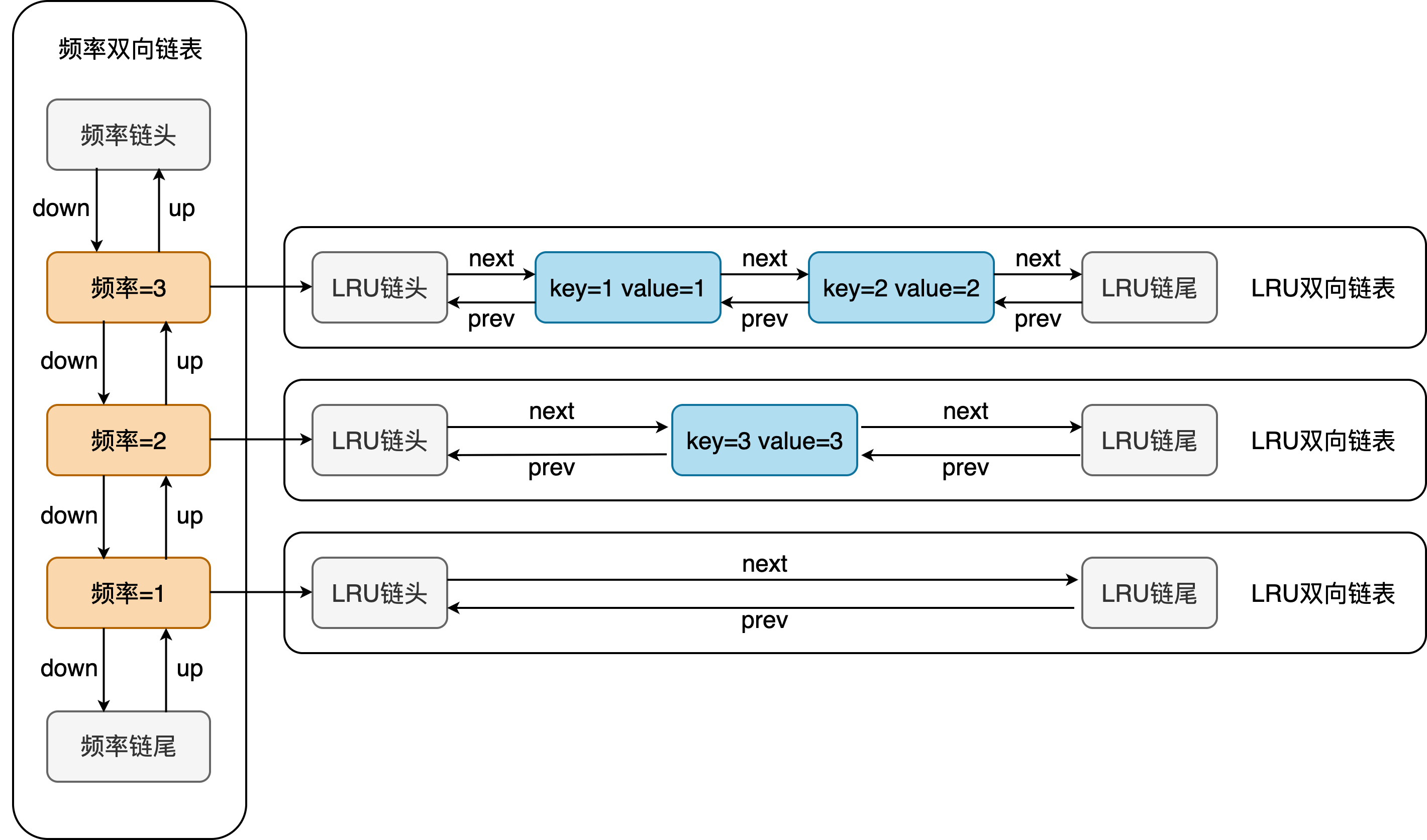
由于频率是会变动的,并且频率之间的变化幅度是1,所以可以使用一个频率双向链表来维护频率的变动:
- 频率增加
1就相当于插入一条频率加1的链 - 频率减
1就相当于删除一条原来频率的链(当原来频率的链没有其他元素时) - 可以
O(1)时间访问到频率最低的链
在频率链的基础上,每个频率链的节点维护的实际上是一条LRU链,根据前面的LRU规则进行维护。
这样就形成频率链+LRU链的两条双向链表的结构:
- 频率链用于维护频率
LRU链用于维护最近最少使用的数据
实现的时候还需要注意以下几点:
- 一般只需要两个类即可,一个是频率链节点,一个是
LRU链节点,当然也可以用四个类,新增LRU链类和频率链类,但是这样代码实现会更复杂 - 建议像之前
LRU一样,将插入链头和移除节点的操作单独一个函数,对频率链节点类也一样 LFU代码量大,非常容易出错,建议小心验证,明确每个变量名和函数名
3.3 整体结构
和前面提到的一样,使用两个双向链表:
- 频率链头连接着最大的频率,链尾连接着最小的频率
- 每个频率链节点连着一个完整的
LRU链 LRU链和之前的一样,遵循最近最少使用原则进行淘汰
本来想展示动图的,由于太小限制了5M,没有一个效果还可以的动图就不放了。
3.4 完整代码
带了非常详细的注释:
cpp
// 频率链节点,C++独有的前向声明
struct FreqListNode;
// LRU链节点
struct LRUListNode {
// LRU前驱
LRUListNode *pre;
// LRU后继
LRUListNode *next;
// 当前LRU链位于哪个频率链节点
FreqListNode *freq_list;
// key
int key;
// value
int value;
};
// 频率链节点
struct FreqListNode {
// LRU链头节点
LRUListNode *head_lru_list;
// LRU链尾节点
LRUListNode *tail_lru_list;
// +1频率链,也就是上面的频率链
FreqListNode *up_freq_list;
// -1频率链,也就是下面的频率链
FreqListNode *down_freq_list;
// 频率
int freq;
// 频率初始化为0
FreqListNode() : head_lru_list(new LRUListNode()), tail_lru_list(new LRUListNode()), up_freq_list(nullptr),
down_freq_list(nullptr), freq(0) {
// 初始化LRU链
head_lru_list->next = tail_lru_list;
tail_lru_list->pre = head_lru_list;
}
// 移除LRU链
void remove_lru_list(const LRUListNode *lru_list) {
lru_list->pre->next = lru_list->next;
lru_list->next->pre = lru_list->pre;
}
// 移动或插入lru链节点到lru链头
void move_or_insert_lru_list_node_to_head(LRUListNode *lru_list) {
lru_list->pre = head_lru_list;
lru_list->next = head_lru_list->next;
head_lru_list->next->pre = lru_list;
head_lru_list->next = lru_list;
}
// lru链是否为空
[[nodiscard]] bool lru_list_empty() const {
return head_lru_list->next == tail_lru_list;
}
};
class LFUCache {
// 总节点数
int node_cnt_;
// 容量
int capacity_;
// 频率链头
FreqListNode *top_freq_list_;
// 频率链尾
FreqListNode *bottom_freq_list_;
// key对应的lru链节点
unordered_map<int, LRUListNode *> m_;
// 移除频率链
void remove_freq_list(const FreqListNode *freq_list) {
freq_list->down_freq_list->up_freq_list = freq_list->up_freq_list;
freq_list->up_freq_list->down_freq_list = freq_list->down_freq_list;
}
// 插入频率链,在down_list上面插入new_list
void insert_freq_list(FreqListNode *down_freq_list, FreqListNode *new_freq_list) {
new_freq_list->up_freq_list = down_freq_list->up_freq_list;
new_freq_list->down_freq_list = down_freq_list;
down_freq_list->up_freq_list->down_freq_list = new_freq_list;
down_freq_list->up_freq_list = new_freq_list;
