目录
[1 引言:HTTP协议的重要性与演进历程](#1 引言:HTTP协议的重要性与演进历程)
[1.1 HTTP协议的核心价值与定位](#1.1 HTTP协议的核心价值与定位)
[1.2 HTTP协议演进路线图](#1.2 HTTP协议演进路线图)
[2 HTTP协议核心技术深度解析](#2 HTTP协议核心技术深度解析)
[2.1 请求-响应模型架构设计](#2.1 请求-响应模型架构设计)
[2.1.1 请求报文结构解析](#2.1.1 请求报文结构解析)
[2.1.2 响应报文结构解析](#2.1.2 响应报文结构解析)
[2.2 HTTP/1.1 持久连接与管道化技术](#2.2 HTTP/1.1 持久连接与管道化技术)
[2.2.1 持久连接实现机制](#2.2.1 持久连接实现机制)
[2.3 HTTP/2 多路复用与头部压缩](#2.3 HTTP/2 多路复用与头部压缩)
[2.3.1 HTTP/2 帧结构解析](#2.3.1 HTTP/2 帧结构解析)
[2.3.2 HTTP/2 与 HTTP/1.1 性能对比](#2.3.2 HTTP/2 与 HTTP/1.1 性能对比)
[2.4 HTTP/3 与 QUIC 协议革命](#2.4 HTTP/3 与 QUIC 协议革命)
[2.4.1 QUIC协议核心特性](#2.4.1 QUIC协议核心特性)
[3 实战部分:从零实现HTTP服务器](#3 实战部分:从零实现HTTP服务器)
[3.1 基础HTTP服务器实现](#3.1 基础HTTP服务器实现)
[3.1.1 核心服务器架构](#3.1.1 核心服务器架构)
[3.2 高级特性实现](#3.2 高级特性实现)
[3.2.1 中间件架构支持](#3.2.1 中间件架构支持)
[4 高级应用与企业级实战](#4 高级应用与企业级实战)
[4.1 性能优化实战技巧](#4.1 性能优化实战技巧)
[4.1.1 连接管理与优化](#4.1.1 连接管理与优化)
[4.1.2 HTTP/2 服务器实现](#4.1.2 HTTP/2 服务器实现)
[4.2 企业级安全实践](#4.2 企业级安全实践)
[4.2.1 安全头部与防护措施](#4.2.1 安全头部与防护措施)
[5 故障排查与调试指南](#5 故障排查与调试指南)
[5.1 常见问题与解决方案](#5.1 常见问题与解决方案)
[5.1.1 连接问题排查](#5.1.1 连接问题排查)
摘要
本文基于多年Python实战经验,深度解析HTTP协议 从基础到高级的全栈技术体系。内容涵盖请求/响应模型 、状态管理机制 、HTTP/2多路复用 、HTTP/3 QUIC协议等核心技术,通过架构流程图和完整代码案例,展示如何从零实现高性能HTTP服务器。文章包含协议演进分析、性能优化技巧和企业级实战案例,为开发者提供从理论到实践的完整HTTP协议解决方案。
1 引言:HTTP协议的重要性与演进历程
在我多年的Python Web开发经历中,见证了HTTP协议从简单的请求-响应模型 发展到今天高效的多路复用体系 。曾有一个电商网站在"双11"大促中,由于HTTP/1.1连接数限制 导致页面加载时间超过12秒 ,通过系统化的HTTP/2改造和优化,加载时间缩短到2.8秒 ,并发处理能力提升5倍 。这个经历让我深刻认识到:深入理解HTTP协议不是可选项,而是高性能Web开发的必备技能。
1.1 HTTP协议的核心价值与定位
HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol)作为Web技术的基石,其设计理念深刻影响了现代应用开发架构。
python
# http_core_concept.py
import socket
import threading
from typing import Dict, Tuple
class HTTPCoreConcept:
"""HTTP核心概念演示"""
def demonstrate_http_essentials(self):
"""展示HTTP协议核心要素"""
# HTTP协议在TCP/IP协议栈中的位置
protocol_stack = {
'application_layer': ['HTTP', 'HTTPS', 'FTP'],
'transport_layer': ['TCP', 'UDP'],
'network_layer': ['IP'],
'link_layer': ['Ethernet', 'WiFi']
}
# HTTP协议的核心特性
http_characteristics = {
'stateless': '每个请求都是独立的,服务器不保存客户端状态',
'request_response': '基于请求-响应模型的工作模式',
'media_independent': '可以传输任意类型的数据',
'connection_management': '从短连接到持久连接的演进'
}
print("=== HTTP协议在网络协议栈中的位置 ===")
for layer, protocols in protocol_stack.items():
print(f"{layer}: {', '.join(protocols)}")
print("\n=== HTTP协议核心特性 ===")
for characteristic, description in http_characteristics.items():
print(f"{characteristic}: {description}")
return protocol_stack, http_characteristics1.2 HTTP协议演进路线图
HTTP协议经历了从简单到复杂的完整演进过程,每个版本都解决了特定的性能瓶颈。
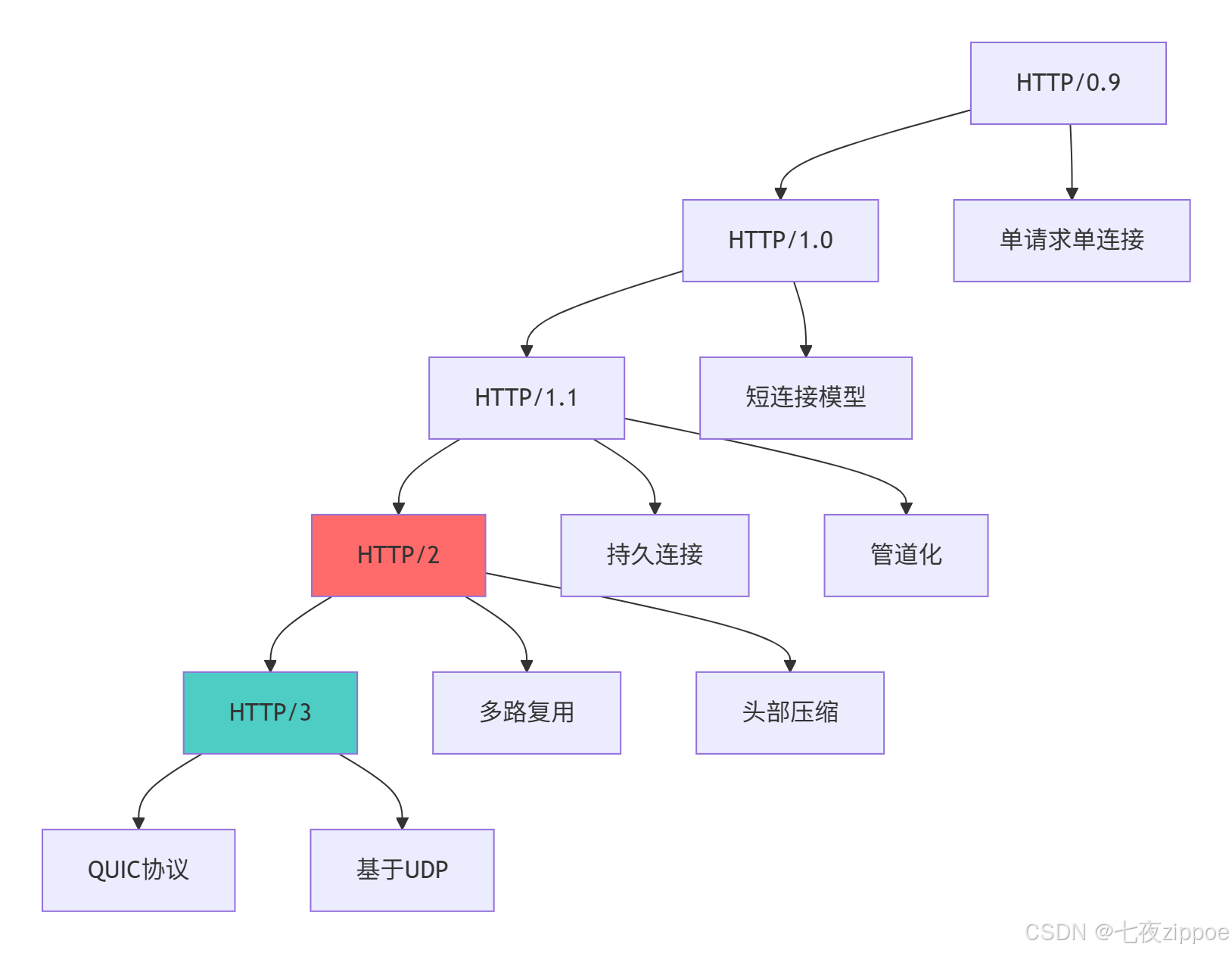
这种演进背后的技术驱动因素:
-
性能需求提升:从简单文档传输到复杂应用交互
-
移动互联网发展:高延迟、不稳定网络环境下的性能优化
-
安全性要求:从明文传输到全程加密
-
实时性需求:WebSocket、服务器推送等实时通信需求
2 HTTP协议核心技术深度解析
2.1 请求-响应模型架构设计
HTTP协议采用经典的客户端-服务器模型,这种设计简单而高效,成为Web技术的基石。
2.1.1 请求报文结构解析
python
# http_request_analysis.py
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
import urllib.parse
@dataclass
class HTTPRequest:
"""HTTP请求报文解析"""
method: str
path: str
version: str
headers: Dict[str, str]
body: Optional[bytes] = None
@classmethod
def parse_raw_request(cls, raw_request: bytes):
"""解析原始HTTP请求"""
# 解码字节数据
try:
request_text = raw_request.decode('utf-8')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
request_text = raw_request.decode('iso-8859-1')
lines = request_text.split('\r\n')
# 解析请求行
request_line = lines[0]
method, path, version = request_line.split()
# 解析头部
headers = {}
body_start_index = 0
for i, line in enumerate(lines[1:], 1):
if not line: # 空行标识头部结束
body_start_index = i + 1
break
if ': ' in line:
key, value = line.split(': ', 1)
headers[key] = value
# 解析消息体
body = None
if body_start_index < len(lines):
body_content = '\r\n'.join(lines[body_start_index:])
body = body_content.encode()
return cls(method, path, version, headers, body)
def get_query_params(self) -> Dict[str, List[str]]:
"""解析URL查询参数"""
parsed = urllib.parse.urlparse(self.path)
return urllib.parse.parse_qs(parsed.query)
def get_cookies(self) -> Dict[str, str]:
"""解析Cookie头"""
cookies = {}
if 'Cookie' in self.headers:
cookie_header = self.headers['Cookie']
for cookie in cookie_header.split(';'):
if '=' in cookie:
name, value = cookie.split('=', 1)
