C++ 数据类型
使用编程语言进行编程时,需要用到各种变量来存储各种信息。变量保留的是它所存储的值的内存位置。这意味着,当您创建一个变量时,就会在内存中保留一些空间。
您可能需要存储各种数据类型(比如字符型、宽字符型、整型、浮点型、双浮点型、布尔型等)的信息,操作系统会根据变量的数据类型,来分配内存和决定在保留内存中存储什么。
基本的内置类型
C++ 为程序员提供了种类丰富的内置数据类型和用户自定义的数据类型。下表列出了七种基本的 C++ 数据类型:
| 类型 | 关键字 |
|---|---|
| 布尔型 | bool |
| 字符型 | char |
| 整型 | int |
| 浮点型 | float |
| 双浮点型 | double |
| 无类型 | void |
| 宽字符型 | wchar_t |
其实 wchar_t 是这样来的:
typedef short int wchar_t;所以 wchar_t 实际上的空间是和 short int 一样。
一些基本类型可以使用一个或多个类型修饰符进行修饰:
| 修饰符 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
signed |
表示有符号类型(默认) | signed int x = -10; |
unsigned |
表示无符号类型 | unsigned int y = 10; |
short |
表示短整型 | short int z = 100; |
long |
表示长整型 | long int a = 100000; |
const |
表示常量,值不可修改 | const int b = 5; |
volatile |
表示变量可能被意外修改,禁止编译器优化 | volatile int c = 10; |
mutable |
表示类成员可以在 const 对象中修改 |
mutable int counter; |
下表显示了各种变量类型在内存中存储值时需要占用的内存,以及该类型的变量所能存储的最大值和最小值。
**注意:**不同系统会有所差异,一字节为 8 位。
**注意:**默认情况下,int、short、long都是带符号的,即 signed。
**注意:**long int 8 个字节,int 都是 4 个字节,早期的 C 编译器定义了 long int 占用 4 个字节,int 占用 2 个字节,新版的 C/C++ 标准兼容了早期的这一设定。
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 大小(字节) | 范围/取值示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
bool |
布尔类型,表示真或假 | 1 | true 或 false |
char |
字符类型,通常用于存储 ASCII 字符 | 1 | -128 到 127 或 0 到 255 |
signed char |
有符号字符类型 | 1 | -128 到 127 |
unsigned char |
无符号字符类型 | 1 | 0 到 255 |
wchar_t |
宽字符类型,用于存储 Unicode 字符 | 2 或 4 | 取决于平台 |
char16_t |
16 位 Unicode 字符类型(C++11 引入) | 2 | 0 到 65,535 |
char32_t |
32 位 Unicode 字符类型(C++11 引入) | 4 | 0 到 4,294,967,295 |
short |
短整型 | 2 | -32,768 到 32,767 |
unsigned short |
无符号短整型 | 2 | 0 到 65,535 |
int |
整型 | 4 | -2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647 |
unsigned int |
无符号整型 | 4 | 0 到 4,294,967,295 |
long |
长整型 | 4 或 8 | 取决于平台 |
unsigned long |
无符号长整型 | 4 或 8 | 取决于平台 |
long long |
长长整型(C++11 引入) | 8 | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 到 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
unsigned long long |
无符号长长整型(C++11 引入) | 8 | 0 到 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
float |
单精度浮点数 | 4 | 约 ±3.4e±38(6-7 位有效数字) |
double |
双精度浮点数 | 8 | 约 ±1.7e±308(15 位有效数字) |
long double |
扩展精度浮点数 | 8、12 或 16 | 取决于平台 |
C++11 新增类型
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
auto |
自动类型推断 | auto x = 10; |
decltype |
获取表达式的类型 | decltype(x) y = 20; |
nullptr |
空指针常量 | int* ptr = nullptr; |
std::initializer_list |
初始化列表类型 | std::initializer_list<int> list = {1, 2, 3}; |
std::tuple |
元组类型,可以存储多个不同类型的值 | std::tuple<int, float, char> t(1, 2.0, 'a'); |
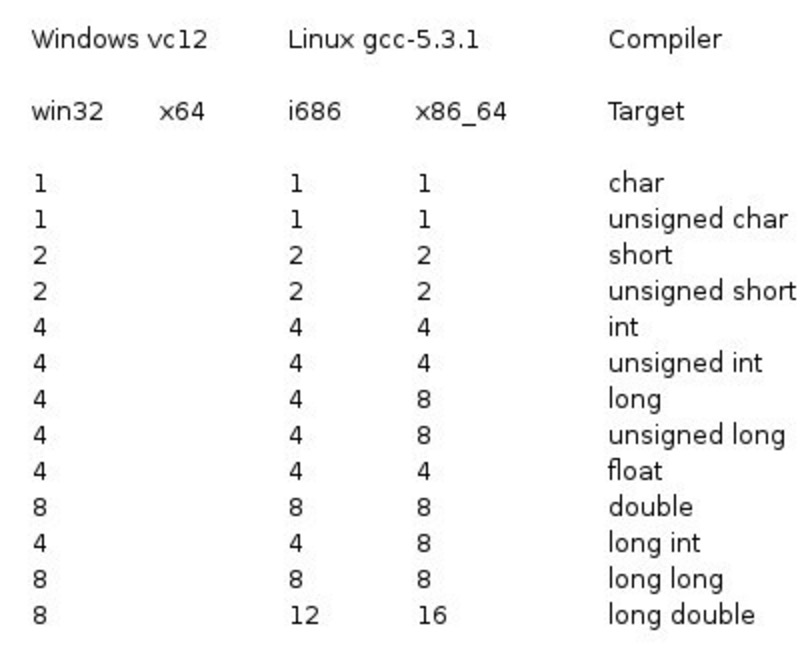
注意,各种类型的存储大小与系统位数有关,但目前通用的以64位系统为主。
以下列出了32位系统与64位系统的存储大小的差别(windows 相同):
从上表可得知,变量的大小会根据编译器和所使用的电脑而有所不同。
下面实例会输出您电脑上各种数据类型的大小。
实例
#include<iostream> #include <limits> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl; cout << "bool: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(bool); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::min)() << endl; cout << "char: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(char); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::min)() << endl; cout << "signed char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(signed char); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::min)() << endl; cout << "unsigned char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned char); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::min)() << endl; cout << "wchar_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(wchar_t); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::min)() << endl; cout << "short: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(short); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::min)() << endl; cout << "int: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(int); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::min)() << endl; cout << "unsigned: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::min)() << endl; cout << "long: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::min)() << endl; cout << "unsigned long: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned long); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::min)() << endl; cout << "double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(double); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::min)() << endl; cout << "long double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long double); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::min)() << endl; cout << "float: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(float); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::min)() << endl; cout << "size_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(size_t); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::min)() << endl; cout << "string: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(string) << endl; // << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<string>::max)() << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<string>::min)() << endl; cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl; return 0; }
本实例使用了 endl ,这将在每一行后插入一个换行符,<< 运算符用于向屏幕传多个值,sizeof() 运算符用来获取各种数据类型的大小。
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生以下的结果,结果会根据所使用的计算机而有所不同:
type: ************size**************
bool: 所占字节数:1 最大值:1 最小值:0
char: 所占字节数:1 最大值: 最小值:?
signed char: 所占字节数:1 最大值: 最小值:?
unsigned char: 所占字节数:1 最大值:? 最小值:
wchar_t: 所占字节数:4 最大值:2147483647 最小值:-2147483648
short: 所占字节数:2 最大值:32767 最小值:-32768
int: 所占字节数:4 最大值:2147483647 最小值:-2147483648
unsigned: 所占字节数:4 最大值:4294967295 最小值:0
long: 所占字节数:8 最大值:9223372036854775807 最小值:-9223372036854775808
unsigned long: 所占字节数:8 最大值:18446744073709551615 最小值:0
double: 所占字节数:8 最大值:1.79769e+308 最小值:2.22507e-308
long double: 所占字节数:16 最大值:1.18973e+4932 最小值:3.3621e-4932
float: 所占字节数:4 最大值:3.40282e+38 最小值:1.17549e-38
size_t: 所占字节数:8 最大值:18446744073709551615 最小值:0
string: 所占字节数:24
type: ************size**************派生数据类型
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
数组 |
相同类型元素的集合 | int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; |
指针 |
存储变量内存地址的类型 | int* ptr = &x; |
引用 |
变量的别名 | int& ref = x; |
函数 |
函数类型,表示函数的签名 | int func(int a, int b); |
结构体 |
用户定义的数据类型,可以包含多个不同类型的成员 | struct Point { int x; int y; }; |
类 |
用户定义的数据类型,支持封装、继承和多态 | class MyClass { ... }; |
联合体 |
多个成员共享同一块内存 | union Data { int i; float f; }; |
枚举 |
用户定义的整数常量集合 | enum Color { RED, GREEN, BLUE }; |
类型别名
| 别名 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
typedef |
为现有类型定义别名 | typedef int MyInt; |
using |
为现有类型定义别名(C++11 引入) | using MyInt = int; |
标准库类型
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
std::string |
字符串类型 | std::string s = "Hello"; |
std::vector |
动态数组 | std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3}; |
std::array |
固定大小数组(C++11 引入) | std::array<int, 3> a = {1, 2, 3}; |
std::pair |
存储两个值的容器 | std::pair<int, float> p(1, 2.0); |
std::map |
键值对容器 | std::map<int, std::string> m; |
std::set |
唯一值集合 | std::set<int> s = {1, 2, 3}; |
typedef 声明
您可以使用 typedef 为一个已有的类型取一个新的名字。下面是使用 typedef 定义一个新类型的语法:
typedef type newname; 例如,下面的语句会告诉编译器,feet 是 int 的另一个名称:
typedef int feet;现在,下面的声明是完全合法的,它创建了一个整型变量 distance:
feet distance;