}
public:
explicit LFUCache(const int capacity) : node_cnt_(0), capacity_(capacity), top_freq_list_(new FreqListNode()),
bottom_freq_list_(new FreqListNode()) {
// 初始化频率链
top_freq_list_->down_freq_list = bottom_freq_list_;
bottom_freq_list_->up_freq_list = top_freq_list_;
}
int get(const int key) {
// 没有就直接返回
if (!m_.contains(key)) {
return -1;
}
// 获取对应的lru链节点
const auto lru_list_node = m_[key];
// 获取对应的频率链
const auto freq_list = lru_list_node->freq_list;
// 获取频率
const int freq = freq_list->freq;
// 先从原来的频率链移除这个lru链节点,因为访问链,所以肯定需要从当前的频率链移除,并将后续频率+1
freq_list->remove_lru_list(lru_list_node);
// 如果上面的频率链之前已经创建过了,并且频率刚好是当前的频率+1
if (freq_list->up_freq_list->freq == freq + 1) {
// 设置lru链节点对应的频率链,也就是将当前的lru链节点移动到上面的频率链
lru_list_node->freq_list = freq_list->up_freq_list;
// 根据lru的访问方式插入到lru链头
freq_list->up_freq_list->move_or_insert_lru_list_node_to_head(lru_list_node);
} else {
// 如果没有创建过,就要创建一条新的频率链
const auto new_freq_list = new FreqListNode();
// 赋值频率链
lru_list_node->freq_list = new_freq_list;
// 新频率链频率+1
new_freq_list->freq = freq + 1;
// 新频率链插入lru节点到lru链头
new_freq_list->move_or_insert_lru_list_node_to_head(lru_list_node);
// 新插入频率链
insert_freq_list(freq_list, new_freq_list);
}
// 如果旧的频率链已经没有lru节点,删除旧的频率链
if (freq_list->lru_list_empty()) {
remove_freq_list(freq_list);
}
// 返回value
return lru_list_node->value;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
// 如果已经有key
if (m_.contains(key)) {
// 覆盖新值
m_[key]->value = value;
// 进行get操作,相当于频率+1以及调整lru链
// 如果不直接调用get的话这里会额外多不少代码
get(key);
return;
}
// 如果没有,创建新的lru链节点
const auto lru_list_node = new LRUListNode();
lru_list_node->key = key;
lru_list_node->value = value;
// 如果节点数量大于等于容量
if (node_cnt_ >= capacity_) {
// 需要移除一个节点,也就是频率链尾中的lru链尾节点
const auto freq_list = bottom_freq_list_->up_freq_list;
// 取lru链尾
const auto lru_list = freq_list->tail_lru_list->pre;
// 删除
freq_list->remove_lru_list(lru_list);
// 如果删除这个节点之后lru链为空,删除这个频率链
if (freq_list->lru_list_empty()) {
remove_freq_list(freq_list);
}
// 从哈希表中删除
m_.erase(lru_list->key);
} else {
// 否则直接+1
++node_cnt_;
}
// 新的节点需要加入频率链尾
const auto freq_list = bottom_freq_list_->up_freq_list;
// 插入哈希表
m_[key] = lru_list_node;
// 如果频率为1,直接在这个lru链中插入节点即可
if (freq_list->freq == 1) {
lru_list_node->freq_list = freq_list;
freq_list->move_or_insert_lru_list_node_to_head(lru_list_node);
} else {
// 如果频率不为1,说明最少的频率不是1,需要创建一条频率为1的频率链
const auto new_freq_list = new FreqListNode();
lru_list_node->freq_list = new_freq_list;
new_freq_list->freq = 1;
