引言:那个让我重写三遍的继承链
还记得两年前维护一个电商系统时,遇到了这样的继承噩梦:
kotlin
// 继承地狱
open class BaseUser {
open fun login() { }
open fun logout() { }
}
open class PremiumUser : BaseUser() {
override fun login() { /* 增强登录 */ }
open fun accessPremiumFeatures() { }
}
class VIPUser : PremiumUser() {
override fun login() { /* VIP登录 */ }
override fun accessPremiumFeatures() { /* VIP特权 */ }
fun getDiscount() { }
}
// 新需求:临时会员(需要登录增强,但不是Premium)
class TemporaryUser : BaseUser() { // ❌ 无法复用PremiumUser的login
override fun login() {
// 只能复制粘贴PremiumUser的login代码
}
}问题 :需要复用PremiumUser的登录增强功能,但又不想继承整个Premium体系。这时候我才理解了 "组合优于继承" 的智慧。
后来用委托模式重构:
kotlin
// 接口 + 委托
interface LoginBehavior {
fun login()
}
class EnhancedLogin : LoginBehavior {
override fun login() {
println("增强登录逻辑")
}
}
// 使用委托
class TemporaryUser(
loginBehavior: LoginBehavior
) : LoginBehavior by loginBehavior // 委托!
val tempUser = TemporaryUser(EnhancedLogin())
tempUser.login() // 调用EnhancedLogin的实现代码量减少70%,灵活性提升100%! 这就是Kotlin委托的威力。
今天,我们就来深入探索Kotlin的委托机制,看看如何用"组合"的思想优雅地解决继承的问题。
委托模式:设计模式的基石
什么是委托
委托(Delegation) 是一种设计模式:一个对象将某些操作委托给另一个对象来处理。
类比:就像老板(委托者)把具体工作委托给助理(被委托者)完成,老板只需要下达指令。
kotlin
// 不使用委托:老板事必躬亲
class Boss {
fun scheduleMeeting() {
// 老板自己安排会议
println("查看日历...")
println("发送邀请...")
println("预定会议室...")
}
}
// 使用委托:老板委托给助理
interface MeetingScheduler {
fun scheduleMeeting()
}
class Assistant : MeetingScheduler {
override fun scheduleMeeting() {
println("助理安排会议...")
}
}
class Boss(private val assistant: MeetingScheduler) {
fun scheduleMeeting() {
assistant.scheduleMeeting() // 委托给助理
}
}委托 vs 继承
| 对比维度 | 继承 | 委托 |
|---|---|---|
| 关系 | is-a(是一个) | has-a(有一个) |
| 耦合度 | 高(父子强耦合) | 低(通过接口) |
| 灵活性 | 低(编译时确定) | 高(运行时可变) |
| 复用性 | 单继承限制 | 可组合多个 |
| 修改影响 | 父类变化影响子类 | 隔离变化 |
继承的问题:
kotlin
// ❌ 继承的限制
open class Bird {
open fun fly() { println("Flying...") }
}
class Penguin : Bird() {
override fun fly() {
throw UnsupportedOperationException("Penguins can't fly!")
}
}
// 企鹅不会飞,但继承了fly方法,违反里氏替换原则委托的解决方案:
kotlin
// ✅ 用委托解决
interface Flyable {
fun fly()
}
class FlyingBehavior : Flyable {
override fun fly() { println("Flying...") }
}
class NoFlyBehavior : Flyable {
override fun fly() { println("Can't fly") }
}
class Bird(private val flyBehavior: Flyable) : Flyable by flyBehavior
val sparrow = Bird(FlyingBehavior())
sparrow.fly() // "Flying..."
