前言:之前我们所学的STL容器包括序列式容器、容器适配器和关联式容器 ,这里序列式容器是指元素按照插入顺序存储,可以通过位置(索引)访问的容器(string、vector、list、deque、forward_list、array等这些线性结构、元素位置可交换且不影响结构和按位置/索引访问的容器);容器适配器是基于其他容器而实现的容器 (stack和queue这些基于vector/list容器为基础来组合 );关联式容器是指元素按照特定顺序(通常是键值排序)存储,基于键(key)进行快速查找的容器(有序set、map、mutiset和mutimap,无序unordered_set、unordered_map、unorderd_mutiset和unorderd_mutimap等这些非线性结构(如树、哈希表)、元素位置由键决定且不能随意交换和按关键字访问);总的来说区分序列式容器和关联式容器就是元素按照位置还是关键字来保存和访问数据。
一、set和multiset的使用
set和二叉搜索树原理(二叉搜索树:数据宇宙中的秩序法典与高效检索圣殿-CSDN博客)差不多,通过key关键字来查询和插入数据。
set的初始化:
cpp
//set<int, less<int>> s1{341, 32, 4, 1, 3, 5, 8};
set<int, greater<int>> s1{ 341, 32, 4, 1, 3, 5, 8 };
auto it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
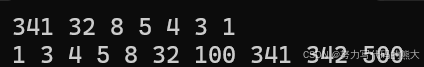
array<int, 10> arr{341, 32, 4, 1, 3, 5, 8, 100, 500, 342};
set<int> s2(arr.begin(), arr.end());
auto it2 = s2.begin();
while (it2 != s2.end())
{
cout << *it2 << ' ';
it2++;
}
set的插入:
cpp
set<int> s3;
s3.insert(313);
s3.insert(3);
auto position1 = s3.insert(13);//返回值pair<iterator,bool>
s3.insert(43);
s3.insert(11);
s3.insert(100);
//set<int>::iterator position2 = s3.insert(position1.first, 10000);//iterator里面包含key,返回iterator
s3.insert(10000);
s3.insert(103231);
//s3.insert(position2, 103231);
s3.insert(131);
auto it3 = s3.begin();
while (it3 != s3.end())
{
cout << *it3 << ' ';
it3++;
}
这里插入过程无论是根据位置插入还是按照顺序插入都不影响,但是对于知道位置取插入如果是确定这个位置后面插入key就能提高效率。
cpp
array<int, 10> arr2 = { 1,3,2231,1323,214,432,16,4,3425,1235 };
s3.insert(arr2.begin(), arr2.end());//void返回值,迭代器插入
it3 = s3.begin();
while (it3 != s3.end())
{
cout << *it3 << ' ';
it3++;
}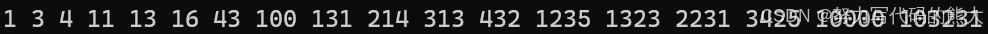
set的删除
cpp
set<int> s4{ 41,2,34,44,2,5,313,53,78,59,9,6 };
auto it1 = s4.begin();
while (it1 != s4.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
s4.erase(41);
it1 = s4.begin();
while (it1 != s4.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
这里当然可以迭代器的方式删除。
set的查询
cpp
//查询
set<int> s5{ 41,2,34,44,2,5,313,53,78,59,9,6 };
set<int>::iterator position1 = find(s5.begin(), s5.end(), 5);//都可以,只不过这底层类似与数组访问查询方式效率很低O(n)
set<int>::iterator position2 = s5.find(5);//这个效率就会很高,O(log n)
if (position1 != s5.end())
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
if (position2 != s5.end())
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}这里需要区分与库里面的find区别,这里set是关联式容器,库里面的std中find是类似于数组访问查询方式效率很低O(n) ,这里set自带的find是根据类似二叉搜索的搜索方式查询,效率较高O(log n)。
set中的key结点个数
cpp
//count查询容器中key结点个数(也能判断是否有这个元素)
set<int> s6{ 41,2,34,44,2,5,313,53,78,59,9,6 };
size_t size1 = s6.count(41);
size_t size2 = s6.count(1);
if (size1)
{
cout << "有" << size1 << "个元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有元素" << endl;
}
if (size2)
{
cout << "有" << size2 << "个元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有元素" << endl;
}set的lower_bound和upper_bound
cpp
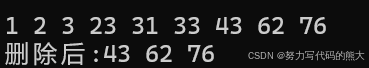
set<int> s7{ 43,23,62,3,1,76,31,33,2 };
auto it1 = s7.begin();
while (it1 != s7.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
//寻找 >= 1的数
set<int>::iterator it2 = s7.lower_bound(1);
//寻找 > 33
set<int>::iterator it3 = s7.upper_bound(33);
s7.erase(it2, it3);
//[it2,it3);
