目录
[1. 快速入门](#1. 快速入门)
[2. 如何调用](#2. 如何调用)
[2.1 使用llm](#2.1 使用llm)
[2.1.1 使用本地部署](#2.1.1 使用本地部署)
[2.1.2 使用云平台](#2.1.2 使用云平台)
[2.2 使用embedding](#2.2 使用embedding)
[2.2.1 使用本地部署](#2.2.1 使用本地部署)
[2.2.2 使用云平台](#2.2.2 使用云平台)
[3. 使用rag进行检索问答](#3. 使用rag进行检索问答)
[4. 切片规则](#4. 切片规则)
[4.1 token 切片](#4.1 token 切片)
[4.2 句子切片](#4.2 句子切片)
[4.3 句子窗口切片](#4.3 句子窗口切片)
[4.4 语义切片](#4.4 语义切片)
LlamaIndex 是一个强大的开源工具,它能帮助开发者构建各种基于大型语言模型 (LLM) 的应用程序。它提供了一套工具和 API,使开发者能够轻松地将 LLM 与外部数据源连接起来,从而赋予 LLM 更强大的能力,从功能上看它与LangChian有点类似
1. 快速入门
使用 OpenAI API 密钥设置一个名为 OPENAI_API_KEY 的环境变量。安装 Python 库
bash
python -m venv LlamaIndex
source LlamaIndex/bin/activate
pip install llama-index包含
llama-index-corellama-index-llms-openaillama-index-embeddings-openaillama-index-program-openaillama-index-question-gen-openaillama-index-agent-openaillama-index-readers-filellama-index-multi-modal-llms-openai
将一些文档放入名为 data 的文件夹中,然后使用我们著名的 5 行入门代码提问。
python
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
#加载文档
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data()
#构建索引
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
#查询
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query("Some question about the data should go here")
print(response)默认使用的是openai的模型
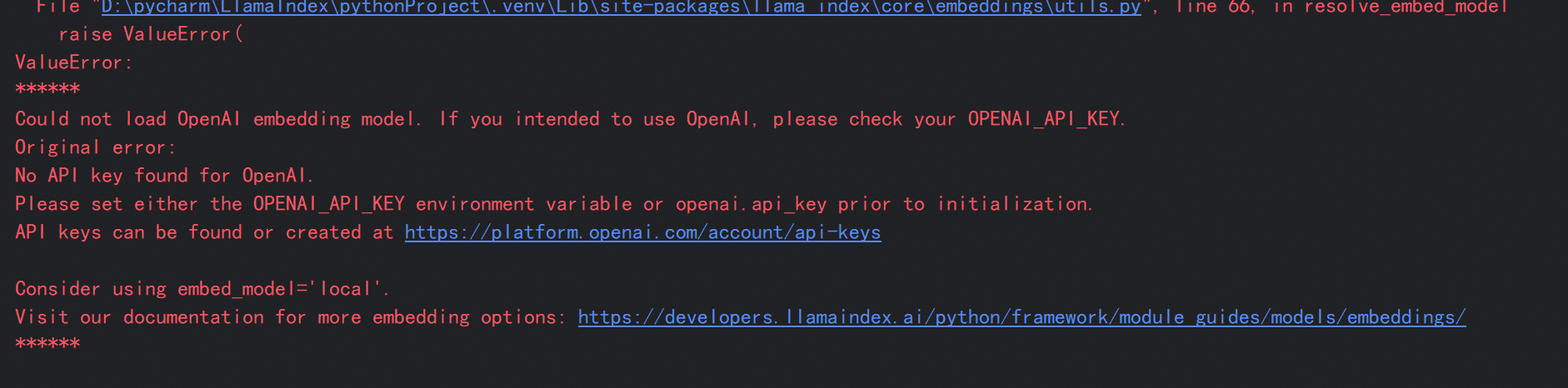
所以如果没有配置key的话会报错,如果想要替换默认的openai可以参考下面的内容
2. 如何调用
2.1 使用llm
https://docs.llamaindex.org.cn/en/stable/api_reference/llms/openai_like/
bash
pip install llama-index-core
pip install llama-index-llms-openai-like2.1.1 使用本地部署
python
import os
from llama_index.core import Settings
from llama_index.llms.openai_like import OpenAILike
# LlamaIndex默认使用的大模型被替换
Settings.llm = OpenAILike(
model="DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B",
api_base="http://localhost:8000/v1",#如vllm,sglang,ollama
is_chat_model=True
)
response = llm.complete("Hello World!")
print(response)2.1.2 使用云平台
python
import os
from llama_index.core import Settings
from llama_index.llms.openai_like import OpenAILike
# LlamaIndex默认使用的大模型被替换为百炼
Settings.llm = OpenAILike(
model="qwen-plus",
api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),
is_chat_model=True
)
response = llm.complete("Hello World!")
