目录
- [一、App 如何访问到硬件](#一、App 如何访问到硬件)
- [二、App 端代码分析](#二、App 端代码分析)
- 三、服务端
- [四、VibratorManagerService 如何访问到 HAL 层](#四、VibratorManagerService 如何访问到 HAL 层)
- [五、HAL 层](#五、HAL 层)
- 六、补充
|-------------------|
| AIDL HAL 整体架构 |
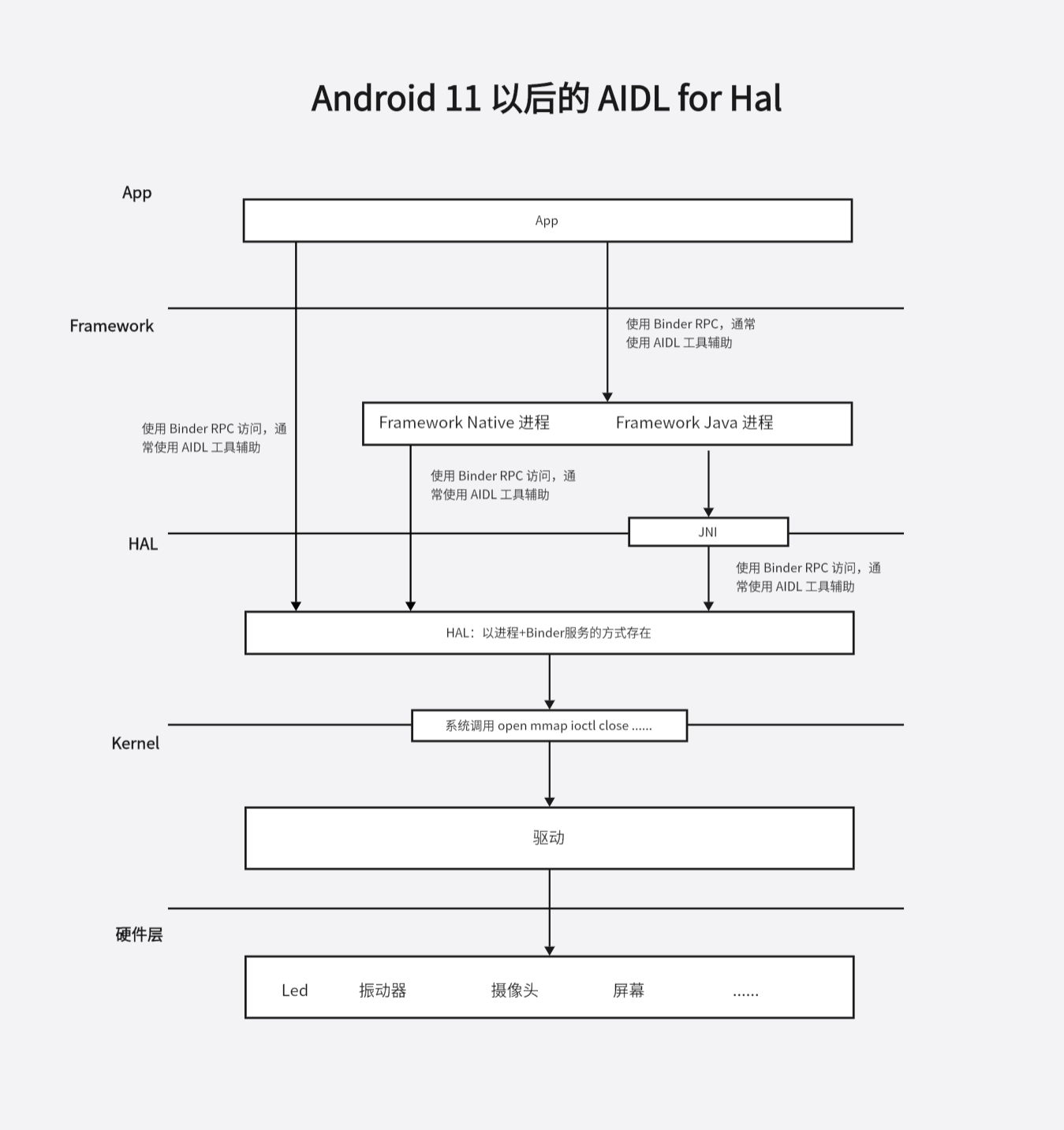
Google 在 Android11 觉得 HIDL 那一套有点多余,把 HIDL HAL 弃用了。并提供了新的 AIDL HAL。
主要有以下几点变化:
- ① 一般情况下 HAL 是一个 binder 服务,注册到 ServiceManager,通过命令 adb shell service list 中有大量的 hal binder 服务。
- ② 通常,App 作为 binder 客户端与 Framework 中的系统进程(SystemServer SurfaceFlinger 等)通信,Framework 中的系统进程会作为 hal binder 服务的客户端,访问 hal。一般情况下,App 访问 hal 要经过两次跨进程通信
- ③ 特殊情况下,比如某个硬件只有一个 App 使用,App 可以直接通过 binder 通信访问到 hal binder 服务。
- ④ 某些 hal 对性能要求高(主要是显示相关的),hal 层是一个 so 库,系统进程通过 dlopen 的方式加载。这类 hal 叫 stable-c hal
还是以振动器的调用过程为主线,来分析 振动器 HAL 的实现细节。
一、App 如何访问到硬件
Android12 及以后,App 中可以通过以下代码操作振动器:
java
val vibratorManager = getSystemService(Context.VIBRATOR_MANAGER_SERVICE) as VibratorManager
val vib = vibratorManager.defaultVibrator
if (vib.hasVibrator()) {
val vibrationEffect = VibrationEffect.createOneShot(500, VibrationEffect.DEFAULT_AMPLITUDE)
vib.vibrate(vibrationEffect)
}当然执行代码之前需要在 AndroidManifest.xml 中申明振动器权限:
c
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE" />二、App 端代码分析
接下来我们来分析 App 端的代码。
getSystemService 的实现如下:
java
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java
@Override
public Object getSystemService(@ServiceName @NonNull String name) {
if (getBaseContext() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"System services not available to Activities before onCreate()");
}
if (WINDOW_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
return mWindowManager;
} else if (SEARCH_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
ensureSearchManager();
return mSearchManager;
}
return super.getSystemService(name);
}接着调用父类的 getSystemService 方法:
java
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ContextThemeWrapper.java
@Override
public Object getSystemService(String name) {
if (LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
if (mInflater == null) {
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(getBaseContext()).cloneInContext(this);
}
return mInflater;
}
return getBaseContext().getSystemService(name);
}getBaseContext 返回的是一个 ContextImpl 对象,这里接着调用 ContextImpl 对象的 getSystemService 方法:
java
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@Override
public Object getSystemService(String name) {
if (vmIncorrectContextUseEnabled()) {
// Check incorrect Context usage.