cout << "删除后:";
it1 = s7.begin();
while (it1 != s7.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
lower_bound寻找>=的值,可以等于,而upper_bound是寻找>的值,不能等于,他们区别就是没有等号,根据需要来选择这其中一个。
multiset使用
cpp
multiset<int> ms{ 1,2,66,5,23,5,1,3,2,2,2,2,4,4,4,4 };//可以重复,set不能重复
auto it1 = ms.begin();
while (it1 != ms.end())
{
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "插入前:" << ms.count(2)<<endl;
ms.insert(2);//set不能插入,并且会返回false,mutiset就能无视重复
cout << "插入后:" << ms.count(2) << endl;
这是mutiset的插入,后面的删除、查询、结点个数和lower_bound这些都是一样的了,唯一和set的区别就是能重复插入,可以插入重复值

二、map和multimap的使用(有一部分和set的使用是一样的,所以这里有些就不列举了)
map和set的使用大差不差,这里map是利用key去存储对应的value,可以在排序过程中随着key关键字去带上value的。
map的初始化
cpp
map<string, int> mp1;
map<string, int> mp2{ pair<string, int>("香蕉", 1) , pair<string,int>("苹果",2) };//匿名对象
map<string, int> mp3{ { "香蕉",1 },{"苹果",2}};//隐式类型转换
map<string, int> mp4(mp2);
map<string, int>::iterator it1 = mp2.begin();
while (it1 != mp2.end())
{
cout << it1->first << ":" << it1->second << endl;
it1++;
}
map的插入
cpp
//直接插入
map<string, int> mp6{ {"苹果",1},{"香蕉",2},{"荔枝",6},{"葡萄",3},{"柚子",2},{"橘子",1},{"苹果",2} };
map<string, int>::iterator it3 = mp6.begin();
cout << "插入前" << endl;
while (it3 != mp6.end())
{
cout << it3->first << ":" << it3->second << endl;
it3++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "插入后" << endl;
mp6.insert(pair<string,int>("杨桃",4));
auto it4 = mp6.begin();
while (it4 != mp6.end())
{
cout << it4->first << ":" << it4->second << endl;
it4++;
}
cout << endl;
//修改value
pair<map<string, int>::iterator, bool> n = mp6.insert(pair<string, int>("杨桃", 4));
auto it5 = mp6.begin();
cout << "修改vaule前:" << endl;
while (it5 != mp6.end())
{
cout << it5->first << ":" << it5->second << endl;
it5++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "修改vaule后:" << endl;
n.first->second = 1;
it5 = mp6.begin();
while (it5 != mp6.end())
{
cout << it5->first << ":" << it5->second << endl;
it5++;
}
cout << endl;
//迭代器后插入(用的好可以提高效率)
map<string, int> mp7;
mp7.insert(mp6.begin(), mp6.end());
//插入前
cout << "结点插入前" << endl;
for (auto& e : mp7)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "结点插入后" << endl;
map<string, int>::iterator it6 = mp7.insert(mp7.end(), { "哈密瓜",3 });
for (auto& e : mp7)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;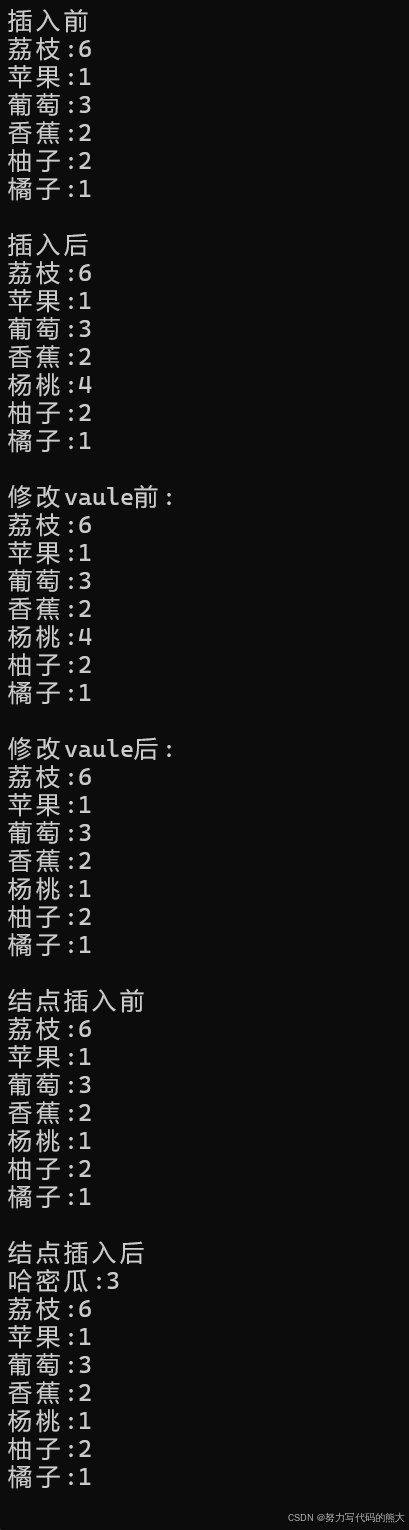
map的查询
cpp
//查询
map<string, int> mp9{ {"苹果",1},{"香蕉",2},{"荔枝",6},{"葡萄",3},{"柚子",2},{"橘子",1},{"苹果",2} };
map<string, int>::iterator pos3 = mp9.find("柚子");//找到返回对应的迭代器位置,没找到返回迭代器end()
if (pos3 != mp9.end())
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
map的删除
cpp
//删除
map<string,int> mp8{ {"苹果",1},{"香蕉",2},{"荔枝",6},{"葡萄",3},{"柚子",2},{"橘子",1},{"苹果",2} };
cout << "删除前:" << endl;
map<string, int>::iterator it7 = mp8.begin();
while (it7 != mp8.end())
{
cout << it7->first << ":" << it7->second << endl;
it7++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "删除葡萄后" << endl;
map<string, int>::iterator pos2 = mp8.find("葡萄");//这里find和库里面的find效率区别很大,一个是logn,一个是n
mp8.erase(pos2);
map<string, int>::iterator it8 = mp8.begin();
while (it8 != mp8.end())
{
