文章目录
链表
概念:链表是逻辑上连续,物理储存结构上非连续、非顺序的储存结构。
数据元素的逻辑连续是通过额外的指针链接次序实现并保持的。
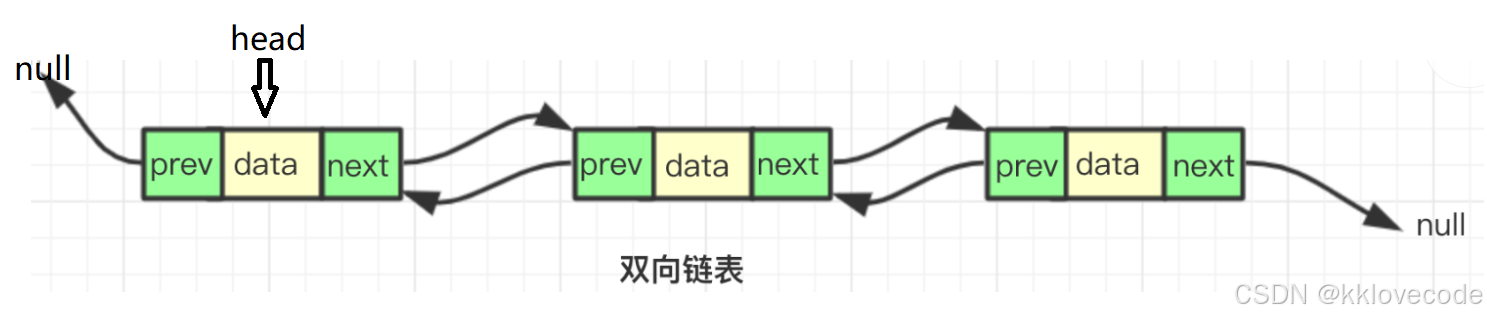
如图,展示的是一个不带头结点的双向循环链表,head是一个结点指针,指向了链表的第一个元素,当然这只是逻辑地址,真实在内存中的物理地址其实是随意分配的,只是通过指针能够找到对应的位置
代码实现
本次代码实现的是一个双向不循环不带头结点的链表
定义结点
c
typedef struct node
{
//数据域
void* data;
//上一个节点 指针
struct node *prev;
//下一个节点 指针
struct node *next;
}node;数据域仍是采用void指针类型,可以代表任意类型的指针
定义链表
c
typedef struct linked_list
{
//头节点
node *head;
//尾节点
node *tail;
//链表中节点的数量
int size;
}linked_list;双向链表的结构体关键就是在于用两个结点指针去指向对应的头结点和尾结点
创建结点
c
node* create_note(void *data){
node *new_node =(node*)calloc(1,sizeof(node));
if (new_node==NULL)
{
printf("创建节点失败!\n");
return NULL;
}
//节点中数组赋值
new_node->data=data;
//新节点 上/下 为NULL
new_node->prev=NULL;
new_node->next=NULL;
return new_node;
}创建链表
c
linked_list* create_linked_list(){
linked_list *new_list =(linked_list*)calloc(1,sizeof(linked_list));
if (new_list==NULL)
{
printf("创建双向链表失败!\n");
return NULL;
}
//空双向链表
new_list->head=NULL;
new_list->tail=NULL;
new_list->size=0;
return new_list;
}头插
c
void push_front(linked_list *list,void *data){
//创建新节点
node *new_node=create_note(data);
//判断链表是否为空
if (list->head==NULL)
{
//头尾节点都为新节点
list->head=new_node;
list->tail=new_node;
}else
{
//新节点的next为旧头节点
new_node->next=list->head;
//旧头节点的prev为新节点
list->head->prev=new_node;
//链表更新头节点为新节点
list->head=new_node;
}
//链表节点数量+1
list->size++;
}1.链表为空,新结点既是头结点,也是尾结点
2.链表不为空,执行头插
3.新结点的next为旧的头结点
4.旧的头结点的prev为新节点
5.更新链表的头节点为新节点
6.结点数量+1
尾插
c
void push_back(linked_list *list,void *data){
//创建新节点
node *new_node=create_note(data);
//判断链表是否为空
if (list->tail==NULL)
{
//头尾节点都为新节点
list->head=new_node;
list->tail=new_node;
}else
{
//新节点的prev为旧尾节点
new_node->prev=list->tail;
//旧尾节点的next为新节点
list->tail->next=new_node;
//链表更新尾节点为新节点
list->tail=new_node;
}
//链表节点数量+1
list->size++;
}1.链表为空,新节点是头结点也是尾结点
2.链表不为空,执行尾插
3.新节点的prev为旧的尾节点
旧的尾节点的next为新节点
5.更新链表的尾节点为新节点
6.节点数量+1
中间插
c
void insert_after(linked_list *list,node *prev_node,void *data){
//判断是否能从中间插入
if (prev_node==NULL)
{
printf("上一个节点不能尾NULL!\n");
return;
}
//创建新节点
node *new_node=create_note(data);
//设置新节点的前驱和后继指针
new_node->prev=prev_node;
new_node->next=prev_node->next;
//判断后继节点是否为NULL
if (prev_node->next!=NULL)
{
//设置后继节点的prev为新节点
prev_node->next->prev=new_node;
}else
{
//执行尾插
list->tail=new_node;
}
//前驱节点的next为新节点
prev_node->next=new_node;
//节点数量+1
list->size++;
}中间插入的函数还要传递上一个结点指针.
