什么是设计模式?
设计模式是指在软件开发过程中,针对反复出现的问题所总结归纳出的通用解决方案;
这些方案是众多软件开发人员经过长期实践和总结得出的,
它们可以帮助开发者更高效、更可靠地构建软件系统:
设计模式根据其目的和用途,通常被分为三大类:创建型模式、结构型模式和行为型模式
·创建型模式:主要关注对象的创建过程,提高系统的灵活性和可扩展性
·结构型模式:关注类和对象的组合,优化系统结构,简化复杂的层次关系;
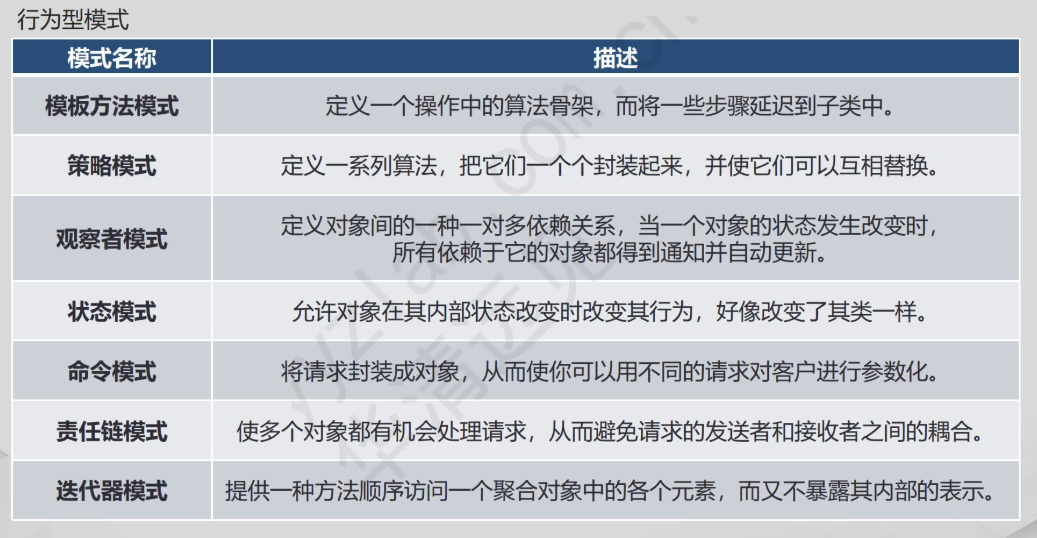
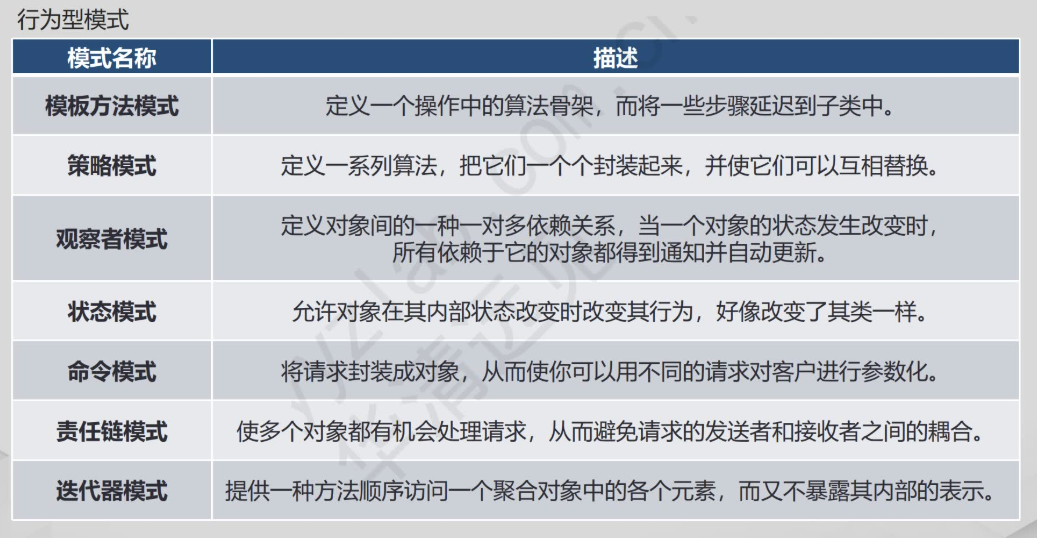
·行为型模式:关注对象之间的通信和职责分配,提高对象之间的交互效率和灵活性,

单例模式是一种创建型设计模式, 它确保一个类只有一个实例, 并提供一个全局访问点来获取该实例。 唯一性: 在整个应用程序生命周期中, 类的实例只有一个; 全局访问: 通过统一的接口访问该实例, 避免重复创建对象;
核心思想: 控制实例化过程: 将类的构造函数设为私有(或受保护) , 防止外部直接实例化对象; 类的内部负责创建和管理唯一实例;
提供唯一的访问入口: 提供一个静态方法, 用于返回类的唯一实例; 确保所有代码都通过该入口访问实例, 避免创建多个对象;
实现方式
饿汉式程序启动时创建实例,天然线程安全实例资源占用小、必被使用
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//单例模式之饿汉式
class Singleton{
public:
//3.提供一个公有的静态方法来获取唯一对象
static Singleton& getInstance(){
cout << "&sing = " << &sing << endl;
return sing;
}
int data; //数据
private:
//1.构造函数私有化
Singleton(int value):data(value){
cout << "Singleton(int value)" << endl;
}
//2.提供一个私有的静态成员变量来维护唯一对象
static Singleton sing;
};
//静态成员变量必须在类外完成初始化
Singleton Singleton::sing(10);
int main(){
//实例化对象 一旦构造函数私有化,就不能在类外进行实例化对象
//Singleton s1(10);
//访问唯一的对象
Singleton& s1 = Singleton::getInstance();
cout << "&s1 = " << &s1 << endl;
cout << "s1.data = " << s1.data << endl;
cout << "-----------------------" << endl;
Singleton& s2 = Singleton::getInstance();
cout << "&s2 = " << &s2 << endl;
cout << "s2.data = " << s2.data << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SingletonHungry {
public:
// 全局访问入口:直接返回已创建的静态实例
static SingletonHungry& getInstance() {
return instance;
}
void show() { cout << "饿汉式实例地址:" << this << endl; }
// 禁用拷贝/赋值,保证实例唯一
SingletonHungry(const SingletonHungry&) = delete;
SingletonHungry& operator=(const SingletonHungry&) = delete;
private:
// 私有化构造/析构,外部无法创建
SingletonHungry() = default;
~SingletonHungry() = default;
// 静态成员:程序启动时初始化,唯一实例
static SingletonHungry instance;
};
// 类外初始化静态实例(必须)
SingletonHungry SingletonHungry::instance;
// 测试
int main() {
SingletonHungry& s1 = SingletonHungry::getInstance();
SingletonHungry& s2 = SingletonHungry::getInstance();
s1.show(); // 地址相同
s2.show();
return 0;
}懒汉式 第一次调用时创建实例,需手动锁保护 实例资源占用大、可能不被使用
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
// 针对于懒汉式考虑线程安全问题 加锁
// 单例模式之懒汉式
class Singleton
{
public:
int data;
// 定义一个静态互斥锁
static mutex mtx;
// 3.提供一个公有的静态方法来获取唯一对象