val penguin = Bird(NoFlyBehavior())
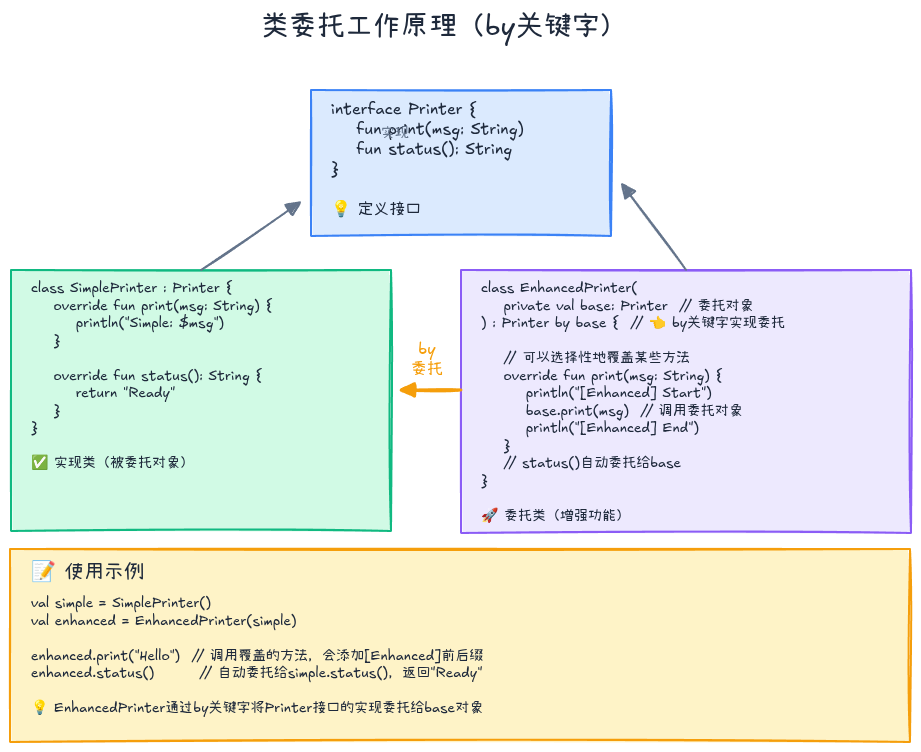
penguin.fly() // "Can't fly"Kotlin的类委托:by关键字
基本用法
Kotlin通过by关键字原生支持委托模式:
kotlin
interface Printer {
fun print(message: String)
fun getStatus(): String
}
class ConsolePrinter : Printer {
override fun print(message: String) {
println("Console: $message")
}
override fun getStatus(): String = "Console Printer Ready"
}
// 使用by委托
class LoggingPrinter(
private val printer: Printer
) : Printer by printer { // 委托所有方法给printer
// 可以选择性覆盖某些方法
override fun print(message: String) {
println("[LOG] Printing...")
printer.print(message) // 调用被委托对象的方法
}
}
val printer = LoggingPrinter(ConsolePrinter())
printer.print("Hello") // 覆盖的方法
println(printer.getStatus()) // 委托的方法工作原理:
kotlin
// 编译器生成的代码(简化版)
class LoggingPrinter(private val printer: Printer) : Printer {
override fun print(message: String) {
println("[LOG] Printing...")
printer.print(message)
}
// 编译器自动生成
override fun getStatus(): String {
return printer.getStatus()
}
}
多接口委托
可以同时委托多个接口:
kotlin
interface Clickable {
fun click()
}
interface Focusable {
fun focus()
fun blur()
}
class ClickHandler : Clickable {
override fun click() { println("Clicked") }
}
class FocusHandler : Focusable {
override fun focus() { println("Focused") }
override fun blur() { println("Blurred") }
}
// 委托多个接口
class Button(
clickHandler: Clickable,
focusHandler: Focusable
) : Clickable by clickHandler,
Focusable by focusHandler {
fun render() {
println("Rendering button")
}
}
val button = Button(ClickHandler(), FocusHandler())
button.click() // 委托给ClickHandler
button.focus() // 委托给FocusHandler
button.render() // Button自己的方法实战案例:装饰器模式
使用委托实现装饰器模式:
kotlin
interface DataSource {
fun readData(): String
fun writeData(data: String)
}
class FileDataSource(private val filename: String) : DataSource {
override fun readData(): String {
println("Reading from file: $filename")
return "file content"
}
override fun writeData(data: String) {
println("Writing to file: $filename")
}
}
// 加密装饰器
class EncryptionDecorator(
private val dataSource: DataSource
) : DataSource by dataSource {
override fun readData(): String {
val data = dataSource.readData()
return decrypt(data)
}
override fun writeData(data: String) {
val encrypted = encrypt(data)
dataSource.writeData(encrypted)
}
private fun encrypt(data: String) = "encrypted($data)"
private fun decrypt(data: String) = data.removePrefix("encrypted(").removeSuffix(")")
}
// 压缩装饰器
class CompressionDecorator(
private val dataSource: DataSource
) : DataSource by dataSource {
override fun readData(): String {
val data = dataSource.readData()
return decompress(data)
}
override fun writeData(data: String) {
val compressed = compress(data)
dataSource.writeData(compressed)
}
private fun compress(data: String) = "compressed($data)"
private fun decompress(data: String) = data.removePrefix("compressed(").removeSuffix(")")
}
// 组合使用
val dataSource = CompressionDecorator(
EncryptionDecorator(
FileDataSource("data.txt")
)
)
dataSource.writeData("Hello World")