cout << it8->first << ":" << it8->second << endl;
it8++;
}
cout << endl;
map<string, int> mp1{ {"香蕉",2},{"荔枝",6},{"葡萄",3},{"柚子",2},{"橘子",1},{"苹果",2} };
cout << "删除结点前:" << endl;
for (auto& e : mp1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "删除结点后:" << endl;
mp1.erase(--mp1.end());
for (auto& e : mp1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "删除key前" << endl;
for (auto& e : mp1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << "删除key后" << endl;
size_t size = mp1.erase("荔枝");//返回删除key的个数,也是针对于muti_map
for (auto& e : mp1)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << "删除个数:" << size << endl;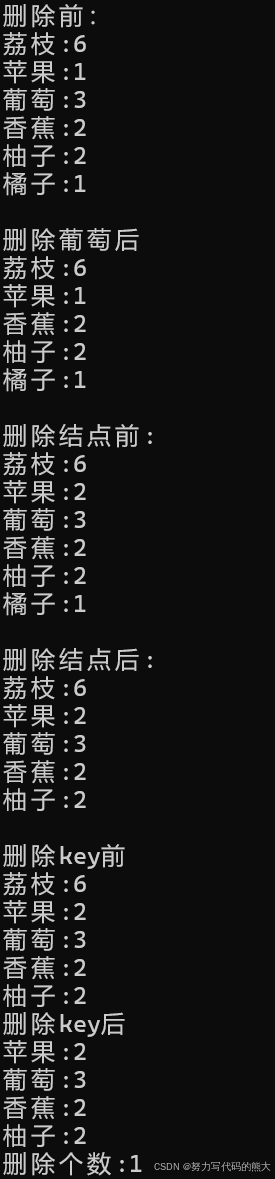
这里删除也是可以用迭代器删除,删除返回的是删除个数(删除的是key个数)。
map的[]访问
cpp
//[]访问
map<string,int> mp10{ {"苹果",1},{"香蕉",2},{"荔枝",6},{"葡萄",3},{"柚子",2},{"橘子",1},{"苹果",2} };
mp10["香蕉"];//如果存在则返回value
cout << "修改香蕉前:" << mp10["香蕉"] << endl;;
mp10["香蕉"]++;//也可以对value修改
cout << "修改香蕉后:" << mp10["香蕉"] << endl;;
cout << endl;
map<string, int>::iterator pos4 = mp10.find("西瓜");
if (pos4 != mp10.end())
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
mp10["西瓜"];//如果不存在则会插入,并value给0/随机值
pos4 = mp10.find("西瓜");
if (pos4 != mp10.end())
{
cout << "找到了:" << mp10["西瓜"] << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
我们平时用到最多的可能就是map的[]访问,既能当插入使用(插入后value会默认变为0),也能修改value值。
map的key结点个数(这里不是统计value个数)
cpp
//count计算key个数(不统计value值)
map<string,int> mp11{ {"苹果",1},{"香蕉",2},{"荔枝",6},{"葡萄",3},{"柚子",2},{"橘子",1},{"苹果",2} };
cout << "荔枝:" << mp11.count("荔枝") << endl;
注意:这里的count是统计key中个数,而不是key中对应的value值,也就是针对于muti_map的使用。
multimap使用
cpp
//muti_map
multimap<string,int> mmp1{ {"苹果",3},{"香蕉",2},{"荔枝",6},{"葡萄",3},{"柚子",2},{"橘子",1},{"苹果",1} };
cout << "苹果:" << mmp1.count("苹果") << endl;//统计key出现个数
cout << endl;
multimap<string, int>::iterator it1 = mmp1.begin();
while (it1 != mmp1.end())
{
cout << it1->first << ":" << it1->second << endl;
it1++;
}
multimap可以重复出现相同的key,count和erase返回的都是key的个数/删除个数。
三、set和map的模拟实现
3.1 insert
根据我们上个博客(掌握红黑树:详解插入过程中的旋转与重着色策略-CSDN博客)中模拟的红黑树,set和map底层就是由红黑树组成的,我们可以利用红黑树中的插入进行修改进而模拟set和map。
set
cpp
//RBTree.h
//RBTree<K,V,KeyOfT>
//RBTNode<V> Node;
//成员 Node* _root;
// KeyOfT Key;
bool Insert(const V& kv)
{
//判断根是否为空
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
//比cur大,往右棵树走
if (Key(cur->_kv) < Key(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
//比cur小,往左课树走
else if (Key(cur->_kv) > Key(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
//相同
else
{
return false;
}
}
//找到空位置了
Node* node = new Node(kv);
//判断和父节点的大小
if (Key(parent->_kv) < Key(kv))
{
parent->_right = node;
}
else
{
parent->_left = node;
}
//更新父节点
Node* child = node;
child->_parent = parent;
//更改颜色维持平衡
while (parent && parent->_parent && parent->_col == Red)//parent颜色为黑就不需要改变了,因为黑色可以连续,后面也有可能把parent变为红的情况,但是都是旋转,旋转后都会跳出循环(因为已经平衡了)
{
//判断uncle是grand的左/右结点
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)//说明右子树是uncle
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//1.uncle存在且为红
// g
// p u
// c
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;//为了平衡根结点到null的黑色结点数量
//继续往上修改
child = grandfather;
parent = child->_parent;
}