搜索
c
//先定义一个比较函数
int compare_int(void *a,void *b){
return *(int*)a-*(int*)b;//0相同,非0不同
}
//8.2搜索节点
node* search_node(linked_list *list,void *data,int (*cmp)(void*,void*)){
//从链表头部开始变量
node* current=list->head;
//遍历比较,通过数据找到节点
while (current!=NULL)
{
if (cmp(current->data,data)==0)
{
//找到对应的节点
return current;
}
//不相同,继续比较下一个
current=current->next;
}
//未找到匹配的节点,返回NULL
return NULL;
}定义了一个比较函数compare(),在函数search_node()中使用函数指针调用比较函数compare();
释放
c
//last.释放链表
void free_linked_list(linked_list *list){
if (list==NULL)
{
printf("链表为NULL,无法释放!\n");
return;
}
//先释放双向链表中的所有节点
//获取头节点
node *current=list->head;
while (current!=NULL)
{
//节点不为NULL
node *tmp=current;//当前节点
current=current->next;
//释放节点
free(tmp);
}
//在释放链表
list->head=NULL;
list->tail=NULL;
list->size=0;
free(list);
}栈
栈的特点就是先进后出(First in Last out)
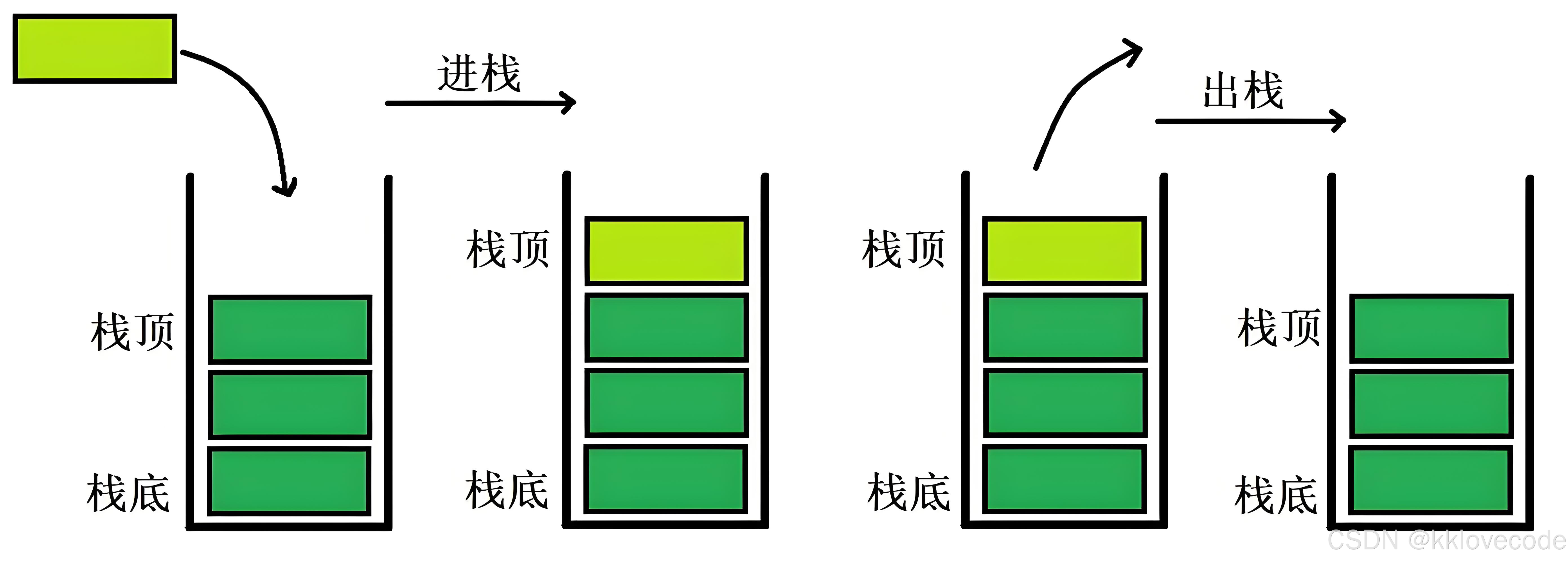
这里我们趁热打铁,使用链表来完成一个栈
牢记栈的特性,如果不 按栈的特性来严格要求代码,就不是 一个栈
定义结点
c
typedef struct node{
void* data;
struct node* next;
}node;定义栈
c
typedef struct stack{
node* top;
int size;
}stack;这里的链表其实就是一个单向链表 ,所以使用一个
top指针就行,top指针始终指向栈顶元素,这个栈只有一个node指针的指针,和一个size,就能表示一个栈,细品
创建结点
c
//创建结点
node* create_node(void* data){
node* n = (node*)calloc(1,sizeof(node));
n->next = NULL;
n->data = data;
return n;
}创建栈
c
//创建栈
stack* create_stack(){
stack* new_stack =(stack*)calloc(1,sizeof(stack));
if(new_stack==NULL)
{
printf("create fail\n");
exit(0);
}
new_stack->top = NULL;
new_stack->size = 0;
return new_stack;
}压栈
c
}
//压栈
void push(stack* s,void* a)
{
node* n = create_node(a);
n->next = s->top;
s->top = n;
}出栈
c
//出栈
void* pop(stack* s)
{
if (s->top==NULL)
{
printf("there is no node\n");
return NULL;
}
node* n = s->top;
void* data = n->data;
s->top=s->top->next;
s->size--;
return data;
}查看栈顶
c
void* peek(stack* s)
{
void* a = s->top->data;
return a;
}释放栈
c
//释放栈
void free_stack(stack* s){
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("stack is NULL");
return;
}
//从栈顶开始获取所有节点,释放所有节点
node* current=s->top;
while (current!=NULL)
{
node *tmp=current;
current=current->next;
free(tmp);
}
s->top=NULL;
s->size=0;
//释放栈
free_stack(s);
}