// 输出:Writing to file: data.txt
// 数据经过加密和压缩
val data = dataSource.readData()
// 读取并解压、解密**委托的优势**: - 减少样板代码:编译器自动生成转发方法 - 灵活组合:可以运行时替换委托对象 - 选择性覆盖:只重写需要定制的方法 - 遵循开闭原则:对扩展开放,对修改封闭
属性委托:懒加载与可观察属性
什么是属性委托
属性委托允许将属性的get和set操作委托给另一个对象:
kotlin
class Example {
var property: String by Delegate() // 属性委托
}
class Delegate {
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): String {
return "$thisRef, thank you for delegating '${property.name}' to me!"
}
operator fun setValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>, value: String) {
println("$value has been assigned to '${property.name}' in $thisRef.")
}
}工作原理:
kotlin
// 编译器生成的代码
class Example {
private val property$delegate = Delegate()
var property: String
get() = property$delegate.getValue(this, ::property)
set(value) {
property$delegate.setValue(this, ::property, value)
}
}标准委托:lazy
懒加载:只在第一次访问时初始化,后续返回缓存值。
kotlin
// 基本用法
class HeavyObject {
val expensiveData: String by lazy {
println("Computing expensive data...")
Thread.sleep(1000) // 模拟耗时操作
"Computed Result"
}
}
val obj = HeavyObject()
println("Object created")
println(obj.expensiveData) // 第一次访问:计算并缓存
println(obj.expensiveData) // 第二次访问:直接返回缓存
// 输出:
// Object created
// Computing expensive data...
// Computed Result
// Computed Resultlazy的模式:
kotlin
// 1. SYNCHRONIZED(默认):线程安全
val lazyValue: String by lazy {
println("Computed once")
"Value"
}
// 2. PUBLICATION:可能被多次初始化,但只有一个值会被使用
val lazyPublic: String by lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode.PUBLICATION) {
"Value"
}
// 3. NONE:不加锁,非线程安全(性能最优)
val lazyUnsafe: String by lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode.NONE) {
"Value"
}实际应用:
kotlin
class UserRepository {
// 延迟初始化数据库连接
private val database: Database by lazy {
println("Initializing database connection...")
Database.connect()
}
// 延迟初始化API客户端
private val apiClient: ApiClient by lazy {
println("Creating API client...")
ApiClient(endpoint = "https://api.example.com")
}
fun getUser(id: String): User {
return database.queryUser(id) // 首次访问时才初始化database
}
fun fetchUser(id: String): User {
return apiClient.getUser(id) // 首次访问时才初始化apiClient
}
}标准委托:observable
可观察属性:属性值变化时触发回调。
kotlin
class User {
var name: String by Delegates.observable("<no name>") { prop, old, new ->
println("${prop.name}: $old -> $new")
}
var age: Int by Delegates.observable(0) { _, old, new ->
println("Age changed: $old -> $new")
}
}
val user = User()
user.name = "Alice" // name: <no name> -> Alice
user.name = "Bob" // name: Alice -> Bob
user.age = 25 // Age changed: 0 -> 25实际应用:MVVM模式:
kotlin
class UserViewModel {
// 可观察属性,变化时自动通知UI
var username: String by Delegates.observable("") { _, _, newValue ->
notifyUI("username", newValue)
}
var isLoading: Boolean by Delegates.observable(false) { _, _, newValue ->
notifyUI("isLoading", newValue)
}
private fun notifyUI(propertyName: String, value: Any) {
println("Notify UI: $propertyName = $value")
// 实际项目中会通知LiveData或StateFlow
}
fun login(username: String) {
isLoading = true // 自动通知UI显示加载状态
