摘要
在上一篇博客中,我们学习了如何使用PyVista构建静态的3D战场场景。本文是"PyVista雷达电子对抗战场态势仿真"系列的第二篇,将深入探讨如何让战场"活"起来。通过详细的代码示例和原理讲解,我们将掌握PyVista中实现动态更新的核心技术,包括网格更新、动画制作、回调函数、实时交互等。文章包含三个完整的实战案例,帮助读者从静态可视化向动态仿真迈出关键一步。
1. 引言:为什么需要动态可视化?
在军事仿真、作战训练和态势分析中,静态的场景展示远远不够。真实的战场是动态变化的:飞机在飞行、雷达在扫描、导弹在追击、部队在机动。动态可视化不仅能提供更真实的环境感知,还能支持时间序列分析、决策推演和作战效果评估。
1.1 动态可视化的关键价值
时间维度的重要性
传统的3D可视化主要关注空间维度,而战场态势的本质是时空一体化的。动态可视化引入了时间轴,使我们能够:
-
观察作战单元的移动轨迹和运动规律
-
分析战术动作的时间协调性
-
评估作战行动的时序约束
-
回放历史态势用于复盘分析
交互反馈的实时性
动态系统需要实时响应用户交互和外部数据输入,这对于指挥决策支持系统尤为重要。PyVista的回调函数机制和实时更新能力,使其成为构建交互式战场仿真的理想选择。
教学演示的生动性
对于教学和训练场景,动态演示比静态图片更能吸引注意力,帮助学员理解复杂的时空关系和战术动作。
1.2 PyVista动态可视化的核心技术
PyVista提供了多种实现动态可视化的方法,我们将重点介绍:
| 技术手段 | 适用场景 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
plotter.open_gif() |
预计算动画 | 生成GIF/MP4文件,适合演示和报告 |
| 回调函数(callback) | 实时交互 | 支持用户输入和外部数据驱动 |
| 网格实时更新 | 动态场景 | 更新位置、姿态、属性 |
| 时间标签系统 | 时空同步 | 显示仿真时间和时间缩放 |
2. 动态可视化基础:动画制作与实时更新
2.1 PyVista动画系统架构
PyVista的动画系统建立在两个核心概念上:时间步 和更新回调。让我们通过一个简单的架构图来理解:
2.2 基础动画制作:open_gif方法
open_gif是PyVista生成动画最简单的方法。我们先从一个基础示例开始:
python
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
def basic_animation_demo():
"""基础动画演示:旋转的立方体"""
# 创建绘图器
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[800, 600], title="基础动画演示")
# 创建立方体
cube = pv.Cube(center=(0, 0, 0))
# 添加立方体到场景
actor = plotter.add_mesh(cube, color='red', show_edges=True)
# 打开GIF文件
plotter.open_gif("basic_animation.gif", fps=20)
# 动画循环
n_frames = 50
for i in range(n_frames):
# 计算旋转角度
angle = i * 360 / n_frames
# 创建新的立方体(旋转后)
rotated_cube = cube.copy()
rotated_cube.rotate_z(angle, inplace=True)
# 更新actor
plotter.add_mesh(rotated_cube, color='red', show_edges=True, name='cube')
# 写入帧
plotter.write_frame()
# 关闭GIF
plotter.close()
print("动画已保存为 basic_animation.gif")
if __name__ == "__main__":
basic_animation_demo()关键要点:
-
open_gif方法创建动画文件 -
每次循环需要重新添加网格(或更新actor)
-
write_frame捕获当前帧 -
控制帧率(fps)影响动画流畅度
2.3 高级动画制作:open_movie方法
对于更复杂、更长的动画,推荐使用open_movie方法,它支持更多格式和编码选项:
python
def advanced_animation_demo():
"""高级动画演示:多对象协同动画"""
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[1024, 768], title="高级动画演示")
# 创建多个几何体
sphere = pv.Sphere(center=(-2, 0, 0), radius=0.5)
cube = pv.Cube(center=(0, 0, 0))
cylinder = pv.Cylinder(center=(2, 0, 0), direction=(0, 0, 1), radius=0.5, height=1)
# 添加网格
sphere_actor = plotter.add_mesh(sphere, color='red')
cube_actor = plotter.add_mesh(cube, color='green', show_edges=True)
cylinder_actor = plotter.add_mesh(cylinder, color='blue')
# 设置相机位置
plotter.camera_position = [(0, 0, 8), (0, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0)]
# 打开电影文件
plotter.open_movie(
"advanced_animation.mp4",
framerate=30,
quality=8, # 0-10,越高画质越好
codec='libx264' # 视频编码
)
# 动画参数
n_frames = 150
orbit_radius = 3.0
orbit_height = 1.0
for i in range(n_frames):
# 计算时间参数
t = i / n_frames * 2 * np.pi
# 1. 球体:轨道运动
sphere_x = orbit_radius * np.cos(t)
sphere_y = orbit_radius * np.sin(t)
sphere_z = orbit_height * np.sin(2 * t)
new_sphere = sphere.copy()
new_sphere.translate([sphere_x + 2, sphere_y, sphere_z], inplace=True)
# 2. 立方体:旋转+脉动
scale = 1.0 + 0.3 * np.sin(t * 2)
new_cube = cube.copy()
new_cube.scale([scale, scale, scale], inplace=True)
new_cube.rotate_x(t * 180 / np.pi, inplace=True)
new_cube.rotate_y(t * 90 / np.pi, inplace=True)
# 3. 圆柱体:沿Z轴旋转+上下移动
new_cylinder = cylinder.copy()
new_cylinder.rotate_z(t * 360 / np.pi, inplace=True)
cylinder_z = np.sin(t * 3) * 2
new_cylinder.translate([2, 0, cylinder_z], inplace=True)
# 清除旧网格
plotter.remove_actor(sphere_actor)
plotter.remove_actor(cube_actor)
plotter.remove_actor(cylinder_actor)
# 添加新网格
sphere_actor = plotter.add_mesh(new_sphere, color='red')
cube_actor = plotter.add_mesh(new_cube, color='green', show_edges=True)
cylinder_actor = plotter.add_mesh(new_cylinder, color='blue')
# 更新相机(模拟轨道观察)
if i % 30 == 0: # 每30帧更新一次相机
cam_pos = (8 * np.sin(t/5), 8 * np.cos(t/5), 4)
plotter.camera_position = [cam_pos, (0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1)]
# 写入帧
plotter.write_frame()
# 打印进度
if i % 10 == 0:
progress = (i + 1) / n_frames * 100
print(f"生成进度: {progress:.1f}%")
# 关闭电影文件
plotter.close()
print("动画已保存为 advanced_animation.mp4")
# 运行演示
advanced_animation_demo()编码选项说明:
-
framerate:帧率,控制动画流畅度
-
quality:视频质量,0-10,数值越高文件越大
-
codec:视频编码器,常用有:
-
'libx264':H.264编码,兼容性好 -
'libx265':H.265编码,压缩率高 -
'mpeg4':MPEG-4编码
-
2.4 性能优化:网格复用与增量更新
在动态场景中,频繁创建和销毁网格对象会导致性能问题。下面介绍两种优化方法:
python
def optimized_animation_demo():
"""优化动画演示:网格复用技术"""
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[800, 600], title="优化动画演示")
# 创建初始网格
sphere = pv.Sphere(center=(0, 0, 0), radius=1.0)
# 添加网格并获取actor
actor = plotter.add_mesh(sphere, color='red')
# 打开GIF
plotter.open_gif("optimized_animation.gif", fps=30)
n_frames = 100
for i in range(n_frames):
# 方法1:直接更新actor的属性(高效)
# 计算新的位置
t = i / n_frames * 2 * np.pi
x = 3 * np.sin(t)
y = 3 * np.cos(t)
z = 2 * np.sin(2 * t)
# 创建变换矩阵
transform_matrix = np.eye(4)
transform_matrix[:3, 3] = [x, y, z] # 平移
# 直接设置actor的变换矩阵
actor.user_matrix = transform_matrix
# 方法2:更新颜色(随时间变化)
# 计算HSV颜色
hue = i / n_frames # 0-1
import colorsys
rgb = colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(hue, 1.0, 1.0)
# 更新actor颜色
actor.mapper.dataset.active_scalars_name = None
plotter.update_scalars(rgb, actor.renderer)
# 写入帧
plotter.write_frame()
# 方法3:增量更新(适用于轨迹)
if i > 0:
# 添加轨迹线
prev_t = (i-1) / n_frames * 2 * np.pi
prev_x = 3 * np.sin(prev_t)
prev_y = 3 * np.cos(prev_t)
prev_z = 2 * np.sin(2 * prev_t)
# 创建线段
line = pv.Line(pointa=(prev_x, prev_y, prev_z),
pointb=(x, y, z))
# 只添加新线段,保留旧的
if i == 1: # 第一段轨迹
line_actor = plotter.add_mesh(line, color='blue', line_width=2)
else:
# 更新轨迹网格
line_actor.mapper.dataset.overwrite(line)
plotter.close()
print("优化动画已保存")
# 运行演示
optimized_animation_demo()优化技巧总结:
-
复用网格对象:避免频繁创建新网格
-
直接更新actor属性 :使用
user_matrix等属性 -
增量更新:只更新变化的部分
-
批处理更新:合并多个更新操作
3. 实时更新:回调函数与交互控制
对于需要用户交互或实时数据驱动的应用,预计算的动画不够用。PyVista的回调函数机制提供了实时更新的能力。
3.1 回调函数基础
回调函数是在特定事件发生时被调用的函数。在PyVista中,主要通过add_callback和add_key_event等方法实现。
python
def callback_basic_demo():
"""回调函数基础演示"""
import time
class RealtimeVisualizer:
def __init__(self):
self.plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[1000, 700],
title="回调函数演示")
self.cube = pv.Cube(center=(0, 0, 0))
self.actor = None
self.angle = 0
self.last_time = time.time()
self.fps = 0
self.frame_count = 0
def initialize(self):
"""初始化场景"""
# 添加立方体
self.actor = self.plotter.add_mesh(self.cube, color='cyan',
show_edges=True)
# 添加坐标系
self.plotter.add_axes()
# 添加信息文本
self.info_text = self.plotter.add_text("", position='upper_left',
font_size=10, color='white')
# 添加网格统计
self.stats_text = self.plotter.add_text("", position='upper_right',
font_size=10, color='yellow')
# 设置相机
self.plotter.camera_position = [(5, 5, 5), (0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1)]
# 添加键盘事件
self.plotter.add_key_event("r", self.reset_scene)
self.plotter.add_key_event("space", self.toggle_rotation)
self.plotter.add_key_event("c", self.change_color)
self.plotter.add_key_event("Up", self.increase_speed)
self.plotter.add_key_event("Down", self.decrease_speed)
# 添加鼠标事件
self.plotter.track_click_position(self.on_click, side='left')