//2.uncle存在且为黑
else if (uncle == nullptr || uncle->_col == Black)
{
//右单旋
// g(黑) 右单旋+变色 p(黑)
// p(红) u(黑) -----> c(红) g(红)
// c u(黑)
if (parent->_left == child)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
//左右双旋
// g(黑) 左单旋 g(黑) 右单旋+变色 c(黑)
// p(红) u(黑) ----> c(红) u(黑) ---> p(红) g(红)
// c p(红) u(黑)
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
child->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else//左子树是uncle
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//1.uncle存在且为红
// g
// p u
// c
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;//为了平衡根结点到null的黑色结点数量
//继续往上修改
child = grandfather;
parent = child->_parent;
}
//2.uncle存在且为黑
else if (uncle == nullptr || uncle->_col == Black)
{
//左单旋
// g(黑) 左单旋+变色 p(黑)
// u(黑) p(红) -----> c(红) g(红)
// c u(黑)
if (parent->_right == child)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
//右左双旋
// g(黑) 右单旋 g(黑) 左单旋+变色 c(黑)
// u(黑) p(红) ----> u(黑) c(红) ---> g(红) p(红)
// c p(红) u(黑)
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
child->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return true;
}
//set.h
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKey
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)const
{
return key;
}
};
public:
bool insert(const K& key)
{
return _rb_set_root.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, const K,SetKey> _rb_set_root;
};map
cpp
//map
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKey
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)const
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
bool insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _rb_map_root.Insert(kv);
}
void Order()
{
_rb_map_root.InOrder();
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>,MapKey> _rb_map_root;
};这里修改主要修改了红黑树中的key转换,直接通过仿函数KeyOfT来转换key做对比,当然这里还对红黑树结点模板修改为一个,以便兼容set和map。
3.2 迭代器
cpp
//迭代器
template<class T>
struct RBTIterator
{
typedef RBTNode<T>* PNode;
PNode _t_iterator = nullptr;
//初始化
RBTIterator(PNode t_iterator)
:_t_iterator(t_iterator)
{ }
//解引用(针对于set)
T& operator*()
{
return _t_iterator->_kv;
}
//->指针解引用(针对于map)
T* operator->()
{
return &(_t_iterator->_kv);
}
//operator重载 !=
bool operator!=(PNode t_iterator)
{
return _t_iterator != t_iterator;
}
//operator重载 ==
bool operator==(PNode t_iterator)
{
return _t_iterator == t_iterator;
}
//前置++
RBTIterator<T>& operator++()
{
PNode cur = _t_iterator;
if (cur == nullptr)
return *this;
//根据遍历顺序左根右,都是先到达根结点,这个时候就只需要判断是否有右子树
//右子树存在
if (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
//右子树的最左结点为++结果
while(cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
}
//右子树为空
else
{
PNode parent = cur->_parent;
//cur为父节点的左孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)//说明此时已经左右子树已经遍历完,往父节点上面靠
{
cur = cur->_parent;//parent的作用
}
//cur为父节点的右孩子
else
{
//此时parent的左右棵树都已经遍历完,往parent的父节点上面靠
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
}
//更新迭代器
_t_iterator = cur;
return *this;
}
//后置++
RBTIterator<T>& operator++(int)
{
PNode cur = _t_iterator;
RBTIterator<T> tmp(cur);
if (cur == nullptr)
{
return tmp;
}
//cur右子树存在
