目录
[2.1 查询表达式 vs 方法链](#2.1 查询表达式 vs 方法链)
[2.2 高级LINQ操作](#2.2 高级LINQ操作)
[3.1 集合操作的性能考量](#3.1 集合操作的性能考量)
[3.2 内存高效的算法实现](#3.2 内存高效的算法实现)
[4.1 内置排序与自定义排序](#4.1 内置排序与自定义排序)
[4.2 高级搜索算法](#4.2 高级搜索算法)
[5.1 数学与统计函数](#5.1 数学与统计函数)
[6.1 并行LINQ(PLINQ)](#6.1 并行LINQ(PLINQ))
[6.2 异步流(C# 8.0+)](# 8.0+))
[7.1 哈希与加密](#7.1 哈希与加密)
[8.1 BenchmarkDotNet实战](#8.1 BenchmarkDotNet实战)
如果您喜欢此文章,请收藏、点赞、评论,谢谢,祝您快乐每一天。
一、C#算法设计的现代范式
1.1 C#算法的演进:从过程式到函数式
C#算法设计经历了三次革命性演进:
- 1.0时代:传统过程式算法,类似Java/C++
- 3.0时代:LINQ引入声明式编程
- 8.0+时代:模式匹配、记录类型、异步流
1.2 C#算法的核心优势
// 1. LINQ:声明式编程
var results = numbers
.Where(n => n % 2 == 0)
.Select(n => n * n)
.OrderByDescending(n => n)
.Take(10);
// 2. 异步算法:async/await
public async Task<int> ProcessDataAsync(IEnumerable<int> data) {
var tasks = data.Select(async item => {
await Task.Delay(100);
return item * 2;
});
return (await Task.WhenAll(tasks)).Sum();
}
// 3. 模式匹配(C# 8.0+)
public static decimal CalculateDiscount(object customer) => customer switch {
PremiumCustomer p when p.Years > 5 => 0.3m,
PremiumCustomer p => 0.2m,
RegularCustomer r when r.PurchaseAmount > 1000 => 0.1m,
_ => 0.0m
};

二、LINQ算法:声明式编程典范
2.1 查询表达式 vs 方法链
// 方法链风格(更函数式)
var topProducts = products
.Where(p => p.Price > 100)
.OrderByDescending(p => p.Rating)
.Select(p => new { p.Name, p.Price, Discount = p.Price * 0.9 })
.Take(5);
// 查询表达式风格(类似SQL)
var topProductsQuery =
from p in products
where p.Price > 100
orderby p.Rating descending
select new { p.Name, p.Price, Discount = p.Price * 0.9 }
into discounted
select discounted;
// 性能优化:延迟执行 vs 立即执行
var deferred = products.Where(p => p.Price > 100); // 延迟执行
var immediate = products.Where(p => p.Price > 100).ToList(); // 立即执行
2.2 高级LINQ操作
// 1. 分组操作
var salesByRegion = orders
.GroupBy(o => o.Region)
.Select(g => new {
Region = g.Key,
TotalSales = g.Sum(o => o.Amount),
AverageOrder = g.Average(o => o.Amount),
Count = g.Count()
});
// 2. 连接操作
var customerOrders = customers
.Join(orders,
c => c.Id,
o => o.CustomerId,
(c, o) => new { c.Name, o.OrderDate, o.Amount })
.GroupBy(x => x.Name)
.Select(g => new {
Customer = g.Key,
TotalSpent = g.Sum(x => x.Amount),
LastOrder = g.Max(x => x.OrderDate)
});
// 3. 窗口函数模拟(C# 8.0+)
var salesWithRank = orders
.Select((o, index) => new { Order = o, Index = index })
.GroupBy(x => x.Order.Region)
.SelectMany(g => g.OrderByDescending(x => x.Order.Amount)
.Select((x, rank) => new {
x.Order.Region,
x.Order.Amount,
RegionalRank = rank + 1
}));
// 4. 递归查询(树形结构)
public static IEnumerable<Employee> GetSubordinates(Employee manager) {
yield return manager;
foreach (var subordinate in manager.Subordinates) {
foreach (var sub in GetSubordinates(subordinate)) {
yield return sub;
}
}
}
// 使用递归方法
var allEmployees = GetSubordinates(ceo).ToList();

三、集合算法与性能优化
3.1 集合操作的性能考量
// 1. 选择合适的集合类型
public class CollectionBenchmark {
// List<T>:随机访问O(1),插入删除O(n)
private List<int> _list = new();
// LinkedList<T>:插入删除O(1),随机访问O(n)
private LinkedList<int> _linkedList = new();
// HashSet<T>:查找O(1),无序
private HashSet<int> _hashSet = new();
// SortedSet<T>:有序,查找O(log n)
private SortedSet<int> _sortedSet = new();
// Dictionary<TKey, TValue>:键值对查找O(1)
private Dictionary<string, int> _dictionary = new();
// ConcurrentDictionary:线程安全字典