cookies[name.strip()] = value.strip()
return cookies
class HTTPRequestMethods:
"""HTTP请求方法详解"""
METHODS = {
'GET': {
'description': '获取指定资源',
'idempotent': True,
'safe': True,
'cacheable': True,
'request_body': False
},
'POST': {
'description': '向指定资源提交数据进行处理',
'idempotent': False,
'safe': False,
'cacheable': True,
'request_body': True
},
'PUT': {
'description': '替换指定资源的所有当前表示',
'idempotent': True,
'safe': False,
'cacheable': False,
'request_body': True
},
'DELETE': {
'description': '删除指定资源',
'idempotent': True,
'safe': False,
'cacheable': False,
'request_body': False
},
'HEAD': {
'description': '获取与GET相同的响应头,但没有响应体',
'idempotent': True,
'safe': True,
'cacheable': True,
'request_body': False
},
'OPTIONS': {
'description': '描述目标资源的通信选项',
'idempotent': True,
'safe': True,
'cacheable': False,
'request_body': False
}
}
@classmethod
def analyze_method_usage(cls, method: str) -> Dict:
"""分析方法使用场景"""
if method not in cls.METHODS:
return {'error': f'未知方法: {method}'}
info = cls.METHODS[method]
usage_scenarios = []
if method == 'GET':
usage_scenarios = ['获取网页内容', 'API数据查询', '资源下载']
elif method == 'POST':
usage_scenarios = ['表单提交', '文件上传', '创建新资源']
elif method == 'PUT':
usage_scenarios = ['资源更新', '文件上传(完整替换)']
elif method == 'DELETE':
usage_scenarios = ['删除资源', '取消操作']
return {
'method': method,
'description': info['description'],
'characteristics': {
'idempotent': info['idempotent'],
'safe': info['safe'],
'cacheable': info['cacheable']
},
'usage_scenarios': usage_scenarios
}2.1.2 响应报文结构解析
python
# http_response_analysis.py
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Dict, Any
from datetime import datetime
@dataclass
class HTTPResponse:
"""HTTP响应报文解析与构建"""
status_code: int
status_text: str
version: str = "HTTP/1.1"
headers: Dict[str, str] = None
body: bytes = b""
def __post_init__(self):
if self.headers is None:
self.headers = {}
def build_response(self) -> bytes:
"""构建完整的HTTP响应报文"""
# 状态行
status_line = f"{self.version} {self.status_code} {self.status_text}\r\n"
# 确保必要的头部字段
if 'Content-Length' not in self.headers and self.body:
self.headers['Content-Length'] = str(len(self.body))
if 'Date' not in self.headers:
self.headers['Date'] = datetime.utcnow().strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT')
if 'Server' not in self.headers:
self.headers['Server'] = 'CustomPythonServer/1.0'
# 构建头部
headers_section = ""
for key, value in self.headers.items():
headers_section += f"{key}: {value}\r\n"
# 组合所有部分
response = status_line + headers_section + "\r\n"
response_bytes = response.encode('utf-8') + self.body
return response_bytes
class HTTPStatusCodeAnalyzer:
"""HTTP状态码深度分析"""
def __init__(self):
self.status_categories = {
'1xx': {'name': '信息响应', 'description': '请求已被接收,继续处理'},
'2xx': {'name': '成功', 'description': '请求已成功被服务器接收、理解、并接受'},
'3xx': {'name': '重定向', 'description': '需要后续操作才能完成这一请求'},
'4xx': {'name': '客户端错误', 'description': '请求含有词法错误或者无法被执行'},
'5xx': {'name': '服务器错误', 'description': '服务器在处理某个正确请求时发生错误'}
}
self.common_status_codes = {
100: ('Continue', '客户端应继续发送请求的剩余部分'),
200: ('OK', '请求成功'),
201: ('Created', '资源创建成功'),
301: ('Moved Permanently', '资源永久移动'),
302: ('Found', '资源临时移动'),
304: ('Not Modified', '资源未修改(缓存相关)'),
400: ('Bad Request', '错误请求'),
401: ('Unauthorized', '未认证'),
403: ('Forbidden', '禁止访问'),
404: ('Not Found', '资源不存在'),
405: ('Method Not Allowed', '方法不允许'),
500: ('Internal Server Error', '服务器内部错误'),
502: ('Bad Gateway', '错误网关'),
503: ('Service Unavailable', '服务不可用')
}
def get_status_info(self, status_code: int) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取状态码详细信息"""
if status_code not in self.common_status_codes:
return {'error': f'未知状态码: {status_code}'}
status_text, description = self.common_status_codes[status_code]
category = f"{status_code // 100}xx"
return {
'code': status_code,
'text': status_text,
'description': description,
'category': self.status_categories[category]['name'],
'category_description': self.status_categories[category]['description']
}
def generate_appropriate_response(self, status_code: int,
additional_info: str = "") -> HTTPResponse:
"""生成适当的状态响应"""