# 添加回调函数
self.plotter.add_callback(self.update_callback, interval=16) # ~60FPS
# 控制变量
self.rotation_speed = 1.0
self.is_rotating = True
self.colors = ['cyan', 'red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'magenta']
self.color_index = 0
def update_callback(self):
"""更新回调函数"""
current_time = time.time()
delta_time = current_time - self.last_time
self.last_time = current_time
# 更新FPS计算
self.frame_count += 1
if self.frame_count % 30 == 0:
self.fps = 1.0 / delta_time if delta_time > 0 else 0
# 更新旋转
if self.is_rotating:
self.angle += self.rotation_speed * delta_time * 60
self.angle %= 360
# 创建旋转后的立方体
rotated_cube = self.cube.copy()
rotated_cube.rotate_x(self.angle, inplace=True)
rotated_cube.rotate_y(self.angle * 0.7, inplace=True)
rotated_cube.rotate_z(self.angle * 0.3, inplace=True)
# 更新actor
self.actor.mapper.dataset.overwrite(rotated_cube)
# 更新信息文本
info = f"FPS: {self.fps:.1f}\n"
info += f"角度: {self.angle:.1f}°\n"
info += f"旋转速度: {self.rotation_speed:.1f}x\n"
info += f"旋转: {'开启' if self.is_rotating else '关闭'}\n"
info += f"颜色: {self.colors[self.color_index]}"
self.info_text.SetText(3, info) # VTK方法更新文本
# 更新网格统计
stats = f"顶点数: {self.cube.n_points}\n"
stats += f"面数: {self.cube.n_faces}\n"
stats += f"内存: {self.cube.n_bytes / 1024:.1f} KB"
self.stats_text.SetText(3, stats)
# 请求重绘
self.plotter.update()
def reset_scene(self):
"""重置场景"""
self.angle = 0
self.rotation_speed = 1.0
self.is_rotating = True
print("场景已重置")
def toggle_rotation(self):
"""切换旋转状态"""
self.is_rotating = not self.is_rotating
state = "开启" if self.is_rotating else "关闭"
print(f"旋转{state}")
def change_color(self):
"""改变颜色"""
self.color_index = (self.color_index + 1) % len(self.colors)
self.actor.prop.color = self.colors[self.color_index]
print(f"颜色更改为: {self.colors[self.color_index]}")
def increase_speed(self):
"""增加旋转速度"""
self.rotation_speed = min(self.rotation_speed + 0.5, 10.0)
print(f"旋转速度: {self.rotation_speed:.1f}x")
def decrease_speed(self):
"""减少旋转速度"""
self.rotation_speed = max(self.rotation_speed - 0.5, 0.1)
print(f"旋转速度: {self.rotation_speed:.1f}x")
def on_click(self, position):
"""鼠标点击事件"""
if position: # position是(x, y)屏幕坐标
# 转换为3D坐标
picker = self.plotter.iren.get_picker()
if picker:
# 这里可以添加点击拾取逻辑
print(f"点击位置: {position}")
def run(self):
"""运行可视化"""
self.initialize()
print("控制说明:")
print(" R键: 重置场景")
print(" 空格: 切换旋转")
print(" C键: 改变颜色")
print(" 上箭头: 增加速度")
print(" 下箭头: 减少速度")
print(" 鼠标左键: 点击交互")
print(" Q键: 退出")
self.plotter.show()
# 创建并运行可视化
visualizer = RealtimeVisualizer()
visualizer.run()
# 运行演示
callback_basic_demo()回调函数的核心机制:
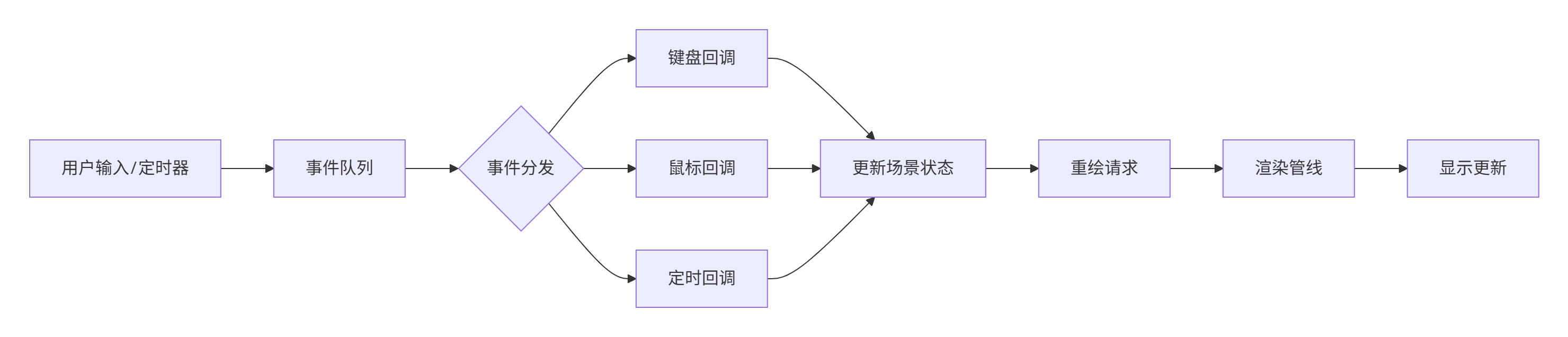
3.2 高级回调:多线程与异步更新
对于需要处理复杂计算或外部数据源的场景,我们需要多线程支持:
python
import threading
import queue
import time
class ThreadedVisualizer:
"""多线程可视化器"""
def __init__(self):
self.plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[1200, 800],
title="多线程可视化演示")
# 数据队列
self.data_queue = queue.Queue(maxsize=100)
# 线程控制
self.data_thread = None
self.is_running = False
# 可视化对象
self.point_cloud = None
self.point_actor = None
# 统计
self.point_count = 0
self.update_rate = 0
def initialize(self):
"""初始化场景"""
# 创建初始点云
self.point_cloud = pv.PolyData()
# 添加点云
self.point_actor = self.plotter.add_mesh(
self.point_cloud,
color='white',
point_size=5,
render_points_as_spheres=True
)
# 添加统计信息
self.stats_text = self.plotter.add_text(
"",
position='upper_left',
font_size=12,
color='yellow'
)
# 添加控制说明
self.help_text = self.plotter.add_text(
"空格: 开始/停止数据流",
position='lower_left',
font_size=10,
color='cyan'
)
# 设置相机
self.plotter.camera_position = [(0, 0, 20), (0, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0)]
# 添加键盘事件
self.plotter.add_key_event("space", self.toggle_data_stream)
# 添加回调函数
self.plotter.add_callback(self.update_callback, interval=33) # ~30FPS
def data_generation_thread(self):
"""数据生成线程"""
print("数据生成线程启动")
frame_id = 0
while self.is_running:
try:
# 生成模拟雷达点云数据
n_points = np.random.randint(100, 1000)
# 生成点在球坐标系
theta = np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi, n_points)
phi = np.random.uniform(0, np.pi, n_points)
r = np.random.uniform(5, 10, n_points)
# 转换为直角坐标
x = r * np.sin(phi) * np.cos(theta)
y = r * np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta)
z = r * np.cos(phi)
# 添加噪声
x += np.random.normal(0, 0.2, n_points)
y += np.random.normal(0, 0.2, n_points)
z += np.random.normal(0, 0.2, n_points)
# 创建点云
points = np.column_stack([x, y, z])
# 添加强度信息
intensities = np.random.uniform(0.1, 1.0, n_points)
# 创建PolyData
cloud = pv.PolyData(points)
cloud['intensity'] = intensities
# 添加到队列
data = {
'frame_id': frame_id,
'cloud': cloud,
'timestamp': time.time()
}
self.data_queue.put(data, timeout=0.1)
frame_id += 1
# 控制数据生成速率
time.sleep(0.05) # 20Hz
except queue.Full:
# 队列满,跳过一帧
pass
except Exception as e:
print(f"数据生成错误: {e}")
break
print("数据生成线程停止")
def update_callback(self):
"""更新回调函数"""
# 从队列获取数据
data_list = []
while not self.data_queue.empty():
try:
data = self.data_queue.get_nowait()
data_list.append(data)
except queue.Empty:
break
if data_list:
# 使用最新数据
latest_data = data_list[-1]
# 更新点云
self.point_cloud = latest_data['cloud']
# 更新actor
self.point_actor.mapper.dataset.overwrite(self.point_cloud)
# 根据强度设置颜色
if 'intensity' in self.point_cloud.array_names:
self.point_actor.mapper.set_scalars(
self.point_cloud['intensity']
)
self.plotter.update_scalars(
self.point_cloud['intensity'],
self.point_actor.renderer
)
# 更新统计
self.point_count = self.point_cloud.n_points
self.update_rate = len(data_list) / 0.033 # 估算更新率
# 更新文本
stats = f"点云帧ID: {latest_data['frame_id']}\n"
stats += f"点数: {self.point_count}\n"
stats += f"更新率: {self.update_rate:.1f} Hz\n"
stats += f"队列深度: {self.data_queue.qsize()}"
self.stats_text.SetText(3, stats)
# 请求重绘
self.plotter.update()
def toggle_data_stream(self):
"""切换数据流"""
if self.is_running:
# 停止数据流
self.is_running = False
if self.data_thread:
self.data_thread.join(timeout=2.0)
print("数据流已停止")
else:
# 启动数据流
self.is_running = True
self.data_thread = threading.Thread(
target=self.data_generation_thread,
daemon=True
)
self.data_thread.start()
print("数据流已启动")
def run(self):
"""运行可视化"""
self.initialize()
print("多线程可视化演示")
print("控制说明:")
print(" 空格: 开始/停止数据流")
print(" Q键: 退出")
self.plotter.show()
# 清理
self.is_running = False
if self.data_thread:
self.data_thread.join(timeout=1.0)
# 运行演示
visualizer = ThreadedVisualizer()
visualizer.run()多线程架构说明:
python
"""
线程安全注意事项:
1. 数据传递使用队列(queue.Queue),避免共享状态
2. 主线程(GUI线程)只从队列读取数据
3. 工作线程只生成数据,不进行GUI操作
4. 使用超时机制避免线程阻塞
"""4. 案例1:目标沿预定轨迹运动
在这个案例中,我们将创建一个完整的战场目标运动演示,包括直线运动、圆周运动和复杂轨迹。
4.1 轨迹运动基类设计
python
class MovingTarget:
"""运动目标基类"""
def __init__(self, initial_position, target_type, color='red'):
self.initial_position = np.array(initial_position, dtype=float)
self.current_position = self.initial_position.copy()
self.target_type = target_type
self.color = color
self.mesh = None
self.trajectory = []
self.trajectory_mesh = None
self.velocity = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
self.acceleration = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
self.max_speed = 50.0 # 单位/秒
self.orientation = 0.0 # 朝向角度(度)
def create_geometry(self, scale=1.0):
