引言
当你的团队需要同时维护iOS、Android、Web三个平台的应用时,你是否曾经历过这样的场景:同一个业务逻辑需要用Swift、Kotlin、TypeScript各实现一遍,API返回结构变更时三端都要修改,单元测试也要写三份?这不仅耗费大量开发资源,还极易导致平台间行为不一致的bug。
Kotlin Multiplatform(KMP)的出现改变了这一切。它不是又一个"write once, run anywhere"的空想,而是一个务实的解决方案------让你可以在保留各平台UI原生性的同时,共享业务逻辑、网络层、数据处理等核心代码。Google在其多个项目中采用了KMP,JetBrains的旗舰产品也在使用,这证明了其生产级的可靠性。
本文将带你从零开始掌握Kotlin Multiplatform开发,通过实战案例理解其架构设计、平台互操作机制以及最佳实践。
一、Kotlin Multiplatform核心概念
1.1 什么是Kotlin Multiplatform?
Kotlin Multiplatform是一个跨平台技术方案,它允许你:
- 共享业务逻辑:在多个平台间复用Kotlin代码
- 保留平台特性:每个平台可以使用原生UI和平台API
- 灵活的共享粒度:从完全共享到部分共享,自由选择
- 无运行时开销:编译为各平台原生代码,无虚拟机
1.2 KMP架构全景
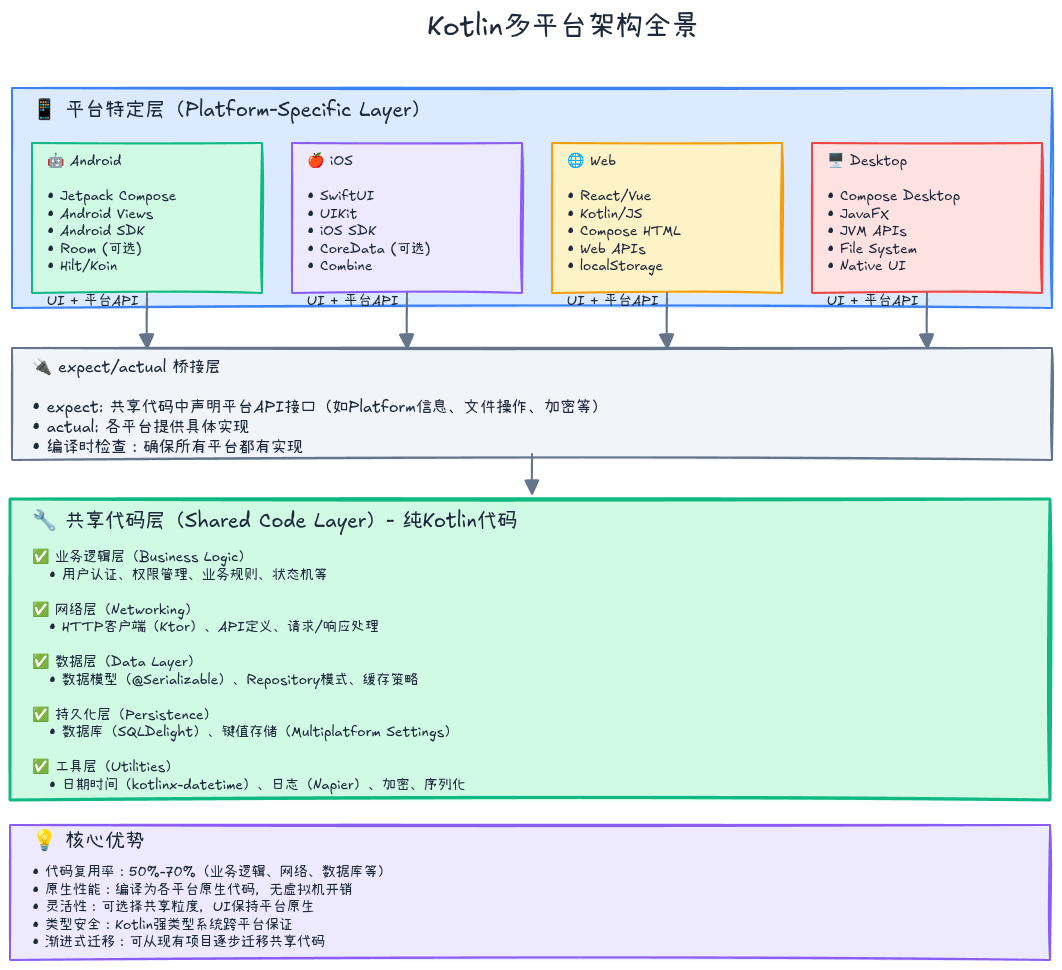
关键点:
- 共享代码层:纯Kotlin代码,可在所有目标平台运行
- 平台特定层:使用各平台原生技术(SwiftUI、Jetpack Compose、React等)
- expect/actual机制:连接共享代码与平台实现的桥梁
1.3 expect/actual机制详解
expect/actual是KMP最核心的机制,用于定义跨平台API:
共享模块中声明预期(expect):
kotlin
// commonMain/Platform.kt
expect class Platform() {
val name: String
}
expect fun getPlatformInfo(): StringAndroid平台实现(actual):
kotlin
// androidMain/Platform.kt
actual class Platform {
actual val name: String = "Android ${android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT}"
}
actual fun getPlatformInfo(): String {
return "Running on Android"
}iOS平台实现(actual):
kotlin
// iosMain/Platform.kt
import platform.UIKit.UIDevice
actual class Platform {
actual val name: String =
UIDevice.currentDevice.systemName() + " " +
UIDevice.currentDevice.systemVersion
}
actual fun getPlatformInfo(): String {
return "Running on iOS"
}原理:
- 编译时,编译器会根据目标平台选择对应的
actual实现 expect声明必须在所有目标平台都有actual实现,否则编译失败- 保证了类型安全和API一致性
二、创建你的第一个KMP项目
2.1 项目结构
使用Kotlin Multiplatform Wizard(https://kmp.jetbrains.com)创建项目后,得到如下结构:
my-kmp-app/
├── shared/ # 共享模块
│ ├── src/
│ │ ├── commonMain/ # 通用代码
│ │ │ └── kotlin/
│ │ │ ├── models/ # 数据模型
│ │ │ ├── repository/ # 业务逻辑
│ │ │ └── util/ # 工具类
│ │ ├── androidMain/ # Android特定代码
│ │ │ └── kotlin/
│ │ ├── iosMain/ # iOS特定代码
│ │ │ └── kotlin/
│ │ ├── commonTest/ # 通用测试
│ │ └── ...
│ └── build.gradle.kts
├── androidApp/ # Android应用
│ ├── src/
│ └── build.gradle.kts
└── iosApp/ # iOS应用(Xcode项目)
└── iosApp.xcodeproj2.2 配置Gradle构建脚本
shared/build.gradle.kts配置示例:
kotlin
plugins {
kotlin("multiplatform")
kotlin("plugin.serialization") version "1.9.22"
id("com.android.library")
