工具使用(函数调用)模式概述
截至目前,我们探讨的 Agent 模式主要聚焦于语言模型间的交互编排及 Agent 内部工作流的信息管理(链 式、路由、并行化、反思)。然而,要让 Agent 真正发挥价值并与现实世界或外部系统互动,它们需要具备工具使用能力。
工具使用模式通常通过函数调用机制实现,使 Agent 能连接外部 API、数据库、服务,甚至执行代码。该机制让位于 Agent 核心的大语言模型(LLM)能基于用户请求或任务状态,决策何时以及如何调用特定外部函数。
该过程通常包括:
-
1、工具定义:
-
外部函数或能力被定义并描述给 LLM。此描述包括函数的目的、名称以及它接受的参数及 其类型和描述。
-
2、LLM决策:
-
LLM接收用户的请求和可用的工具定义。基于其对请求和工具的理解,LLM决定是否需要 调用一个或多个工具来满足请求。
-
3、函数调用生成:
-
如果LLM决定使用工具,它会生成一个结构化输出(通常是JSON对象),指定要调用 的工具名称和要传递给它的参数(参数),这些参数从用户的请求中提取。
-
4、工具执行:
-
Agent 框架或编排层拦截此结构化输出。它识别请求的工具并使用提供的参数执行实际的 外部函数。
-
5、观察/结果:
-
工具执行的输出或结果返回给Agent。
-
6、LLM 处理(可选但常见):
-
LLM 接收工具的输出作为上下文,并使用它向用户制定最终响应或决定工
作流中的下一步(可能涉及调用另一个工具、反思或提供最终答案)。
此模式是基础性的,因为它打破了 LLM 训练数据的限制,允许它访问最新信息、执行它内部无法完成的计 算、与用户特定数据交互或触发现实世界的行动。函数调用是连接 LLM 推理能力与可用的大量外部功能之 间差距的技术机制。
虽然"函数调用"精确描述了调用预定义代码函数的过程,但采用更广泛的"工具调用"概念更具实践价值。 这一概念承认 Agent 的能力远超简单函数执行范畴------"工具"既可以是传统函数,也可以是复杂的 API 端 点、数据库查询请求,甚至是向其他专业 Agent 发送的指令。这种视角帮助我们构建更复杂的系统,例如主 Agent 可将数据分析任务委托给专用"分析师 Agent",或通过 API 查询外部知识库。以"工具调用"的思维 方式,能更全面把握 Agent 作为跨数字资源和智能实体生态系统的编排者潜力。
像 LangChain、LangGraph 和 Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) 这样的框架为定义工具并将它们集成到 Agent 工作流中提供了强大的支持,通常利用现代 LLM(如 Gemini 或 OpenAI 系列中的那些)的原生函数 调用能力。在这些框架的"画布"上,您定义工具,然后配置 Agent(通常是 LLM Agent)以意识到并能够 使用这些工具。
工具使用是构建强大、交互式且具环境感知能力 Agent 的基础模式。
实际应用与用例
工具使用模式几乎适用于 Agent 需要超越生成文本来执行操作或检索特定动态信息的任何场景:
1、从外部源检索信息:
访问 LLM 训练数据中不存在的实时数据或信息。
**用例:**天气Agent。
-
**-- 工具:**接受位置并返回当前天气状况的天气API。
-
**-- Agent流程:**用户问"伦敦的天气如何?",LLM识别需要天气工具,用"伦敦"调用工具,工具返回数据,LLM 将数据格式化为用户友好的响应。
2、与数据库和API交互:
对结构化数据执行查询、更新或其他操作。
**用例:**电子商务Agent。
-
-- 工具: API调用以检查产品库存、获取订单状态或处理付款。
-
-- Agent流程: 用户问"产品X有库存吗?",LLM调用库存API,工具返回库存数量,LLM告诉用户库存状态。
3、执行计算和数据分析:
使用外部计算器、数据分析库或统计工具。
**用例:**金融Agent。
-
**-- 工具:**计算器函数、股票市场数据API、电子表格工具。
-
**-- Agent流程:**用户问"AAPL的当前价格是多少,如果我以150美元购买100股,计算潜在利润?",LLM 调用股票 API,获取当前价格,然后调用计算器工具,获取结果,格式化响应。
4、发送通信:
发送电子邮件、消息或对外部通信服务进行 API 调用。
**用例:**个人助理Agent。
-
**-- 工具:**电子邮件发送API。
-
**-- Agent流程:**用户说"给John发一封关于明天会议的电子邮件。",LLM使用从请求中提取的收 件人、主题和正文调用电子邮件工具。
5、执行代码:
在安全环境中运行代码片段以执行特定任务。
**用例:**编码助手Agent。
-