"""创建目标几何体"""
if self.target_type == 'aircraft':
# 飞机模型
fuselage = pv.Cylinder(center=[0, 0, 0], direction=[1, 0, 0],
radius=1*scale, height=6*scale)
wing = pv.Box(bounds=[-0.5, 0.5, -4*scale, 4*scale, -0.2*scale, 0.2*scale])
tail = pv.Box(bounds=[-3*scale, -2*scale, -1.5*scale, 1.5*scale, -0.5*scale, 0.5*scale])
self.mesh = fuselage.boolean_union(wing)
self.mesh = self.mesh.boolean_union(tail)
elif self.target_type == 'missile':
# 导弹模型
body = pv.Cylinder(center=[0, 0, 0], direction=[1, 0, 0],
radius=0.5*scale, height=8*scale)
nose = pv.Cone(center=[4*scale, 0, 0], direction=[1, 0, 0],
height=2*scale, radius=0.5*scale)
fins = []
for angle in [0, 90, 180, 270]:
fin = pv.Box(bounds=[-4*scale, -3*scale, -0.1*scale, 0.1*scale,
-1*scale, 1*scale])
fin.rotate_z(angle, inplace=True)
fins.append(fin)
self.mesh = body.boolean_union(nose)
for fin in fins:
self.mesh = self.mesh.boolean_union(fin)
elif self.target_type == 'vehicle':
# 车辆模型
chassis = pv.Cube(center=[0, 0, 0.8*scale],
x_length=4*scale, y_length=2*scale, z_length=1.6*scale)
turret = pv.Cylinder(center=[0.5*scale, 0, 1.8*scale],
direction=[0, 0, 1], radius=0.8*scale, height=0.8*scale)
self.mesh = chassis.boolean_union(turret)
# 初始位置
self.mesh.translate(self.current_position, inplace=True)
return self.mesh
def update_position(self, delta_time):
"""更新目标位置"""
# 更新速度
self.velocity += self.acceleration * delta_time
# 限制最大速度
speed = np.linalg.norm(self.velocity)
if speed > self.max_speed:
self.velocity = self.velocity / speed * self.max_speed
# 更新位置
displacement = self.velocity * delta_time
self.current_position += displacement
# 记录轨迹
self.trajectory.append(self.current_position.copy())
# 保持轨迹长度
if len(self.trajectory) > 1000:
self.trajectory.pop(0)
# 更新朝向
if speed > 0.1:
# 计算前进方向
forward = self.velocity / speed
self.orientation = np.degrees(np.arctan2(forward[1], forward[0]))
return self.current_position
def get_trajectory_mesh(self):
"""获取轨迹网格"""
if len(self.trajectory) < 2:
return None
points = np.array(self.trajectory)
lines = np.arange(len(points))
lines = np.insert(lines, 0, len(points))
self.trajectory_mesh = pv.PolyData(points, lines=lines)
# 添加时间属性(用于颜色映射)
time_values = np.linspace(0, 1, len(points))
self.trajectory_mesh['time'] = time_values
return self.trajectory_mesh
def reset(self):
"""重置目标"""
self.current_position = self.initial_position.copy()
self.velocity = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
self.acceleration = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
self.trajectory = []
class LinearTrajectoryTarget(MovingTarget):
"""直线运动目标"""
def __init__(self, initial_position, target_type, direction, speed=20.0):
super().__init__(initial_position, target_type)
self.direction = np.array(direction, dtype=float)
self.direction = self.direction / np.linalg.norm(self.direction) # 归一化
self.speed = speed
self.velocity = self.direction * self.speed
def update_position(self, delta_time):
"""直线运动更新"""
# 简单直线运动
displacement = self.velocity * delta_time
self.current_position += displacement
# 记录轨迹
self.trajectory.append(self.current_position.copy())
if len(self.trajectory) > 1000:
self.trajectory.pop(0)
return self.current_position
class CircularTrajectoryTarget(MovingTarget):
"""圆周运动目标"""
def __init__(self, initial_position, target_type, center, radius=50.0,
angular_speed=30.0, plane='xy'):
super().__init__(initial_position, target_type)
self.center = np.array(center, dtype=float)
self.radius = radius
self.angular_speed = angular_speed # 度/秒
self.plane = plane
self.current_angle = 0.0 # 度
# 计算初始角度
if plane == 'xy':
dx = initial_position[0] - center[0]
dy = initial_position[1] - center[1]
self.current_angle = np.degrees(np.arctan2(dy, dx))
def update_position(self, delta_time):
"""圆周运动更新"""
# 更新角度
self.current_angle += self.angular_speed * delta_time
self.current_angle %= 360
# 计算新位置
angle_rad = np.radians(self.current_angle)
if self.plane == 'xy':
x = self.center[0] + self.radius * np.cos(angle_rad)
y = self.center[1] + self.radius * np.sin(angle_rad)
z = self.center[2]
elif self.plane == 'xz':
x = self.center[0] + self.radius * np.cos(angle_rad)
y = self.center[1]
z = self.center[2] + self.radius * np.sin(angle_rad)
else: # 'yz'
x = self.center[0]
y = self.center[1] + self.radius * np.cos(angle_rad)
z = self.center[2] + self.radius * np.sin(angle_rad)
self.current_position = np.array([x, y, z])
# 计算速度方向(切线方向)
if self.plane == 'xy':
tangent_x = -np.sin(angle_rad)
tangent_y = np.cos(angle_rad)
tangent_z = 0
elif self.plane == 'xz':
tangent_x = -np.sin(angle_rad)
tangent_y = 0
tangent_z = np.cos(angle_rad)
else:
tangent_x = 0
tangent_y = -np.sin(angle_rad)
tangent_z = np.cos(angle_rad)
tangent = np.array([tangent_x, tangent_y, tangent_z])
tangent = tangent / np.linalg.norm(tangent)
# 计算线速度
circumference = 2 * np.pi * self.radius
linear_speed = circumference * (self.angular_speed / 360)
self.velocity = tangent * linear_speed
# 更新朝向
if np.linalg.norm(self.velocity) > 0.1:
forward = self.velocity / np.linalg.norm(self.velocity)
self.orientation = np.degrees(np.arctan2(forward[1], forward[0]))
# 记录轨迹
self.trajectory.append(self.current_position.copy())
if len(self.trajectory) > 1000:
self.trajectory.pop(0)
return self.current_position
class SplineTrajectoryTarget(MovingTarget):
"""样条曲线轨迹目标"""
def __init__(self, initial_position, target_type, waypoints, speed=20.0):
super().__init__(initial_position, target_type)
self.waypoints = np.array(waypoints, dtype=float)
self.speed = speed
self.current_segment = 0
self.segment_progress = 0.0
# 计算样条曲线
self.spline_points = self._calculate_spline()
self.total_length = self._calculate_spline_length()
# 初始化位置
self.current_position = self.spline_points[0]
self.target_position = initial_position
def _calculate_spline(self):
"""计算样条曲线"""
from scipy import interpolate
# 使用三次样条插值
t = np.arange(len(self.waypoints))
# 分别对x,y,z插值
t_new = np.linspace(0, len(self.waypoints)-1, 1000)
spline_x = interpolate.CubicSpline(t, self.waypoints[:, 0])
spline_y = interpolate.CubicSpline(t, self.waypoints[:, 1])
spline_z = interpolate.CubicSpline(t, self.waypoints[:, 2])
x_new = spline_x(t_new)
y_new = spline_y(t_new)
z_new = spline_z(t_new)
return np.column_stack([x_new, y_new, z_new])
def _calculate_spline_length(self):
"""计算样条曲线总长度"""
distances = np.linalg.norm(
np.diff(self.spline_points, axis=0),
axis=1
)
return np.sum(distances)
def update_position(self, delta_time):
"""样条曲线运动更新"""
# 计算移动距离
move_distance = self.speed * delta_time
# 在当前样条曲线上移动
current_index = 0
remaining_distance = move_distance
# 查找当前点在样条曲线上的位置
distances = np.linalg.norm(
self.spline_points - self.current_position,
axis=1
)
current_index = np.argmin(distances)
# 向前移动
while remaining_distance > 0 and current_index < len(self.spline_points) - 1:
# 到下一个点的距离
to_next = np.linalg.norm(
self.spline_points[current_index + 1] -
self.spline_points[current_index]
)
if remaining_distance <= to_next:
# 在当前线段内移动
direction = (self.spline_points[current_index + 1] -
self.spline_points[current_index])
direction = direction / np.linalg.norm(direction)
self.current_position += direction * remaining_distance
remaining_distance = 0
