目录
[1. 什么是 Node.js?](#1. 什么是 Node.js?)
[2. 什么是前端工程化?](#2. 什么是前端工程化?)
[3. Node.js 为何能执行 JS?](#3. Node.js 为何能执行 JS?)
[4. Node.js 安装](#4. Node.js 安装)
[5. 使用 Node.js](#5. 使用 Node.js)
[6. fs 模块 - 读写文件](#6. fs 模块 - 读写文件)
[7. path 模块 - 路径处理](#7. path 模块 - 路径处理)
[8. 案例 - 压缩前端 html](#8. 案例 - 压缩前端 html)
[9. URL 中的端口号](#9. URL 中的端口号)
[10. 常见的服务程序](#10. 常见的服务程序)
[11. http 模块-创建 Web 服务](#11. http 模块-创建 Web 服务)
[12. 案例 - 浏览时钟](#12. 案例 - 浏览时钟)
1. 什么是 Node.js?
作用:使用 Node.js 编写服务器端程序
- ✓ 编写数据接口,提供网页资源浏览功能等等
- ✓ 前端工程化:为后续学习 Vue 和 React 等框架做铺垫
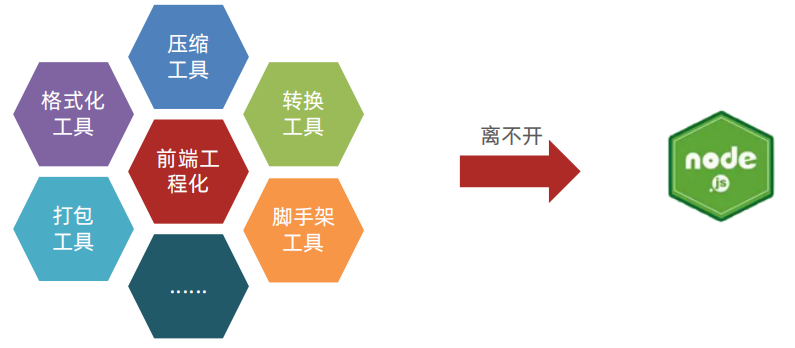
2. 什么是前端工程化?
前端工程化:开发项目直到上线,过程中集成的所有 工具和技术
Node.js 是前端工程化的基础(因为 Node.js 可以主动读取前端代码内容)
3. Node.js 为何能执行 JS?
首先:浏览器能执行 JS 代码,依靠的是内核中的 V8 引擎 (C++ 程序)
其次:Node.js 是基于 Chrome V8 引擎进行封装(运行环境)
区别:都支持 ECMAScript 标准语法,Node.js 有独立的 API

4. Node.js 安装
要求:下载 node-v 16.19.0 .msi 安装程序(指定版本:兼容 vue-admin-template 模板)
安装过程:默认下一步即可
注释事项:
-
- 安装在非中文路径下
-
- 无需勾选自动安装其他配套软件
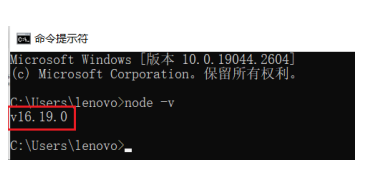
成功验证:
-
- 打开 cmd 终端,输入 node -v 命令查看版本号
-
- 如果有显示,则代表安装成功
5. 使用 Node.js
需求:新建 JS 文件,并编写代码后,在 node 环境下执行
命令:在 VSCode 集成终端中,输入 node xxx.js,回车即可执行

