目录
[1-1 Introduction](#1-1 Introduction)
[Machine Learning](#Machine Learning)
[1-2 What is machine learning](#1-2 What is machine learning)
[Machine learning definition](#Machine learning definition)
[Machine learning algorithms:](#Machine learning algorithms:)
[1-3 Supervised learning](#1-3 Supervised learning)
[Housing price prediction](#Housing price prediction)
[Breast cancer (malignant, benign)](#Breast cancer (malignant, benign))
[1-4 Unsupervised Learning](#1-4 Unsupervised Learning)
[Cocktail party problem](#Cocktail party problem):
1-1 Introduction
Machine Learning
-
Grew out of work in AI
-
New capability for computers
Examples:
- Database mining 数据挖掘
Large datasets from growth of automation/web.
E.g., Web click data, medical records, biology, engineering
- Applications can't program by hand. 无法手动编程实现的应用
E.g., Autonomous helicopter, handwriting recognition, most of
Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision.
- Self-customizing programs 自适应程序
E.g., Amazon, Netflix product recommendations
- Understanding human learning (brain, real AI). 理解人类学习机制
1-2 What is machine learning
Machine learning definition
• Arthur Samuel (1959). Machine Learning: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn
without being explicitly programmed.
• Tom Mitchell (1998) Well-posed Learning Problem: A computer program is said to learnfrom experience E with respect to some task Tand some performance measure P, if itsperformance on T, as measured by P, improveswith experience E.
Question:
Suppose your email program watches which emails you do or do not mark as spam, and based on that learns how to better filter spam. What is the task T in this setting?
Machine learning algorithms:
-Supervised learning 监督学习
-Unsupervised learning 无监督学习
Others: Reinforcement learning, recommender systems. 强化学习,推荐系统
Also talk about: Practical advice for applying learning algorithms.
1-3 Supervised learning
Housing price prediction
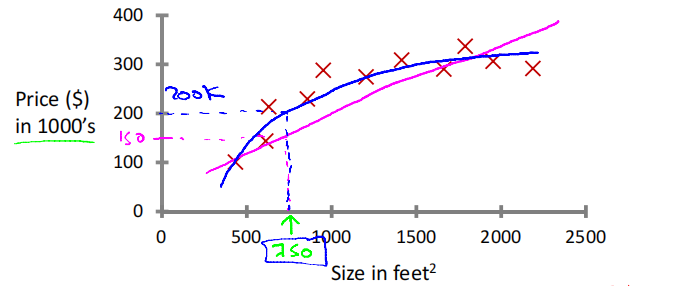
Supervised Learning: "right answers" given
Regression回归: Predict continuous valued output (price)
Breast cancer (malignant, benign)
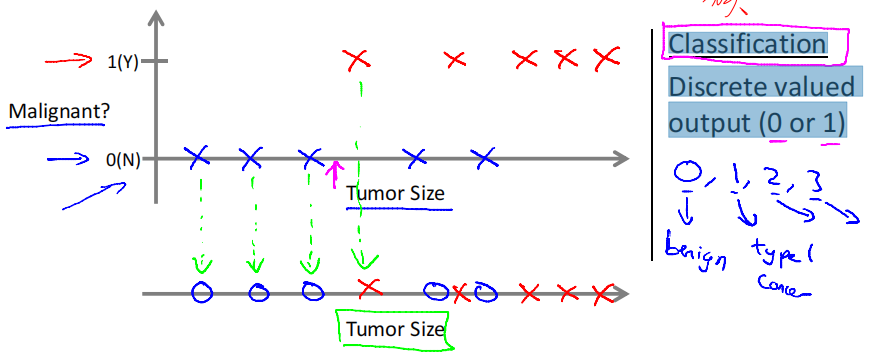
Classification: Discrete valued output (0 or 1) or (0, 1, 2, 3)
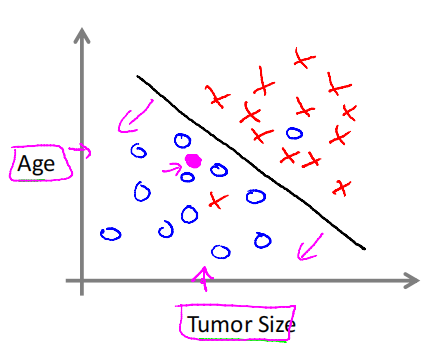
one feature, two features or more features
-
Tumor Size
-
Age
-
Clump Thickness
-
Uniformity of Cell Size
-
Uniformity of Cell Shape
...