else:
# 移动到下一个点
remaining_distance -= to_next
current_index += 1
self.current_position = self.spline_points[current_index].copy()
# 如果到达终点,回到起点
if current_index >= len(self.spline_points) - 1:
self.current_position = self.spline_points[0].copy()
current_index = 0
# 计算速度方向
if current_index < len(self.spline_points) - 1:
self.velocity = (self.spline_points[current_index + 1] -
self.spline_points[current_index])
self.velocity = self.velocity / np.linalg.norm(self.velocity) * self.speed
else:
self.velocity = np.zeros(3)
# 更新朝向
if np.linalg.norm(self.velocity) > 0.1:
forward = self.velocity / np.linalg.norm(self.velocity)
self.orientation = np.degrees(np.arctan2(forward[1], forward[0]))
# 记录轨迹
self.trajectory.append(self.current_position.copy())
if len(self.trajectory) > 1000:
self.trajectory.pop(0)
return self.current_position4.2 轨迹运动演示
python
def trajectory_demo():
"""轨迹运动演示"""
class TrajectoryDemo:
def __init__(self):
self.plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[1400, 900],
title="目标轨迹运动演示")
self.targets = []
self.actors = {}
self.trajectory_actors = {}
self.is_running = True
self.last_time = time.time()
self.demo_time = 0.0
def initialize(self):
"""初始化演示"""
# 创建多个运动目标
# 1. 直线运动目标
linear_target = LinearTrajectoryTarget(
initial_position=[-50, -50, 20],
target_type='aircraft',
direction=[1, 0.5, 0.2],
speed=30.0
)
linear_target.create_geometry(scale=1.0)
linear_target.color = 'red'
self.targets.append(linear_target)
# 2. 圆周运动目标(水平)
circular_target_xy = CircularTrajectoryTarget(
initial_position=[0, 50, 30],
target_type='missile',
center=[0, 0, 30],
radius=40.0,
angular_speed=45.0,
plane='xy'
)
circular_target_xy.create_geometry(scale=0.8)
circular_target_xy.color = 'green'
self.targets.append(circular_target_xy)
# 3. 圆周运动目标(垂直)
circular_target_xz = CircularTrajectoryTarget(
initial_position=[50, 0, 50],
target_type='missile',
center=[0, 0, 30],
radius=50.0,
angular_speed=-30.0,
plane='xz'
)
circular_target_xz.create_geometry(scale=0.8)
circular_target_xz.color = 'blue'
self.targets.append(circular_target_xz)
# 4. 样条曲线目标
waypoints = np.array([
[-30, -30, 10],
[-20, 20, 40],
[10, 30, 20],
[30, 10, 50],
[20, -20, 30],
[-10, -30, 20]
])
spline_target = SplineTrajectoryTarget(
initial_position=waypoints[0],
target_type='aircraft',
waypoints=waypoints,
speed=25.0
)
spline_target.create_geometry(scale=1.0)
spline_target.color = 'yellow'
self.targets.append(spline_target)
# 添加目标到场景
for i, target in enumerate(self.targets):
actor_name = f'target_{i}'
self.actors[actor_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
target.mesh,
color=target.color,
name=actor_name
)
# 添加轨迹
trajectory_mesh = target.get_trajectory_mesh()
if trajectory_mesh:
trajectory_name = f'trajectory_{i}'
self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
color=target.color,
line_width=2,
opacity=0.5,
name=trajectory_name
)
# 添加信息显示
self.info_text = self.plotter.add_text(
"",
position='upper_left',
font_size=10,
color='white'
)
# 添加轨迹点
self.waypoints_actor = self.plotter.add_points(
waypoints,
color='white',
point_size=10,
render_points_as_spheres=True,
name='waypoints'
)
# 添加控制说明
controls = "控制说明:\n"
controls += "空格: 暂停/继续\n"
controls += "R: 重置场景\n"
controls += "1-4: 切换目标轨迹显示\n"
controls += "T: 切换所有轨迹\n"
controls += "C: 切换轨迹颜色映射\n"
self.control_text = self.plotter.add_text(
controls,
position='lower_left',
font_size=9,
color='cyan'
)
# 设置相机
self.plotter.camera_position = [(150, 150, 100), (0, 0, 30), (0, 0, 1)]
# 添加网格背景
self.plotter.add_floor('-z', show_edges=True, opacity=0.3)
# 添加键盘事件
self.plotter.add_key_event("space", self.toggle_pause)
self.plotter.add_key_event("r", self.reset_scene)
self.plotter.add_key_event("t", self.toggle_trajectories)
self.plotter.add_key_event("c", self.toggle_trajectory_colormap)
for i in range(len(self.targets)):
self.plotter.add_key_event(str(i+1),
lambda idx=i: self.toggle_target_trajectory(idx))
# 添加回调函数
self.plotter.add_callback(self.update_callback, interval=16)
# 控制变量
self.show_trajectories = True
self.use_colormap = True
def update_callback(self):
"""更新回调函数"""
if not self.is_running:
return
current_time = time.time()
delta_time = current_time - self.last_time
self.last_time = current_time
self.demo_time += delta_time
# 更新所有目标
for i, target in enumerate(self.targets):
# 更新目标位置
new_position = target.update_position(delta_time)
# 更新目标网格
actor_name = f'target_{i}'
if actor_name in self.actors:
# 移除旧网格
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.actors[actor_name])
# 创建新位置和姿态的网格
new_mesh = target.mesh.copy()
new_mesh.translate(-target.current_position, inplace=True)
new_mesh.rotate_z(target.orientation, inplace=True)
new_mesh.translate(new_position, inplace=True)
# 添加新网格
self.actors[actor_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
new_mesh,
color=target.color,
name=actor_name
)
# 更新轨迹
trajectory_name = f'trajectory_{i}'
if self.show_trajectories:
trajectory_mesh = target.get_trajectory_mesh()
if trajectory_mesh:
if trajectory_name in self.trajectory_actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name])
# 使用颜色映射
if self.use_colormap and 'time' in trajectory_mesh.array_names:
self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
scalars='time',
cmap='plasma',
line_width=2,
opacity=0.7,
name=trajectory_name
)
else:
self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
color=target.color,
line_width=2,
opacity=0.5,
name=trajectory_name
)
# 更新信息
info = f"仿真时间: {self.demo_time:.1f}s\n"
info += f"目标数量: {len(self.targets)}\n"
info += f"轨迹显示: {'开启' if self.show_trajectories else '关闭'}\n"
info += f"颜色映射: {'开启' if self.use_colormap else '关闭'}\n"
for i, target in enumerate(self.targets):
speed = np.linalg.norm(target.velocity)
info += f"目标{i+1}: 速度{speed:.1f} 位置{target.current_position[:2]}\n"
self.info_text.SetText(3, info)
# 请求重绘
self.plotter.update()
def toggle_pause(self):
"""切换暂停状态"""
self.is_running = not self.is_running
if self.is_running:
self.last_time = time.time()
state = "继续" if self.is_running else "暂停"
print(f"仿真{state}")
def reset_scene(self):
"""重置场景"""
for target in self.targets:
target.reset()
self.demo_time = 0.0
print("场景已重置")
def toggle_trajectories(self):
"""切换所有轨迹显示"""
self.show_trajectories = not self.show_trajectories
state = "开启" if self.show_trajectories else "关闭"
print(f"轨迹显示{state}")
# 更新轨迹显示
for trajectory_name in list(self.trajectory_actors.keys()):
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name])
del self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name]
def toggle_target_trajectory(self, target_index):
"""切换单个目标轨迹显示"""
if 0 <= target_index < len(self.targets):
trajectory_name = f'trajectory_{target_index}'
if trajectory_name in self.trajectory_actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name])
del self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name]
print(f"目标{target_index+1}轨迹关闭")
else:
# 重新添加轨迹
target = self.targets[target_index]
trajectory_mesh = target.get_trajectory_mesh()
if trajectory_mesh:
self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
color=target.color,
line_width=2,
opacity=0.5,
name=trajectory_name
)