static Singleton *getInstance()
{
#if 0
//未加锁的情况
//如果sing为空,则创建一个对象,否则返回已有对象
if(sing == NULL){
sing = new Singleton(10);
}
cout << "&sing=" << sing << endl;
return sing;
#else
// 加锁
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
// 如果sing为空,则创建一个对象,否则返回已有对象
if (sing == NULL)
{
sing = new Singleton(10);
}
cout << "&sing=" << sing << endl;
return sing;
#endif
}
// 4.提供一个公有的静态方法来释放资源
static void destory()
{
if (sing != NULL)
{
cout << "destory()" << endl;
delete sing;
sing = NULL; // 释放后,将指针置为空
}
}
private:
// 1.构造函数私有化
Singleton(int value) : data(value)
{
cout << "Singleton(int value)" << endl;
}
// 2.提供一个私有权限静态成员指针变量来维护唯一对象
static Singleton *sing;
};
// 静态成员变量必须在类外完成初始化
Singleton *Singleton::sing = NULL;
// 初始化静态互斥锁
mutex Singleton::mtx;
int main()
{
// 获取唯一对象
Singleton *s1 = Singleton::getInstance();
cout << "s1->data = " << s1->data << endl;
cout << "&s1=" << s1 << endl;
// 释放资源
Singleton::destory();
cout << "-----------------------" << endl;
Singleton *s2 = Singleton::getInstance();
cout << "s2->data = " << s2->data << endl;
cout << "&s2=" << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SingletonLazy {
public:
// 全局访问入口:局部静态变量,C++11保证初始化线程安全
static SingletonLazy& getInstance() {
static SingletonLazy instance; // 第一次调用时创建
return instance;
}
void show() { cout << "懒汉式实例地址:" << this << endl; }
// 禁用拷贝/赋值
SingletonLazy(const SingletonLazy&) = delete;
SingletonLazy& operator=(const SingletonLazy&) = delete;
private:
SingletonLazy() = default;
~SingletonLazy() = default;
};
// 测试
int main() {
cout << "调用前:实例未创建" << endl;
SingletonLazy& s1 = SingletonLazy::getInstance(); // 首次调用,创建实例
SingletonLazy& s2 = SingletonLazy::getInstance();
s1.show(); // 地址相同
s2.show();
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
class SingletonLazyDCL {
public:
static SingletonLazyDCL* getInstance() {
// 第一层校验:避免每次加锁,提高效率
if (instance == nullptr) {
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx); // 加锁
// 第二层校验:防止多线程重复创建
if (instance == nullptr) {
instance = new SingletonLazyDCL();
}
}
return instance;
}
private:
SingletonLazyDCL() = default;
~SingletonLazyDCL() = default;
static SingletonLazyDCL* volatile instance; // volatile 防止指令重排
static mutex mtx; // 互斥锁
};
// 初始化静态成员
SingletonLazyDCL* volatile SingletonLazyDCL::instance = nullptr;
mutex SingletonLazyDCL::mtx;