6. fs 模块 - 读写文件
模块:类似插件,封装了 方法/属性
fs 模块:封装了与本机文件系统进行交互的,方法/属性
语法:
-
- 加载 fs 模块对象
-
- 写入文件内容
-
- 读取文件内容
javascript
/**
* 目标:基于 fs 模块读写文件内容
* 1. 加载 fs 模块对象
* 2. 写入文件内容
* 3. 读取文件内容
*/
// 1. 加载 fs 模块对象
const fs = require('fs')
// 2. 写入文件内容
fs.writeFile('./test.txt', 'hello, Node.js', (err) => {
if (err) console.log(err)
else console.log('写入成功')
})
// 3. 读取文件内容
fs.readFile('./test.txt', (err, data) => {
if (err) console.log(err)
// data 是 buffer 16 进制数据流对象
// .toString() 转换成字符串
else console.log(data.toString())
})7. path 模块 - 路径处理
问题:Node.js 代码中,相对路径是根据 终端所在路径 来查找的,可能无法找到你想要的文件
建议:在 Node.js 代码中,使用 绝对路径
补充: __dirname 内置变量(获取当前模块目录-绝对路径)
✓ windows: D:\备课代码\3-B站课程\03_Node.js与Webpack\03-code\03
✓ mac: /Users/xxx/Desktop/备课代码/3-B站课程/03_Node.js与Webpack/03-code/03
注意: path.join() 会使用特定于平台的分隔符,作为定界符,将所有给定的路径片段连接在一起
语法:
-
- 加载 path 模块
-
- 使用 path.join 方法,拼接路径
javascript
/**
* 目标:在 Node.js 环境的代码中,应使用绝对路径
* 原因:代码的相对路径是以终端所在文件夹为起点,而不是 Vscode 资源管理器
* 容易造成目标文件找不到的错误
*/
const fs = require('fs')
// 1. 引入 path 模块对象
const path = require('path')
// 2. 调用 path.join() 配合 __dirname 组成目标文件的绝对路径
console.log(__dirname)
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, '../test.txt'), (err, data) => {
if (err) console.log(err)
else console.log(data.toString())
})8. 案例 - 压缩前端 html
需求:把 回车符(\r)和换行符(\n)去掉后,写入到新 html 文件中
步骤:
-
- 读取源 html 文件内容
-
- 正则替换字符串
-
- 写入到新的 html 文件中
javascript
/**
* 目标1:压缩 html 代码
* 需求:把回车符 \r,换行符 \n 去掉,写入到新 html 文件中
* 1.1 读取源 html 文件内容
* 1.2 正则替换字符串
* 1.3 写入到新的 html 文件中
*/
// 1.1 读取源 html 文件内容
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, 'public/index.html'), (err, data) => {
if (err) console.log(err)
else {
const htmlStr = data.toString()
// 1.2 正则替换字符串
const resultStr = htmlStr.replace(/[\r\n]/g, '')
console.log(resultStr)
// 1.3 写入到新的 html 文件中
fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname, 'dist/index.html'), resultStr, err => {
if (err) console.log(err)
else console.log('写入成功')
})
}
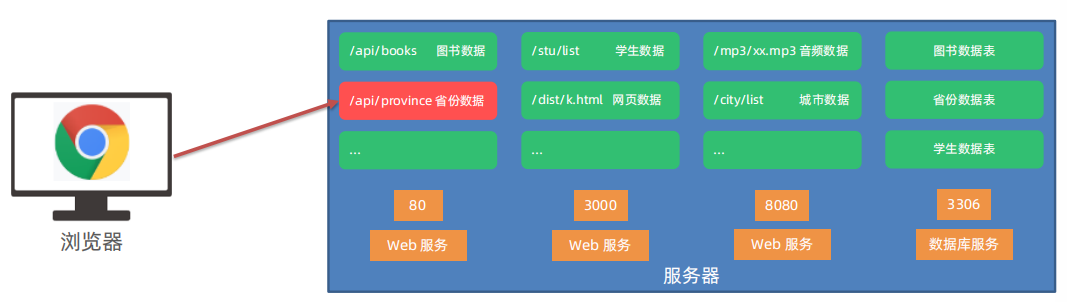
})9. URL 中的端口号
URL: 统一资源定位符,简称网址,用于访问服务器里的资源
端口号:标记服务器里不同功能的 服务程序
端口号范围:0-65535 之间的任意整数

注意:http 协议, 默认 访问 80 端口
10. 常见的服务程序
Web 服务程序 :用于提供网上信息浏览功能
注意:0-1023 和一些特定端口号被占用,我们自己编写服务程序请避开使用
11. http 模块-创建 Web 服务
需求:创建 Web 服务并响应内容给浏览器
步骤:
- 加载 http 模块 ,创建 Web 服务对象
- 监听 request 请求事件,设置响应头和响应体
- 配置 端口号 并 启动 Web 服务
- 浏览器请求 http:// localhost :3000 测试 (localhost:固定代表本机的域名)
javascript
/**
* 目标:基于 http 模块创建 Web 服务程序
* 1.1 加载 http 模块,创建 Web 服务对象
* 1.2 监听 request 请求事件,设置响应头和响应体
* 1.3 配置端口号并启动 Web 服务
* 1.4 浏览器请求(http://localhost:3000)测试
*/
// 1.1 加载 http 模块,创建 Web 服务对象
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer()
// 1.2 监听 request 请求事件,设置响应头和响应体
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// 设置响应头-内容类型-普通文本以及中文编码格式
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain;charset=utf-8')
// 设置响应体内容,结束本次请求与响应
res.end('欢迎使用 Node.js 和 http 模块创建的 Web 服务')
})
// 1.3 配置端口号并启动 Web 服务
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Web 服务启动成功了')
})12. 案例 - 浏览时钟
需求:基于 Web 服务,开发提供 网页资源 的功能

步骤:
-
- 基于 http 模块,创建 Web 服务
-
- 使用 req.url 获取请求资源路径,判断并读取 index.html 里字符串内容返回给请求方
-
- 其他路径,暂时返回不存在的提示
-
- 运行 Web 服务,用浏览器发起请求测试
javascript
/**
* 目标:基于 Web 服务,开发提供网页资源的功能
* 步骤:
* 1. 基于 http 模块,创建 Web 服务
* 2. 使用 req.url 获取请求资源路径,并读取 index.html 里字符串内容返回给请求方
* 3. 其他路径,暂时返回不存在提示
* 4. 运行 Web 服务,用浏览器发起请求
*/
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
// 1. 基于 http 模块,创建 Web 服务
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer()
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// 2. 使用 req.url 获取请求资源路径,并读取 index.html 里字符串内容返回给请求方
if (req.url === '/index.html') {
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, 'dist/index.html'), (err, data) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html;charset=utf-8')
res.end(data.toString())
})
} else {
// 3. 其他路径,暂时返回不存在提示
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html;charset=utf-8')
res.end('你要访问的资源路径不存在')
}
})
server.listen(8080, () => {
console.log('Web 服务启动成功了')
})