if (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
}
//不存在
else
{
PNode parent = cur->_parent;
//cur为parent的左结点
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
}
//cur为右节点
else
{
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
}
//更新
_t_iterator = cur;
return tmp;
}
//前置--
RBTIterator<T>& operator--()
{
PNode cur = _i_iterator;
if (cur == nullptr)
return *this;
//--就是根据右根左的方向反过来
//左结点不为空
if (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
}
//左节点为空
else
{
PNode parent = cur->_parent;
//cur 为parent的左孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
//parent的左右都减完了,往上走
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
//cur 为parent的右孩子
else
{
cur = parent;
}
}
_t_iterator = cur;
return *this;
}
//后置--
RBTIterator<T>& operator--(int)
{
PNode cur = _t_iterator;
RBTIterator<T>& tmp(cur);
if (cur == nullptr)
return tmp;
//cur左子树不为空
if (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
}
else
{
PNode parent = cur;
//cur为parent的左孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
else
{
cur = parent;
}
}
_t_iterator = cur;
return *tmp;
}
};
//RBTree类
//迭代器
typedef RBTIterator<V,V&,V*> Iterator;
typedef RBTIterator<V,const V&,const V*> Const_Iterator;
Iterator Begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Iterator(cur);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr);
}
Const_Iterator CBegin()const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Const_Iterator(cur);
}
Const_Iterator CEnd()const
{
return Const_Iterator(nullptr);
}set
cpp
//迭代器
//当使用依赖模板参数的嵌套类型时,必须使用typename关键字告诉编译器这是一个类型,而不是静态成员
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKey>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKey>::Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_rb_set_root.Begin());
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_rb_set_root.End());
}
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_set_root.CBegin());
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_set_root.CEnd());
}map
cpp
//迭代器
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKey>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const pair<const K, V>, MapKey>::Const_Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_rb_map_root.Begin());
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_rb_map_root.End());
}
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_map_root.CBegin());
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_map_root.cend);
}需要注意:这里当使用依赖模板参数的嵌套类型时,必须使用typename关键字告诉编译器这是一个类型,而不是静态成员。
3.3 map的[]实现
cpp
V& operator[](const K key)
{
iterator it = _rb_map_root.Insert({key,V()}).first;
return it->second;
}这里我通过修改了Insert插入的返回值,Insert的返回值为pair<iterator,bool>,所以这里实现map的[]就是利用返回值中pair的iterator去访问迭代器中的value值(这里迭代器指的就是结点指针)。
3.4完整代码
RBTree.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace bear
{
//颜色枚举
enum Color
{
Red,
Black
};
//红黑树结点
template<class T>
struct RBTNode
{
T _kv;
Color _col = Red;
RBTNode<T>* _parent;
RBTNode<T>* _left;
RBTNode<T>* _right;
//初始化
RBTNode(const T& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
{
}
};
//迭代器
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct RBTIterator