print(response)2.2 使用embedding
https://docs.llamaindex.org.cn/en/stable/examples/embeddings/textembed/
2.2.1 使用本地部署
python
from llama_index.embeddings.textembed import TextEmbedEmbedding
# 初始化 TextEmbedEmbedding 类
embed = TextEmbedEmbedding(
model_name="Qwen3-Embedding-8B",
base_url="http://0.0.0.0:8000/v1",
auth_token="TextEmbed", )
# 获取一批文本的 embeddings
embeddings = embed.get_text_embedding_batch( [ "这里下着倾盆大雨!", "印度拥有多元化的文化遗产。", ] )
print(embeddings)2.2.2 使用云平台
bash
pip install llama-index-core
pip install llama-index-embeddings-dashscope
pip install llama-index-readers-file
pip install docx2txt
python
from llama_index.embeddings.dashscope import DashScopeEmbedding
# 初始化 Embedding 模型
embedder = DashScopeEmbedding(
model_name="text-embedding-v2"
)
text_to_embedding = ["风急天高猿啸哀", "渚清沙白鸟飞回", "无边落木萧萧下", "不尽长江滚滚来"]
# 调用 Embedding 模型
result_embeddings = embedder.get_text_embedding_batch(text_to_embedding)
# 显示 Embedding 后结果
for index, embedding in enumerate(result_embeddings):
print("Dimension of embeddings: %s" % len(embedding))
print(
"Input: %s, embedding is: %s"
% (text_to_embedding[index], embedding[:5])
)3. 使用rag进行检索问答
demo
python
import os
import dashscope
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader, Settings
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, get_response_synthesizer
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter, TokenTextSplitter, SemanticSplitterNodeParser
from llama_index.core.retrievers import VectorIndexRetriever
from llama_index.core.query_engine import RetrieverQueryEngine
from llama_index.core.postprocessor import SimilarityPostprocessor
from llama_index.embeddings.dashscope import DashScopeEmbedding
from llama_index.llms.openai_like import OpenAILike
os.environ['DASHSCOPE_API_KEY']=''
dashscope.api_key=api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY")
# LlamaIndex默认使用的Embedding模型被替换为百炼的Embedding模型
Settings.embed_model = DashScopeEmbedding(
model_name="text-embedding-v2"
)
# 替换掉默认的openai的llm
Settings.llm = OpenAILike(
model="qwen-plus",
api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),
is_chat_model=True
)
#使用最常用的加载器加载文档
#https://docs.llamaindex.org.cn/en/stable/module_guides/loading/simpledirectoryreader/
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data",
exclude=['text.txt'], #过滤某些文件
exclude_hidden=True, #过滤隐藏文件
recursive=True, #递归
required_exts=['.jsonl'] #只加载
).load_data()
print(f"加载了 {len(documents)} 个文档")
#不同的切片规则
# token_splitter = TokenTextSplitter(
# chunk_size=1024,
# chunk_overlap=20
# )
# semantic_splitter = SemanticSplitterNodeParser(
# buffer_size=1,
# breakpoint_percentile_threshold=95,
# embed_model=Settings.embed_model
# )
#chunk_size:定义单块文本的最大字符/Token 数量。例如 chunk_size=1024 表示每块最多包含 1024 个字符或 Token。
#chunk_overlap:指定相邻文本块之间的重叠字符数,用于保持语义连贯性(如 chunk_overlap=200)。
#切片规则
splitter = SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=200)
#嵌入建立索引