**-- 工具:**代码解释器。
-
**-- Agent流程:**用户提供Python代码片段并问"这段代码做什么?",LLM使用解释器工具运行代码并分析其输出。
6、控制其他系统或设备:
与智能家居设备、物联网平台或其他连接系统交互。
**用例:**智能家居Agent。
-- 工具: 控制智能灯的API。
**-- Agent流程:**用户说"关闭客厅的灯。"LLM使用命令和目标设备调用智能家居工具。
工具使用将语言模型从文本生成器转变为能够在数字或物理世界中感知、推理和行动的 Agent
(见下图 1)
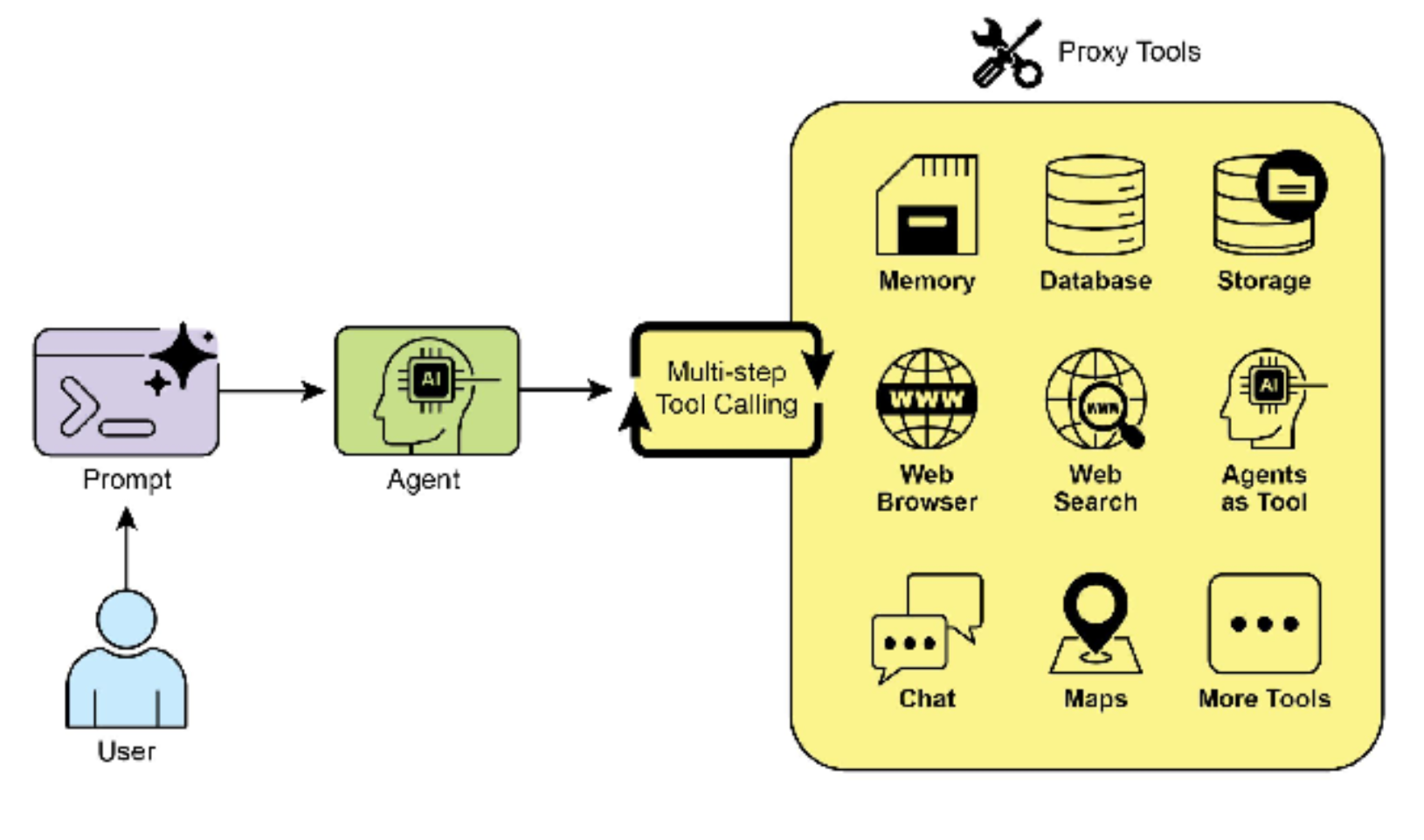
-
图 1:Agent 使用工具的一些示例
概览
是什么:大型语言模型(LLM)是强大的文本生成器,但它们基本上与外部世界断开连接。它们的知识是静 态的,仅限于训练数据,并且缺乏执行操作或检索实时信息的能力。这种固有的限制阻止它们完成需要与外 部 API、数据库或服务交互的任务。没有通往这些外部系统的桥梁,它们解决现实世界问题的效用受到严重 限制。
为什么:工具使用模式(通常通过函数调用实现)为此问题提供了标准化解决方案。它的工作原理是以 LLM 可以理解的方式向其描述可用的外部函数或"工具"。基于用户的请求,Agent LLM 可以决定是否需要工具, 并生成指定要调用哪个函数以及使用什么参数的结构化数据对象(如 JSON)。编排层执行此函数调用,检索 结果,并将其反馈给 LLM。这允许 LLM 将最新的外部信息或操作结果合并到其最终响应中,有效地赋予其 行动能力。
经验法则:当 Agent 需要突破 LLM 的内部知识并与外部世界交互时,使用工具使用模式。这对于需要实时 数据(例如,检查天气、股票价格)、访问私有或专有信息(例如,查询公司数据库)、执行精确计算、执行 代码或触发其他系统中的操作(例如,发送电子邮件、控制智能设备)的任务至关重要。
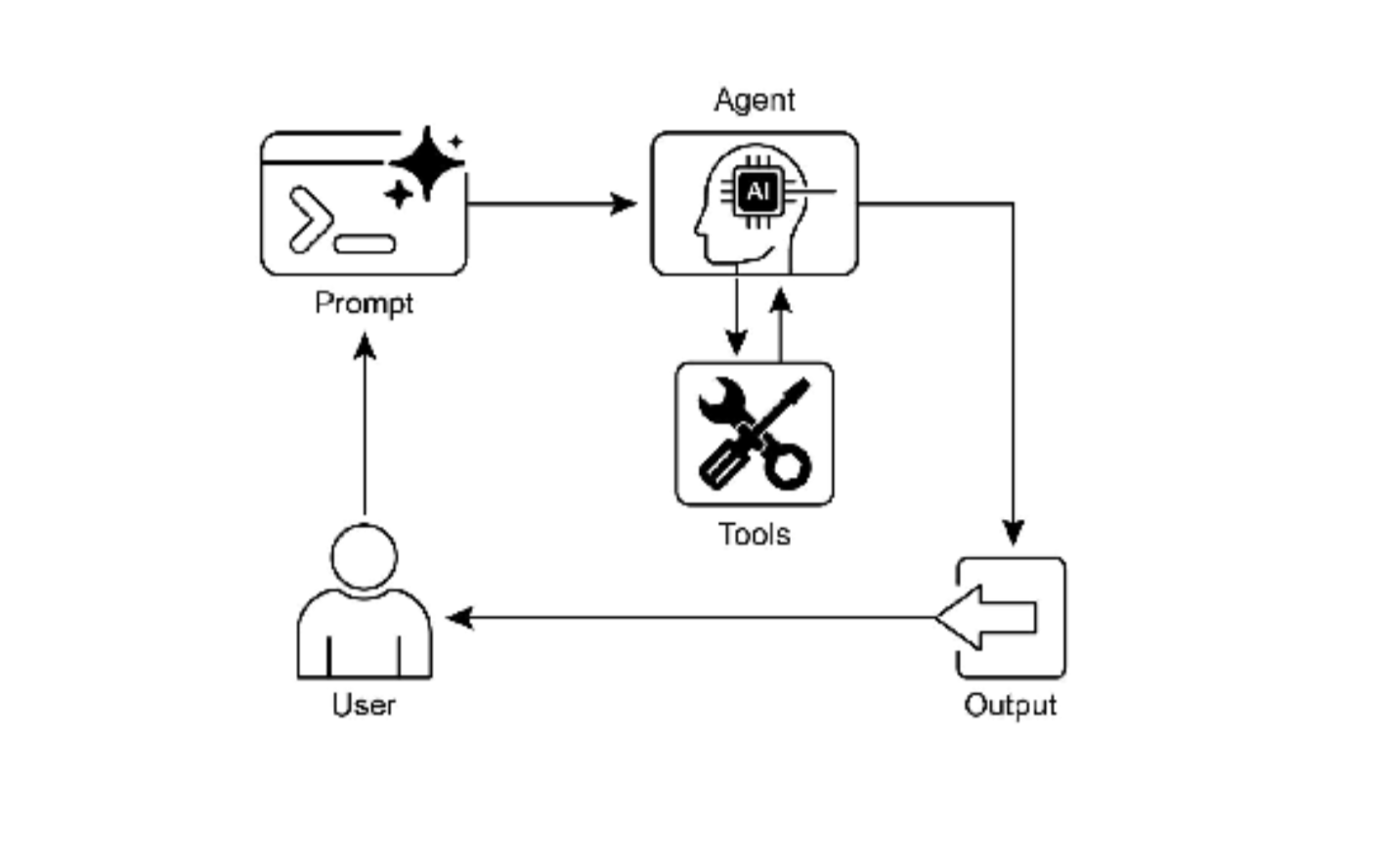
图 2:工具使用设计模式
关键要点
-
・ 工具使用(函数调用)允许Agent与外部系统交互并访问动态信息。
-
・ 它涉及定义具有LLM可以理解的清晰描述和参数的工具。
-
・ LLM决定何时使用工具并生成结构化函数调用。
-
・ Agent 框架执行实际的工具调用并将结果返回给 LLM。
-
・ 工具使用对于构建可以执行现实世界操作并提供最新信息的Agent至关重要。
-
・ LangChain 使用 @tool 装饰器简化工具定义,并提供 create_tool_calling_agent 和 AgentExecutor
用于构建工具使用 Agent。
-
・ GoogleADK有许多非常有用的预构建工具,如Google搜索、代码执行和VertexAI搜索工具。
大模型工具调用:实际应用与用例详解
核心架构概览
python
# 基础Agent框架
class ToolCallingAgent:
def __init__(self, llm, tools):
self.llm = llm # 大语言模型
self.tools = tools # 可用工具集
def process_request(self, user_input):
# 1. 意图识别
intent = self.llm.identify_intent(user_input)
# 2. 工具选择
selected_tool = self.select_tool(intent, user_input)
# 3. 参数提取
params = self.extract_parameters(selected_tool, user_input)
# 4. 工具执行
result = selected_tool.execute(**params)
# 5. 结果整合
response = self.format_response(result)
return response1. 从外部源检索信息
天气Agent实现
python
import requests
from typing import Dict, Any
import json
class WeatherAgent:
def __init__(self, api_key: str):
self.api_key = api_key
self.base_url = "http://api.weather.com/v3"
def get_current_weather(self, location: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取当前天气"""
params = {
'location': location,