{
typedef RBTNode<T>* PNode;
typedef RBTIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
PNode _t_iterator = nullptr;
//初始化
RBTIterator(PNode t_iterator)
:_t_iterator(t_iterator)
{ }
//解引用(针对于set)
Ref operator*()
{
return _t_iterator->_kv;
}
//->指针解引用(针对于map)
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_t_iterator->_kv);
}
//operator重载 !=
bool operator!=(const Self& iterator)const
{
return _t_iterator != iterator._t_iterator;
}
//operator重载 ==
bool operator==(const Self& iterator)const
{
return _t_iterator == iterator._t_iterator;
}
//前置++
Self& operator++()
{
PNode cur = _t_iterator;
if (cur == nullptr)
return *this;
//根据遍历顺序左根右,都是先到达根结点,这个时候就只需要判断是否有右子树
//右子树存在
if (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
//右子树的最左结点为++结果
while(cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
}
//右子树为空
else
{
PNode parent = cur->_parent;
//cur为父节点的左孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)//说明此时已经左右子树已经遍历完,往父节点上面靠
{
cur = cur->_parent;//parent的作用
}
//cur为父节点的右孩子
else
{
//此时parent的左右棵树都已经遍历完,往parent的父节点上面靠
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
}
//更新迭代器
_t_iterator = cur;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Self& operator++(int)
{
PNode cur = _t_iterator;
Self tmp(cur);
if (cur == nullptr)
{
return tmp;
}
//cur右子树存在
if (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
}
//不存在
else
{
PNode parent = cur->_parent;
//cur为parent的左结点
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
}
//cur为右节点
else
{
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
}
//更新
_t_iterator = cur;
return tmp;
}
//前置--
Self& operator--()
{
PNode cur = _t_iterator;
if (cur == nullptr)
return *this;
//--就是根据右根左的方向反过来
//左结点不为空
if (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
}
//左节点为空
else
{
PNode parent = cur->_parent;
//cur 为parent的左孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
//parent的左右都减完了,往上走
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
//cur 为parent的右孩子
else
{
cur = parent;
}
}
_t_iterator = cur;
return *this;
}
//后置--
Self& operator--(int)
{
PNode cur = _t_iterator;
Self& tmp(cur);
if (cur == nullptr)
return tmp;
//cur左子树不为空
if (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
while (cur->_right)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
}
else
{
PNode parent = cur;
//cur为parent的左孩子
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
while (parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->parent;
}
cur = parent;
}
else
{
cur = parent;
}
}
_t_iterator = cur;
return *tmp;
}
};
//红黑树结构
template<class K, class V,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTNode<V> Node;
public:
//迭代器
typedef RBTIterator<V,V&,V*> Iterator;
typedef RBTIterator<V,const V&,const V*> Const_Iterator;
Iterator Begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Iterator(cur);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr);
}
Const_Iterator CBegin()const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Const_Iterator(cur);
}
Const_Iterator CEnd()const
{
return Const_Iterator(nullptr);
}
public:
//初始化