if (WINDOW_SERVICE.equals(name) && !isUiContext()) {
final String errorMessage = "Tried to access visual service "
+ SystemServiceRegistry.getSystemServiceClassName(name)
+ " from a non-visual Context:" + getOuterContext();
final String message = "WindowManager should be accessed from Activity or other "
+ "visual Context. Use an Activity or a Context created with "
+ "Context#createWindowContext(int, Bundle), which are adjusted to "
+ "the configuration and visual bounds of an area on screen.";
final Exception exception = new IllegalAccessException(errorMessage);
StrictMode.onIncorrectContextUsed(message, exception);
Log.e(TAG, errorMessage + " " + message, exception);
}
}
return SystemServiceRegistry.getSystemService(this, name);
}接着调用 SystemServiceRegistry 的 static 方法 getSystemService:
java
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/SystemServiceRegistry.java
private static final Map<String, ServiceFetcher<?>> SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS =
new ArrayMap<String, ServiceFetcher<?>>();
public static Object getSystemService(ContextImpl ctx, String name) {
if (name == null) {
return null;
}
final ServiceFetcher<?> fetcher = SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.get(name);
if (fetcher == null) {
if (sEnableServiceNotFoundWtf) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Unknown manager requested: " + name);
}
return null;
}
final Object ret = fetcher.getService(ctx);
if (sEnableServiceNotFoundWtf && ret == null) {
// Some services do return null in certain situations, so don't do WTF for them.
switch (name) {
case Context.CONTENT_CAPTURE_MANAGER_SERVICE:
case Context.APP_PREDICTION_SERVICE:
case Context.INCREMENTAL_SERVICE:
case Context.ETHERNET_SERVICE:
case Context.CONTEXTHUB_SERVICE:
case Context.VIRTUALIZATION_SERVICE:
case Context.VIRTUAL_DEVICE_SERVICE:
return null;
}
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Manager wrapper not available: " + name);
return null;
}
return ret;
}getSystemService 方法中,会从 Map<String, ServiceFetcher<?>> SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS 获取到一个 ServiceFetcher 对象,然后调用 ServiceFetcher 对象的 getService 函数获取到服务并返回。
接下来的问题是 ServiceFetcher 对象是哪里来的?
在 SystemServiceRegistry 的静态块中,会调用 registerService 方法向 Map<String, ServiceFetcher<?>> SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS 注册 ServiceFetcher 对象。
java
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/SystemServiceRegistry.java
static {
//......
registerService(Context.VIBRATOR_MANAGER_SERVICE, VibratorManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<VibratorManager>() {
@Override
public VibratorManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) {
return new SystemVibratorManager(ctx);
}});
//......
}
private static final Map<Class<?>, String> SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES =
new ArrayMap<Class<?>, String>();
private static final Map<String, ServiceFetcher<?>> SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS =
new ArrayMap<String, ServiceFetcher<?>>();
private static final Map<String, String> SYSTEM_SERVICE_CLASS_NAMES = new ArrayMap<>();
// 参数放到 Map 中
private static <T> void registerService(@NonNull String serviceName,
@NonNull Class<T> serviceClass, @NonNull ServiceFetcher<T> serviceFetcher) {
SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES.put(serviceClass, serviceName);
SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.put(serviceName, serviceFetcher);
SYSTEM_SERVICE_CLASS_NAMES.put(serviceName, serviceClass.getSimpleName());
}这里核心是注册了一个匿名对象 CachedServiceFetcher。
getSystemService 时会先获取到 CachedServiceFetcher 对象,然后调用其 getService 方法
java
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/SystemServiceRegistry.java
// SystemServiceRegistry 的静态内部类
static abstract class CachedServiceFetcher<T> implements ServiceFetcher<T> {
private final int mCacheIndex;
CachedServiceFetcher() {
// Note this class must be instantiated only by the static initializer of the
// outer class (SystemServiceRegistry), which already does the synchronization,
// so bare access to sServiceCacheSize is okay here.
mCacheIndex = sServiceCacheSize++;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public final T getService(ContextImpl ctx) {
final Object[] cache = ctx.mServiceCache;
final int[] gates = ctx.mServiceInitializationStateArray;
boolean interrupted = false;
T ret = null;
for (;;) {
boolean doInitialize = false;
synchronized (cache) {
// Return it if we already have a cached instance.