'apikey': self.api_key,
'language': 'zh-CN',
'unit': 'm'
}
response = requests.get(
f"{self.base_url}/weather/current",
params=params
)
return response.json()
def get_forecast(self, location: str, days: int = 5) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取天气预报"""
params = {
'location': location,
'apikey': self.api_key,
'days': days
}
response = requests.get(
f"{self.base_url}/weather/forecast",
params=params
)
return response.json()
# 工具定义
weather_tools = [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "获取指定位置的当前天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称,如:北京、上海"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
},
{
"name": "get_weather_forecast",
"description": "获取天气预报",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称"
},
"days": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "预报天数,默认5天"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]完整对话示例
python
# LangChain + OpenAI 实现
from langchain.agents import Tool, AgentExecutor, create_openai_tools_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.tools import BaseTool
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
# 1. 定义天气工具
class WeatherTool(BaseTool):
name = "get_weather"
description = "获取指定城市的天气信息"
def _run(self, location: str) -> str:
weather_agent = WeatherAgent(api_key="your_api_key")
data = weather_agent.get_current_weather(location)
return f"""
{location}的当前天气:
- 温度:{data['temperature']}°C
- 天气:{data['condition']}
- 湿度:{data['humidity']}%
- 风速:{data['wind_speed']} km/h
"""
async def _arun(self, location: str) -> str:
return self._run(location)
# 2. 创建Agent
def create_weather_agent():
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4",
temperature=0,
api_key="your_openai_key"
)
tools = [WeatherTool()]
# 创建Agent
agent = create_openai_tools_agent(llm, tools)
# 执行器
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
memory=ConversationBufferMemory()
)
return agent_executor
# 3. 使用Agent
agent = create_weather_agent()
# 用户对话
responses = agent.invoke({
"input": "北京和上海的天气对比如何?"
