EngineCore_DP0 与 RayWorkerWrapper 进程关系
进程关系概述
EngineCore_DP0 和 RayWorkerWrapper 是主从关系:
- EngineCore_DP0 :主控制器进程(pid=8336),负责协调和管理分布式推理 1
- RayWorkerWrapper :工作进程(pid=14610),运行在 Ray 管理的进程中,执行具体模型推理任务 2
创建时序图
RayWorkerWrapper Ray框架 RayDistributedExecutor EngineCore_DP0 EngineCoreClient AsyncLLM 用户 RayWorkerWrapper Ray框架 RayDistributedExecutor EngineCore_DP0 EngineCoreClient AsyncLLM 用户 启动 vLLM make_async_mp_client() 启动进程 (pid=8336) 创建分布式执行器 初始化 Ray 集群 创建 placement group 创建 RayWorkerWrapper (pid=14610) 注册工作进程 分发任务
详细创建流程
1. EngineCore 创建
EngineCore 在独立进程中启动,通过 EngineCoreClient.make_async_mp_client() 创建 3 。
2. RayDistributedExecutor 初始化
EngineCore 创建 RayDistributedExecutor 实例 4 ,调用 _init_executor() 方法 5 。
3. Ray Worker 创建
在 _init_workers_ray() 中创建 RayWorkerWrapper 6 :
python
worker = ray.remote(
num_cpus=0,
num_gpus=num_gpus,
scheduling_strategy=scheduling_strategy,
)(RayWorkerWrapper).remote(rpc_rank=rank)4. 进程通信
Notes
- EngineCore_DP0 运行在独立进程中,实现资源隔离
- RayWorkerWrapper 运行在 Ray 管理的进程内,每个 GPU 对应一个实例
- 两个进程通过 Ray 的 RPC 机制协调工作,实现分布式推理 9
Wiki pages you might want to explore:
Wiki pages you might want to explore:
Citations
File: vllm/v1/engine/core.py (L79-109)
python
class EngineCore:
"""Inner loop of vLLM's Engine."""
def __init__(
self,
vllm_config: VllmConfig,
executor_class: type[Executor],
log_stats: bool,
executor_fail_callback: Callable | None = None,
include_finished_set: bool = False,
):
# plugins need to be loaded at the engine/scheduler level too
from vllm.plugins import load_general_plugins
load_general_plugins()
self.vllm_config = vllm_config
if not vllm_config.parallel_config.data_parallel_rank_local:
logger.info(
"Initializing a V1 LLM engine (v%s) with config: %s",
VLLM_VERSION,
vllm_config,
)
self.log_stats = log_stats
# Setup Model.
self.model_executor = executor_class(vllm_config)
if executor_fail_callback is not None:
self.model_executor.register_failure_callback(executor_fail_callback)File: vllm/v1/engine/core.py (L1457-1485)
python
class EngineCoreActorMixin:
"""
Ray actor for running EngineCore in a data parallel context
"""
def __init__(
self,
vllm_config: VllmConfig,
addresses: EngineZmqAddresses,
dp_rank: int = 0,
local_dp_rank: int = 0,
):
self.addresses = addresses
vllm_config.parallel_config.data_parallel_index = dp_rank
vllm_config.parallel_config.data_parallel_rank_local = local_dp_rank
# Set CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES as early as possible in actor life cycle
# NOTE: in MP we set CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES at process creation time,
# and this cannot be done in the same way for Ray because:
# 1) Ray manages life cycle of all ray workers (including
# DPEngineCoreActor)
# 2) Ray sets CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES based on num_gpus configuration
# To bypass 2, we need to also set
# RAY_EXPERIMENTAL_NOSET_CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES, but vLLM workers created
# thereafter would have CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES set, which is sticky:
# https://github.com/ray-project/ray/blob/e752fc319ddedd9779a0989b6d3613909bad75c9/python/ray/_private/worker.py#L456 # noqa: E501
# This is problematic because when the vLLM worker (a Ray actor)
# executes a task, it indexes into the sticky CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES
# rather than directly using the GPU ID, potentially resulting inFile: vllm/v1/executor/ray_utils.py (L41-66)
python
class RayWorkerWrapper(WorkerWrapperBase):
"""Ray wrapper for vllm.worker.Worker, allowing Worker to be
lazily initialized after Ray sets CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES."""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# Since the compiled DAG runs a main execution