this.username = username // 自动通知UI更新用户名
// ... 登录逻辑
isLoading = false // 自动通知UI隐藏加载状态
}
}标准委托:vetoable
可否决属性:在设置新值前进行验证,可以拒绝修改。
kotlin
class Product {
var price: Double by Delegates.vetoable(0.0) { _, oldValue, newValue ->
// 返回true接受新值,返回false拒绝修改
newValue >= 0 // 价格不能为负数
}
var stock: Int by Delegates.vetoable(0) { _, _, newValue ->
newValue >= 0 // 库存不能为负数
}
}
val product = Product()
product.price = 99.99 // ✅ 接受
println(product.price) // 99.99
product.price = -10.0 // ❌ 拒绝
println(product.price) // 99.99(保持不变)
product.stock = 100 // ✅ 接受
product.stock = -5 // ❌ 拒绝
println(product.stock) // 100实际应用:表单验证:
kotlin
class RegistrationForm {
var email: String by Delegates.vetoable("") { _, _, newValue ->
isValidEmail(newValue)
}
var password: String by Delegates.vetoable("") { _, _, newValue ->
newValue.length >= 8 // 密码至少8位
}
var age: Int by Delegates.vetoable(0) { _, _, newValue ->
newValue in 18..120 // 年龄在18-120之间
}
private fun isValidEmail(email: String): Boolean {
return email.contains("@") && email.contains(".")
}
fun isValid(): Boolean {
return email.isNotEmpty() && password.isNotEmpty() && age >= 18
}
}
val form = RegistrationForm()
form.email = "invalid" // ❌ 拒绝
form.email = "user@test.com" // ✅ 接受
form.password = "123" // ❌ 拒绝(太短)
form.password = "securepass123" // ✅ 接受
form.age = 15 // ❌ 拒绝(未成年)
form.age = 25 // ✅ 接受标准委托:notNull
非空延迟初始化 :比lateinit更灵活,支持基本类型。
kotlin
class Config {
// lateinit只能用于var,且不支持基本类型
// lateinit var port: Int // ❌ 编译错误
// notNull支持所有类型
var port: Int by Delegates.notNull()
var host: String by Delegates.notNull()
fun initialize() {
port = 8080
host = "localhost"
}
}
val config = Config()
// println(config.port) // ❌ 抛出IllegalStateException
config.initialize()
println(config.port) // ✅ 8080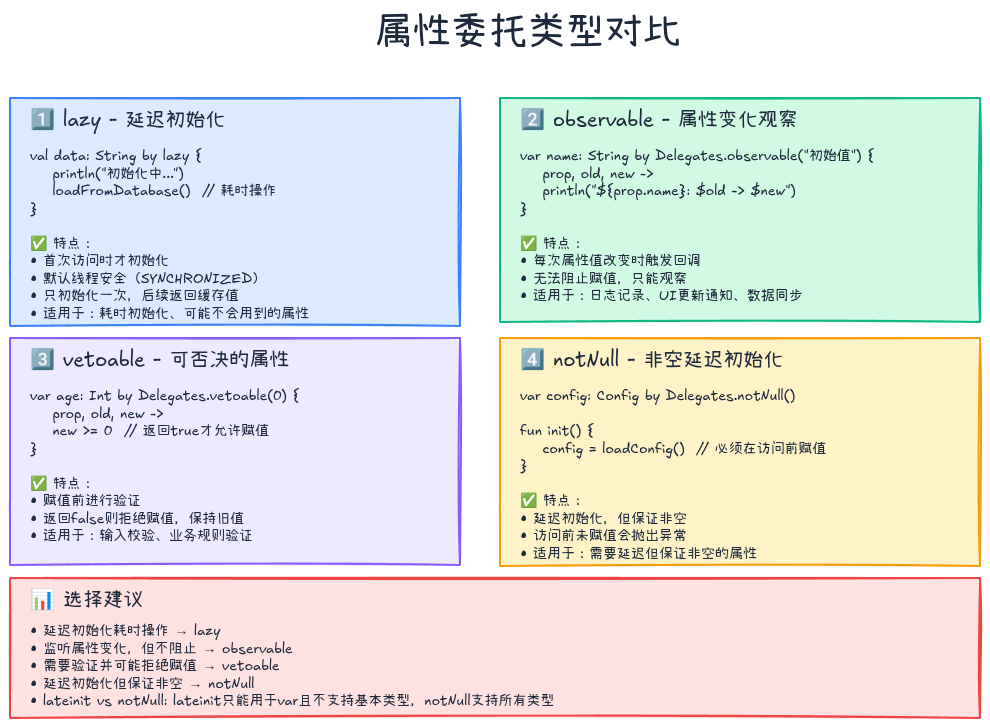
自定义委托:构建可复用的属性行为
实现自定义委托
kotlin
// 只读属性委托(只需要getValue)
class ReadOnlyDelegate(private val value: String) {
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): String {
return value
}
}
// 读写属性委托(需要getValue和setValue)
class MutableDelegate(private var value: String) {
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): String {
return value
}
operator fun setValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>, newValue: String) {
value = newValue
}
}
class Example {
val readOnly: String by ReadOnlyDelegate("constant")
var mutable: String by MutableDelegate("initial")
}实战案例1:SharedPreferences委托
kotlin
// Android SharedPreferences委托
class PreferenceDelegate<T>(
private val key: String,
private val defaultValue: T
) {
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): T {
val prefs = getSharedPreferences() // 获取SharedPreferences
return when (defaultValue) {
is String -> prefs.getString(key, defaultValue as String) as T
is Int -> prefs.getInt(key, defaultValue as Int) as T
is Boolean -> prefs.getBoolean(key, defaultValue as Boolean) as T
is Float -> prefs.getFloat(key, defaultValue as Float) as T
is Long -> prefs.getLong(key, defaultValue as Long) as T