print(f"目标{target_index+1}轨迹开启")
def toggle_trajectory_colormap(self):
"""切换轨迹颜色映射"""
self.use_colormap = not self.use_colormap
state = "开启" if self.use_colormap else "关闭"
print(f"轨迹颜色映射{state}")
# 重新绘制所有轨迹
for trajectory_name in list(self.trajectory_actors.keys()):
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name])
del self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name]
if self.show_trajectories:
for i, target in enumerate(self.targets):
trajectory_name = f'trajectory_{i}'
trajectory_mesh = target.get_trajectory_mesh()
if trajectory_mesh:
if self.use_colormap and 'time' in trajectory_mesh.array_names:
self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
scalars='time',
cmap='plasma',
line_width=2,
opacity=0.7,
name=trajectory_name
)
else:
self.trajectory_actors[trajectory_name] = self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
color=target.color,
line_width=2,
opacity=0.5,
name=trajectory_name
)
def run(self):
"""运行演示"""
self.initialize()
print("目标轨迹运动演示")
print("=" * 50)
self.plotter.show()
# 创建并运行演示
demo = TrajectoryDemo()
demo.run()
# 运行演示
trajectory_demo()5. 案例2:雷达波束周期性扫描
在这个案例中,我们将创建一个雷达波束扫描的动画演示,包括波束的生成、扫描控制、扫描区域可视化等。
5.1 雷达波束类设计
python
class RadarBeam:
"""雷达波束类"""
def __init__(self, radar_position, beam_width=10, max_range=100,
scan_speed=30, scan_sector=120):
"""
初始化雷达波束
参数:
radar_position: 雷达位置 [x, y, z]
beam_width: 波束宽度(度)
max_range: 最大探测距离
scan_speed: 扫描速度(度/秒)
scan_sector: 扫描扇区(度),0-360
"""
self.radar_position = np.array(radar_position, dtype=float)
self.beam_width = beam_width
self.max_range = max_range
self.scan_speed = scan_speed
self.scan_sector = scan_sector
# 状态变量
self.current_angle = 0.0 # 当前波束角度(度)
self.is_scanning = True
self.scan_direction = 1 # 扫描方向:1顺时针,-1逆时针
# 几何网格
self.beam_mesh = None
self.scan_area_mesh = None
self._create_beam_geometry()
# 探测结果
self.detected_points = []
self.detection_history = []
def _create_beam_geometry(self):
"""创建波束几何体"""
# 波束使用锥体表示
beam_height = self.max_range
beam_radius = beam_height * np.tan(np.radians(self.beam_width / 2))
# 创建锥体
cone = pv.Cone(center=[0, 0, 0], direction=[1, 0, 0],
height=beam_height, radius=beam_radius, resolution=20)
# 旋转到当前角度
cone.rotate_z(self.current_angle, inplace=True)
# 定位到雷达位置
cone.translate(self.radar_position, inplace=True)
self.beam_mesh = cone
# 创建扫描区域
self._create_scan_area()
return self.beam_mesh
def _create_scan_area(self):
"""创建扫描区域"""
if self.scan_sector >= 360:
# 全向扫描,创建圆形区域
circle = pv.Disc(center=self.radar_position[:2], inner=0,
outer=self.max_range, normal=[0, 0, 1])
self.scan_area_mesh = circle.extrude([0, 0, 0.1])
else:
# 扇区扫描
n_points = 50
angles = np.linspace(-self.scan_sector/2, self.scan_sector/2, n_points)
points = [self.radar_position[:2]] # 雷达位置
for angle in angles:
x = self.radar_position[0] + self.max_range * np.cos(np.radians(angle))
y = self.radar_position[1] + self.max_range * np.sin(np.radians(angle))
points.append([x, y])
points = np.array(points)
# 创建多边形
faces = [n_points + 1] + list(range(n_points + 1))
faces = np.array(faces, dtype=np.int64)
polygon = pv.PolyData(points, faces=faces)
self.scan_area_mesh = polygon.extrude([0, 0, 0.1])
def update_scan(self, delta_time):
"""更新扫描"""
if not self.is_scanning:
return self.current_angle
# 更新扫描角度
angle_change = self.scan_speed * delta_time * self.scan_direction
self.current_angle += angle_change
# 处理扫描边界
if self.scan_sector < 360:
# 扇区扫描
if self.current_angle > self.scan_sector / 2:
self.current_angle = self.scan_sector / 2
self.scan_direction *= -1
elif self.current_angle < -self.scan_sector / 2:
self.current_angle = -self.scan_sector / 2
self.scan_direction *= -1
else:
# 全向扫描
self.current_angle %= 360
# 更新波束几何
self._create_beam_geometry()
return self.current_angle
def detect_targets(self, targets):
"""检测目标"""
self.detected_points = []
for target in targets:
if self.is_target_in_beam(target.position):
self.detected_points.append(target.position.copy())
# 记录检测
detection = {
'time': time.time(),
'target_position': target.position.copy(),
'beam_angle': self.current_angle
}
self.detection_history.append(detection)
# 保持历史长度
if len(self.detection_history) > 1000:
self.detection_history = self.detection_history[-1000:]
return len(self.detected_points)
def is_target_in_beam(self, target_position):
"""判断目标是否在波束内"""
# 计算相对位置
relative_pos = target_position - self.radar_position
distance = np.linalg.norm(relative_pos)
# 距离检查
if distance > self.max_range:
return False
# 角度检查
target_angle = np.degrees(np.arctan2(relative_pos[1], relative_pos[0]))
angle_diff = abs((target_angle - self.current_angle + 180) % 360 - 180)
if angle_diff > self.beam_width / 2:
return False
return True
def get_detection_points_mesh(self):
"""获取探测点网格"""
if not self.detected_points:
return None
points = np.array(self.detected_points)
mesh = pv.PolyData(points)
# 添加探测强度
distances = np.linalg.norm(points - self.radar_position, axis=1)
intensities = 1.0 - distances / self.max_range
mesh['intensity'] = intensities
return mesh
def toggle_scanning(self):
"""切换扫描状态"""
self.is_scanning = not self.is_scanning
return self.is_scanning
def set_scan_speed(self, speed):
"""设置扫描速度"""
self.scan_speed = speed
def set_scan_sector(self, sector):
"""设置扫描扇区"""
self.scan_sector = sector
self._create_scan_area()
class MultiRadarSystem:
"""多雷达系统"""
def __init__(self):
self.radars = []
self.actors = {}
self.beam_colors = ['#FF0000', '#00FF00', '#0000FF', '#FFFF00', '#FF00FF']
def add_radar(self, position, **kwargs):
"""添加雷达"""
radar = RadarBeam(position, **kwargs)
self.radars.append(radar)
return radar
def update_all(self, delta_time):
"""更新所有雷达"""
for radar in self.radars:
radar.update_scan(delta_time)
def get_visualization_data(self):
"""获取所有雷达可视化数据"""
vis_data = []
for i, radar in enumerate(self.radars):
# 波束
vis_data.append({
'mesh': radar.beam_mesh,
'color': self.beam_colors[i % len(self.beam_colors)],
'opacity': 0.6,
'name': f'radar_beam_{i}'
})
# 扫描区域
if radar.scan_area_mesh:
vis_data.append({
'mesh': radar.scan_area_mesh,
'color': self.beam_colors[i % len(self.beam_colors)],
'opacity': 0.1,
'name': f'scan_area_{i}'
})
# 探测点
detection_mesh = radar.get_detection_points_mesh()
if detection_mesh:
vis_data.append({
'mesh': detection_mesh,
'color': '#FFFFFF',
'point_size': 8,
'render_points_as_spheres': True,
'opacity': 0.9,
'name': f'detection_points_{i}'
})
return vis_data5.2 雷达波束扫描演示
python
def radar_scan_demo():
"""雷达波束扫描演示"""
class RadarScanDemo:
def __init__(self):
self.plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[1400, 900],
title="雷达波束扫描演示")
self.radar_system = MultiRadarSystem()
self.targets = []
self.is_running = True
self.last_time = time.time()
self.sim_time = 0.0
def initialize(self):
"""初始化演示"""
# 创建多个雷达
radar1 = self.radar_system.add_radar(
position=[-50, 0, 5],
beam_width=15,
max_range=80,
scan_speed=45,
scan_sector=120
)
radar2 = self.radar_system.add_radar(
position=[50, 0, 8],
beam_width=10,
max_range=100,
scan_speed=30,
scan_sector=180
)
radar3 = self.radar_system.add_radar(
position=[0, 50, 6],
beam_width=20,
max_range=70,
scan_speed=60,
scan_sector=90
)
radar4 = self.radar_system.add_radar(
position=[0, -50, 7],