Question:
You're running a company, and you want to develop learning algorithms to address each of two problems.
Problem 1: You have a large inventory of identical items. You want to predict how many of these items will sell over the next 3 months.
Problem 2: You'd like software to examine individual customer accounts, and for each account decide if it has been hacked/compromised.
Should you treat these as classification or as regression problems?

1-4 Unsupervised Learning
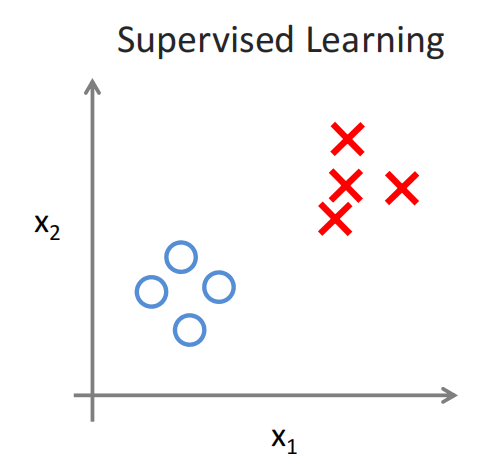
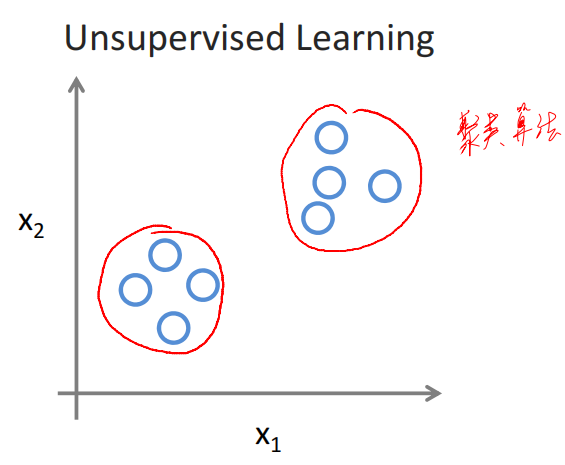
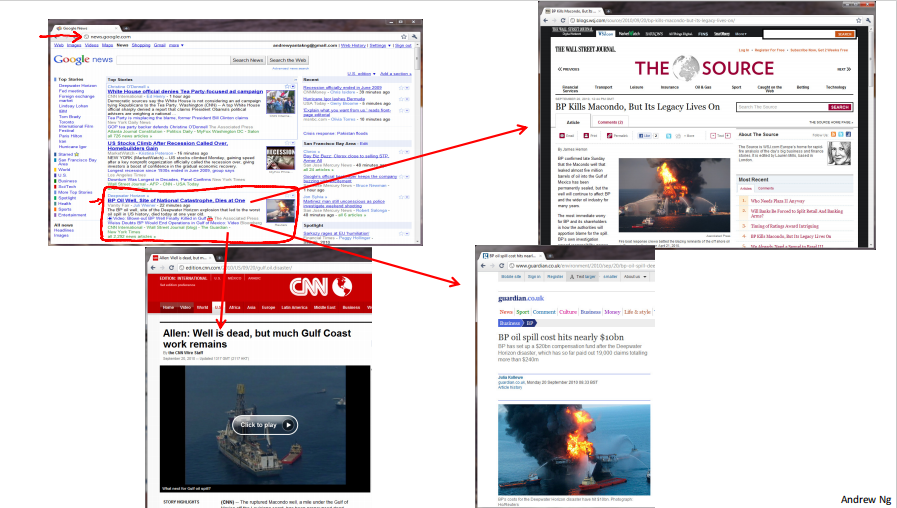
Examples:
- Google news
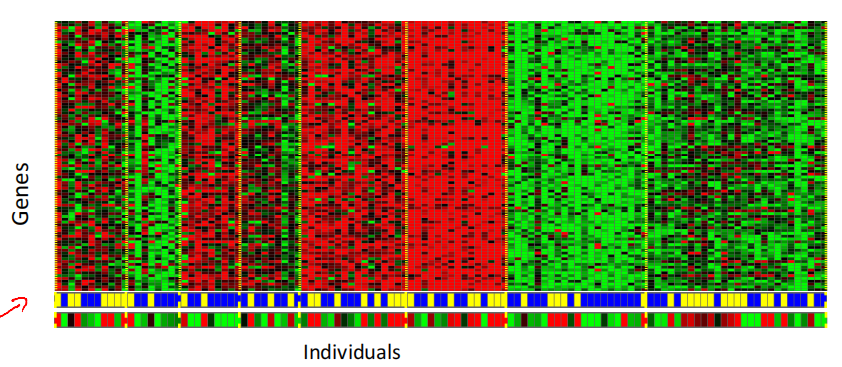
-
Individual genes
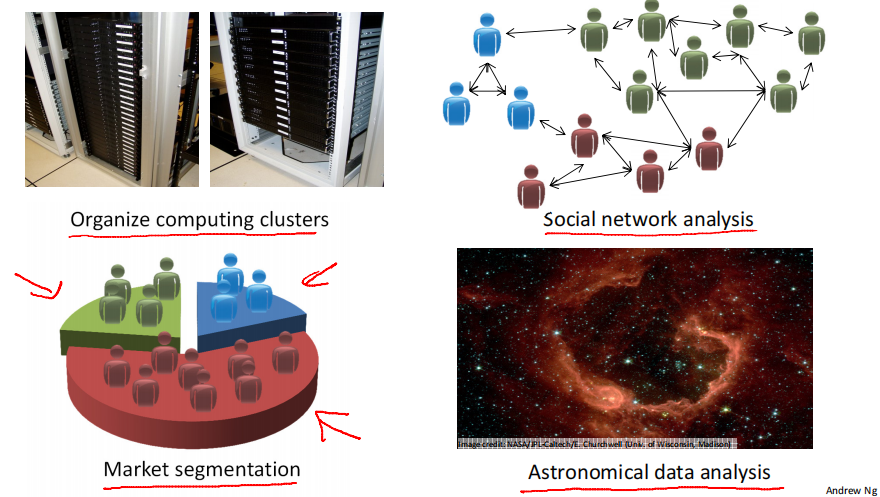
- Organize computing clusters
- Social network analysis
- Market segmentation
-
Astronomical data analysis
Cocktail party problem:
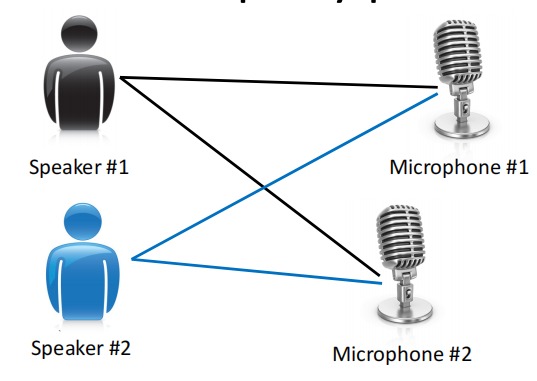
You can solve this problem by just one line program:
W,s,v\] = svd((repmat(sum(x.*x,1),size(x,1),1).*x)\*x'); \[Source: Sam Roweis, Yair Weiss \& Eero Simoncelli
建议:先用Octave建立原型,再用C++、JAVA或Python语言实现
Question:
Of the following examples, which would you address using an unsupervised learning algorithm? (Check all that apply.)