}
kotlin {
// Android目标
android {
compilations.all {
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = "17"
}
}
}
// iOS目标
listOf(
iosX64(),
iosArm64(),
iosSimulatorArm64()
).forEach { iosTarget ->
iosTarget.binaries.framework {
baseName = "shared"
isStatic = true
}
}
// 可选:JVM目标(用于桌面应用)
jvm()
// 可选:JS目标(用于Web应用)
js(IR) {
browser()
nodejs()
}
// 源集配置
sourceSets {
val commonMain by getting {
dependencies {
// Kotlin协程
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.7.3")
// 序列化
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-serialization-json:1.6.2")
// Ktor网络库
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-core:2.3.7")
// 日期时间
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-datetime:0.5.0")
}
}
val androidMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-android:2.3.7")
}
}
val iosMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-darwin:2.3.7")
}
}
val commonTest by getting {
dependencies {
implementation(kotlin("test"))
}
}
}
}
android {
namespace = "com.example.myapp.shared"
compileSdk = 34
defaultConfig {
minSdk = 24
}
}关键配置说明:
- 多目标支持 :
android(),iosX64(),jvm(),js()等 - Framework导出 (iOS):
binaries.framework配置iOS框架 - 源集依赖 :
commonMain中的依赖会自动传递到平台特定源集 - 平台特定依赖:如Ktor的Android和iOS客户端实现
三、实战案例一:共享网络层
3.1 定义通用数据模型
kotlin
// commonMain/models/User.kt
import kotlinx.serialization.Serializable
@Serializable
data class User(
val id: Int,
val name: String,
val email: String,
val avatar: String? = null
)
@Serializable
data class ApiResponse<T>(
val code: Int,
val message: String,
val data: T? = null
)3.2 创建跨平台HTTP客户端
kotlin
// commonMain/network/HttpClient.kt
import io.ktor.client.*
import io.ktor.client.call.*
import io.ktor.client.plugins.contentnegotiation.*
import io.ktor.client.request.*
import io.ktor.serialization.kotlinx.json.*
import kotlinx.serialization.json.Json
expect fun createPlatformHttpClient(): HttpClient
class ApiClient {
private val client = createPlatformHttpClient()
private val json = Json {
ignoreUnknownKeys = true
isLenient = true
prettyPrint = true
}
suspend fun getUsers(): Result<List<User>> = runCatching {
val response: ApiResponse<List<User>> = client.get(
"https://api.example.com/users"
).body()
if (response.code == 200 && response.data != null) {