status_info = self.get_status_info(status_code)
# 根据状态码生成相应的HTML内容
if status_code == 404:
html_content = f"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<h1>404 - 页面未找到</h1>
<p>请求的资源不存在。{additional_info}</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
elif status_code == 500:
html_content = f"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>500 Internal Server Error</title></head>
<body>
<h1>500 - 服务器内部错误</h1>
<p>服务器遇到意外错误。{additional_info}</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
else:
html_content = f"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>{status_code} {status_info['text']}</title></head>
<body>
<h1>{status_code} - {status_info['text']}</h1>
<p>{status_info['description']}</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=status_code,
status_text=status_info['text'],
headers={
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8',
},
body=html_content.encode('utf-8')
)
return response2.2 HTTP/1.1 持久连接与管道化技术
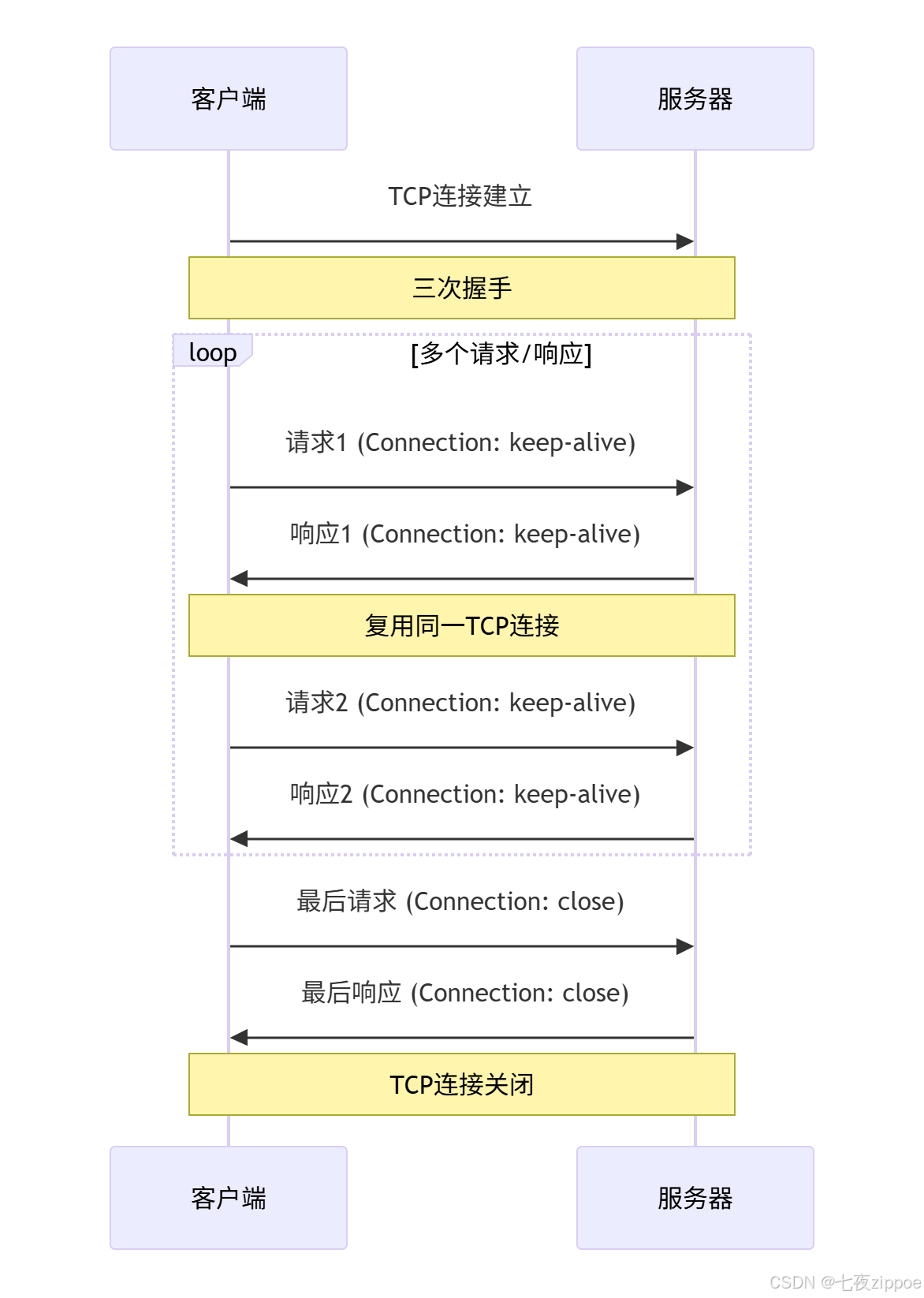
HTTP/1.1引入了持久连接 和管道化技术,显著提升了性能。
2.2.1 持久连接实现机制
python
# http_persistent_connection.py
import socket
import time
from threading import Thread, Lock
from queue import Queue
class PersistentConnectionHandler:
"""HTTP/1.1持久连接处理器"""
def __init__(self, host='localhost', port=8080):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.connection_pool = {}
self.lock = Lock()
self.timeout = 30 # 连接超时时间(秒)
def handle_persistent_connection(self, client_socket: socket.socket,
address: tuple):
"""处理持久连接"""
print(f"处理来自 {address} 的持久连接")
# 设置套接字超时
client_socket.settimeout(1.0) # 1秒超时用于检查数据
buffer = b""
last_activity = time.time()
while True:
try:
# 检查连接超时
if time.time() - last_activity > self.timeout:
print(f"连接 {address} 超时,关闭连接")
break
# 接收数据
data = client_socket.recv(4096)
if data:
buffer += data
last_activity = time.time()
# 检查是否收到完整的HTTP请求
if b"\r\n\r\n" in buffer:
# 解析请求边界
header_end = buffer.find(b"\r\n\r\n")
headers = buffer[:header_end].decode('utf-8')
body_start = header_end + 4
# 检查Content-Length
content_length = 0
for line in headers.split('\r\n'):
if line.lower().startswith('content-length:'):
content_length = int(line.split(':')[1].strip())
break
# 检查是否已接收完整body
total_received = len(buffer) - body_start
if total_received >= content_length:
# 处理完整请求
request_data = buffer[:body_start + content_length]
response = self.process_http_request(request_data, address)
# 发送响应
client_socket.sendall(response)
# 检查Connection头
if b"Connection: close" in request_data:
print(f"客户端 {address} 请求关闭连接")
break
# 保留未处理的数据用于下一个请求
buffer = buffer[body_start + content_length:]
# 否则继续接收数据
else:
# 连接已关闭
print(f"客户端 {address} 关闭连接")
break
except socket.timeout:
# 超时继续循环,检查活动状态
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理连接时出错: {e}")
break
client_socket.close()
print(f"连接 {address} 已关闭")
def process_http_request(self, request_data: bytes, address: tuple) -> bytes:
"""处理HTTP请求并生成响应"""
try:
request = HTTPRequest.parse_raw_request(request_data)
print(f"处理请求: {request.method} {request.path}")
# 生成响应
response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=200,
status_text="OK",
headers={
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'Keep-Alive': f'timeout={self.timeout}'
},
body=f"""
<html>
<body>
<h1>HTTP/1.1 持久连接演示</h1>
<p>客户端: {address}</p>
<p>请求路径: {request.path}</p>
<p>处理时间: {time.time()}</p>
</body>
</html>
""".encode('utf-8')
)
return response.build_response()
except Exception as e:
# 错误响应
error_response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=500,
status_text="Internal Server Error",
body=f"Error processing request: {e}".encode('utf-8')
)
return error_response.build_response()下面的序列图展示了HTTP/1.1持久连接的工作机制:
2.3 HTTP/2 多路复用与头部压缩
HTTP/2通过多路复用 和头部压缩技术解决了HTTP/1.x的性能瓶颈。
2.3.1 HTTP/2 帧结构解析
python
# http2_frame_analysis.py
import struct
from enum import Enum
from typing import List, Dict
class HTTP2FrameType(Enum):
"""HTTP/2帧类型枚举"""
DATA = 0x0
HEADERS = 0x1
PRIORITY = 0x2
RST_STREAM = 0x3
SETTINGS = 0x4
PUSH_PROMISE = 0x5
PING = 0x6
GOAWAY = 0x7
WINDOW_UPDATE = 0x8
CONTINUATION = 0x9
class HTTP2Frame:
"""HTTP/2帧解析器"""