RBTree(Node* root = nullptr)
:_root(root)
{
}
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const V& kv)
{
//判断根是否为空
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = Black;
return {_root, true };
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
//比cur大,往右棵树走
if (Key(cur->_kv) < Key(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
//比cur小,往左课树走
else if (Key(cur->_kv) > Key(kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
//相同
else
{
return { cur,false };
}
}
//找到空位置了
Node* node = new Node(kv);
//判断和父节点的大小
if (Key(parent->_kv) < Key(kv))
{
parent->_right = node;
}
else
{
parent->_left = node;
}
//更新父节点
Node* child = node;
child->_parent = parent;
//更改颜色维持平衡
while (parent && parent->_parent && parent->_col == Red)//parent颜色为黑就不需要改变了,因为黑色可以连续,后面也有可能把parent变为红的情况,但是都是旋转,旋转后都会跳出循环(因为已经平衡了)
{
//判断uncle是grand的左/右结点
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)//说明右子树是uncle
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//1.uncle存在且为红
// g
// p u
// c
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;//为了平衡根结点到null的黑色结点数量
//继续往上修改
child = grandfather;
parent = child->_parent;
}
//2.uncle存在且为黑
else if (uncle == nullptr || uncle->_col == Black)
{
//右单旋
// g(黑) 右单旋+变色 p(黑)
// p(红) u(黑) -----> c(红) g(红)
// c u(黑)
if (parent->_left == child)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
//左右双旋
// g(黑) 左单旋 g(黑) 右单旋+变色 c(黑)
// p(红) u(黑) ----> c(红) u(黑) ---> p(红) g(红)
// c p(红) u(黑)
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
child->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
else//左子树是uncle
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//1.uncle存在且为红
// g
// p u
// c
if (uncle && uncle->_col == Red)
{
parent->_col = Black;
uncle->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;//为了平衡根结点到null的黑色结点数量
//继续往上修改
child = grandfather;
parent = child->_parent;
}
//2.uncle存在且为黑
else if (uncle == nullptr || uncle->_col == Black)
{
//左单旋
// g(黑) 左单旋+变色 p(黑)
// u(黑) p(红) -----> c(红) g(红)
// c u(黑)
if (parent->_right == child)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
//变色
parent->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
//右左双旋
// g(黑) 右单旋 g(黑) 左单旋+变色 c(黑)
// u(黑) p(红) ----> u(黑) c(红) ---> g(红) p(红)
// c p(红) u(黑)
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
child->_col = Black;
grandfather->_col = Red;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = Black;
return { node,true };
}
//查询
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (Key(cur->_kv) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (Key(cur->_kv) < key)
{
cur = cur->right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
Node* _root;
KeyOfT Key;
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << Key(root->_kv) << " ";
//cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
//左单旋
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* Rchild = parent->_right; //右孩子
Node* parentparent = parent->_parent; //父节点的父节点
Node* RchildLchild = Rchild->_left; //Rchild左孩子
//先处理parent与RchildLchild连接关系
if (RchildLchild)//可能为空,导致空指针解引用问题
RchildLchild->_parent = parent;