private ConcurrentDictionary<string, int> _concurrentDict = new();
}
// 2. 批量操作优化
public static void OptimizedBulkOperations() {
var list = new List<int>(10000); // 预分配容量
// 避免在循环中重复计算Count
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++) { // 每次循环都调用Count
// 优化:缓存Count
}
// 使用Span<T>减少分配
Span<int> span = stackalloc int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < span.Length; i++) {
span[i] = i * 2;
}
// 使用ArrayPool共享数组
var pool = ArrayPool<int>.Shared;
int[] rentedArray = pool.Rent(1000);
try {
// 使用rentedArray
} finally {
pool.Return(rentedArray);
}
}
3.2 内存高效的算法实现
// 1. 使用结构体减少堆分配
public readonly struct Point3D : IEquatable<Point3D> {
public readonly double X, Y, Z;
public Point3D(double x, double y, double z) {
X = x; Y = y; Z = z;
}
// 实现IEquatable避免装箱
public bool Equals(Point3D other) {
return X == other.X && Y == other.Y && Z == other.Z;
}
public override int GetHashCode() {
return HashCode.Combine(X, Y, Z);
}
}
// 2. 对象池模式
public class ObjectPool<T> where T : new() {
private readonly ConcurrentBag<T> _objects = new();
private readonly Func<T> _objectGenerator;
public ObjectPool(Func<T> objectGenerator = null) {
_objectGenerator = objectGenerator ?? (() => new T());
}
public T Get() {
return _objects.TryTake(out T item) ? item : _objectGenerator();
}
public void Return(T item) {
_objects.Add(item);
}
}
// 使用对象池
var pool = new ObjectPool<StringBuilder>();
var sb = pool.Get();
try {
sb.Append("Hello");
sb.Append(" World");
Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString());
} finally {
sb.Clear();
pool.Return(sb);
}
四、排序与搜索算法
4.1 内置排序与自定义排序
// 1. 基本排序
var numbers = new List<int> { 5, 2, 8, 1, 9, 3 };
numbers.Sort(); // 升序
numbers.Sort((a, b) => b.CompareTo(a)); // 降序
// 2. 对象排序(多种方式)
public class Product {
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public int Rating { get; set; }
}
var products = new List<Product>();
// 方法1:实现IComparable<T>
public class Product : IComparable<Product> {
public int CompareTo(Product other) {
return Price.CompareTo(other.Price);
}
}
// 方法2:使用Comparison委托
products.Sort((p1, p2) => p1.Price.CompareTo(p2.Price));
// 方法3:使用LINQ(不改变原集合)
var sorted = products.OrderBy(p => p.Price)
.ThenByDescending(p => p.Rating)
.ToList();
// 方法4:使用IComparer(可复用)
public class ProductPriceComparer : IComparer<Product> {
public int Compare(Product x, Product y) {
return x.Price.CompareTo(y.Price);
}
}
products.Sort(new ProductPriceComparer());
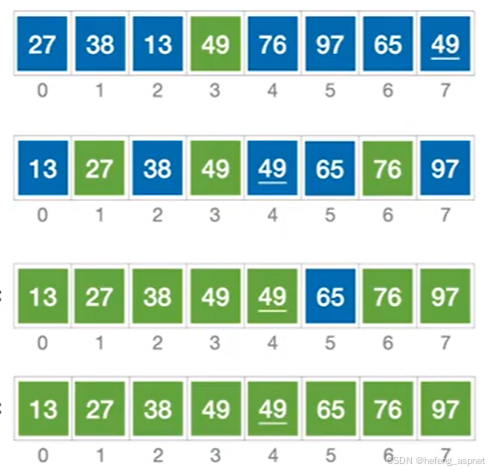
4.2 高级搜索算法
// 1. 二分查找(要求有序)
public static int BinarySearch<T>(IList<T> list, T value)
where T : IComparable<T> {
int left = 0, right = list.Count - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int comparison = list[mid].CompareTo(value);
if (comparison == 0) return mid;
if (comparison < 0) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
// 2. 使用内置二分查找
var list = new List<int> { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
int index = list.BinarySearch(5); // 返回2
// 3. 模糊搜索(Levenshtein距离)
public static class FuzzySearch {
public static int LevenshteinDistance(string s, string t) {
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(s)) return t?.Length ?? 0;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(t)) return s.Length;