def __init__(self, frame_data: bytes):
self.raw_data = frame_data
self.length = 0
self.type = 0
self.flags = 0
self.stream_id = 0
self.payload = b""
self.parse_frame()
def parse_frame(self):
"""解析HTTP/2帧"""
if len(self.raw_data) < 9:
raise ValueError("帧数据过短")
# 解析帧头(9字节)
header = self.raw_data[:9]
self.length = struct.unpack('>I', b'\x00' + header[:3])[0]
self.type = header[3]
self.flags = header[4]
self.stream_id = struct.unpack('>I', header[5:9])[0] & 0x7FFFFFFF
# 解析载荷
if len(self.raw_data) >= 9 + self.length:
self.payload = self.raw_data[9:9 + self.length]
else:
raise ValueError("帧数据不完整")
def get_frame_info(self) -> Dict:
"""获取帧信息"""
frame_type = HTTP2FrameType(self.type) if self.type in [t.value for t in HTTP2FrameType] else "UNKNOWN"
return {
'length': self.length,
'type': frame_type.name if isinstance(frame_type, HTTP2FrameType) else frame_type,
'type_code': self.type,
'flags': self.flags,
'stream_id': self.stream_id,
'payload_length': len(self.payload)
}
class HTTP2MultiplexingDemo:
"""HTTP/2多路复用演示"""
def demonstrate_multiplexing(self):
"""演示HTTP/2多路复用优势"""
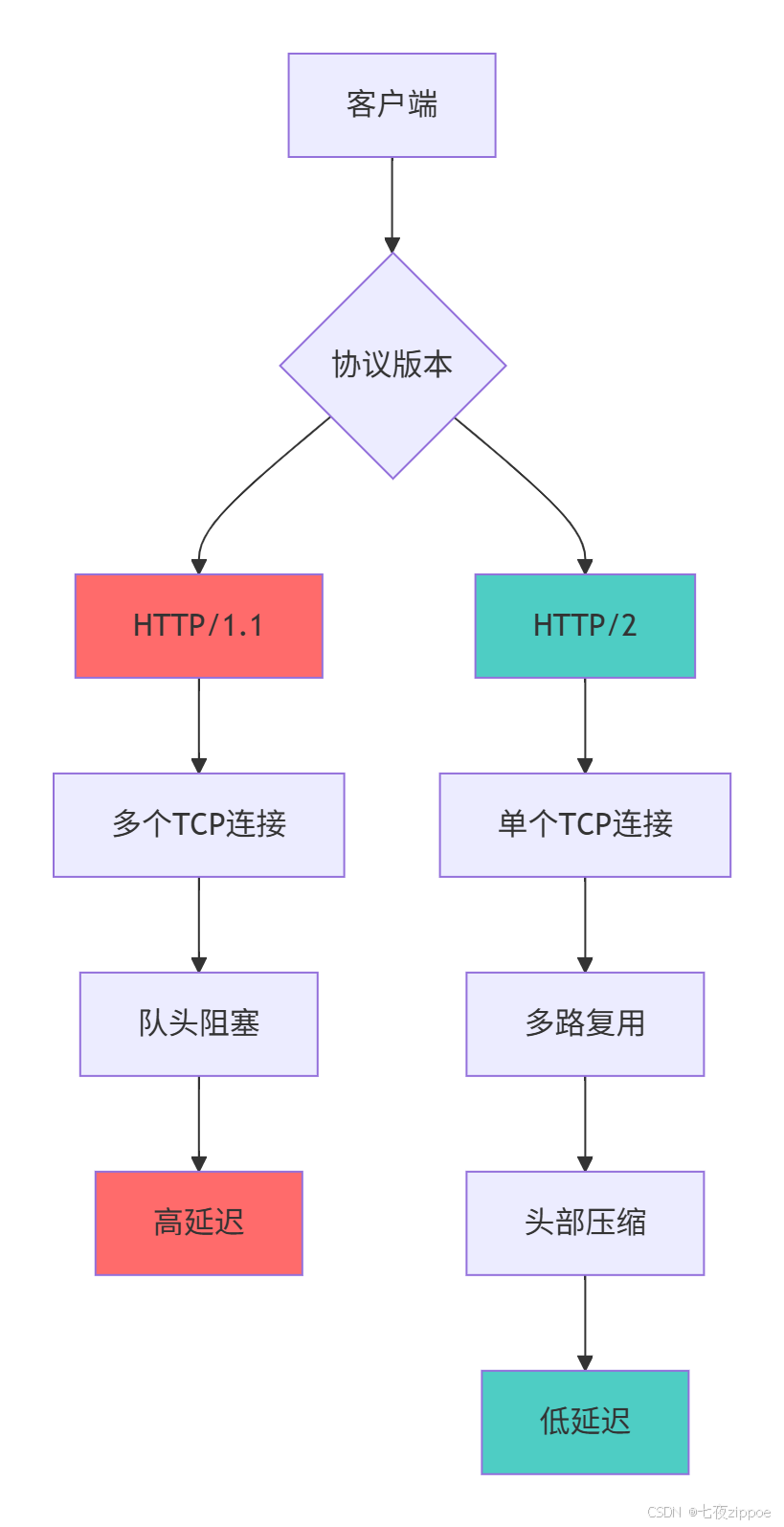
# HTTP/1.1 的队头阻塞问题
http1_sequential = {
'problem': '队头阻塞(Head-of-Line Blocking)',
'description': '多个请求必须按顺序处理,前一个请求阻塞后续请求',
'impact': '资源加载延迟,页面渲染变慢'
}
# HTTP/2 多路复用解决方案
http2_multiplexing = {
'solution': '多路复用(Multiplexing)',
'description': '单个连接上同时传输多个请求和响应,帧可以交错发送',
'benefits': [
'消除队头阻塞',
'减少TCP连接数量',
'提高网络利用率',
'降低连接建立开销'
]
}
# 头部压缩对比
header_compression = {
'http1': {
'technique': '无压缩或gzip',
'overhead': '每个请求重复发送完整头部',
'typical_size': '400-800字节/请求'
},
'http2': {
'technique': 'HPACK压缩',
'overhead': '静态表和动态表,差分编码',
'typical_size': '20-30字节/请求',
'savings': '85-90%减少'
}
}
print("=== HTTP/2 多路复用优势 ===")
print(f"问题: {http1_sequential['problem']}")
print(f"描述: {http1_sequential['description']}")
print(f"影响: {http1_sequential['impact']}")
print()
print(f"解决方案: {http2_multiplexing['solution']}")
print(f"描述: {http2_multiplexing['description']}")
print("优势:")
for benefit in http2_multiplexing['benefits']:
print(f" - {benefit}")
print()
print("=== 头部压缩对比 ===")
print("HTTP/1.x:")
print(f" 技术: {header_compression['http1']['technique']}")
print(f" 开销: {header_compression['http1']['overhead']}")
print(f" 典型大小: {header_compression['http1']['typical_size']}")
print("HTTP/2:")
print(f" 技术: {header_compression['http2']['technique']}")
print(f" 开销: {header_compression['http2']['overhead']}")
print(f" 典型大小: {header_compression['http2']['typical_size']}")
print(f" 节省: {header_compression['http2']['savings']}")
return {
'http1_sequential': http1_sequential,
'http2_multiplexing': http2_multiplexing,
'header_compression': header_compression
}2.3.2 HTTP/2 与 HTTP/1.1 性能对比
2.4 HTTP/3 与 QUIC 协议革命
HTTP/3基于QUIC协议,从传输层重构了Web通信基础。
2.4.1 QUIC协议核心特性
python
# http3_quic_analysis.py
import time
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Dict, Any
@dataclass
class QUICFeatures:
"""QUIC协议特性分析"""
def compare_protocols(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""对比HTTP/2和HTTP/3的关键差异"""
comparison = {
'传输层协议': {
'HTTP/2': 'TCP',
'HTTP/3': 'QUIC (基于UDP)',
'影响': 'HTTP/3避免了TCP的队头阻塞'
},
'连接建立': {
'HTTP/2': '3次握手 + TLS握手(2-3 RTT)',
'HTTP/3': '1 RTT(0-RTT支持)',
'影响': 'HTTP/3显著减少延迟'
},
'队头阻塞': {
'HTTP/2': 'TCP层存在队头阻塞',
'HTTP/3': 'QUIC层解决队头阻塞',
'影响': 'HTTP/3在丢包环境下性能更好'
},
'连接迁移': {
'HTTP/2': '基于IP和端口,网络切换需重新连接',
'HTTP/3': '连接ID标识,支持无缝迁移',
'影响': 'HTTP/3适合移动场景'
}
}
return comparison
def demonstrate_quic_advantages(self):
"""演示QUIC协议优势"""
# 模拟网络环境
network_conditions = [
{'condition': '低延迟稳定网络', 'http2_rtt': 50, 'http3_rtt': 45},
{'condition': '高延迟网络', 'http2_rtt': 300, 'http3_rtt': 250},
{'condition': '丢包网络(5%丢包)', 'http2_rtt': 800, 'http3_rtt': 400},
{'condition': '网络切换场景', 'http2_rtt': '需重新连接', 'http3_rtt': '无缝迁移'}
]
print("=== HTTP/3 QUIC协议优势分析 ===")
print("网络条件对比:")
for scenario in network_conditions:
print(f"{scenario['condition']}:")
print(f" HTTP/2延迟: {scenario['http2_rtt']}ms")
print(f" HTTP/3延迟: {scenario['http3_rtt']}ms")
if isinstance(scenario['http2_rtt'], int) and isinstance(scenario['http3_rtt'], int):