T service = (T) cache[mCacheIndex];
if (service != null) {
ret = service;
break; // exit the for (;;)
}
// If we get here, there's no cached instance.
// Grr... if gate is STATE_READY, then this means we initialized the service
// once but someone cleared it.
// We start over from STATE_UNINITIALIZED.
// Similarly, if the previous attempt returned null, we'll retry again.
if (gates[mCacheIndex] == ContextImpl.STATE_READY
|| gates[mCacheIndex] == ContextImpl.STATE_NOT_FOUND) {
gates[mCacheIndex] = ContextImpl.STATE_UNINITIALIZED;
}
// It's possible for multiple threads to get here at the same time, so
// use the "gate" to make sure only the first thread will call createService().
// At this point, the gate must be either UNINITIALIZED or INITIALIZING.
if (gates[mCacheIndex] == ContextImpl.STATE_UNINITIALIZED) {
doInitialize = true;
gates[mCacheIndex] = ContextImpl.STATE_INITIALIZING;
}
}
if (doInitialize) {
// Only the first thread gets here.
T service = null;
@ServiceInitializationState int newState = ContextImpl.STATE_NOT_FOUND;
try {
// This thread is the first one to get here. Instantiate the service
// *without* the cache lock held.
//调用 createService 构建一个 Service 对象
service = createService(ctx);
newState = ContextImpl.STATE_READY;
} catch (ServiceNotFoundException e) {
onServiceNotFound(e);
} finally {
synchronized (cache) {
cache[mCacheIndex] = service;
gates[mCacheIndex] = newState;
cache.notifyAll();
}
}
ret = service;
break; // exit the for (;;)
}
// The other threads will wait for the first thread to call notifyAll(),
// and go back to the top and retry.
synchronized (cache) {
// Repeat until the state becomes STATE_READY or STATE_NOT_FOUND.
// We can't respond to interrupts here; just like we can't in the "doInitialize"
// path, so we remember the interrupt state here and re-interrupt later.
while (gates[mCacheIndex] < ContextImpl.STATE_READY) {
try {
// Clear the interrupt state.
interrupted |= Thread.interrupted();
cache.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// This shouldn't normally happen, but if someone interrupts the
// thread, it will.
Slog.w(TAG, "getService() interrupted");
interrupted = true;
}
}
}
}
if (interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
// 返回 createService 方法构建的对象
return ret;
}
// 由子类实现
public abstract T createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException;
}可以看出 getService 中会调用 createService 创建服务对象并返回,createService 是一个抽象方法,由子类返回。
对于振动器服务,返回的是一个 SystemVibratorManager 对象:
java
public class SystemVibratorManager extends VibratorManager {
private static final String TAG = "VibratorManager";
private final IVibratorManagerService mService;
private final Context mContext;
private final Binder mToken = new Binder();
private final Object mLock = new Object();
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private int[] mVibratorIds;
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private final SparseArray<Vibrator> mVibrators = new SparseArray<>();
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private final ArrayMap<Vibrator.OnVibratorStateChangedListener,
OnVibratorStateChangedListenerDelegate> mListeners = new ArrayMap<>();
/**
* @hide to prevent subclassing from outside of the framework
*/
public SystemVibratorManager(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
// 获取到 IVibratorManagerService 服务的客户代理端
// 其他方法的功能都是通过 mService 来实现的
mService = IVibratorManagerService.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.VIBRATOR_MANAGER_SERVICE));
}
@NonNull
@Override
public int[] getVibratorIds() {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mVibratorIds != null) {
return mVibratorIds;
}
try {
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to retrieve vibrator ids; no vibrator manager service.");
} else {
return mVibratorIds = mService.getVibratorIds();
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
return new int[0];
}
}
@NonNull
@Override
public Vibrator getVibrator(int vibratorId) {
synchronized (mLock) {
Vibrator vibrator = mVibrators.get(vibratorId);
if (vibrator != null) {
return vibrator;
}
VibratorInfo info = null;
try {
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to retrieve vibrator; no vibrator manager service.");
} else {
info = mService.getVibratorInfo(vibratorId);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
if (info != null) {
vibrator = new SingleVibrator(info);
mVibrators.put(vibratorId, vibrator);
} else {
vibrator = NullVibrator.getInstance();
}
return vibrator;
}
}
@NonNull
@Override
public Vibrator getDefaultVibrator() {
return mContext.getSystemService(Vibrator.class);
}
@Override
public boolean setAlwaysOnEffect(int uid, String opPkg, int alwaysOnId,
@Nullable CombinedVibration effect, @Nullable VibrationAttributes attributes) {
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to set always-on effect; no vibrator manager service.");
return false;
}
try {
return mService.setAlwaysOnEffect(uid, opPkg, alwaysOnId, effect, attributes);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to set always-on effect.", e);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void vibrate(int uid, String opPkg, @NonNull CombinedVibration effect,
String reason, @Nullable VibrationAttributes attributes) {
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to vibrate; no vibrator manager service.");
return;
}
try {
mService.vibrate(uid, mContext.getAssociatedDisplayId(), opPkg, effect, attributes,