// 将节点插入到这条频率为1的频率链中对应的lru链
new_freq_list->move_or_insert_lru_list_node_to_head(lru_list_node);
// 插入整条频率链
insert_freq_list(bottom_freq_list_, new_freq_list);
}
}
};当然,这个代码也有内存泄漏的问题,修改方式和前面介绍的LRU类似,手动delete即可。
另一方面,实际上这里的top_freq_list_在代码中没有任何的引用,所以可以删去(别的实现方式可能会用到),这是一个小的优化点,这里为了代码的完整性就保留下来了。
3.5 Java版本
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class LRUListNode {
LRUListNode pre;
LRUListNode next;
FreqListNode freqList;
int key;
int val;
}
class FreqListNode {
LRUListNode headLruList;
LRUListNode tailLruList;
FreqListNode upFreqList;
FreqListNode downFreqList;
int freq;
public FreqListNode() {
headLruList = new LRUListNode();
tailLruList = new LRUListNode();
upFreqList = downFreqList = null;
freq = 0;
headLruList.next = tailLruList;
tailLruList.pre = headLruList;
}
void removeLruList(LRUListNode lruList) {
lruList.pre.next = lruList.next;
lruList.next.pre = lruList.pre;
}
void moveOtInsertLruListNodeToHead(LRUListNode lruListNode) {
lruListNode.pre = headLruList;
lruListNode.next = headLruList.next;
headLruList.next.pre = lruListNode;
headLruList.next = lruListNode;
}
boolean lruListEmpty() {
return headLruList.next == tailLruList;
}
}
public class LFUCache {
private int nodeCount;
private final int capacity;
private final FreqListNode topFreqList;
private final FreqListNode bottomFreqList;
Map<Integer, LRUListNode> map = new HashMap<>();
private void removeFreqList(FreqListNode freqList) {
freqList.downFreqList.upFreqList = freqList.upFreqList;
freqList.upFreqList.downFreqList = freqList.downFreqList;
}
private void insertFreqList(FreqListNode downFreqList, FreqListNode newFreqList) {
newFreqList.upFreqList = downFreqList.upFreqList;
newFreqList.downFreqList = downFreqList;
downFreqList.upFreqList.downFreqList = newFreqList;
downFreqList.upFreqList = newFreqList;
}
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
nodeCount = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
topFreqList = new FreqListNode();
bottomFreqList = new FreqListNode();
topFreqList.downFreqList = bottomFreqList;
bottomFreqList.upFreqList = topFreqList;
}
public int get(int key) {
LRUListNode lruListNode = map.get(key);
if (lruListNode == null) {
return -1;
}
FreqListNode freqList = lruListNode.freqList;
int freq = freqList.freq;
freqList.removeLruList(lruListNode);
if (freqList.upFreqList.freq == freq + 1) {
lruListNode.freqList = freqList.upFreqList;
freqList.upFreqList.moveOtInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode);