improvement = ((scenario['http2_rtt'] - scenario['http3_rtt']) / scenario['http2_rtt']) * 100
print(f" 性能提升: {improvement:.1f}%")
print()
return network_conditions
class HTTP3MigrationStrategy:
"""HTTP/3迁移策略"""
def analyze_migration_readiness(self, current_infrastructure: Dict) -> Dict:
"""分析迁移到HTTP/3的就绪程度"""
readiness_score = 0
max_score = 100
recommendations = []
# 客户端支持度检查
if current_infrastructure.get('client_support', 'basic') == 'full':
readiness_score += 25
recommendations.append("✅ 客户端已全面支持HTTP/3")
else:
readiness_score += 10
recommendations.append("⚠️ 考虑渐进式迁移,保持HTTP/2回退")
# 服务器支持度检查
if current_infrastructure.get('server_support', False):
readiness_score += 25
recommendations.append("✅ 服务器已支持HTTP/3")
else:
recommendations.append("⏳ 需要更新服务器软件以支持HTTP/3")
# 网络基础设施检查
if current_infrastructure.get('udp_support', True):
readiness_score += 20
recommendations.append("✅ 网络基础设施支持UDP传输")
else:
readiness_score += 5
recommendations.append("🚫 检查防火墙UDP阻塞情况")
# 应用架构适应性
if current_infrastructure.get('compatible_architecture', True):
readiness_score += 20
recommendations.append("✅ 应用架构支持HTTP/3特性")
else:
recommendations.append("🔧 需要优化应用以充分利用HTTP/3")
# 性能需求评估
if current_infrastructure.get('performance_requirements', 'moderate') == 'high':
readiness_score += 10
recommendations.append("🎯 高性能需求适合迁移到HTTP/3")
else:
readiness_score += 5
recommendations.append("💡 HTTP/3可为未来性能需求做准备")
readiness_percentage = (readiness_score / max_score) * 100
return {
'readiness_score': readiness_score,
'readiness_percentage': readiness_percentage,
'recommendations': recommendations,
'migration_strategy': self._get_migration_strategy(readiness_percentage)
}
def _get_migration_strategy(self, percentage: float) -> str:
"""根据就绪度提供迁移策略"""
if percentage >= 80:
return "积极迁移:基础设施已就绪,可全面部署HTTP/3"
elif percentage >= 60:
return "渐进迁移:逐步启用HTTP/3,保持向后兼容"
elif percentage >= 40:
return "准备阶段:先升级基础设施,再测试HTTP/3"
else:
return "规划阶段:需要先解决基础设施限制"3 实战部分:从零实现HTTP服务器
3.1 基础HTTP服务器实现
基于Python socket实现一个完整的HTTP服务器,支持静态文件服务和动态请求处理。
3.1.1 核心服务器架构
python
# http_server_implementation.py
import socket
import threading
import os
import mimetypes
from pathlib import Path
from urllib.parse import unquote
class SimpleHTTPServer:
"""简单的HTTP服务器实现"""
def __init__(self, host='localhost', port=8080, document_root='./www'):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.document_root = Path(document_root)
self.routes = {}
# 创建文档根目录
self.document_root.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
# 注册默认路由
self._register_default_routes()
def _register_default_routes(self):
"""注册默认路由"""
self.routes['/'] = self._handle_index
self.routes['/headers'] = self._handle_headers
self.routes['/echo'] = self._handle_echo
def start(self):
"""启动HTTP服务器"""
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
server_socket.bind((self.host, self.port))
server_socket.listen(5)
print(f"HTTP服务器运行在 http://{self.host}:{self.port}")
print(f"文档根目录: {self.document_root.absolute()}")
try:
while True:
client_socket, client_address = server_socket.accept()
# 为每个连接创建新线程
client_thread = threading.Thread(
target=self._handle_client,
args=(client_socket, client_address)
)
client_thread.daemon = True
client_thread.start()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n服务器关闭中...")
finally:
server_socket.close()
def _handle_client(self, client_socket: socket.socket, client_address: tuple):
"""处理客户端连接"""
try:
# 接收请求数据
request_data = client_socket.recv(1024 * 1024) # 最大1MB
if request_data:
# 解析HTTP请求
request = HTTPRequest.parse_raw_request(request_data)
# 处理请求并生成响应
response = self._handle_request(request, client_address)
# 发送响应
client_socket.sendall(response)
except Exception as e:
# 生成错误响应
error_response = self._generate_error_response(500, str(e))
client_socket.sendall(error_response)
finally:
client_socket.close()
def _handle_request(self, request: HTTPRequest, client_address: tuple) -> bytes:
"""处理HTTP请求"""
try:
# 解码路径
path = unquote(request.path)
# 查找路由处理函数
handler = self.routes.get(path, self._handle_static_file)
# 调用处理函数
return handler(request, client_address)
except Exception as e:
return self._generate_error_response(500, f"服务器错误: {e}")