reason, mToken);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to vibrate.", e);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
cancelVibration(VibrationAttributes.USAGE_FILTER_MATCH_ALL);
}
@Override
public void cancel(int usageFilter) {
cancelVibration(usageFilter);
}
private void cancelVibration(int usageFilter) {
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to cancel vibration; no vibrator manager service.");
return;
}
try {
mService.cancelVibrate(usageFilter, mToken);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to cancel vibration.", e);
}
}
/** Listener for vibrations on a single vibrator. */
private static class OnVibratorStateChangedListenerDelegate extends
IVibratorStateListener.Stub {
private final Executor mExecutor;
private final Vibrator.OnVibratorStateChangedListener mListener;
OnVibratorStateChangedListenerDelegate(
@NonNull Vibrator.OnVibratorStateChangedListener listener,
@NonNull Executor executor) {
mExecutor = executor;
mListener = listener;
}
@Override
public void onVibrating(boolean isVibrating) {
mExecutor.execute(() -> mListener.onVibratorStateChanged(isVibrating));
}
}
/** Controls vibrations on a single vibrator. */
private final class SingleVibrator extends Vibrator {
private final VibratorInfo mVibratorInfo;
SingleVibrator(@NonNull VibratorInfo vibratorInfo) {
mVibratorInfo = vibratorInfo;
}
@Override
protected VibratorInfo getInfo() {
return mVibratorInfo;
}
@Override
public boolean hasVibrator() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean hasAmplitudeControl() {
return mVibratorInfo.hasAmplitudeControl();
}
@Override
public boolean setAlwaysOnEffect(int uid, String opPkg, int alwaysOnId,
@Nullable VibrationEffect effect, @Nullable VibrationAttributes attrs) {
CombinedVibration combined = CombinedVibration.startParallel()
.addVibrator(mVibratorInfo.getId(), effect)
.combine();
return SystemVibratorManager.this.setAlwaysOnEffect(uid, opPkg, alwaysOnId, combined,
attrs);
}
@Override
public void vibrate(int uid, String opPkg, @NonNull VibrationEffect vibe, String reason,
@NonNull VibrationAttributes attributes) {
CombinedVibration combined = CombinedVibration.startParallel()
.addVibrator(mVibratorInfo.getId(), vibe)
.combine();
SystemVibratorManager.this.vibrate(uid, opPkg, combined, reason, attributes);
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
SystemVibratorManager.this.cancel();
}
@Override
public void cancel(int usageFilter) {
SystemVibratorManager.this.cancel(usageFilter);
}
@Override
public boolean isVibrating() {
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to check status of vibrator " + mVibratorInfo.getId()
+ "; no vibrator service.");
return false;
}
try {
return mService.isVibrating(mVibratorInfo.getId());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void addVibratorStateListener(@NonNull OnVibratorStateChangedListener listener) {
Objects.requireNonNull(listener);
if (mContext == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to add vibrate state listener; no vibrator context.");
return;
}
addVibratorStateListener(mContext.getMainExecutor(), listener);
}
@Override
public void addVibratorStateListener(
@NonNull @CallbackExecutor Executor executor,
@NonNull OnVibratorStateChangedListener listener) {
Objects.requireNonNull(listener);
Objects.requireNonNull(executor);
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG,
"Failed to add vibrate state listener to vibrator " + mVibratorInfo.getId()
+ "; no vibrator service.");
return;
}
synchronized (mLock) {
// If listener is already registered, reject and return.
if (mListeners.containsKey(listener)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Listener already registered.");
return;
}
try {
OnVibratorStateChangedListenerDelegate delegate =
new OnVibratorStateChangedListenerDelegate(listener, executor);
if (!mService.registerVibratorStateListener(mVibratorInfo.getId(), delegate)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to add vibrate state listener to vibrator "
+ mVibratorInfo.getId());
return;
}
mListeners.put(listener, delegate);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
@Override
public void removeVibratorStateListener(@NonNull OnVibratorStateChangedListener listener) {
Objects.requireNonNull(listener);
if (mService == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to remove vibrate state listener from vibrator "
+ mVibratorInfo.getId() + "; no vibrator service.");
return;
}
synchronized (mLock) {
// Check if the listener is registered, otherwise will return.
if (mListeners.containsKey(listener)) {
OnVibratorStateChangedListenerDelegate delegate = mListeners.get(listener);
try {
if (!mService.unregisterVibratorStateListener(mVibratorInfo.getId(),
delegate)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to remove vibrate state listener from vibrator "
+ mVibratorInfo.getId());
return;
}
mListeners.remove(listener);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
}
}
}在 SystemVibratorManager 构造函数中,会获取到 IVibratorManagerService binder 服务的客户端代理类对象,SystemVibratorManager 对象的对外功能都是通过这个客户端代理类对象实现的。
接下来,我们就来看看这个 binder 服务的服务端实现
三、服务端
我们先看看 IVibratorManagerService 的服务端在哪里注册的。
如果你对系统启动过程有所了解,应该知道,这类系统传感器类的服务通常在 SystemServer 的 startOtherServices 方法中完成注册
java
// frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
// ......
t.traceBegin("StartVibratorManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(VibratorManagerService.Lifecycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
//......