response.data
} else {
throw Exception(response.message)
}
}
suspend fun getUserById(id: Int): Result<User> = runCatching {
val response: ApiResponse<User> = client.get(
"https://api.example.com/users/$id"
).body()
response.data ?: throw Exception("User not found")
}
fun close() {
client.close()
}
}Android平台实现:
kotlin
// androidMain/network/HttpClient.kt
import io.ktor.client.*
import io.ktor.client.engine.android.*
import io.ktor.client.plugins.contentnegotiation.*
import io.ktor.serialization.kotlinx.json.*
actual fun createPlatformHttpClient(): HttpClient = HttpClient(Android) {
install(ContentNegotiation) {
json()
}
engine {
connectTimeout = 30_000
socketTimeout = 30_000
}
}iOS平台实现:
kotlin
// iosMain/network/HttpClient.kt
import io.ktor.client.*
import io.ktor.client.engine.darwin.*
import io.ktor.client.plugins.contentnegotiation.*
import io.ktor.serialization.kotlinx.json.*
actual fun createPlatformHttpClient(): HttpClient = HttpClient(Darwin) {
install(ContentNegotiation) {
json()
}
engine {
configureRequest {
setAllowsCellularAccess(true)
}
}
}3.3 Repository模式封装
kotlin
// commonMain/repository/UserRepository.kt
class UserRepository {
private val apiClient = ApiClient()
suspend fun fetchUsers(): Result<List<User>> {
return apiClient.getUsers()
}
suspend fun fetchUserById(id: Int): Result<User> {
return apiClient.getUserById(id)
}
}3.4 在Android中使用
kotlin
// androidApp/MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
private val repository = UserRepository()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
var users by remember { mutableStateOf<List<User>>(emptyList()) }
var isLoading by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
var error by remember { mutableStateOf<String?>(null) }
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
isLoading = true
repository.fetchUsers()
.onSuccess { users = it }
.onFailure { error = it.message }
isLoading = false
}
UserListScreen(
users = users,
isLoading = isLoading,
error = error
)
}
}
}3.5 在iOS中使用
swift
// iosApp/ContentView.swift
import SwiftUI
import shared
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var users: [User] = []
@State private var isLoading = false
@State private var errorMessage: String?