})
print(responses['output'])2. 与数据库和API交互
电商库存Agent
python
import sqlite3
from datetime import datetime
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
class ECommerceAgent:
def __init__(self, db_path: str = "ecommerce.db"):
self.db_path = db_path
self.init_database()
def init_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 创建产品表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS products (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
sku TEXT UNIQUE NOT NULL,
price REAL,
stock INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
category TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
''')
# 创建订单表
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS orders (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INTEGER,
product_id INTEGER,
quantity INTEGER,
total_price REAL,
status TEXT DEFAULT 'pending',
order_date TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products (id)
)
''')
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def check_stock(self, product_sku: str) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""检查库存"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
SELECT name, stock, price
FROM products
WHERE sku = ?
''', (product_sku,))
result = cursor.fetchone()
conn.close()
if result:
return {
"product_name": result[0],
"stock": result[1],
"price": result[2]
}
return {"error": "产品不存在"}
def place_order(self, product_sku: str, quantity: int, customer_id: int) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""下订单"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 检查库存
cursor.execute('SELECT id, stock, price FROM products WHERE sku = ?', (product_sku,))
product = cursor.fetchone()
if not product:
conn.close()
return {"error": "产品不存在"}
product_id, stock, price = product
if stock < quantity:
conn.close()
return {"error": "库存不足"}
# 更新库存
new_stock = stock - quantity
cursor.execute('UPDATE products SET stock = ? WHERE id = ?', (new_stock, product_id))
# 创建订单
total_price = price * quantity
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO orders (customer_id, product_id, quantity, total_price, status)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (customer_id, product_id, quantity, total_price, 'confirmed'))
order_id = cursor.lastrowid
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return {
"order_id": order_id,
"status": "confirmed",
"total": total_price,
"estimated_delivery": "3-5个工作日"
}
def get_order_status(self, order_id: int) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""获取订单状态"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
SELECT o.id, p.name, o.quantity, o.total_price, o.status, o.order_date
FROM orders o
JOIN products p ON o.product_id = p.id
WHERE o.id = ?
''', (order_id,))
result = cursor.fetchone()
conn.close()
if result:
return {
"order_id": result[0],
"product": result[1],
"quantity": result[2],
"total": result[3],
"status": result[4],
"order_date": result[5]
}
return {"error": "订单不存在"}
# 工具定义
ecommerce_tools = [
{
"name": "check_product_stock",
"description": "检查产品库存",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"product_sku": {
"type": "string",
"description": "产品SKU编号"
}
},
"required": ["product_sku"]
}
},
{
"name": "place_order",
"description": "下单购买产品",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"product_sku": {"type": "string"},
"quantity": {"type": "integer"},
"customer_id": {"type": "integer"}
},
"required": ["product_sku", "quantity", "customer_id"]
}
},
{
"name": "get_order_status",
"description": "查询订单状态",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"order_id": {"type": "integer"}
},
"required": ["order_id"]
}
}
]3. 执行计算和数据分析
金融分析Agent
python
import yfinance as yf
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Tuple, List, Dict
import plotly.graph_objects as go
class FinancialAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.calculations = {
"simple_return": self.calculate_simple_return,
"log_return": self.calculate_log_return,
"volatility": self.calculate_volatility,
"sharpe_ratio": self.calculate_sharpe_ratio,
"max_drawdown": self.calculate_max_drawdown
}
def get_stock_data(self, symbol: str, period: str = "1y") -> pd.DataFrame:
"""获取股票数据"""
ticker = yf.Ticker(symbol)
df = ticker.history(period=period)
return df
def calculate_simple_return(self, prices: pd.Series) -> float:
"""计算简单收益率"""
return (prices.iloc[-1] - prices.iloc[0]) / prices.iloc[0]
def calculate_log_return(self, prices: pd.Series) -> float:
"""计算对数收益率"""
return np.log(prices.iloc[-1] / prices.iloc[0])
def calculate_volatility(self, prices: pd.Series) -> float:
"""计算波动率"""
returns = np.log(prices / prices.shift(1))
return returns.std() * np.sqrt(252) # 年化波动率
def calculate_sharpe_ratio(self, prices: pd.Series, risk_free_rate: float = 0.02) -> float:
"""计算夏普比率"""
returns = np.log(prices / prices.shift(1)).dropna()
excess_returns = returns - risk_free_rate/252
sharpe = excess_returns.mean() / returns.std() * np.sqrt(252)
return sharpe
def calculate_max_drawdown(self, prices: pd.Series) -> Tuple[float, pd.Timestamp, pd.Timestamp]:
"""计算最大回撤"""
cumulative = (1 + np.log(prices / prices.shift(1)).cumsum())
running_max = cumulative.expanding().max()
drawdown = (cumulative - running_max) / running_max
max_dd = drawdown.min()
max_dd_date = drawdown.idxmin()
peak_date = running_max.loc[:max_dd_date].idxmax()
return max_dd, peak_date, max_dd_date
def analyze_stock(self, symbol: str, investment: float = 10000) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""分析股票"""
# 获取数据
df = self.get_stock_data(symbol)
prices = df['Close']
# 计算各项指标
current_price = prices.iloc[-1]
shares = investment / current_price
current_value = shares * current_price
analysis = {
"symbol": symbol,
"current_price": round(current_price, 2),
"investment": investment,
"current_value": round(current_value, 2),
"profit_loss": round(current_value - investment, 2),
"simple_return": round(self.calculate_simple_return(prices) * 100, 2),
"annual_volatility": round(self.calculate_volatility(prices) * 100, 2),
"sharpe_ratio": round(self.calculate_sharpe_ratio(prices), 3),
}
# 计算最大回撤
max_dd, peak_date, trough_date = self.calculate_max_drawdown(prices)
analysis["max_drawdown"] = round(max_dd * 100, 2)