else -> throw IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported type")
}
}
operator fun setValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>, value: T) {
val editor = getSharedPreferences().edit()
when (value) {
is String -> editor.putString(key, value)
is Int -> editor.putInt(key, value)
is Boolean -> editor.putBoolean(key, value)
is Float -> editor.putFloat(key, value)
is Long -> editor.putLong(key, value)
else -> throw IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported type")
}
editor.apply()
}
}
// 使用
class AppSettings {
var username: String by PreferenceDelegate("username", "")
var isLoggedIn: Boolean by PreferenceDelegate("is_logged_in", false)
var fontSize: Int by PreferenceDelegate("font_size", 14)
}
val settings = AppSettings()
settings.username = "Alice" // 自动保存到SharedPreferences
println(settings.username) // 自动从SharedPreferences读取实战案例2:带范围验证的委托
kotlin
class RangeDelegate<T : Comparable<T>>(
private var value: T,
private val range: ClosedRange<T>
) {
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): T {
return value
}
operator fun setValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>, newValue: T) {
if (newValue in range) {
value = newValue
} else {
throw IllegalArgumentException(
"${property.name} must be in range $range, but got $newValue"
)
}
}
}
// 扩展函数简化使用
fun <T : Comparable<T>> range(initial: T, range: ClosedRange<T>) =
RangeDelegate(initial, range)
class GameCharacter {
var health: Int by range(100, 0..100)
var level: Int by range(1, 1..100)
var experience: Int by range(0, 0..Int.MAX_VALUE)
}
val character = GameCharacter()
character.health = 80 // ✅
// character.health = 150 // ❌ 抛出异常
character.level = 10 // ✅
println("Character: HP=${character.health}, Level=${character.level}")实战案例3:带历史记录的委托
kotlin
class HistoryDelegate<T>(initialValue: T) {
private val history = mutableListOf(initialValue)
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): T {
return history.last()
}
operator fun setValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>, value: T) {
history.add(value)
}
fun getHistory(): List<T> = history.toList()
fun undo(): T? {
return if (history.size > 1) {
history.removeLast()
history.last()
} else {
null
}
}
}
class TextEditor {
private val contentDelegate = HistoryDelegate("")
var content: String by contentDelegate
fun undo() {
contentDelegate.undo()
}
fun showHistory() {
println("Edit history:")
contentDelegate.getHistory().forEachIndexed { index, value ->
println(" $index: $value")
}
}
}
val editor = TextEditor()
editor.content = "Hello"
editor.content = "Hello World"
editor.content = "Hello Kotlin"
editor.showHistory()
// Edit history:
// 0:
// 1: Hello
// 2: Hello World
// 3: Hello Kotlin
editor.undo()
println(editor.content) // "Hello World"Map委托:将Map用作属性存储
Kotlin标准库提供了将Map用作属性委托的功能:
kotlin
class User(map: Map<String, Any?>) {
val name: String by map
val age: Int by map
val email: String? by map // 可空属性
}
val userMap = mapOf(
"name" to "Alice",
"age" to 25,
"email" to "alice@example.com"
)