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents,transformations=[splitter],show_progress=True)
#查询
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(streaming=True, similarity_top_k=5) # 一次检索出 5 个文档切片,默认为 2
response = query_engine.query(
"基本竞争战略是什么"
)
print(response)
#data文件夹的数据内容
#{"text":"基本竞争战略是由美国哈佛商学院著名的战略管理学家迈克尔·波特提出的,分别为:成本领先战略,差异化战略,集中化战略.企业必须从这三种战略中选择一种,作为其主导战略.要么把成本控制到比竞争者更低的程度;要么在企业产品和服务中形成与众不同的特色,让顾客感觉到你提供了比其他竞争者更多的价值;要么企业致力于服务于某一特定的市场细分,某一特定的产品种类或某一特定的地理范围."}
#{"text":"交通运行监测调度中心,简称TOCC(Transportation Operations Coordination Center)TOCC围绕综合交通运输协调体系的构建,实施交通运行的监测,预测和预警,面向公众提供交通信息服务,开展多种运输方式的调度协调,提供交通行政管理和应急处置的信息保障.\nTOCC是综合交通运行监测协调体系的核心组成部分,实现了涵盖城市道路,高速公路,国省干线三大路网,轨道交通,地面公交,出租汽车三大市内交通方式,公路客运,铁路客运,民航客运三大城际交通方式的综合运行监测和协调联动,在综合交通的政府决策,行业监管,企业运营,百姓出行方面发挥了突出的作用."}
#{"text":"美国职业摄影师协会(简称PPA)创立于1880年,是一个几乎与摄影术诞生历史一样悠久的享誉世界的非赢利性国际摄影组织,是由世界上54个国家的25000余名职业摄影师个人会员和近二百个附属组织和分支机构共同组成的,是世界上最大的专业摄影师协会.本世纪初PPA创立了美国视觉艺术家联盟及其所隶属的美国国际商业摄影师协会,美国新闻及体育摄影师协会,美国学生摄影联合会等组织.PPA在艺术,商业,纪实,体育等摄影领域一直引领世界潮流,走在世界摄影艺术与技术应用及商业规划管理的最前沿."}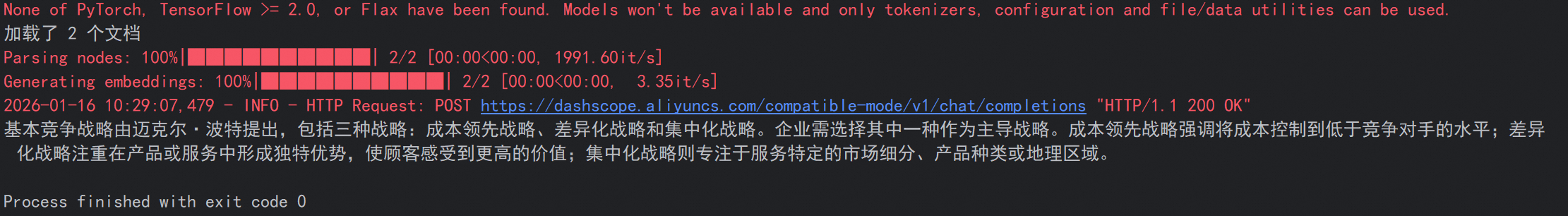
详情可以参考 RAG 简介 - LlamaIndex 框架

4. 切片规则
4.1 token 切片
适合对 Token 数量有严格要求的场景,比如使用上下文长度较小的模型时。
示例文本: "LlamaIndex是一个强大的RAG框架。它提供了多种文档处理方式。用户可以根据需要选择合适的方法。"
使用Token切片(chunk_size=10)后可能的结果:
-
切片1: "LlamaIndex是一个强大的RAG"
-
切片2: "框架。它提供了多种文"
-
切片3: "档处理方式。用户可以"
token_splitter = TokenTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1024,
chunk_overlap=20
)
evaluate_splitter(token_splitter, documents, question, ground_truth, "Token")
4.2 句子切片
这是默认的切片策略,会保持句子的完整性。
同样的文本使用句子切片后:
-
切片1: "LlamaIndex是一个强大的RAG框架。"
-
切片2: "它提供了多种文档处理方式。"
-
切片3: "用户可以根据需求选择合适的方法。"
sentence_splitter = SentenceSplitter(
chunk_size=512,
chunk_overlap=50
)
evaluate_splitter(sentence_splitter, documents, question, ground_truth, "Sentence")
4.3 句子窗口切片
每个切片都包含周围的句子作为上下文窗口。
示例文本使用句子窗口切片(window_size=1)后:
-
切片1: "LlamaIndex是一个强大的RAG框架。" 上下文: "它提供了多种文档处理方式。"
-
切片2: "它提供了多种文档处理方式。" 上下文: "LlamaIndex是一个强大的RAG框架。用户可以根据需求选择合适的方法。"
-
切片3: "用户可以根据需求选择合适的方法。" 上下文: "它提供了多种文档处理方式。"
sentence_window_splitter = SentenceWindowNodeParser.from_defaults(
window_size=3,
window_metadata_key="window",
original_text_metadata_key="original_text"
)注意:句子窗口切片需要特殊的后处理器
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(
similarity_top_k=5,
streaming=True,
node_postprocessors=[MetadataReplacementPostProcessor(target_metadata_key="window")]
)
evaluate_splitter(sentence_window_splitter, documents, question, ground_truth, "Sentence Window")
4.4 语义切片
根据语义相关性自适应地选择切片点。
示例文本: "LlamaIndex是一个强大的RAG框架。它提供了多种文档处理方式。用户可以根据需求选择合适的方法。此外,它还支持向量检索。这种检索方式非常高效。"
语义切片可能的结果:
-
切片1: "LlamaIndex是一个强大的RAG框架。它提供了多种文档处理方式。用户可以根据需求选择合适的方法。"
-
切片2: "此外,它还支持向量检索。这种检索方式非常高效。" (注意这里是按语义相关性分组的)
semantic_splitter = SemanticSplitterNodeParser(
buffer_size=1,
breakpoint_percentile_threshold=95,
embed_model=Settings.embed_model
)
evaluate_splitter(semantic_splitter, documents, question, ground_truth, "Semantic")