analysis["peak_date"] = peak_date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
analysis["trough_date"] = trough_date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
return analysis
def create_portfolio_report(self, portfolio: Dict[str, float], investment: float = 10000) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""创建投资组合报告"""
total_weights = sum(portfolio.values())
if abs(total_weights - 1) > 0.01:
# 标准化权重
portfolio = {k: v/total_weights for k, v in portfolio.items()}
results = {}
total_value = 0
for symbol, weight in portfolio.items():
allocation = investment * weight
analysis = self.analyze_stock(symbol, allocation)
results[symbol] = analysis
total_value += analysis["current_value"]
portfolio_return = (total_value - investment) / investment * 100
return {
"portfolio_analysis": results,
"total_investment": investment,
"total_value": round(total_value, 2),
"portfolio_return": round(portfolio_return, 2),
"recommendation": self.generate_recommendation(results)
}
def generate_recommendation(self, analysis: Dict[str, Dict]) -> str:
"""生成投资建议"""
recommendations = []
for symbol, data in analysis.items():
if data["sharpe_ratio"] > 1.5:
recommendations.append(f"{symbol}: 强烈推荐 (夏普比率优秀)")
elif data["sharpe_ratio"] > 0.5:
recommendations.append(f"{symbol}: 推荐")
elif data["max_drawdown"] < -20:
recommendations.append(f"{symbol}: 谨慎 (回撤较大)")
else:
recommendations.append(f"{symbol}: 持有")
return "; ".join(recommendations)
# 使用示例
financial_agent = FinancialAgent()
# 分析单只股票
apple_analysis = financial_agent.analyze_stock("AAPL", investment=10000)
print(f"苹果股票分析: {apple_analysis}")
# 分析投资组合
portfolio = {
"AAPL": 0.4, # 40%
"MSFT": 0.3, # 30%
"GOOGL": 0.3 # 30%
}
portfolio_report = financial_agent.create_portfolio_report(portfolio, 50000)
print(f"投资组合报告: {portfolio_report}")4. 发送通信
邮件/消息发送Agent
python
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
import requests
from typing import List, Dict
import json
class CommunicationAgent:
def __init__(self, config: Dict):
self.email_config = config.get('email', {})
self.slack_config = config.get('slack', {})
self.telegram_config = config.get('telegram', {})
def send_email(self, to_email: str, subject: str, body: str,
html_body: str = None) -> Dict[str, bool]:
"""发送电子邮件"""
try:
# 创建邮件
msg = MIMEMultipart('alternative')
msg['Subject'] = subject
msg['From'] = self.email_config['sender']
msg['To'] = to_email
# 添加纯文本版本
text_part = MIMEText(body, 'plain')
msg.attach(text_part)
# 添加HTML版本(如果有)
if html_body:
html_part = MIMEText(html_body, 'html')
msg.attach(html_part)
# 连接SMTP服务器并发送
with smtplib.SMTP(self.email_config['smtp_server'],
self.email_config['smtp_port']) as server:
server.starttls()
server.login(self.email_config['username'],
self.email_config['password'])
server.send_message(msg)
return {"success": True, "message": "邮件发送成功"}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "error": str(e)}
def send_slack_message(self, channel: str, message: str,
attachments: List[Dict] = None) -> Dict[str, bool]:
"""发送Slack消息"""
try:
webhook_url = self.slack_config['webhook_url']
payload = {
"channel": channel,
"text": message,
"username": "AI Assistant",
"icon_emoji": ":robot_face:"
}
if attachments:
payload["attachments"] = attachments
response = requests.post(
webhook_url,
data=json.dumps(payload),
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
)
if response.status_code == 200:
return {"success": True, "message": "Slack消息发送成功"}
else:
return {"success": False, "error": response.text}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "error": str(e)}
def send_telegram_message(self, chat_id: str, message: str,
parse_mode: str = "HTML") -> Dict[str, bool]:
"""发送Telegram消息"""
try:
bot_token = self.telegram_config['bot_token']
url = f"https://api.telegram.org/bot{bot_token}/sendMessage"
payload = {
"chat_id": chat_id,
"text": message,
"parse_mode": parse_mode
}
response = requests.post(url, json=payload)
if response.status_code == 200:
return {"success": True, "message": "Telegram消息发送成功"}
else:
return {"success": False, "error": response.text}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "error": str(e)}
def send_bulk_emails(self, recipients: List[Dict], template: str,
variables: Dict[str, Dict]) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""批量发送邮件"""
results = []
successes = 0
failures = 0
for recipient in recipients:
email = recipient['email']
name = recipient.get('name', '用户')
# 个性化邮件内容
personalized_body = template.format(
name=name,
**variables.get(email, {})
)
result = self.send_email(
to_email=email,
subject="重要通知",
body=personalized_body
)
results.append({
"email": email,
"success": result["success"],
"error": result.get("error")
})
if result["success"]:
successes += 1
else:
failures += 1
return {
"total": len(recipients),
"successes": successes,
"failures": failures,
"details": results
}
def schedule_communication(self, schedule: Dict) -> Dict[str, bool]:
"""安排定时通信"""
# 这里可以集成APScheduler等定时任务库
# 简化示例
try:
communication_type = schedule['type']
scheduled_time = schedule['time']
message = schedule['message']
recipients = schedule['recipients']
# 在实际应用中,这里会将任务加入调度器
# 例如:scheduler.add_job(send_function, 'date', run_date=scheduled_time)
return {
"success": True,
"message": f"已安排在 {scheduled_time} 发送{communication_type}",
"job_id": "mock_job_id_123"
}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "error": str(e)}5. 执行代码
代码解释器Agent
python
import subprocess
import sys
import io
import contextlib
from typing import Dict, Tuple
import traceback
class CodeInterpreterAgent:
def __init__(self, timeout: int = 30):
self.timeout = timeout
self.safe_modules = {
'math', 'datetime', 'json', 'collections',
'itertools', 'functools', 'random', 'statistics'
}
def execute_python_code(self, code: str, inputs: Dict = None) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""执行Python代码"""
# 创建安全的执行环境
safe_globals = {
'__builtins__': {
'print': print,
'len': len,
'range': range,
'list': list,
'dict': dict,
'set': set,
'tuple': tuple,
'str': str,
'int': int,
'float': float,
'bool': bool,
'type': type,
'isinstance': isinstance,
'enumerate': enumerate,
'zip': zip,
'map': map,
'filter': filter,
'sum': sum,
'min': min,