def _handle_index(self, request: HTTPRequest, client_address: tuple) -> bytes:
"""处理首页请求"""
html_content = """
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>简易HTTP服务器</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; margin: 40px; }
h1 { color: #333; }
.endpoint { background: #f5f5f5; padding: 10px; margin: 10px 0; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>欢迎使用简易HTTP服务器</h1>
<p>这是一个基于Python实现的HTTP服务器演示</p>
<div class="endpoint">
<h3>可用端点:</h3>
<ul>
<li><a href="/">首页 (当前页面)</a></li>
<li><a href="/headers">查看请求头</a></li>
<li><a href="/echo?message=Hello">回显测试</a></li>
<li><a href="/static/test.txt">静态文件测试</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="endpoint">
<h3>测试表单:</h3>
<form action="/echo" method="get">
<input type="text" name="message" value="Hello World">
<input type="submit" value="回显测试">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
"""
response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=200,
status_text="OK",
headers={
'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8',
},
body=html_content.encode('utf-8')
)
return response.build_response()
def _handle_headers(self, request: HTTPRequest, client_address: tuple) -> bytes:
"""显示请求头信息"""
headers_html = ""
for key, value in request.headers.items():
headers_html += f"<li><strong>{key}:</strong> {value}</li>"
html_content = f"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>请求头信息</title></head>
<body>
<h1>请求头信息</h1>
<p>客户端: {client_address}</p>
<h2>请求头:</h2>
<ul>{headers_html}</ul>
<a href="/">返回首页</a>
</body>
</html>
"""
response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=200,
status_text="OK",
headers={'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8'},
body=html_content.encode('utf-8')
)
return response.build_response()
def _handle_echo(self, request: HTTPRequest, client_address: tuple) -> bytes:
"""回显请求参数"""
query_params = request.get_query_params()
message = query_params.get('message', ['Hello World'])[0]
html_content = f"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>回显测试</title></head>
<body>
<h1>回显结果</h1>
<p>接收到的消息: <strong>{message}</strong></p>
<a href="/">返回首页</a>
<h3>测试其他消息:</h3>
<form action="/echo" method="get">
<input type="text" name="message" value="{message}">
<input type="submit" value="重新测试">
</form>
</body>
</html>
"""
response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=200,
status_text="OK",
headers={'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8'},
body=html_content.encode('utf-8')
)
return response.build_response()
def _handle_static_file(self, request: HTTPRequest, client_address: tuple) -> bytes:
"""处理静态文件请求"""
try:
# 解析请求路径
path = unquote(request.path)
if path.startswith('/static/'):
file_path = path[7:] # 移除 '/static/'
else:
file_path = path[1:] # 移除开头的 '/'
# 安全路径检查
file_path = Path(file_path)
if '..' in file_path.parts:
return self._generate_error_response(403, "禁止访问")
# 构建完整文件路径
full_path = self.document_root / file_path
if full_path.is_file():
# 获取MIME类型
mime_type, _ = mimetypes.guess_type(str(full_path))
mime_type = mime_type or 'application/octet-stream'
# 读取文件内容
with open(full_path, 'rb') as f:
content = f.read()
response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=200,
status_text="OK",
headers={
'Content-Type': mime_type,
'Content-Length': str(len(content))
},
body=content
)
return response.build_response()
else:
return self._generate_error_response(404, f"文件未找到: {path}")
except Exception as e:
return self._generate_error_response(500, f"文件处理错误: {e}")
def _generate_error_response(self, status_code: int, message: str) -> bytes:
"""生成错误响应"""
analyzer = HTTPStatusCodeAnalyzer()
return analyzer.generate_appropriate_response(status_code, message).build_response()
# 启动服务器
def run_http_server():
"""运行HTTP服务器示例"""
# 创建示例静态文件
www_dir = Path('./www')
www_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
static_dir = www_dir / 'static'
static_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
# 创建测试文件
test_file = static_dir / 'test.txt'
test_file.write_text('这是一个测试静态文件\nHello from HTTP Server!')