}startService 的实现如下:
java
// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/SystemServiceManager.java
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + name);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartService " + name);
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
// 反射调用构造函数
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service could not be instantiated", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}这里使用反射调用了传入的 VibratorManagerService.Lifecycle.class 的构造函数,接着构造函数返回的对象传入另一个 startService 重载。
java
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Check if already started
String className = service.getClass().getName();
if (mServiceClassnames.contains(className)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Not starting an already started service " + className);
return;
}
mServiceClassnames.add(className);
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
service.onStart(); // 调用 SystemService 的 onStart 方法
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
} 这里会调用传入的 SystemService 的 onStart 方法。
接下来看 VibratorManagerService.Lifecycle 类中的 onStart 方法:
java
public class VibratorManagerService extends IVibratorManagerService.Stub {
//......
public static class Lifecycle extends SystemService {
private VibratorManagerService mService;
public Lifecycle(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
mService = new VibratorManagerService(getContext(), new Injector());
publishBinderService(Context.VIBRATOR_MANAGER_SERVICE, mService);
}
@Override
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
if (phase == SystemService.PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY) {
mService.systemReady();
}
}
}
//......
}在 onStart 中,会 new 一个 VibratorManagerService 对象,VibratorManagerService 继承自 IVibratorManagerService.Stub, 是 IVibratorManagerService binder 服务的服务端实现。接着调用 publishBinderService 方法:
java
protected final void publishBinderService(@NonNull String name, @NonNull IBinder service) {
publishBinderService(name, service, false);
}
protected final void publishBinderService(@NonNull String name, @NonNull IBinder service,
boolean allowIsolated) {
publishBinderService(name, service, allowIsolated, DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT);
}
protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service,
boolean allowIsolated, int dumpPriority) {
ServiceManager.addService(name, service, allowIsolated, dumpPriority);
} 绕了一大圈,实际就是 addService. 向 ServiceManager 注册一个 binder 服务。
接下来的问题就是 VibratorManagerService 怎么访问到 HAL 层。
四、VibratorManagerService 如何访问到 HAL 层
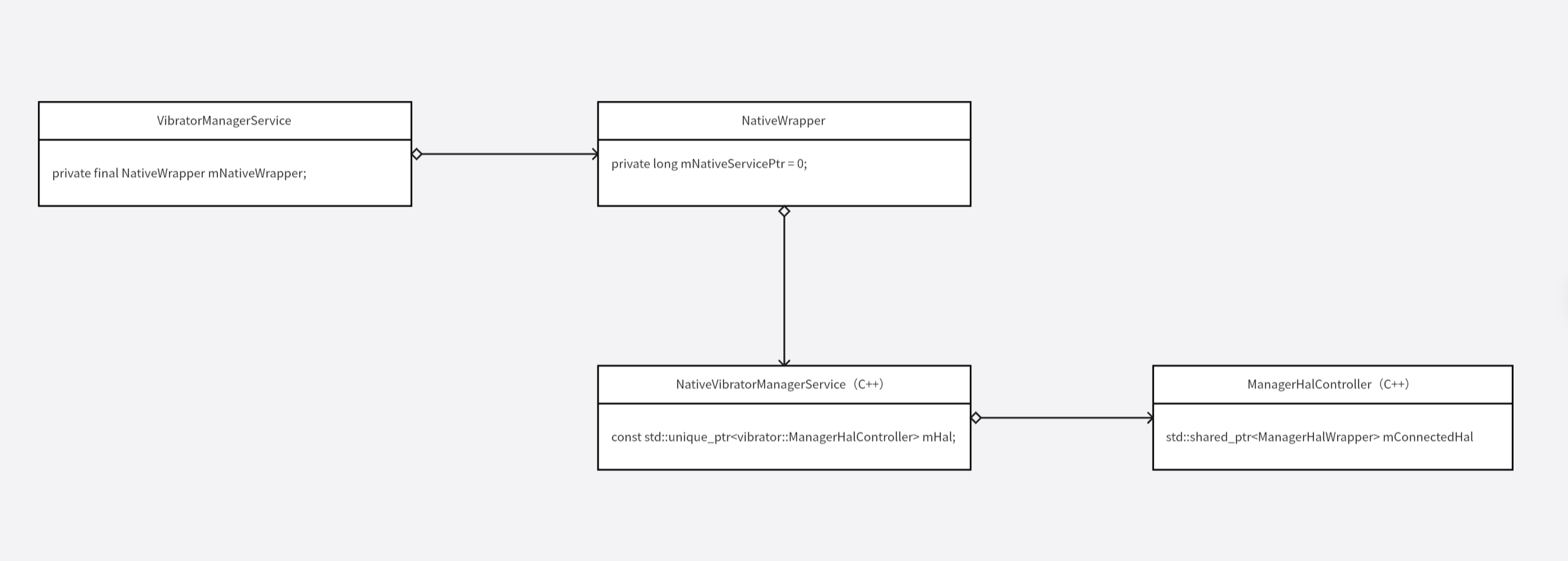
先看下 VibratorManagerService 的构造函数:
java
VibratorManagerService(Context context, Injector injector) {
// ......
mNativeWrapper = injector.getNativeWrapper();
mNativeWrapper.init(listener);
// .....
}实际代码很多,我们先关注一下 mNativeWrapper:
java
NativeWrapper getNativeWrapper() {
// 默认构造函数
return new NativeWrapper();
}这里就是简单 new 一个 NativeWrapper 对象。
接会调用 NativeWrapper 对象的 init 方法:
java
public static class NativeWrapper {
private long mNativeServicePtr = 0;
/** Returns native pointer to newly created controller and connects with HAL service. */
public void init(OnSyncedVibrationCompleteListener listener) {
mNativeServicePtr = nativeInit(listener);
// ......
}
// ......