'max': max,
'abs': abs,
'round': round,
'sorted': sorted,
'reversed': reversed,
'any': any,
'all': all
}
}
# 添加安全的模块
for module_name in self.safe_modules:
try:
module = __import__(module_name)
safe_globals[module_name] = module
except ImportError:
pass
# 添加输入变量
if inputs:
safe_globals.update(inputs)
# 捕获输出
output_capture = io.StringIO()
error_capture = io.StringIO()
try:
# 执行代码
with contextlib.redirect_stdout(output_capture):
with contextlib.redirect_stderr(error_capture):
exec(code, safe_globals)
output = output_capture.getvalue()
return {
"success": True,
"output": output,
"error": None,
"variables": {k: v for k, v in safe_globals.items()
if not k.startswith('__') and k != '__builtins__'}
}
except Exception as e:
error_msg = traceback.format_exc()
return {
"success": False,
"output": output_capture.getvalue(),
"error": error_msg,
"traceback": traceback.format_exception_only(type(e), e)[0]
}
def execute_shell_command(self, command: str) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""执行Shell命令(有限制)"""
allowed_commands = {'ls', 'pwd', 'echo', 'date', 'whoami', 'uname'}
command_parts = command.strip().split()
if not command_parts:
return {"success": False, "error": "空命令"}
cmd = command_parts[0]
if cmd not in allowed_commands:
return {
"success": False,
"error": f"命令 '{cmd}' 不在允许列表中"
}
try:
result = subprocess.run(
command,
shell=True,
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=self.timeout
)
return {
"success": True,
"stdout": result.stdout,
"stderr": result.stderr,
"returncode": result.returncode
}
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
return {"success": False, "error": "命令执行超时"}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "error": str(e)}
def analyze_code(self, code: str) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""分析代码"""
try:
# 检查语法
ast.parse(code)
# 计算复杂度(简化版)
lines = code.split('\n')
non_empty_lines = [line for line in lines if line.strip()]
comment_lines = [line for line in lines if line.strip().startswith('#')]
complexity = {
"total_lines": len(lines),
"non_empty_lines": len(non_empty_lines),
"comment_lines": len(comment_lines),
"comment_ratio": len(comment_lines) / max(len(non_empty_lines), 1)
}
# 识别潜在问题
issues = []
if "eval(" in code:
issues.append("使用了不安全的eval函数")
if "exec(" in code:
issues.append("使用了不安全的exec函数")
if "__import__(" in code:
issues.append("动态导入模块")
return {
"success": True,
"syntax_valid": True,
"complexity": complexity,
"potential_issues": issues,
"suggestions": self.generate_suggestions(code)
}
except SyntaxError as e:
return {
"success": False,
"syntax_valid": False,
"error": str(e),
"line": e.lineno,
"offset": e.offset
}
def generate_suggestions(self, code: str) -> List[str]:
"""生成代码改进建议"""
suggestions = []
# 检查代码风格
if len(code) > 1000:
suggestions.append("代码过长,建议拆分为小函数")
# 检查变量命名
import re
bad_vars = re.findall(r'\b([a-z][a-z0-9_]*)\s*=', code)
if len(bad_vars) > 5:
suggestions.append("变量命名不够描述性,建议使用更有意义的名称")
return suggestions
def generate_test_cases(self, function_code: str) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""为函数生成测试用例"""
try:
# 提取函数信息
tree = ast.parse(function_code)
functions = [node for node in ast.walk(tree) if isinstance(node, ast.FunctionDef)]
if not functions:
return {"success": False, "error": "未找到函数定义"}
func = functions[0]
func_name = func.name
args = [arg.arg for arg in func.args.args]
# 生成测试用例模板
test_template = f'''
import unittest
def {function_code}
class Test{func_name.capitalize()}(unittest.TestCase):
"""
test_cases = []
# 根据参数类型生成示例测试用例
if args:
example_args = ', '.join(['1' for _ in args])
test_cases.append(f'''
def test_{func_name}_basic(self):
result = {func_name}({example_args})
# TODO: 添加断言
self.assertIsNotNone(result)
''')
test_code = test_template + '\n'.join(test_cases)
test_code += '''
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
'''
return {
"success": True,
"function_name": func_name,
"arguments": args,
"test_code": test_code
}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "error": str(e)}6. 控制其他系统或设备
智能家居Agent
python
import asyncio
import aiohttp
from typing import Dict, List
import json
from enum import Enum
class DeviceType(Enum):
LIGHT = "light"
THERMOSTAT = "thermostat"
LOCK = "lock"
CAMERA = "camera"
SPEAKER = "speaker"
class SmartHomeAgent:
def __init__(self, hub_url: str, api_key: str):
self.hub_url = hub_url
self.api_key = api_key
self.headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
async def discover_devices(self) -> List[Dict]:
"""发现设备"""
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(
f"{self.hub_url}/devices",
headers=self.headers
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
devices = await response.json()
return devices
return []
async def get_device_status(self, device_id: str) -> Dict:
"""获取设备状态"""
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(
f"{self.hub_url}/devices/{device_id}",
headers=self.headers
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
return await response.json()
return {"error": "设备不可用"}
async def control_light(self, device_id: str, action: str,
brightness: int = None, color: str = None) -> Dict:
"""控制灯光"""
payload = {"action": action}
if brightness is not None:
payload["brightness"] = brightness
if color is not None:
payload["color"] = color
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.hub_url}/devices/{device_id}/control",
headers=self.headers,
json=payload
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
return await response.json()
return {"error": "控制失败"}
async def set_thermostat(self, device_id: str, temperature: float,
mode: str = "heat") -> Dict:
"""设置恒温器"""
payload = {
"temperature": temperature,
"mode": mode,
"unit": "celsius"
}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.hub_url}/devices/{device_id}/set",
headers=self.headers,
json=payload
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
return await response.json()
return {"error": "设置失败"}
async def control_lock(self, device_id: str, action: str) -> Dict:
"""控制门锁"""
if action not in ["lock", "unlock"]:
return {"error": "无效的操作"}
payload = {"action": action}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.hub_url}/devices/{device_id}/control",
headers=self.headers,