} else {
FreqListNode newFreqList = new FreqListNode();
lruListNode.freqList = newFreqList;
newFreqList.freq = freq + 1;
newFreqList.moveOtInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode);
insertFreqList(freqList, newFreqList);
}
if (freqList.lruListEmpty()) {
removeFreqList(freqList);
}
return lruListNode.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
LRUListNode lruListNode = map.get(key);
if (lruListNode != null) {
lruListNode.val = value;
get(key);
return;
}
lruListNode = new LRUListNode();
lruListNode.key = key;
lruListNode.val = value;
if (nodeCount >= capacity) {
FreqListNode freqList = bottomFreqList.upFreqList;
LRUListNode lruList = freqList.tailLruList.pre;
freqList.removeLruList(lruList);
if (freqList.lruListEmpty()) {
removeFreqList(freqList);
}
map.remove(lruList.key);
} else {
++nodeCount;
}
FreqListNode freqList = bottomFreqList.upFreqList;
map.put(key, lruListNode);
if (freqList.freq == 1) {
lruListNode.freqList = freqList;
freqList.moveOtInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode);
} else {
FreqListNode newFreqList = new FreqListNode();
lruListNode.freqList = newFreqList;
newFreqList.freq = 1;
newFreqList.moveOtInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode);
insertFreqList(bottomFreqList, newFreqList);
}
}
}3.6 Go版本
go
type LRUListNode struct {
Pre, Next *LRUListNode
FreqList *FreqListNode
Key int
Val int
}
type FreqListNode struct {
HeadLruList, TailLruList *LRUListNode
UpFreqList, DownFreqList *FreqListNode
Freq int
}
func FreqConstructor() FreqListNode {
headLruList, tailLruList := &LRUListNode{}, &LRUListNode{}
headLruList.Next, tailLruList.Pre = tailLruList, headLruList
return FreqListNode{headLruList, tailLruList, nil, nil, 0}
}
func (freqList *FreqListNode) RemoveLruList(lruList *LRUListNode) {
lruList.Pre.Next, lruList.Next.Pre = lruList.Next, lruList.Pre
}
func (freqList *FreqListNode) moveOrInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruList *LRUListNode) {
lruList.Pre, lruList.Next = freqList.HeadLruList, freqList.HeadLruList.Next
freqList.HeadLruList.Next.Pre, freqList.HeadLruList.Next = lruList, lruList
}
func (freqList *FreqListNode) lruListEmpty() bool {
return freqList.HeadLruList.Next == freqList.TailLruList
}
type LFUCache struct {
nodeCount, capacity int
topFreqList, bottomFreqList *FreqListNode
m map[int]*LRUListNode
}
func Constructor(capacity int) LFUCache {
topFreqList, bottomFreqList := FreqConstructor(), FreqConstructor()