# 启动服务器
server = SimpleHTTPServer(port=8080, document_root=www_dir)
server.start()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_http_server()3.2 高级特性实现
3.2.1 中间件架构支持
python
# http_middleware.py
from typing import Callable, Optional
import json
class HTTPMiddleware:
"""HTTP中间件基类"""
def process_request(self, request: HTTPRequest) -> Optional[HTTPResponse]:
"""处理请求,返回None则继续处理,返回Response则直接返回"""
return None
def process_response(self, request: HTTPRequest, response: HTTPResponse) -> HTTPResponse:
"""处理响应"""
return response
class AuthenticationMiddleware(HTTPMiddleware):
"""认证中间件"""
def __init__(self, api_keys=None):
self.api_keys = api_keys or []
def process_request(self, request: HTTPRequest) -> Optional[HTTPResponse]:
# 检查需要认证的路径
if request.path.startswith('/api/'):
auth_header = request.headers.get('Authorization', '')
if not auth_header.startswith('Bearer '):
return self._unauthorized_response()
api_key = auth_header[7:] # 移除 'Bearer '
if api_key not in self.api_keys:
return self._unauthorized_response()
return None
def _unauthorized_response(self) -> HTTPResponse:
response = HTTPResponse(
status_code=401,
status_text="Unauthorized",
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'},
body=json.dumps({'error': '认证失败'}).encode('utf-8')
)
return response
class LoggingMiddleware(HTTPMiddleware):
"""日志中间件"""
def process_request(self, request: HTTPRequest) -> None:
print(f"[{time.time()}] 请求: {request.method} {request.path}")
return None
def process_response(self, request: HTTPRequest, response: HTTPResponse) -> HTTPResponse:
print(f"[{time.time()}] 响应: {request.method} {request.path} -> {response.status_code}")
return response
class MiddlewareHTTPServer(SimpleHTTPServer):
"""支持中间件的HTTP服务器"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.middlewares = []
def add_middleware(self, middleware: HTTPMiddleware):
"""添加中间件"""
self.middlewares.append(middleware)
def _handle_request(self, request: HTTPRequest, client_address: tuple) -> bytes:
"""重写请求处理,加入中间件支持"""
# 处理请求中间件
for middleware in self.middlewares:
result = middleware.process_request(request)
if result is not None:
return result.build_response()
# 执行实际处理
response_bytes = super()._handle_request(request, client_address)
# 解析响应以便中间件处理
response = self._parse_response(response_bytes)
# 处理响应中间件
for middleware in self.middlewares:
response = middleware.process_response(request, response)
return response.build_response()
def _parse_response(self, response_bytes: bytes) -> HTTPResponse:
"""解析响应字节为HTTPResponse对象"""
# 简化实现,实际需要完整解析
return HTTPResponse(200, "OK", body=response_bytes)4 高级应用与企业级实战
4.1 性能优化实战技巧
基于真实项目经验,总结HTTP性能优化的核心技巧。
4.1.1 连接管理与优化
python
# http_optimization.py
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from functools import lru_cache
class HTTPOptimizer:
"""HTTP性能优化器"""
def __init__(self):
self.optimization_strategies = {
'connection_reuse': '持久连接和连接池',
'compression': 'gzip/brotli压缩',
'caching': '适当的缓存策略',
'cdn': '内容分发网络',
'http2': 'HTTP/2多路复用'
}
def analyze_performance_bottlenecks(self, request_logs: list) -> dict:
"""分析性能瓶颈"""
analysis = {
'total_requests': len(request_logs),
'average_response_time': 0,
'slow_requests': [],
'common_issues': []
}
if not request_logs:
return analysis
total_time = 0
for log in request_logs:
response_time = log.get('response_time', 0)
total_time += response_time
if response_time > 1000: # 超过1秒的请求
analysis['slow_requests'].append({
'url': log.get('path', ''),
'time': response_time,
'method': log.get('method', 'GET')
})
analysis['average_response_time'] = total_time / len(request_logs)
# 识别常见问题
if analysis['average_response_time'] > 500:
analysis['common_issues'].append('高延迟:考虑启用HTTP/2和CDN')
slow_count = len(analysis['slow_requests'])
if slow_count > len(request_logs) * 0.1: # 10%以上请求慢
analysis['common_issues'].append('大量慢请求:需要数据库和代码优化')
return analysis
@lru_cache(maxsize=1000)
def expensive_operation(self, key: str) -> str:
"""模拟昂贵操作,使用缓存优化"""
time.sleep(0.1) # 模拟耗时操作
return f"processed_{key}"
def generate_optimization_report(self, current_performance: dict) -> list:
"""生成优化建议报告"""
recommendations = []
avg_response_time = current_performance.get('average_response_time', 0)
request_count = current_performance.get('total_requests', 0)
if avg_response_time > 1000:
recommendations.append({
'priority': 'high',
'area': '连接管理',
'suggestion': '启用HTTP/2多路复用,减少连接建立开销',
'expected_improvement': '40-60%'
})
if request_count > 100:
recommendations.append({
'priority': 'medium',
'area': '缓存策略',
'suggestion': '实施积极的缓存策略,减少重复计算',
'expected_improvement': '30-50%'
})
if current_performance.get('image_requests', 0) > 10:
recommendations.append({
'priority': 'medium',
'area': '资源优化',
'suggestion': '启用图片压缩和WebP格式',
'expected_improvement': '20-40%'
})
return recommendations4.1.2 HTTP/2 服务器实现
python
# http2_server.py
import asyncio
import h2.config
import h2.connection
import h2.events
class HTTP2Server:
"""HTTP/2服务器实现示例"""
def __init__(self, host='localhost', port=8443):
self.host = host
self.port = port
async def handle_http2_connection(self, reader, writer):
"""处理HTTP/2连接"""