let repository = UserRepository()
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
if isLoading {
ProgressView()
} else if let error = errorMessage {
Text("Error: \(error)")
} else {
List(users, id: \.id) { user in
HStack {
AsyncImage(url: URL(string: user.avatar ?? ""))
.frame(width: 50, height: 50)
VStack(alignment: .leading) {
Text(user.name).font(.headline)
Text(user.email).font(.caption)
}
}
}
}
}
.task {
await loadUsers()
}
}
func loadUsers() async {
isLoading = true
do {
let result = try await repository.fetchUsers()
users = result
} catch {
errorMessage = error.localizedDescription
}
isLoading = false
}
}关键点:
- Kotlin的
suspend函数在Swift中自动转换为async函数 Result<T>类型在Swift中正常工作- 数据类在Swift中表现为不可变结构
四、实战案例二:跨平台数据持久化
4.1 使用SQLDelight实现数据库
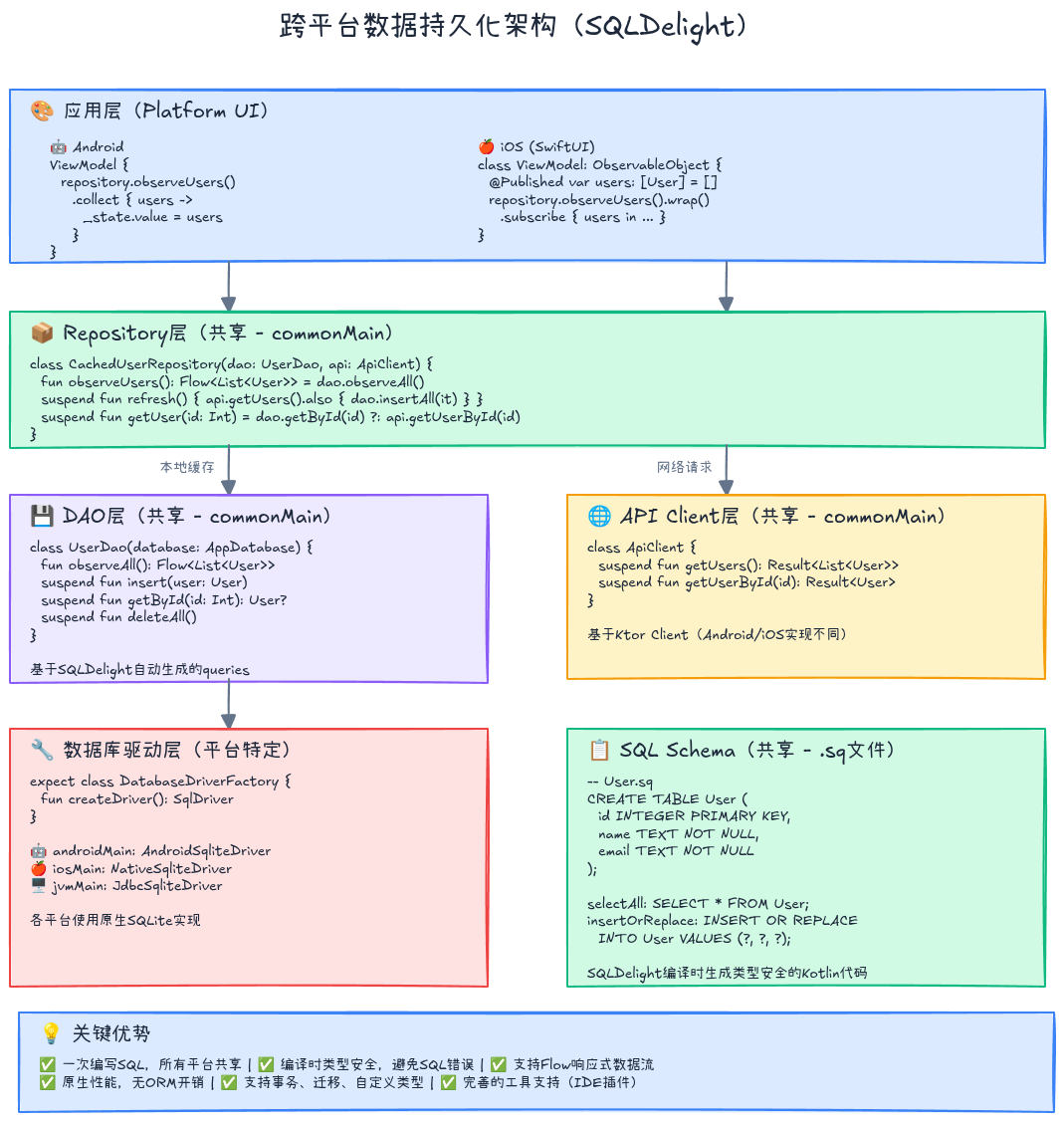
添加依赖 (shared/build.gradle.kts):
kotlin
plugins {
id("app.cash.sqldelight") version "2.0.1"
}
sqldelight {
databases {
create("AppDatabase") {
packageName.set("com.example.db")
}
}
}
kotlin {
sourceSets {
val commonMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("app.cash.sqldelight:runtime:2.0.1")
implementation("app.cash.sqldelight:coroutines-extensions:2.0.1")
}
}
val androidMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("app.cash.sqldelight:android-driver:2.0.1")
}
}
val iosMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("app.cash.sqldelight:native-driver:2.0.1")
}
}
}
}4.2 定义数据库Schema
sql
-- commonMain/sqldelight/com/example/db/User.sq
CREATE TABLE User (
id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT NOT NULL,
avatar TEXT,
createdAt INTEGER NOT NULL
);
-- 插入或替换用户
insertOrReplace:
INSERT OR REPLACE INTO User(id, name, email, avatar, createdAt)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?);
-- 查询所有用户
selectAll:
SELECT * FROM User
ORDER BY createdAt DESC;
-- 根据ID查询用户
selectById:
SELECT * FROM User
WHERE id = ?;
-- 删除用户
deleteById:
DELETE FROM User
WHERE id = ?;
-- 清空表
deleteAll:
DELETE FROM User;4.3 创建数据库驱动
通用接口:
kotlin
// commonMain/database/DatabaseDriverFactory.kt
import app.cash.sqldelight.db.SqlDriver
import com.example.db.AppDatabase
expect class DatabaseDriverFactory {
fun createDriver(): SqlDriver
}
fun createDatabase(driverFactory: DatabaseDriverFactory): AppDatabase {
val driver = driverFactory.createDriver()