json=payload
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
return await response.json()
return {"error": "控制失败"}
async def get_camera_feed(self, device_id: str) -> Dict:
"""获取摄像头画面"""
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(
f"{self.hub_url}/devices/{device_id}/feed",
headers=self.headers
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
data = await response.json()
return {"success": True, "feed_url": data.get("stream_url")}
return {"success": False, "error": "无法获取画面"}
async def create_scene(self, name: str, actions: List[Dict]) -> Dict:
"""创建场景(一组设备操作)"""
payload = {
"name": name,
"actions": actions,
"enabled": True
}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.hub_url}/scenes",
headers=self.headers,
json=payload
) as response:
if response.status == 201:
return await response.json()
return {"error": "创建场景失败"}
async def execute_scene(self, scene_id: str) -> Dict:
"""执行场景"""
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.hub_url}/scenes/{scene_id}/execute",
headers=self.headers
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
return await response.json()
return {"error": "执行场景失败"}
async def schedule_device_action(self, device_id: str, action: Dict,
schedule: Dict) -> Dict:
"""安排设备定时操作"""
payload = {
"device_id": device_id,
"action": action,
"schedule": schedule
}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.post(
f"{self.hub_url}/schedules",
headers=self.headers,
json=payload
) as response:
if response.status == 201:
return await response.json()
return {"error": "安排失败"}
async def monitor_energy_usage(self, period: str = "daily") -> Dict:
"""监控能耗"""
params = {"period": period}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(
f"{self.hub_url}/energy/usage",
headers=self.headers,
params=params
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
data = await response.json()
# 分析能耗
total_usage = sum(item['usage'] for item in data)
avg_usage = total_usage / len(data) if data else 0
return {
"total_usage": total_usage,
"average_usage": avg_usage,
"period": period,
"devices": data,
"recommendations": self.generate_energy_recommendations(data)
}
return {"error": "无法获取能耗数据"}
def generate_energy_recommendations(self, usage_data: List[Dict]) -> List[str]:
"""生成节能建议"""
recommendations = []
# 分析高能耗设备
high_usage_devices = [
device for device in usage_data
if device['usage'] > 100 # 假设100为阈值
]
for device in high_usage_devices:
recommendations.append(
f"设备 {device['name']} 能耗较高,考虑优化使用时间"
)
# 时间建议
peak_usage = max(usage_data, key=lambda x: x['usage'], default=None)
if peak_usage:
recommendations.append(
f"用电高峰在 {peak_usage.get('time', '未知时间')},建议错峰使用"
)
return recommendations
# 使用示例
async def main():
# 初始化智能家居Agent
home_agent = SmartHomeAgent(
hub_url="http://smart-home-hub.local",
api_key="your_api_key"
)
# 发现设备
devices = await home_agent.discover_devices()
print(f"发现 {len(devices)} 个设备")
# 控制客厅灯光
living_room_light = next(
(d for d in devices if d['name'] == 'Living Room Light'),
None
)
if living_room_light:
result = await home_agent.control_light(
device_id=living_room_light['id'],
action="turn_on",
brightness=75,
color="warm_white"
)
print(f"控制灯光结果: {result}")
# 创建"电影之夜"场景
scene_actions = [
{
"device_id": living_room_light['id'],
"action": {"action": "turn_on", "brightness": 20, "color": "blue"}
},
# 可以添加更多设备操作
]
scene = await home_agent.create_scene("电影之夜", scene_actions)
print(f"创建场景: {scene}")
# 监控能耗
energy_report = await home_agent.monitor_energy_usage("weekly")
print(f"能耗报告: {energy_report}")
# 运行
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())综合架构:多Agent系统
python
from typing import Dict, List, Any
import asyncio
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Tool:
name: str
description: str
function: callable
parameters: Dict[str, Any]
class MultiAgentSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.agents = {}
self.tool_registry = {}
def register_agent(self, name: str, agent: Any):
"""注册Agent"""
self.agents[name] = agent
# 自动注册工具
if hasattr(agent, 'get_tools'):
tools = agent.get_tools()
for tool in tools:
self.tool_registry[tool.name] = tool
async def orchestrate(self, user_request: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""编排多个Agent处理请求"""
# 1. 分析请求,确定需要哪些Agent
required_agents = self.analyze_request(user_request)
# 2. 并行调用相关Agent
tasks = []
for agent_name in required_agents:
agent = self.agents.get(agent_name)
if agent:
task = asyncio.create_task(
agent.process(user_request)
)
tasks.append((agent_name, task))
# 3. 收集结果
results = {}
for agent_name, task in tasks:
try:
result = await task
results[agent_name] = result
except Exception as e:
results[agent_name] = {"error": str(e)}
# 4. 整合结果
final_response = self.integrate_results(results)
return {
"request": user_request,
"agents_used": required_agents,
"results": results,
"final_response": final_response
}
def analyze_request(self, request: str) -> List[str]:
"""分析请求需要哪些Agent"""
required_agents = []
# 简单的关键词匹配(实际可以使用NLP)
request_lower = request.lower()
if any(word in request_lower for word in ['天气', '温度', '预报']):
required_agents.append('weather')
if any(word in request_lower for word in ['股票', '投资', '价格']):
required_agents.append('finance')
if any(word in request_lower for word in ['邮件', '发送', '通知']):
required_agents.append('communication')
if any(word in request_lower for word in ['家居', '灯光', '设备']):
required_agents.append('smarthome')
if any(word in request_lower for word in ['代码', '执行', '程序']):
required_agents.append('code_interpreter')
return required_agents
def integrate_results(self, results: Dict[str, Any]) -> str:
"""整合各个Agent的结果"""
response_parts = []
for agent_name, result in results.items():
if 'error' not in result:
if agent_name == 'weather':
response_parts.append(f"天气信息: {result.get('summary', '')}")
elif agent_name == 'finance':
response_parts.append(f"金融分析: {result.get('recommendation', '')}")
elif agent_name == 'communication':
response_parts.append(f"通信状态: {result.get('status', '')}")
# ... 其他Agent
return "\n".join(response_parts) if response_parts else "暂时无法处理您的请求"
# 使用示例
async def main():
# 创建多Agent系统
system = MultiAgentSystem()
# 注册各个Agent
system.register_agent('weather', WeatherAgent(api_key="..."))