int[,] d = new int[s.Length + 1, t.Length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= s.Length; i++) d[i, 0] = i;
for (int j = 0; j <= t.Length; j++) d[0, j] = j;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.Length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= t.Length; j++) {
int cost = (s[i - 1] == t[j - 1]) ? 0 : 1;
d[i, j] = Math.Min(
Math.Min(d[i - 1, j] + 1, d[i, j - 1] + 1),
d[i - 1, j - 1] + cost
);
}
}
return d[s.Length, t.Length];
}
public static IEnumerable<string> FindSimilar(
IEnumerable<string> words, string target, int maxDistance) {
return words.Where(w =>
LevenshteinDistance(w, target) <= maxDistance);
}
}

五、数值计算与统计
5.1 数学与统计函数
// 1. 基本统计
public static class Statistics {
public static double Mean(IEnumerable<double> values) {
double sum = 0;
int count = 0;
foreach (var value in values) {
sum += value;
count++;
}
return count == 0 ? 0 : sum / count;
}
public static double Median(IEnumerable<double> values) {
var sorted = values.OrderBy(v => v).ToList();
int count = sorted.Count;
if (count == 0) return 0;
if (count % 2 == 1) return sorted[count / 2];
return (sorted[count / 2 - 1] + sorted[count / 2]) / 2.0;
}
public static double StandardDeviation(IEnumerable<double> values) {
var mean = Mean(values);
var sumOfSquares = values.Sum(v => Math.Pow(v - mean, 2));
return Math.Sqrt(sumOfSquares / values.Count());
}
// 2. 移动平均
public static IEnumerable<double> MovingAverage(
IEnumerable<double> values, int windowSize) {
var queue = new Queue<double>();
foreach (var value in values) {
queue.Enqueue(value);
if (queue.Count > windowSize) {
queue.Dequeue();
}
if (queue.Count == windowSize) {
yield return queue.Average();
}
}
}
}
// 3. 使用SIMD加速计算(System.Numerics)
public static class SimdOperations {
public static float SumSimd(float[] array) {
var vectorSize = Vector<float>.Count;
var sumVector = Vector<float>.Zero;
int i = 0;
for (; i <= array.Length - vectorSize; i += vectorSize) {
var vector = new Vector<float>(array, i);
sumVector += vector;
}
float sum = 0;
for (; i < array.Length; i++) {
sum += array[i];
}
for (int j = 0; j < vectorSize; j++) {
sum += sumVector[j];
}
return sum;
}
}
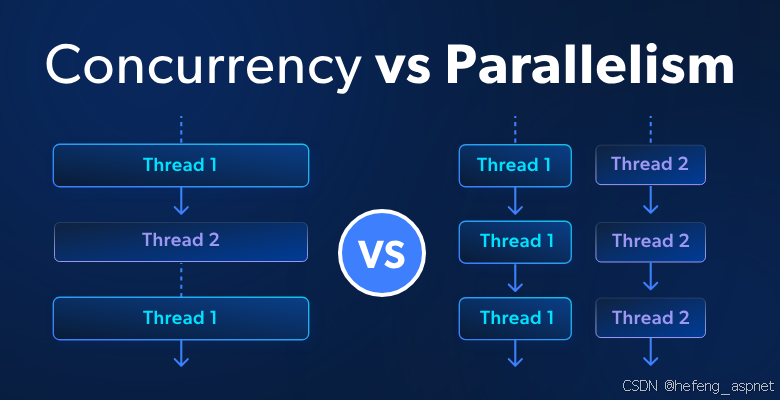
六、并发与并行算法
6.1 并行LINQ(PLINQ)
// 1. 基本并行查询
var parallelResults = numbers
.AsParallel() // 启用并行
.Where(n => n % 2 == 0)
.Select(n => n * n)
.ToList();
// 2. 控制并行度
var controlledParallel = numbers
.AsParallel()
.WithDegreeOfParallelism(Environment.ProcessorCount)
.WithExecutionMode(ParallelExecutionMode.ForceParallelism)
.Where(n => IsPrime(n))
.ToList();
// 3. 并行聚合
var parallelAggregate = numbers
.AsParallel()
.Aggregate(
seed: 0, // 初始值
updateAccumulatorFunc: (sum, item) => sum + item,
combineAccumulatorsFunc: (sum1, sum2) => sum1 + sum2,
resultSelector: sum => sum / (double)numbers.Count
);
// 4. 并行For和ForEach
Parallel.For(0, 100, i => {
// 并行执行100次
Console.WriteLine($"Processing {i} on thread {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}");
});
Parallel.ForEach(numbers, number => {
// 并行处理每个元素
Process(number);
});
6.2 异步流(C# 8.0+)
// 1. 异步枚举
public static async IAsyncEnumerable<int> GenerateNumbersAsync(int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