beam_width=12,
max_range=90,
scan_speed=25,
scan_sector=360
)
# 设置不同的扫描方向
radar2.scan_direction = -1
radar3.scan_direction = -1
# 创建目标
self._create_targets()
# 添加可视化对象
self._add_visualizations()
# 添加信息显示
self.info_text = self.plotter.add_text(
"",
position='upper_left',
font_size=10,
color='white'
)
# 添加控制说明
controls = "雷达扫描演示控制:\n"
controls += "空格: 暂停/继续扫描\n"
controls += "1-4: 切换雷达扫描\n"
controls += "+/-: 调整扫描速度\n"
controls += "R: 重置所有雷达\n"
controls += "D: 切换探测点显示\n"
controls += "A: 切换扫描区域显示\n"
self.control_text = self.plotter.add_text(
controls,
position='lower_left',
font_size=9,
color='cyan'
)
# 设置相机
self.plotter.camera_position = [(0, 0, 150), (0, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0)]
# 添加网格
self.plotter.add_floor('-z', show_edges=True, opacity=0.2)
# 添加坐标轴
self.plotter.add_axes()
# 添加键盘事件
self.plotter.add_key_event("space", self.toggle_scan)
self.plotter.add_key_event("r", self.reset_radars)
self.plotter.add_key_event("d", self.toggle_detections)
self.plotter.add_key_event("a", self.toggle_scan_areas)
self.plotter.add_key_event("equal", self.increase_speed) # +键
self.plotter.add_key_event("minus", self.decrease_speed) # -键
for i in range(len(self.radar_system.radars)):
self.plotter.add_key_event(str(i+1),
lambda idx=i: self.toggle_radar_scan(idx))
# 添加回调函数
self.plotter.add_callback(self.update_callback, interval=16)
# 控制变量
self.show_detections = True
self.show_scan_areas = True
def _create_targets(self):
"""创建测试目标"""
# 直线运动目标
for i in range(3):
target = LinearTrajectoryTarget(
initial_position=[np.random.uniform(-60, 60),
np.random.uniform(-60, 60),
np.random.uniform(10, 50)],
target_type='aircraft',
direction=[np.random.uniform(-1, 1),
np.random.uniform(-1, 1),
np.random.uniform(-0.5, 0.5)],
speed=np.random.uniform(10, 30)
)
self.targets.append(target)
# 圆周运动目标
for i in range(2):
target = CircularTrajectoryTarget(
initial_position=[0, 0, 30],
target_type='missile',
center=[np.random.uniform(-30, 30),
np.random.uniform(-30, 30),
30],
radius=np.random.uniform(20, 40),
angular_speed=np.random.uniform(20, 60),
plane='xy'
)
self.targets.append(target)
# 创建目标网格
for target in self.targets:
target.create_geometry(scale=0.5)
target.color = 'gray'
def _add_visualizations(self):
"""添加可视化对象"""
# 添加雷达站
for i, radar in enumerate(self.radar_system.radars):
# 雷达站模型
radar_base = pv.Cylinder(center=radar.radar_position,
direction=[0, 0, 1],
radius=3, height=5)
self.plotter.add_mesh(radar_base, color='darkgray',
name=f'radar_base_{i}')
# 添加目标
for i, target in enumerate(self.targets):
self.plotter.add_mesh(target.mesh, color=target.color,
name=f'target_{i}')
# 初始化雷达可视化
self._update_radar_visualizations()
def _update_radar_visualizations(self):
"""更新雷达可视化"""
# 移除旧的雷达可视化
for actor_name in list(self.plotter.actors.keys()):
if actor_name.startswith(('radar_beam_', 'scan_area_', 'detection_points_')):
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[actor_name])
# 添加新的雷达可视化
vis_data = self.radar_system.get_visualization_data()
for vis in vis_data:
if ((vis['name'].startswith('radar_beam_')) or
(vis['name'].startswith('scan_area_') and self.show_scan_areas) or
(vis['name'].startswith('detection_points_') and self.show_detections)):
if 'point_size' in vis:
# 点数据
self.plotter.add_mesh(
vis['mesh'],
color=vis['color'],
point_size=vis['point_size'],
render_points_as_spheres=vis.get('render_points_as_spheres', False),
opacity=vis.get('opacity', 1.0),
name=vis['name']
)
elif 'scalars' in vis:
# 标量数据
self.plotter.add_mesh(
vis['mesh'],
scalars=vis['scalars'],
cmap=vis.get('cmap', 'hot'),
opacity=vis.get('opacity', 1.0),
name=vis['name']
)
else:
# 普通网格
self.plotter.add_mesh(
vis['mesh'],
color=vis['color'],
opacity=vis.get('opacity', 1.0),
show_edges=vis.get('show_edges', False),
name=vis['name']
)
def update_callback(self):
"""更新回调函数"""
if not self.is_running:
return
current_time = time.time()
delta_time = current_time - self.last_time
self.last_time = current_time
self.sim_time += delta_time
# 更新雷达扫描
self.radar_system.update_all(delta_time)
# 更新目标位置
for target in self.targets:
target.update_position(delta_time)
# 更新目标网格
actor_name = f'target_{self.targets.index(target)}'
if actor_name in self.plotter.actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[actor_name])
new_mesh = target.mesh.copy()
new_mesh.translate(-target.current_position, inplace=True)
new_mesh.rotate_z(target.orientation, inplace=True)
new_mesh.translate(target.current_position, inplace=True)
self.plotter.add_mesh(new_mesh, color=target.color,
name=actor_name)
# 检测目标
total_detections = 0
for radar in self.radar_system.radars:
detections = radar.detect_targets(self.targets)
total_detections += detections
# 更新雷达可视化
self._update_radar_visualizations()
# 更新信息
info = f"仿真时间: {self.sim_time:.1f}s\n"
info += f"雷达数量: {len(self.radar_system.radars)}\n"
info += f"目标数量: {len(self.targets)}\n"
info += f"当前探测: {total_detections} 个目标\n"
info += f"扫描区域显示: {'开启' if self.show_scan_areas else '关闭'}\n"
info += f"探测点显示: {'开启' if self.show_detections else '关闭'}\n\n"
for i, radar in enumerate(self.radar_system.radars):
detections = len(radar.detected_points)
info += f"雷达{i+1}: 角度{radar.current_angle:.1f}° 速度{radar.scan_speed}°/s 探测{detections}\n"
self.info_text.SetText(3, info)
# 请求重绘
self.plotter.update()
def toggle_scan(self):
"""切换扫描状态"""
self.is_running = not self.is_running
if self.is_running:
self.last_time = time.time()
state = "继续" if self.is_running else "暂停"
print(f"雷达扫描{state}")
def reset_radars(self):
"""重置所有雷达"""
for radar in self.radar_system.radars:
radar.current_angle = 0.0
self.sim_time = 0.0
print("所有雷达已重置")
def toggle_detections(self):
"""切换探测点显示"""
self.show_detections = not self.show_detections
state = "开启" if self.show_detections else "关闭"
print(f"探测点显示{state}")
self._update_radar_visualizations()
def toggle_scan_areas(self):
"""切换扫描区域显示"""
self.show_scan_areas = not self.show_scan_areas
state = "开启" if self.show_scan_areas else "关闭"
print(f"扫描区域显示{state}")
self._update_radar_visualizations()
def toggle_radar_scan(self, radar_index):
"""切换单个雷达扫描状态"""
if 0 <= radar_index < len(self.radar_system.radars):
radar = self.radar_system.radars[radar_index]
radar.is_scanning = not radar.is_scanning
state = "开启" if radar.is_scanning else "关闭"
print(f"雷达{radar_index+1}扫描{state}")
def increase_speed(self):
"""增加所有雷达扫描速度"""
for radar in self.radar_system.radars:
radar.scan_speed = min(radar.scan_speed + 10, 180)
print(f"扫描速度增加,当前速度: {[r.scan_speed for r in self.radar_system.radars]}")
def decrease_speed(self):
"""减少所有雷达扫描速度"""
for radar in self.radar_system.radars:
radar.scan_speed = max(radar.scan_speed - 10, 5)
print(f"扫描速度减少,当前速度: {[r.scan_speed for r in self.radar_system.radars]}")
def run(self):
"""运行演示"""
self.initialize()
print("雷达波束扫描演示")
print("=" * 50)
print("演示说明:")
print("- 不同颜色的锥体表示不同雷达的波束")
print("- 半透明区域表示雷达扫描范围")
print("- 白色点表示当前探测到的目标")
print("- 灰色模型表示运动目标")
self.plotter.show()
# 创建并运行演示
demo = RadarScanDemo()
demo.run()
# 运行演示
radar_scan_demo()6. 案例3:导弹追踪目标(简易模型)
在这个案例中,我们将实现导弹追踪目标的简易模型,展示导弹如何根据目标位置调整飞行方向。
6.1 导弹追踪系统设计
python
class Missile:
"""导弹类"""