system.register_agent('finance', FinancialAgent())
system.register_agent('communication', CommunicationAgent(config={}))
system.register_agent('smarthome', SmartHomeAgent("...", "..."))
system.register_agent('code_interpreter', CodeInterpreterAgent())
# 处理复杂请求
complex_request = """
帮我做以下事情:
1. 检查北京的天气
2. 分析苹果股票的当前表现
3. 如果天气好且股票上涨,给我发邮件
4. 同时调暗客厅的灯光
"""
result = await system.orchestrate(complex_request)
print(f"处理结果: {result}")
# 运行
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())最佳实践与建议
1. 工具设计原则
python
class ToolDesignPrinciples:
"""工具设计最佳实践"""
@staticmethod
def design_tool():
return {
"原则": [
"单一职责:每个工具只做一件事",
"明确的输入输出:定义清晰的参数和返回值",
"错误处理:提供有意义的错误信息",
"幂等性:重复调用产生相同结果",
"安全性:验证输入,防止恶意调用",
"可观测性:记录工具调用日志",
"版本管理:支持向后兼容"
],
"示例": '''
# 好的工具设计
class GoodTool:
def process(self, input_data: Dict) -> Dict:
# 输入验证
if not self.validate_input(input_data):
raise ValueError("无效输入")
# 核心逻辑
result = self._core_process(input_data)
# 标准化输出
return self.format_result(result)
# 不好的工具设计
class BadTool:
def do_everything(self, *args, **kwargs):
# 太多职责
# 输入输出不明确
# 缺乏错误处理
pass
'''
}2. 性能优化
python
class AgentPerformanceOptimizer:
"""Agent性能优化"""
def __init__(self):
self.cache = {}
self.metrics = {}
def optimize(self):
strategies = [
"工具调用缓存",
"批量处理请求",
"异步并发执行",
"负载均衡",
"连接池复用",
"结果预计算",
"惰性加载工具"
]
return {
"策略": strategies,
"实施示例": '''
# 缓存示例
@lru_cache(maxsize=128)
def cached_weather(location: str):
return get_weather(location)
# 异步示例
async def process_multiple_tools(tools):
tasks = [tool.execute_async() for tool in tools]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
return results
# 批量处理
def batch_process(requests):
# 合并类似请求
batched = self.batch_similar_requests(requests)
# 一次性处理
results = self.process_batch(batched)
# 拆分结果
return self.split_results(results)
'''
}3. 安全考虑
python
class SecurityConsiderations:
"""安全考虑"""
def security_measures(self):
return {
"措施": [
"输入验证和清理",
"访问控制和认证",
"速率限制和配额",
"敏感数据脱敏",
"审计日志记录",
"沙箱环境执行",
"错误信息不泄露敏感数据"
],
"实施": '''
# 输入验证
def safe_execute(tool, user_input):
# 白名单验证
if not self.is_allowed_tool(tool):
raise SecurityError("工具未授权")
# 参数验证
validated = self.validate_parameters(tool, user_input)
# 执行限制
with self.execution_time_limit(seconds=30):
return tool.execute(validated)
# 访问控制
class AccessControlledTool:
def __init__(self, required_role):
self.required_role = required_role
def execute(self, user, params):
if not self.has_permission(user, self.required_role):
raise PermissionError("权限不足")
# ... 执行逻辑
'''
}学习资源
推荐学习路径
-
基础掌握
-
LangChain官方文档
-
OpenAI Function Calling
-
Hugging Face Transformers Agents
-
-
进阶项目
-
实现个性化新闻聚合Agent
-
创建智能客服系统
-
构建数据分析助手
-
-
生产部署
-
FastAPI封装Agent服务
-
Docker容器化部署
-
性能监控和日志收集
-
关键库和框架
python
essential_libraries = {
"框架": ["LangChain", "AutoGen", "CrewAI"],
"LLM接口": ["OpenAI", "Anthropic", "Cohere", "本地模型"],
"工具开发": ["FastAPI", "Pydantic", "SQLAlchemy"],
"异步处理": ["asyncio", "aiohttp", "celery"],
"监控": ["Prometheus", "Grafana", "ELK Stack"],
"部署": ["Docker", "Kubernetes", "AWS Lambda"]
}结论
工具使用模式是将大型语言模型的功能范围扩展到其固有文本生成能力之外的关键架构原则。通过为模型配 备与外部软件和数据源交互的能力,此范式允许 Agent 执行操作、进行计算并从其他系统检索信息。此过程 涉及模型在确定满足用户查询需要时生成调用外部工具的结构化请求。LangChain、Google ADK 和 CrewAI 等框架提供结构化抽象和组件,促进这些外部工具的集成。这些框架管理向模型公开工具规范并解析其后续 工具使用请求的过程。这简化了可以与外部数字环境交互并在其中采取行动的复杂 Agent 系统的开发。
参考文献
-
1、LangChainDocumentation(Tools):
-
2、Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) Documentation (Tools): https://google.github.io/adk‐docs/tools/
-
3、OpenAI Function Calling Documentation: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function‐calling