await Task.Delay(100); // 模拟异步操作
yield return i;
}
}
// 2. 消费异步流
await foreach (var number in GenerateNumbersAsync(10)) {
Console.WriteLine($"Received: {number}");
}
// 3. 异步LINQ扩展(System.Linq.Async包)
using System.Linq.Async;
var asyncQuery = GenerateNumbersAsync(100)
.WhereAwait(async n => {
await Task.Delay(10);
return n % 2 == 0;
})
.SelectAwait(async n => {
await Task.Delay(10);
return n * 2;
})
.Take(10);
await foreach (var item in asyncQuery) {
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
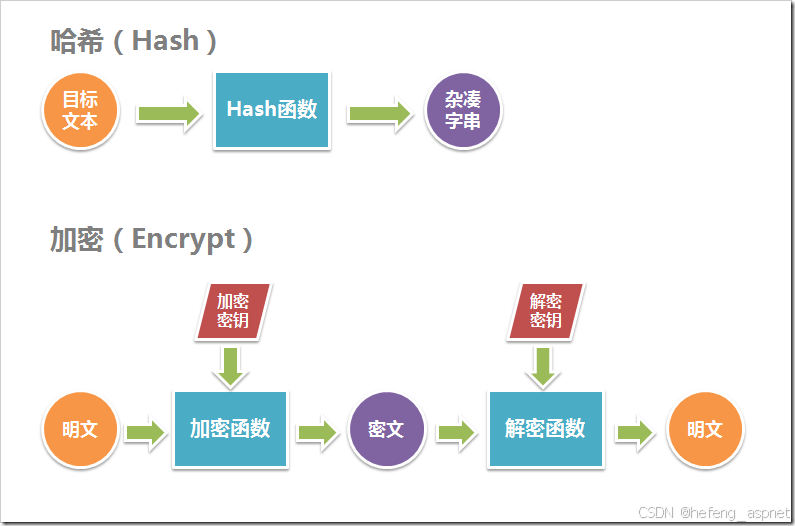
七、安全与加密算法
7.1 哈希与加密
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
public static class SecurityAlgorithms {
// 1. 哈希算法
public static string ComputeSHA256(string input) {
using var sha256 = SHA256.Create();
byte[] bytes = sha256.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(input));
return Convert.ToHexString(bytes);
}
// 2. 密码哈希(使用PBKDF2)
public static string HashPassword(string password, out byte[] salt) {
salt = RandomNumberGenerator.GetBytes(32);
using var pbkdf2 = new Rfc2898DeriveBytes(
password, salt, 100000, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256);
byte[] hash = pbkdf2.GetBytes(32);
return Convert.ToHexString(hash);
}
public static bool VerifyPassword(string password, string storedHash, byte[] salt) {
using var pbkdf2 = new Rfc2898DeriveBytes(
password, salt, 100000, HashAlgorithmName.SHA256);
byte[] hash = pbkdf2.GetBytes(32);
return CryptographicOperations.FixedTimeEquals(hash, Convert.FromHexString(storedHash));
}
// 3. 对称加密(AES)
public static byte[] EncryptAes(string plainText, byte[] key, byte[] iv) {
using var aes = Aes.Create();
aes.Key = key;
aes.IV = iv;
using var encryptor = aes.CreateEncryptor();
using var ms = new MemoryStream();
using var cs = new CryptoStream(ms, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write);
byte[] plainBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(plainText);
cs.Write(plainBytes, 0, plainBytes.Length);
cs.FlushFinalBlock();
return ms.ToArray();
}
}

八、算法性能测试与基准
8.1 BenchmarkDotNet实战
MemoryDiagnoser
Orderer(SummaryOrderPolicy.FastestToSlowest)
public class AlgorithmBenchmarks {
private readonly int[] _numbers = Enumerable.Range(1, 10000).ToArray();
Benchmark
public int LinqSum() => _numbers.Sum();
Benchmark
public int ForLoopSum() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _numbers.Length; i++) {
sum += _numbers[i];
}
return sum;
}
Benchmark
public int ForEachSum() {
int sum = 0;
foreach (var num in _numbers) {
sum += num;
}
return sum;
}
Benchmark
public int SpanSum() {
var span = _numbers.AsSpan();
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < span.Length; i++) {
sum += span[i];
}
return sum;
}
Benchmark
public int SimdSum() {
var vectorSize = Vector<int>.Count;
var sumVector = Vector<int>.Zero;
int i = 0;
for (; i <= _numbers.Length - vectorSize; i += vectorSize) {
var vector = new Vector<int>(_numbers, i);
sumVector += vector;
}
int sum = 0;
for (; i < _numbers.Length; i++) {
sum += _numbers[i];
}
for (int j = 0; j < vectorSize; j++) {
sum += sumVector[j];
}
return sum;
}
}
// 运行基准测试
// var summary = BenchmarkRunner.Run<AlgorithmBenchmarks>();
希望以上内容对你有帮助。
如果您喜欢此文章,请收藏、点赞、评论,谢谢,祝您快乐每一天。