config = h2.config.H2Configuration(client_side=False)
conn = h2.connection.H2Connection(config=config)
conn.initiate_connection()
# 发送初始设置帧
writer.write(conn.data_to_send())
await writer.drain()
try:
while True:
data = await reader.read(65535)
if not data:
break
# 处理接收到的数据
events = conn.receive_data(data)
for event in events:
if isinstance(event, h2.events.RequestReceived):
await self.handle_request(event, conn, writer)
elif isinstance(event, h2.events.DataReceived):
# 处理数据帧
conn.acknowledge_received_data(
event.flow_controlled_length,
event.stream_id
)
# 发送待发送数据
if conn.data_to_send:
writer.write(conn.data_to_send())
await writer.drain()
except Exception as e:
print(f"HTTP/2连接错误: {e}")
finally:
writer.close()
async def handle_request(self, event, conn, writer):
"""处理HTTP/2请求"""
stream_id = event.stream_id
headers = dict(event.headers)
# 构建响应
response_headers = [
(':status', '200'),
('content-type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8'),
('server', 'python-http2-server'),
]
response_body = f"""
<html>
<body>
<h1>HTTP/2 Server</h1>
<p>Stream ID: {stream_id}</p>
<p>这是一个HTTP/2响应示例</p>
</body>
</html>
""".encode('utf-8')
# 发送响应头
conn.send_headers(stream_id, response_headers)
conn.send_data(stream_id, response_body, end_stream=True)
# 发送数据
writer.write(conn.data_to_send())
await writer.drain()4.2 企业级安全实践
4.2.1 安全头部与防护措施
python
# http_security.py
from typing import Dict, List
class HTTPSecurityHeaders:
"""HTTP安全头部管理"""
def __init__(self):
self.security_headers = {
'Strict-Transport-Security': 'max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains',
'X-Content-Type-Options': 'nosniff',
'X-Frame-Options': 'SAMEORIGIN',
'X-XSS-Protection': '1; mode=block',
'Referrer-Policy': 'strict-origin-when-cross-origin',
'Content-Security-Policy': "default-src 'self'",
'Permissions-Policy': 'geolocation=(), camera=()'
}
def add_security_headers(self, response: HTTPResponse) -> HTTPResponse:
"""添加安全头部到响应"""
for header, value in self.security_headers.items():
response.headers[header] = value
return response
def generate_csp_policy(self, directives: Dict[str, List[str]]) -> str:
"""生成内容安全策略"""
policy_parts = []
for directive, sources in directives.items():
sources_str = ' '.join(f"'{src}'" if src in ['self', 'none', 'unsafe-inline', 'unsafe-eval'] else src
for src in sources)
policy_parts.append(f"{directive} {sources_str}")
return '; '.join(policy_parts)
class RateLimiter:
"""API速率限制器"""
def __init__(self, max_requests: int = 100, window: int = 3600):
self.max_requests = max_requests
self.window = window
self.requests = {}
def is_rate_limited(self, client_ip: str) -> bool:
"""检查客户端是否被限流"""
now = time.time()
if client_ip not in self.requests:
self.requests[client_ip] = []
# 清理过期请求
self.requests[client_ip] = [
req_time for req_time in self.requests[client_ip]
if now - req_time < self.window
]
# 检查请求次数
if len(self.requests[client_ip]) >= self.max_requests:
return True
# 记录本次请求
self.requests[client_ip].append(now)
return False5 故障排查与调试指南
5.1 常见问题与解决方案
基于真实项目经验,总结HTTP协议相关的常见问题及解决方案。
5.1.1 连接问题排查
python
# http_troubleshooting.py
import subprocess
import sys
from typing import Dict, List
class HTTPTroubleshooter:
"""HTTP故障排查工具"""
def diagnose_connection_issues(self, url: str) -> Dict:
"""诊断连接问题"""
diagnostics = {
'url': url,
'checks': [],
'issues': [],
'solutions': []
}
# 检查DNS解析
try:
import socket
hostname = url.split('//')[-1].split('/')[0]
socket.gethostbyname(hostname)
diagnostics['checks'].append({'check': 'DNS解析', 'status': '成功'})
except socket.gaierror:
diagnostics['issues'].append('DNS解析失败')
diagnostics['solutions'].append('检查DNS配置或使用IP直接访问')
# 检查端口连通性
try:
import socket
hostname = url.split('//')[-1].split('/')[0]
port = 80 if url.startswith('http:') else 443
if ':' in hostname:
hostname, port_str = hostname.split(':', 1)
port = int(port_str)
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.settimeout(5)
result = sock.connect_ex((hostname, port))
sock.close()
if result == 0:
diagnostics['checks'].append({'check': '端口连通性', 'status': '成功'})
else:
diagnostics['issues'].append(f'端口{port}无法连通')
diagnostics['solutions'].append('检查防火墙和网络连接')
except Exception as e:
diagnostics['issues'].append(f'端口检查失败: {e}')
return diagnostics
def analyze_http_errors(self, status_code: int, headers: Dict, body: str) -> List[str]:
"""分析HTTP错误"""
suggestions = []
error_patterns = {
400: ['检查请求语法', '验证参数格式'],
401: ['检查认证信息', '验证API密钥'],
403: ['检查权限设置', '验证访问令牌'],
404: ['检查URL路径', '验证资源是否存在'],
500: ['检查服务器日志', '查看应用错误信息'],
502: ['检查上游服务', '验证负载均衡配置'],
503: ['检查服务状态', '查看系统负载'],
504: ['检查网络延迟', '验证上游服务响应时间']
}
if status_code in error_patterns:
suggestions.extend(error_patterns[status_code])
# 特定错误模式识别
if status_code == 500 and 'database' in body.lower():
suggestions.append('检查数据库连接和查询')
if status_code == 413:
suggestions.extend(['减少请求体大小', '检查上传限制'])
return suggestions官方文档与参考资源
-
HTTP/1.1 RFC 7230- HTTP/1.1 协议标准
-
HTTP/2 RFC 7540- HTTP/2 协议规范
-
HTTP/3 RFC 9114- HTTP/3 协议标准
-
Mozilla HTTP文档- MDN HTTP 参考
通过本文的完整学习路径,您应该已经掌握了HTTP协议从基础到高级的全栈知识。HTTP协议的深入理解是Web开发的基石,希望本文能帮助您在未来的项目中构建更高性能、更可靠的应用。