# in a different thread that calls cuda.set_device.
# The flag indicates is set_device is called on
# that thread.
self.compiled_dag_cuda_device_set = False
def get_node_ip(self) -> str:
return get_ip()
def get_node_and_gpu_ids(self) -> tuple[str, list[int]]:
node_id = ray.get_runtime_context().get_node_id()
device_key = vllm.platforms.current_platform.ray_device_key
if not device_key:
raise RuntimeError(
"current platform %s does not support ray.",
vllm.platforms.current_platform.device_name,
)
gpu_ids = ray.get_runtime_context().get_accelerator_ids()[device_key]
return node_id, gpu_idsFile: vllm/v1/executor/ray_utils.py (L83-123)
python
def execute_model_ray(
self,
execute_model_input: tuple["SchedulerOutput", "GrammarOutput"]
| tuple["SchedulerOutput", "GrammarOutput", "IntermediateTensors"],
) -> Union[
"ModelRunnerOutput",
tuple["SchedulerOutput", "GrammarOutput", "IntermediateTensors"],
]:
# This method is used by Ray Compiled Graph to execute the model,
# and it needs a special logic of self.setup_device_if_necessary()
self.setup_device_if_necessary()
assert self.worker is not None, "Worker is not initialized"
if len(execute_model_input) == 3:
scheduler_output, grammar_output, intermediate_tensors = (
execute_model_input
)
else:
scheduler_output, grammar_output = execute_model_input
intermediate_tensors = None
assert self.worker.model_runner is not None
output = self.worker.model_runner.execute_model(
scheduler_output, intermediate_tensors
)
if isinstance(output, IntermediateTensors):
return scheduler_output, grammar_output, output
if isinstance(output, AsyncModelRunnerOutput):
output = output.get_output()
if not get_pp_group().is_last_rank:
# Case where there are no scheduled requests
# but may still be finished requests.
assert not output or not output.req_ids
output = scheduler_output, grammar_output, None
elif output is None:
output = self.worker.model_runner.sample_tokens(grammar_output)
# Ensure outputs crossing Ray compiled DAG are serializable.
# AsyncModelRunnerOutput holds CUDA events and cannot be
# pickled.
if isinstance(output, AsyncModelRunnerOutput):
output = output.get_output()
return outputFile: vllm/v1/executor/ray_executor.py (L80-97)
python
def _init_executor(self) -> None:
self.forward_dag: ray.dag.CompiledDAG | None = None
# For TPU or XPU, avoid compiling NVIDIA's NCCL
if current_platform.is_tpu() or current_platform.is_xpu():
os.environ["VLLM_USE_RAY_COMPILED_DAG_CHANNEL_TYPE"] = "shm"
assert self.uses_ray
initialize_ray_cluster(self.parallel_config)
placement_group = self.parallel_config.placement_group
# Disable Ray usage stats collection.
ray_usage = os.environ.get("RAY_USAGE_STATS_ENABLED", "0")
if ray_usage != "1":
os.environ["RAY_USAGE_STATS_ENABLED"] = "0"
# Create the parallel GPU workers.
self._init_workers_ray(placement_group)File: vllm/v1/executor/ray_executor.py (L154-221)
python
def _init_workers_ray(self, placement_group: "PlacementGroup", **ray_remote_kwargs):