parent->_right = RchildLchild;
//处理Rchild与parent的关系
Rchild->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = Rchild;
//然后处理parentparent与Rchild的连接关系
//判断是否为根节点
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = Rchild;
Rchild->_parent = nullptr;//可读性,明确为空
}
else
{
//衔接Rchild与parentparent的关系
//判断Rchild是parentparent的左右孩子
if (parentparent->_left == parent)
{
parentparent->_left = Rchild;
}
else
{
parentparent->_right = Rchild;
}
Rchild->_parent = parentparent;//最后更新Rchild的父节点
}
}
//右单旋
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* Lchild = parent->_left;
Node* LchildRchild = Lchild->_right;
Node* parentparent = parent->_parent;
//先连接与parent与LchildRchild的连接关系
if (LchildRchild)//可能为空,避免空指针解引用
LchildRchild->_parent = parent;
parent->_left = LchildRchild;
//再连接parent与Lchild的连接关系
Lchild->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = Lchild;
//最后连接parentparent与Lchild的关系
if (parent == _root)//为根
{
_root = Lchild;
Lchild->_parent = nullptr;//明确为空
}
else//不为根
{
//判断是parentparent的左右孩子
if (parentparent->_left == parent)
{
parentparent->_left = Lchild;
}
else
{
parentparent->_right = Lchild;
}
Lchild->_parent = parentparent;
}
}
};
}set.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace bear
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKey
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)const
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//迭代器
//当使用依赖模板参数的嵌套类型时,必须使用typename关键字告诉编译器这是一个类型,而不是静态成员
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKey>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKey>::Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_rb_set_root.Begin());
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_rb_set_root.End());
}
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_set_root.CBegin());
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_set_root.CEnd());
}
public:
//插入
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _rb_set_root.Insert(key);
}
//递归
void Order()
{
_rb_set_root.InOrder();
}
private:
RBTree<K, const K,SetKey> _rb_set_root;
};
}map.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace bear
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKey
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)const
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//迭代器
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKey>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const pair<const K, V>, MapKey>::Const_Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_rb_map_root.Begin());
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_rb_map_root.End());
}
const_iterator cbegin()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_map_root.CBegin());
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return const_iterator(_rb_map_root.cend);
}
public:
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _rb_map_root.Insert(kv);
}
void Order()
{
_rb_map_root.InOrder();
}
V& operator[](const K key)
{
iterator it = _rb_map_root.Insert({key,V()}).first;
return it->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>,MapKey> _rb_map_root;
};
}