}init 方法中会调用到 nativeInit 方法,nativeInit 是一个 native 方法,对应的 JNI 函数是:
java
// frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_vibrator_VibratorManagerService.cpp
static vibrator::ManagerHalController* gManager GUARDED_BY(gManagerMutex) = nullptr;
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jobject callbackListener) {
std::unique_ptr<NativeVibratorManagerService> service =
std::make_unique<NativeVibratorManagerService>(env, callbackListener);
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(gManagerMutex);
gManager = service->hal();
}
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(service.release());
}初始化一个指针 NativeVibratorManagerService,然后拿到内部的 hal 成员保存在 gManager 中,最后返回 NativeVibratorManagerService 指针地址给 Java 层,Java 层把这个地址保存在 mNativeServicePtr 成员中。
接下来我们来看 NativeVibratorManagerService 的内部实现:
c
// frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_vibrator_VibratorManagerService.cpp
class NativeVibratorManagerService {
public:
NativeVibratorManagerService(JNIEnv* env, jobject callbackListener)
: mHal(std::make_unique<vibrator::ManagerHalController>()),
mCallbackListener(env->NewGlobalRef(callbackListener)) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mHal == nullptr, "Unable to find reference to vibrator manager hal");
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mCallbackListener == nullptr,
"Unable to create global reference to vibration callback handler");
}
~NativeVibratorManagerService() {
auto jniEnv = GetOrAttachJNIEnvironment(sJvm);
jniEnv->DeleteGlobalRef(mCallbackListener);
}
vibrator::ManagerHalController* hal() const { return mHal.get(); }
std::function<void()> createCallback(jlong vibrationId) {
return [vibrationId, this]() {
auto jniEnv = GetOrAttachJNIEnvironment(sJvm);
jniEnv->CallVoidMethod(mCallbackListener, sMethodIdOnComplete, vibrationId);
};
}
private:
const std::unique_ptr<vibrator::ManagerHalController> mHal;
const jobject mCallbackListener;
};我们重点关注成员 mHal, mHal 在构造函数中,被初始化为一个 ManagerHalController 对象。
到这里,初始化过程就分析完了,整体的类关系如下图所示:
App 端振动器相关的功能最终都会调用到 ManagerHalController 中的方法,比如 getCapabilities 方法,用于获取振动器的能力范围:
c
HalResult<ManagerCapabilities> ManagerHalController::getCapabilities() {
hal_fn<ManagerCapabilities> getCapabilitiesFn = [](std::shared_ptr<ManagerHalWrapper> hal) {
return hal->getCapabilities();
};
return apply(getCapabilitiesFn, "getCapabilities");
}构建一个 lamda 表达式然后传入 apply 方法:
c
template <typename T>
HalResult<T> ManagerHalController::apply(ManagerHalController::hal_fn<T>& halFn,
const char* functionName) {
std::shared_ptr<ManagerHalWrapper> hal = nullptr;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mConnectedHalMutex);
if (mConnectedHal == nullptr) {
// Init was never called, so connect to HAL for the first time during this call.
mConnectedHal = mConnector(mCallbackScheduler);
if (mConnectedHal == nullptr) {
ALOGV("Skipped %s because VibratorManager HAL is not available", functionName);
return HalResult<T>::unsupported();
}
}
hal = mConnectedHal;
}
HalResult<T> ret = processHalResult(halFn(hal), functionName);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_RETRIES && ret.isFailed(); i++) {
ret = processHalResult(halFn(hal), functionName);
}
return ret;
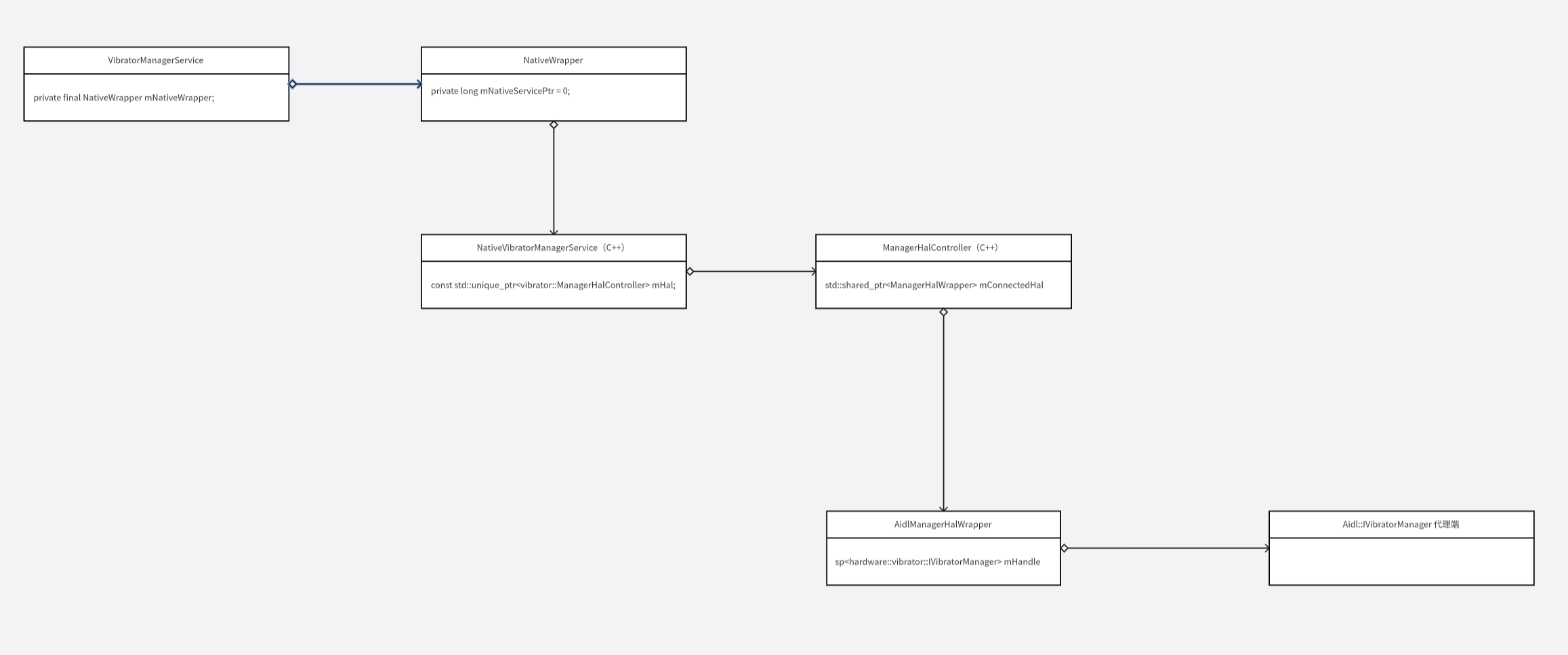
}先调用 mConnector 方法,mConnector 在构造函数中初始化为 connectManagerHal 函数:
ManagerHalController 构造函数:
c
ManagerHalController()
: ManagerHalController(std::make_shared<CallbackScheduler>(), &connectManagerHal) {}
ManagerHalController(std::shared_ptr<CallbackScheduler> callbackScheduler, Connector connector)
: mConnector(connector), mCallbackScheduler(callbackScheduler), mConnectedHal(nullptr) {}connectManagerHal 函数的具体实现:
c
std::shared_ptr<ManagerHalWrapper> connectManagerHal(std::shared_ptr<CallbackScheduler> scheduler) {
static bool gHalExists = true;
if (gHalExists) {
sp<Aidl::IVibratorManager> hal = waitForVintfService<Aidl::IVibratorManager>();
if (hal) {
ALOGV("Successfully connected to VibratorManager HAL AIDL service.");
return std::make_shared<AidlManagerHalWrapper>(std::move(scheduler), hal);
}
}
gHalExists = false;
return std::make_shared<LegacyManagerHalWrapper>();
}接着看 waitForVintfService 函数的具体实现:
c
template<typename INTERFACE>
sp<INTERFACE> waitForVintfService(
const String16& instance = String16("default")) {
return waitForDeclaredService<INTERFACE>(
INTERFACE::descriptor + String16("/") + instance);
}
template<typename INTERFACE>
sp<INTERFACE> waitForDeclaredService(const String16& name) {
const sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
if (!sm->isDeclared(name)) return nullptr;
return interface_cast<INTERFACE>(sm->waitForService(name));
}实际就是调用 waitForService 获取 aidl hal 服务,返回 aidl hal 服务的客户端代理对象。
接着就会执行传入的 lamda 回调,在回调中通过 aidl hal 服务的客户端代理对象发起远程调用。
到目前为止,整体的类结构如下:
五、HAL 层
Google 给出了振动器的实现:
hardware/interfaces/vibrator
给出了 HAL 层实现的整体框架,也给出了实例,实例并没有真的访问驱动,只是返回一些假数据。
先看最顶层的 Android.bp:
java
// hardware/interfaces/vibrator/aidl/Android.bp
package {
default_applicable_licenses: ["hardware_interfaces_license"],
}
aidl_interface {
name: "android.hardware.vibrator",
vendor_available: true,
host_supported: true,
srcs: [
"android/hardware/vibrator/*.aidl",
],
stability: "vintf",
backend: {
java: {
sdk_version: "system_current",
},
},
versions: [
"1",
"2",
],
}这里定义一个 aidl_interface 类型,aidl 文件需要配置在 srcs 中。
配置完成后,编译系统会帮助我们生成 C++/JAVA/NDK/RUST 四种服务端代码。
Google 推荐使用 NDK 类型的代码。
主要几点原因:
- ① HAL 使用 C++ 语言实现更方便,因为要访问驱动。
- ② C++ 类型的代码会依赖 vndk 中的 libbinder 库,Google 的文档说这个库的内部实现和对外接口都不稳定
- ③ NDK 类型的代码依赖 libbinder_ndk,这个库基于 libbinder 库构建,不同的是,它的对外接口稳定。
接着看 hardware/interfaces/vibrator/aidl/default/Android.bp:
c
package {
// See: http://go/android-license-faq
// A large-scale-change added 'default_applicable_licenses' to import
// all of the 'license_kinds' from "hardware_interfaces_license"
// to get the below license kinds:
// SPDX-license-identifier-Apache-2.0
default_applicable_licenses: ["hardware_interfaces_license"],
}
cc_library_static {
name: "libvibratorexampleimpl",
vendor_available: true,
host_supported: true,
shared_libs: [
"libbase",
"libbinder_ndk",
"android.hardware.vibrator-V2-ndk",
],
export_include_dirs: ["include"],
srcs: [
"Vibrator.cpp",
"VibratorManager.cpp",
],
visibility: [
":__subpackages__",
"//hardware/interfaces/tests/extension/vibrator:__subpackages__",
],
target: {
darwin: {
enabled: false,
},
},
}
filegroup {
name: "android.hardware.vibrator.xml",
srcs: ["android.hardware.vibrator.xml"],
}
cc_binary {
name: "android.hardware.vibrator-service.example",
relative_install_path: "hw",
init_rc: ["vibrator-default.rc"],
vintf_fragments: [":android.hardware.vibrator.xml"],
vendor: true,
shared_libs: [
"libbase",
"libbinder_ndk",
"android.hardware.vibrator-V2-ndk",
],
static_libs: [
"libvibratorexampleimpl",
],
srcs: ["main.cpp"],
}
cc_fuzz {
name: "android.hardware.vibrator-service.example_fuzzer",
host_supported: true,
defaults: ["service_fuzzer_defaults"],
static_libs: [
"android.hardware.vibrator-V2-ndk",
"liblog",
"libvibratorexampleimpl",
],
srcs: ["fuzzer.cpp"],
fuzz_config: {
cc: [
"smoreland@google.com",
],
},
}libvibratorexampleimpl 是一个静态库,包含了 Vibrator.cpp VibratorManager.cpp 源码。源码中主要是对 aidl hal 服务端对象的具体实现。
android.hardware.vibrator-service.example 是一个 native 可执行程序,源码是 main.cpp:
c