num_gpus = envs.VLLM_RAY_PER_WORKER_GPUS
# The driver dummy worker does not actually use any resources.
# It holds the resource for the driver worker.
self.driver_dummy_worker: RayWorkerWrapper | None = None
# The remaining workers are the actual ray actors.
self.workers: list[RayWorkerWrapper] = []
# Used in ray compiled DAG: indexed first by PP rank,
# and then TP rank. In other words, the inner list is
# the TP group of workers for a PP rank.
self.pp_tp_workers: list[list[RayWorkerWrapper]] = []
if self.parallel_config.ray_workers_use_nsight:
ray_remote_kwargs = self._configure_ray_workers_use_nsight(
ray_remote_kwargs
)
# Create the workers.
bundle_indices: list[int]
if envs.VLLM_RAY_BUNDLE_INDICES:
# Use the bundle indices specified by the user.
bundle_indices = list(map(int, envs.VLLM_RAY_BUNDLE_INDICES.split(",")))
assert len(bundle_indices) == self.parallel_config.world_size, (
"VLLM_RAY_BUNDLE_INDICES must have the same size"
f" as the world size, but got {bundle_indices=} "
f"and {self.parallel_config.world_size=}"
)
assert len(set(bundle_indices)) == len(bundle_indices), (
"VLLM_RAY_BUNDLE_INDICES cannot have duplicate values,"
f" but got {bundle_indices=}"
)
else:
# use the first N bundles that have GPU resources.
bundle_indices = []
for bundle_id, bundle in enumerate(placement_group.bundle_specs):
if bundle.get(current_platform.ray_device_key, 0):
bundle_indices.append(bundle_id)
bundle_indices = bundle_indices[: self.parallel_config.world_size]
worker_metadata: list[RayWorkerMetaData] = []
driver_ip = get_ip()
for rank, bundle_id in enumerate(bundle_indices):
scheduling_strategy = PlacementGroupSchedulingStrategy(
placement_group=placement_group,
placement_group_capture_child_tasks=True,
placement_group_bundle_index=bundle_id,
)
if current_platform.ray_device_key == "GPU":
# NV+AMD GPUs, and Intel XPUs
worker = ray.remote(
num_cpus=0,
num_gpus=num_gpus,
scheduling_strategy=scheduling_strategy,
**ray_remote_kwargs,
)(RayWorkerWrapper).remote(rpc_rank=rank)
else:
worker = ray.remote(
num_cpus=0,
num_gpus=0,
resources={current_platform.ray_device_key: num_gpus},
scheduling_strategy=scheduling_strategy,
**ray_remote_kwargs,
)(RayWorkerWrapper).remote(rpc_rank=rank)
worker_metadata.append(RayWorkerMetaData(worker=worker, created_rank=rank))File: vllm/v1/executor/ray_executor.py (L517-517)
python
"cupy is not installed but required since "CoreEngineProcManager。EngineCoreClient SyncMPClient MPClient 之间的关系?

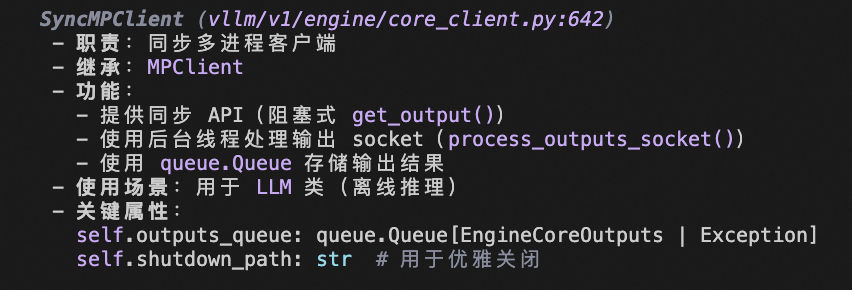


现在我明白了。让我解释为什么 SyncMPClient 需要调用父类 MPClient 的 init:
为什么 SyncMPClient 需要调用父类的 init
- 父类 MPClient.init 完成的工作
MPClient.init (vllm/v1/engine/core_client.py:423-520) 执行了大量初始化工作:
def init (
self,
asyncio_mode: bool,
vllm_config: VllmConfig,
executor_class: type[Executor],
log_stats: bool,
client_addresses: dict[str, str] | None = None,
):
1. 存储配置
self.vllm_config = vllm_config
# 2. 设置序列化器
self.encoder = MsgpackEncoder()
self.decoder = MsgpackDecoder(EngineCoreOutputs)
# 3. 创建 ZMQ 上下文
sync_ctx = zmq.Context(io_threads=2)
self.ctx = zmq.asyncio.Context(sync_ctx) if asyncio_mode else sync_ctx
# 4. 创建资源管理器(用于清理)
self.resources = BackgroundResources(ctx=sync_ctx)
self._finalizer = weakref.finalize(self, self.resources)
# 5. 启动 EngineCore 进程(通过 launch_core_engines)
with launch_core_engines(vllm_config, executor_class, log_stats) as (
engine_manager,
coordinator,
addresses,
):
self.resources.coordinator = coordinator
self.resources.engine_manager = engine_manager
# 6. 创建 ZMQ sockets
self.input_socket = make_zmq_socket(self.ctx, input_address, zmq.ROUTER, bind=True)
self.resources.output_socket = make_zmq_socket(self.ctx, output_address, zmq.PULL)
# 7. 设置数据并行相关状态
self.engine_ranks_managed = [...]