def __init__(self, initial_position, initial_velocity=None, max_speed=50.0,
acceleration=20.0, turn_rate=90.0):
"""
初始化导弹
参数:
initial_position: 初始位置 [x, y, z]
initial_velocity: 初始速度向量 [vx, vy, vz]
max_speed: 最大速度
acceleration: 加速度
turn_rate: 转向速率(度/秒)
"""
self.position = np.array(initial_position, dtype=float)
self.velocity = (initial_velocity if initial_velocity is not None
else np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]))
self.max_speed = max_speed
self.acceleration = acceleration
self.turn_rate = turn_rate
# 导弹属性
self.mesh = None
self.trajectory = []
self.target = None
self.is_active = True
self.launch_time = time.time()
self.orientation = 0.0 # 朝向角度
# 创建导弹几何
self._create_missile_geometry()
def _create_missile_geometry(self):
"""创建导弹几何体"""
# 导弹主体
body = pv.Cylinder(center=[0, 0, 0], direction=[1, 0, 0],
radius=0.5, height=6)
# 导弹头部
nose = pv.Cone(center=[3, 0, 0], direction=[1, 0, 0],
height=2, radius=0.5)
# 尾翼
fin_positions = [
[-2, 0, 1], [-2, 0, -1], # 垂直尾翼
[-2, 1, 0], [-2, -1, 0] # 水平尾翼
]
self.mesh = body.boolean_union(nose)
for pos in fin_positions:
fin = pv.Box(bounds=[-0.5, 0.5, -0.1, 0.1, -0.5, 0.5])
fin.translate(pos, inplace=True)
self.mesh = self.mesh.boolean_union(fin)
# 初始位置和朝向
self.mesh.translate(self.position, inplace=True)
def set_target(self, target_position):
"""设置目标位置"""
self.target = np.array(target_position, dtype=float)
def update(self, delta_time):
"""更新导弹状态"""
if not self.is_active or self.target is None:
return self.position
# 计算到目标的向量
to_target = self.target - self.position
distance_to_target = np.linalg.norm(to_target)
# 如果接近目标,爆炸
if distance_to_target < 2.0:
self.is_active = False
print("导弹命中目标!")
return self.position
# 计算当前速度方向
current_speed = np.linalg.norm(self.velocity)
if current_speed > 0.1:
current_direction = self.velocity / current_speed
else:
current_direction = np.array([1.0, 0.0, 0.0])
# 计算目标方向
target_direction = to_target / distance_to_target
# 计算转向角度
dot_product = np.dot(current_direction, target_direction)
dot_product = np.clip(dot_product, -1.0, 1.0)
angle_to_target = np.degrees(np.arccos(dot_product))
# 计算转向量
if angle_to_target > 1.0: # 避免微小角度抖动
# 计算转向轴
turn_axis = np.cross(current_direction, target_direction)
if np.linalg.norm(turn_axis) > 0.001:
turn_axis = turn_axis / np.linalg.norm(turn_axis)
# 计算最大可转向角度
max_turn_angle = self.turn_rate * delta_time
turn_ratio = min(1.0, max_turn_angle / angle_to_target)
# 使用球面线性插值计算新方向
new_direction = self.slerp(current_direction, target_direction, turn_ratio)
# 更新速度方向
new_speed = min(current_speed + self.acceleration * delta_time, self.max_speed)
self.velocity = new_direction * new_speed
else:
# 方向一致,直接加速
new_speed = min(current_speed + self.acceleration * delta_time, self.max_speed)
self.velocity = current_direction * new_speed
else:
# 方向基本一致,直接加速
new_speed = min(current_speed + self.acceleration * delta_time, self.max_speed)
self.velocity = target_direction * new_speed
# 更新位置
displacement = self.velocity * delta_time
self.position += displacement
# 更新朝向
if np.linalg.norm(self.velocity) > 0.1:
forward = self.velocity / np.linalg.norm(self.velocity)
self.orientation = np.degrees(np.arctan2(forward[1], forward[0]))
# 记录轨迹
self.trajectory.append(self.position.copy())
if len(self.trajectory) > 1000:
self.trajectory.pop(0)
return self.position
def slerp(self, start, end, ratio):
"""球面线性插值"""
dot = np.dot(start, end)
dot = np.clip(dot, -1.0, 1.0)
theta = np.arccos(dot) * ratio
relative_vec = end - start * dot
relative_vec = relative_vec / np.linalg.norm(relative_vec)
return start * np.cos(theta) + relative_vec * np.sin(theta)
def get_trajectory_mesh(self):
"""获取轨迹网格"""
if len(self.trajectory) < 2:
return None
points = np.array(self.trajectory)
lines = np.arange(len(points))
lines = np.insert(lines, 0, len(points))
trajectory_mesh = pv.PolyData(points, lines=lines)
# 添加时间属性
time_values = np.linspace(0, 1, len(points))
trajectory_mesh['time'] = time_values
return trajectory_mesh
class MovingTarget:
"""运动目标类(简化版)"""
def __init__(self, initial_position, velocity=None):
self.position = np.array(initial_position, dtype=float)
self.velocity = (velocity if velocity is not None
else np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]))
self.mesh = None
self.trajectory = []
# 创建目标几何
self._create_target_geometry()
def _create_target_geometry(self):
"""创建目标几何体"""
# 简单球体表示目标
self.mesh = pv.Sphere(center=self.position, radius=2.0)
def update(self, delta_time):
"""更新目标位置"""
# 简单直线运动
displacement = self.velocity * delta_time
self.position += displacement
# 记录轨迹
self.trajectory.append(self.position.copy())
if len(self.trajectory) > 1000:
self.trajectory.pop(0)
return self.position
def get_trajectory_mesh(self):
"""获取轨迹网格"""
if len(self.trajectory) < 2:
return None
points = np.array(self.trajectory)
lines = np.arange(len(points))
lines = np.insert(lines, 0, len(points))
trajectory_mesh = pv.PolyData(points, lines=lines)
return trajectory_mesh6.2 导弹追踪演示
python
def missile_tracking_demo():
"""导弹追踪目标演示"""
class MissileTrackingDemo:
def __init__(self):
self.plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[1400, 900],
title="导弹追踪目标演示")
self.missiles = []
self.targets = []
self.is_running = True
self.last_time = time.time()
self.sim_time = 0.0
self.missile_counter = 0
def initialize(self):
"""初始化演示"""
# 创建目标
self._create_targets()
# 添加可视化对象
self._add_visualizations()
# 添加信息显示
self.info_text = self.plotter.add_text(
"",
position='upper_left',
font_size=10,
color='white'
)
# 添加控制说明
controls = "导弹追踪演示控制:\n"
controls += "空格: 暂停/继续仿真\n"
controls += "M: 发射新导弹\n"
controls += "T: 创建新目标\n"
controls += "R: 重置场景\n"
controls += "D: 切换导弹轨迹显示\n"
controls += "1-9: 选择目标编号发射导弹\n"
self.control_text = self.plotter.add_text(
controls,
position='lower_left',
font_size=9,
color='cyan'
)
# 设置相机
self.plotter.camera_position = [(0, 0, 100), (0, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0)]
# 添加网格地面
self.plotter.add_floor('-z', show_edges=True, opacity=0.2)
# 添加坐标轴
self.plotter.add_axes()
# 添加键盘事件
self.plotter.add_key_event("space", self.toggle_simulation)
self.plotter.add_key_event("m", self.launch_missile)
self.plotter.add_key_event("t", self.create_target)
self.plotter.add_key_event("r", self.reset_scene)
self.plotter.add_key_event("d", self.toggle_trajectories)
for i in range(1, 10):
self.plotter.add_key_event(str(i),
lambda idx=i: self.launch_missile_at_target(idx-1))
# 添加回调函数
self.plotter.add_callback(self.update_callback, interval=16)
# 控制变量
self.show_trajectories = True
def _create_targets(self):
"""创建初始目标"""
# 创建3个运动目标
target1 = MovingTarget(
initial_position=[-30, -30, 20],
velocity=np.array([10, 8, 0])
)
target2 = MovingTarget(
initial_position=[0, 30, 30],
velocity=np.array([-5, -12, 2])
)
target3 = MovingTarget(
initial_position=[40, -10, 25],
velocity=np.array([-8, 6, -1])
)
self.targets = [target1, target2, target3]
def _add_visualizations(self):
"""添加可视化对象"""
# 添加目标
for i, target in enumerate(self.targets):
self.plotter.add_mesh(
target.mesh,
color='red',
name=f'target_{i}'
)
# 添加导弹发射基地
base_positions = [[-50, -50, 0], [50, -50, 0], [0, 50, 0]]
for i, pos in enumerate(base_positions):
base = pv.Cylinder(center=pos, direction=[0, 0, 1],