val user = User(userMap)
println(user.name) // Alice
println(user.age) // 25
println(user.email) // alice@example.com可变Map委托:
kotlin
class MutableUser(map: MutableMap<String, Any?>) {
var name: String by map
var age: Int by map
}
val userMap = mutableMapOf<String, Any?>()
val user = MutableUser(userMap)
user.name = "Bob"
user.age = 30
println(userMap) // {name=Bob, age=30}实际应用:JSON解析:
kotlin
// 简化JSON对象的属性访问
class JsonObject(private val map: Map<String, Any?>) {
val id: String by map
val title: String by map
val userId: Int by map
val completed: Boolean by map
}
val json = mapOf(
"id" to "1",
"title" to "Task 1",
"userId" to 123,
"completed" to false
)
val obj = JsonObject(json)
println("${obj.title} by user ${obj.userId}")
委托的最佳实践
1. 优先使用委托而非继承
kotlin
// ❌ 不好:使用继承
open class Logger {
open fun log(message: String) {
println("[LOG] $message")
}
}
class NetworkLogger : Logger() {
override fun log(message: String) {
super.log("Network: $message")
}
}
// ✅ 好:使用委托
interface Logger {
fun log(message: String)
}
class ConsoleLogger : Logger {
override fun log(message: String) {
println("[LOG] $message")
}
}
class NetworkLogger(
private val logger: Logger
) : Logger by logger {
override fun log(message: String) {
logger.log("Network: $message")
}
}2. 合理使用lazy提升性能
kotlin
// ✅ 好:懒加载重对象
class ViewModel {
private val repository: Repository by lazy {
createRepository() // 只在需要时创建
}
private val analytics: Analytics by lazy {
Analytics.initialize()
}
}
// ❌ 不好:立即初始化所有对象
class ViewModel {
private val repository = createRepository() // 即使不用也会创建
private val analytics = Analytics.initialize()
}3. 自定义委托要考虑线程安全
kotlin
// ❌ 不安全:没有同步
class UnsafeDelegate<T>(private var value: T) {
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): T = value
operator fun setValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>, newValue: T) {
value = newValue // 多线程不安全
}
}
// ✅ 安全:使用同步
class SafeDelegate<T>(private var value: T) {
private val lock = Any()
operator fun getValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>): T {
synchronized(lock) {
return value
}
}
operator fun setValue(thisRef: Any?, property: KProperty<*>, newValue: T) {
synchronized(lock) {
value = newValue
}
}
}4. 使用扩展函数简化委托创建
kotlin
// 创建便捷的工厂函数
fun <T> cached(compute: () -> T): Lazy<T> = lazy(compute)
fun <T : Comparable<T>> rangeValidated(initial: T, range: ClosedRange<T>) =
RangeDelegate(initial, range)
// 使用
class Config {
val heavyConfig by cached {
loadConfigFromFile()
}
var port by rangeValidated(8080, 1024..65535)
}常见问题解答
Q1: lazy和lateinit有什么区别?
A:
| 特性 | lazy | lateinit |
|---|---|---|
| 初始化时机 | 首次访问 | 手动初始化 |
| 线程安全 | 默认安全 | 需自行保证 |
| 支持类型 | 所有类型 | 非空引用类型 |
| 只读/可变 | 只读(val) | 可变(var) |
| 初始化逻辑 | lambda表达式 | 赋值语句 |
kotlin
class Example {
// lazy:自动初始化,线程安全
val config: Config by lazy {
Config.load()
}
// lateinit:手动初始化
lateinit var database: Database
fun init() {
database = Database.connect()
}
// lateinit不支持基本类型
// lateinit var count: Int // ❌ 编译错误
// lazy支持所有类型
val count: Int by lazy { 0 } // ✅
}Q2: 委托会影响性能吗?