#include "vibrator-impl/Vibrator.h"
#include "vibrator-impl/VibratorManager.h"
#include <android-base/logging.h>
#include <android/binder_manager.h>
#include <android/binder_process.h>
using aidl::android::hardware::vibrator::Vibrator;
using aidl::android::hardware::vibrator::VibratorManager;
int main() {
ABinderProcess_setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(0);
// make a default vibrator service
auto vib = ndk::SharedRefBase::make<Vibrator>();
binder_status_t status = AServiceManager_addService(
vib->asBinder().get(), Vibrator::makeServiceName("default").c_str());
CHECK_EQ(status, STATUS_OK);
// make the vibrator manager service with a different vibrator
auto managedVib = ndk::SharedRefBase::make<Vibrator>();
auto vibManager = ndk::SharedRefBase::make<VibratorManager>(std::move(managedVib));
status = AServiceManager_addService(vibManager->asBinder().get(),
VibratorManager::makeServiceName("default").c_str());
CHECK_EQ(status, STATUS_OK);
ABinderProcess_joinThreadPool();
return EXIT_FAILURE; // should not reach
}这里就是通过 AServiceManager_addService 函数来向 ServiceManager 注册 aidl hal 服务端。
这里注册了两个服务 Vibrator VibratorManager,Vibrator 是为了兼容老的 api,VibratorManager 是新 API 实现的基础。
六、补充
在 Google 给的 Vibrator hal 实现中,还有一个 App 端的示例:
hardware/interfaces/vibrator/aidl/default/example_java_client
其中核心的 hardware/interfaces/vibrator/aidl/default/example_java_client/example/vib/MyActivity.java 的实现如下:
java
package example.vib;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.vibrator.IVibrator;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
private static native IBinder gimme(String name);
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle b) {
super.onCreate(b);
System.loadLibrary("example_vib_getter");
IVibrator v =
IVibrator.Stub.asInterface(gimme("android.hardware.vibrator.IVibrator/default"));
try {
v.on(100 /*ms*/, null /*cb*/);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
finish();
}
}可以看出在 App 中可以直接访问到 HAL 层的 aidl HAL 服务。省略 Framework 中冗长的逻辑。提供了一种全新的硬件访问方式。
这样固然更快更简单,但是硬件如果存在多个进程同时使用的情况,建议还是通过 Framework 中系统服务来使用,系统服务统一协调管理来自多个进程的访问。
App 其对应的 hardware/interfaces/vibrator/aidl/default/example_java_client/Android.bp:
c
cc_library {
name: "libexample_vib_getter",
srcs: ["getter.cpp"],
product_available: true,
vendor_available: true,
shared_libs: [
"liblog",
"libbinder_ndk",
],
header_libs: ["jni_headers"],
stl: "c++_shared",
visibility: [":__subpackages__"],
}
android_app {
name: "ExampleVibratorJavaVendorClient",
vendor: true,
static_libs: ["android.hardware.vibrator-V1-java"],
jni_libs: ["libexample_vib_getter"],
use_embedded_native_libs: true,
jarjar_rules: "jarjar.txt",
stl: "c++_shared",
srcs: ["example/vib/MyActivity.java"],
sdk_version: "system_current",
visibility: [":__subpackages__"],
}
android_app {
name: "ExampleVibratorJavaProductClient",
product_specific: true,
static_libs: ["android.hardware.vibrator-V1-java"],
jni_libs: ["libexample_vib_getter"],
use_embedded_native_libs: true,
jarjar_rules: "jarjar.txt",
stl: "c++_shared",
srcs: ["example/vib/MyActivity.java"],
sdk_version: "system_current",
visibility: [":__subpackages__"],
// If PRODUCT_ENFORCE_PRODUCT_PARTITION_INTERFACE is not true, product apps
// may use unstable APIs. jni_uses_platform_apis must set to use the
// non-SDK jni libs in this case.
// This is not required if PRODUCT_ENFORCE_PRODUCT_PARTITION_INTERFACE is
// set to true.
jni_uses_platform_apis: true,
}这里给了两个 App 的构建,一个在 Vendor 分区,一个在 Product 分区。他们都需要 android.hardware.vibrator-V1-java 和 libexample_vib_getter 库的支持.
其中 libexample_vib_getter 库有依赖于 libbinder_ndk 库。android.hardware.vibrator-V1-java 是 aidl 文件生成的 java 支持。