radius=3, height=5)
self.plotter.add_mesh(base, color='gray', name=f'base_{i}')
def update_callback(self):
"""更新回调函数"""
if not self.is_running:
return
current_time = time.time()
delta_time = current_time - self.last_time
self.last_time = current_time
self.sim_time += delta_time
# 更新目标位置
for target in self.targets:
target.update(delta_time)
# 更新目标网格
target_idx = self.targets.index(target)
actor_name = f'target_{target_idx}'
if actor_name in self.plotter.actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[actor_name])
new_mesh = pv.Sphere(center=target.position, radius=2.0)
self.plotter.add_mesh(new_mesh, color='red', name=actor_name)
# 更新导弹
active_missiles = []
for missile in self.missiles:
if missile.is_active:
# 更新导弹位置
missile.update(delta_time)
# 更新导弹网格
missile_idx = self.missiles.index(missile)
actor_name = f'missile_{missile_idx}'
if actor_name in self.plotter.actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[actor_name])
# 创建新位置和姿态的导弹
new_mesh = missile.mesh.copy()
new_mesh.translate(-missile.position, inplace=True)
new_mesh.rotate_z(missile.orientation, inplace=True)
new_mesh.translate(missile.position, inplace=True)
self.plotter.add_mesh(new_mesh, color='orange', name=actor_name)
# 更新导弹轨迹
trajectory_name = f'missile_trajectory_{missile_idx}'
if trajectory_name in self.plotter.actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[trajectory_name])
if self.show_trajectories:
trajectory_mesh = missile.get_trajectory_mesh()
if trajectory_mesh:
self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
color='yellow',
line_width=2,
opacity=0.7,
name=trajectory_name
)
active_missiles.append(missile)
else:
# 导弹已失效,显示爆炸效果
missile_idx = self.missiles.index(missile)
actor_name = f'missile_{missile_idx}'
if actor_name in self.plotter.actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[actor_name])
# 创建爆炸效果
explosion = pv.Sphere(center=missile.position, radius=5.0)
explosion_actor = self.plotter.add_mesh(
explosion,
color='red',
opacity=0.8,
name=f'explosion_{missile_idx}'
)
# 短暂显示后移除爆炸效果
def remove_explosion():
if f'explosion_{missile_idx}' in self.plotter.actors:
self.plotter.remove_actor(
self.plotter.actors[f'explosion_{missile_idx}']
)
# 设置定时器移除爆炸效果
threading.Timer(1.0, remove_explosion).start()
self.missiles = active_missiles
# 更新信息
info = f"仿真时间: {self.sim_time:.1f}s\n"
info += f"目标数量: {len(self.targets)}\n"
info += f"活跃导弹: {len(self.missiles)}\n"
info += f"轨迹显示: {'开启' if self.show_trajectories else '关闭'}\n\n"
for i, target in enumerate(self.targets):
info += f"目标{i+1}: 位置{target.position[:2]} 速度{np.linalg.norm(target.velocity):.1f}\n"
for i, missile in enumerate(self.missiles):
if missile.target is not None:
dist = np.linalg.norm(missile.target - missile.position)
info += f"导弹{i+1}: 距目标{dist:.1f} 速度{np.linalg.norm(missile.velocity):.1f}\n"
self.info_text.SetText(3, info)
# 请求重绘
self.plotter.update()
def toggle_simulation(self):
"""切换仿真状态"""
self.is_running = not self.is_running
if self.is_running:
self.last_time = time.time()
state = "继续" if self.is_running else "暂停"
print(f"仿真{state}")
def launch_missile(self):
"""发射新导弹"""
if not self.targets:
print("没有目标可供攻击")
return
# 随机选择发射基地和目标
base_positions = [[-50, -50, 5], [50, -50, 5], [0, 50, 5]]
launch_base = base_positions[np.random.randint(0, len(base_positions))]
target = self.targets[np.random.randint(0, len(self.targets))]
# 创建导弹
missile = Missile(
initial_position=launch_base,
max_speed=60.0,
acceleration=25.0,
turn_rate=120.0
)
# 设置目标
missile.set_target(target.position)
# 设置初始速度(指向目标的大致方向)
to_target = target.position - launch_base
if np.linalg.norm(to_target) > 0:
initial_direction = to_target / np.linalg.norm(to_target)
missile.velocity = initial_direction * 10.0
self.missiles.append(missile)
self.missile_counter += 1
print(f"发射导弹 #{self.missile_counter} 攻击目标")
def launch_missile_at_target(self, target_index):
"""向指定目标发射导弹"""
if 0 <= target_index < len(self.targets):
base_positions = [[-50, -50, 5], [50, -50, 5], [0, 50, 5]]
launch_base = base_positions[np.random.randint(0, len(base_positions))]
target = self.targets[target_index]
missile = Missile(
initial_position=launch_base,
max_speed=60.0,
acceleration=25.0,
turn_rate=120.0
)
missile.set_target(target.position)
to_target = target.position - launch_base
if np.linalg.norm(to_target) > 0:
initial_direction = to_target / np.linalg.norm(to_target)
missile.velocity = initial_direction * 10.0
self.missiles.append(missile)
self.missile_counter += 1
print(f"发射导弹 #{self.missile_counter} 攻击目标 {target_index+1}")
else:
print(f"目标 {target_index+1} 不存在")
def create_target(self):
"""创建新目标"""
# 随机位置和速度
pos = np.random.uniform(-40, 40, 3)
pos[2] = np.random.uniform(10, 40) # 确保一定高度
vel = np.random.uniform(-15, 15, 3)
vel[2] = np.random.uniform(-3, 3)
target = MovingTarget(initial_position=pos, velocity=vel)
self.targets.append(target)
# 添加到场景
target_idx = len(self.targets) - 1
self.plotter.add_mesh(target.mesh, color='red', name=f'target_{target_idx}')
print(f"创建新目标 #{len(self.targets)}")
def reset_scene(self):
"""重置场景"""
self.missiles = []
self.targets = []
self.missile_counter = 0
self.sim_time = 0.0
# 重新创建目标
self._create_targets()
# 清除所有actor
for actor_name in list(self.plotter.actors.keys()):
if not actor_name.startswith(('base_', 'floor', 'axes')):
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[actor_name])
# 重新添加可视化
self._add_visualizations()
print("场景已重置")
def toggle_trajectories(self):
"""切换轨迹显示"""
self.show_trajectories = not self.show_trajectories
state = "开启" if self.show_trajectories else "关闭"
print(f"导弹轨迹显示{state}")
# 更新轨迹显示
for actor_name in list(self.plotter.actors.keys()):
if actor_name.startswith('missile_trajectory_'):
self.plotter.remove_actor(self.plotter.actors[actor_name])
if self.show_trajectories:
for i, missile in enumerate(self.missiles):
trajectory_mesh = missile.get_trajectory_mesh()
if trajectory_mesh:
self.plotter.add_mesh(
trajectory_mesh,
color='yellow',
line_width=2,
opacity=0.7,
name=f'missile_trajectory_{i}'
)
def run(self):
"""运行演示"""
self.initialize()
print("导弹追踪目标演示")
print("=" * 50)
print("演示说明:")
print("- 红色球体表示运动目标")
print("- 橙色模型表示追踪导弹")
print("- 黄色线条表示导弹飞行轨迹")
print("- 导弹会自动调整方向追踪目标")
self.plotter.show()
# 创建并运行演示
demo = MissileTrackingDemo()
demo.run()
# 运行演示
missile_tracking_demo()7. 知识点总结与提高
7.1 核心技术要点总结
1. 动画制作技术
-
open_gif()和open_movie()方法用于生成预计算动画 -
帧率控制影响动画流畅度
-
合适的编码器选择优化文件大小和质量
2. 实时更新机制
-
回调函数 (
add_callback) 实现实时更新 -
键盘和鼠标事件处理 (
add_key_event,track_click_position) -
多线程架构处理复杂计算和实时渲染
3. 动态对象管理
-
网格位置和姿态的实时更新
-
对象生命周期管理(创建、更新、销毁)
-
轨迹记录和可视化
4. 物理运动模型
-
直线运动、圆周运动、样条曲线运动
-
导弹追踪的转向和加速模型
-
碰撞检测和交互逻辑
7.2 性能优化技巧
内存管理
python
# 重用网格对象,避免频繁创建销毁
mesh = original_mesh.copy()
mesh.transform(transformation_matrix)
# 使用 overwrite 方法更新现有网格
actor.mapper.dataset.overwrite(updated_mesh)渲染优化
python
# 批量更新减少渲染调用
plotter.render()
# 使用适当的细节层次(LOD)
simplified_mesh = complex_mesh.decimate(0.5)
# 视锥体裁剪
visible_objects = filter_visible_objects(all_objects, camera_frustum)7.3 扩展应用方向
军事仿真应用
-
实时战场态势可视化
-
作战方案推演和评估
-
训练模拟系统
科学研究应用
-
物理过程动态模拟
-
数据实时监控和分析
-
科学计算可视化
工业应用
-
机械运动仿真
-
工艺流程可视化
-
实时监控系统