topFreqList.DownFreqList, bottomFreqList.UpFreqList = &bottomFreqList, &topFreqList
return LFUCache{0, capacity, &topFreqList, &bottomFreqList,
map[int]*LRUListNode{}}
}
func (lfuCache *LFUCache) removeFreqList(freqList *FreqListNode) {
freqList.DownFreqList.UpFreqList, freqList.UpFreqList.DownFreqList = freqList.UpFreqList, freqList.DownFreqList
}
func (lfuCache *LFUCache) insertFreqList(downFreqList, newFreqList *FreqListNode) {
newFreqList.UpFreqList, newFreqList.DownFreqList = downFreqList.UpFreqList, downFreqList
downFreqList.UpFreqList.DownFreqList, downFreqList.UpFreqList = newFreqList, newFreqList
}
func (lfuCache *LFUCache) Get(key int) int {
lruListNode, ok := lfuCache.m[key]
if !ok {
return -1
}
freqList := lruListNode.FreqList
freq := freqList.Freq
freqList.RemoveLruList(lruListNode)
if freqList.UpFreqList.Freq == freq+1 {
lruListNode.FreqList = freqList.UpFreqList
freqList.UpFreqList.moveOrInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode)
} else {
newFreqList := FreqConstructor()
lruListNode.FreqList, newFreqList.Freq = &newFreqList, freq+1
newFreqList.moveOrInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode)
lfuCache.insertFreqList(freqList, &newFreqList)
}
if freqList.lruListEmpty() {
lfuCache.removeFreqList(freqList)
}
return lruListNode.Val
}
func (lfuCache *LFUCache) Put(key int, value int) {
lruListNode, ok := lfuCache.m[key]
if ok {
lfuCache.m[key].Val = value
lfuCache.Get(key)
return
}
lruListNode = &LRUListNode{}
lruListNode.Key, lruListNode.Val = key, value
if lfuCache.nodeCount >= lfuCache.capacity {
freqList := lfuCache.bottomFreqList.UpFreqList
lruList := freqList.TailLruList.Pre
freqList.RemoveLruList(lruList)
if freqList.lruListEmpty() {
lfuCache.removeFreqList(freqList)
}
delete(lfuCache.m, lruList.Key)
} else {
lfuCache.nodeCount++
}
freqList := lfuCache.bottomFreqList.UpFreqList
lfuCache.m[key] = lruListNode
if freqList.Freq == 1 {
lruListNode.FreqList = freqList
freqList.moveOrInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode)
} else {
newFreqList := FreqConstructor()
lruListNode.FreqList, newFreqList.Freq = &newFreqList, 1
newFreqList.moveOrInsertLruListNodeToHead(lruListNode)
lfuCache.insertFreqList(lfuCache.bottomFreqList, &newFreqList)
}
}4 总结
本文详细地介绍了LRU和LFU的底层实现,并提供了对应的代码。
实际上,LRU和LFU只是最简单的缓存淘汰算法之一,现实应用中基本不会直接使用,因为:
LRU中,对突发性的遍历访问敏感,例如扫描一遍大列表,就很有可能把真正的热点数据挤出去LFU中,初期频率低的热点难以进入长久存在,而长期运行后频率会膨胀,越来越难以淘汰
现实会使用改良后的算法,例如W-TinyLFU,结合了滑动窗口、TinyLFU和分段LRU,有兴趣的读者可以自行去了解。