A: 影响很小,几乎可以忽略:
kotlin
// 委托版本
class Delegated(printer: Printer) : Printer by printer
// 等价的手写版本
class Manual(private val printer: Printer) : Printer {
override fun print(msg: String) = printer.print(msg)
}
// 性能差异:委托只是多了一次方法调用,现代JVM会内联优化建议:
- 属性委托在访问时有轻微开销(getter/setter调用)
- lazy首次访问有同步开销,后续访问直接返回缓存值
- 不要在性能关键路径上过度使用委托
Q3: 何时使用类委托,何时使用属性委托?
A:
类委托:整个接口的行为需要委托
kotlin
// 整个Printer接口的行为都委托
class LoggingPrinter(printer: Printer) : Printer by printer属性委托:单个属性的访问逻辑需要委托
kotlin
// 只有属性的get/set需要特殊处理
class User {
var name: String by observable("") { _, _, new ->
println("Name changed to $new")
}
}Q4: 可以链式委托吗?
A: 可以,委托可以多层嵌套:
kotlin
interface Logger {
fun log(message: String)
}
class ConsoleLogger : Logger {
override fun log(message: String) {
println(message)
}
}
class TimestampLogger(private val logger: Logger) : Logger by logger {
override fun log(message: String) {
logger.log("[${System.currentTimeMillis()}] $message")
}
}
class PrefixLogger(private val logger: Logger, private val prefix: String) : Logger by logger {
override fun log(message: String) {
logger.log("$prefix: $message")
}
}
// 链式组合
val logger = PrefixLogger(
TimestampLogger(
ConsoleLogger()
),
"APP"
)
logger.log("Hello")
// 输出:APP: [1642384920123] Hello练习题
练习1:实现线程安全的单例委托
kotlin
// TODO: 实现一个线程安全的单例委托
class SingletonDelegate<T>(private val initializer: () -> T) {
// 实现 getValue
}
// 使用
class DatabaseManager {
companion object {
val instance: DatabaseManager by SingletonDelegate {
DatabaseManager()
}
}
}练习2:实现带过期时间的缓存委托
kotlin
// TODO: 实现一个带过期时间的缓存委托
// 提示:保存值和时间戳,超过ttl返回null并重新计算
class CachedDelegate<T>(
private val ttlMillis: Long,
private val compute: () -> T
) {
// 实现 getValue
}
// 使用
class DataService {
val cachedData: String by CachedDelegate(5000) {
// 5秒缓存
fetchDataFromNetwork()
}
}练习3:实现可撤销修改的委托
kotlin
// TODO: 实现支持commit和rollback的委托
class TransactionalDelegate<T>(initialValue: T) {
// 实现 getValue, setValue, commit, rollback
}
// 使用
class Form {
private val nameDelegate = TransactionalDelegate("")
var name: String by nameDelegate
fun save() {
nameDelegate.commit()
}
fun cancel() {
nameDelegate.rollback()
}
}总结
Kotlin的委托机制是实现"组合优于继承"设计原则的强大工具。
核心要点回顾
-
类委托(by关键字)
- 将接口实现委托给其他对象
- 减少样板代码,提高代码复用
- 支持选择性覆盖方法
-
属性委托
- 标准委托:
lazy、observable、vetoable、notNull - 自定义委托:实现
getValue和setValue - Map委托:将Map用作属性存储
- 标准委托:
-
委托 vs 继承
- 委托更灵活:运行时可变,支持组合多个行为
- 继承更简单:编译时确定,单继承限制
- 优先使用委托,除非真的是"is-a"关系
最佳实践
- ✅ 优先使用委托而非继承
- ✅ 使用
lazy延迟初始化重对象 - ✅ 使用
observable实现响应式属性 - ✅ 自定义委托时考虑线程安全
- ✅ 用扩展函数简化委托创建
- ✅ Map委托简化JSON/配置对象
委托的设计哲学
委托体现了Kotlin的三个核心理念:
- 简洁性 - 用
by关键字消除样板代码 - 安全性 - 编译期检查委托契约
- 实用性 - 提供标准委托解决常见问题
相关资料
系列文章导航:
- 👉 上一篇: 泛型进阶:从型变到具体化类型参数的类型安全之旅
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、分享!有任何问题或建议,欢迎在评论区留言讨论。让我们一起学习,一起成长!
也欢迎访问我的个人主页发现更多宝藏资源