self.core_engines = [...]
self.utility_results = {}- 子类 SyncMPClient.init 需要父类的初始化结果
SyncMPClient.init (vllm/v1/engine/core_client.py:642-690) 依赖父类初始化的属性:
def init (
self, vllm_config: VllmConfig, executor_class: type[Executor], log_stats: bool
):
调用父类 init ,传入 asyncio_mode=False
super().init (
asyncio_mode=False, # 同步模式
vllm_config=vllm_config,
executor_class=executor_class,
log_stats=log_stats,
)
# 使用父类初始化的属性
self.is_dp = self.vllm_config.parallel_config.data_parallel_size > 1 # 使用 self.vllm_config
self.outputs_queue = queue.Queue[EngineCoreOutputs | Exception]()
# 依赖父类初始化的属性
ctx = self.ctx # 父类创建的 ZMQ 上下文
out_socket = self.resources.output_socket # 父类创建的输出 socket
decoder = self.decoder # 父类创建的解码器
utility_results = self.utility_results # 父类创建的字典
# 创建后台线程处理输出
def process_outputs_socket():
# 使用 out_socket, decoder, utility_results
...- 不调用父类 init 的后果
如果不调用 super().init(),会导致:
-
self.vllm_config未定义 → 访问时抛出 AttributeError -
self.ctx未定义 → 无法创建 ZMQ socket -
self.resources未定义 → 无法访问 output_socket -
self.decoder未定义 → 无法解码输出消息 -
self.utility_results未定义 → 无法存储工具调用结果 -
EngineCore 进程未启动 → 没有后台进程处理请求
-
为什么使用 super().init()
这是 Python 面向对象编程的标准做法:
class SyncMPClient(MPClient):
def init (self, vllm_config, executor_class, log_stats):
参数适配:SyncMPClient 不需要 asyncio_mode 参数
但父类需要,所以在这里硬编码为 False
super().init (
asyncio_mode=False, # 明确指定为同步模式
vllm_config=vllm_config,
executor_class=executor_class,
log_stats=log_stats,
)
# 子类特有的初始化
self.outputs_queue = queue.Queue()
# ... 其他同步模式特有的设置- 设计优势
这种设计的好处:
- 代码复用:MPClient 的初始化逻辑被 SyncMPClient 和 AsyncMPClient 共享
- 职责分离:
- MPClient:负责通用的多进程客户端初始化(ZMQ、EngineCore 启动)
- SyncMPClient:负责同步模式特有的初始化(队列、后台线程)
- 易于维护:修改通用逻辑只需在 MPClient 中修改一次
- 类型安全:通过 asyncio_mode 参数控制创建同步或异步的 ZMQ 上下文
总结
SyncMPClient 调用父类 MPClient 的 init 是因为:
- 父类完成了核心初始化:ZMQ 上下文、EngineCore 进程启动、socket 创建
- 子类依赖父类的属性:ctx、resources、decoder、utility_results 等
- 遵循继承原则:子类应该确保父类正确初始化,这是面向对象编程的基本要求
✦ 如果不调用父类的 init,SyncMPClient 将无法正常工作,因为缺少必要的初始化状态。