return AppDatabase(driver)
}Android实现:
kotlin
// androidMain/database/DatabaseDriverFactory.kt
import android.content.Context
import app.cash.sqldelight.db.SqlDriver
import app.cash.sqldelight.driver.android.AndroidSqliteDriver
import com.example.db.AppDatabase
actual class DatabaseDriverFactory(private val context: Context) {
actual fun createDriver(): SqlDriver {
return AndroidSqliteDriver(
AppDatabase.Schema,
context,
"app.db"
)
}
}iOS实现:
kotlin
// iosMain/database/DatabaseDriverFactory.kt
import app.cash.sqldelight.db.SqlDriver
import app.cash.sqldelight.driver.native.NativeSqliteDriver
import com.example.db.AppDatabase
actual class DatabaseDriverFactory {
actual fun createDriver(): SqlDriver {
return NativeSqliteDriver(
AppDatabase.Schema,
"app.db"
)
}
}4.4 封装数据访问层
kotlin
// commonMain/database/UserDao.kt
import app.cash.sqldelight.coroutines.asFlow
import app.cash.sqldelight.coroutines.mapToList
import com.example.db.AppDatabase
import kotlinx.coroutines.Dispatchers
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.Flow
import kotlinx.coroutines.withContext
import kotlinx.datetime.Clock
class UserDao(database: AppDatabase) {
private val queries = database.userQueries
// 观察所有用户(Flow)
fun observeAll(): Flow<List<User>> {
return queries.selectAll(::mapToUser)
.asFlow()
.mapToList(Dispatchers.Default)
}
// 插入用户
suspend fun insert(user: User) = withContext(Dispatchers.Default) {
queries.insertOrReplace(
id = user.id.toLong(),
name = user.name,
email = user.email,
avatar = user.avatar,
createdAt = Clock.System.now().toEpochMilliseconds()
)
}
// 批量插入
suspend fun insertAll(users: List<User>) = withContext(Dispatchers.Default) {
queries.transaction {
users.forEach { user ->
queries.insertOrReplace(
id = user.id.toLong(),
name = user.name,
email = user.email,
avatar = user.avatar,
createdAt = Clock.System.now().toEpochMilliseconds()
)
}
}
}
// 根据ID查询
suspend fun getById(id: Int): User? = withContext(Dispatchers.Default) {
queries.selectById(id.toLong(), ::mapToUser)
.executeAsOneOrNull()
}
// 删除用户
suspend fun delete(id: Int) = withContext(Dispatchers.Default) {
queries.deleteById(id.toLong())
}
// 清空所有用户
suspend fun deleteAll() = withContext(Dispatchers.Default) {
queries.deleteAll()
}
private fun mapToUser(
id: Long,
name: String,
email: String,
avatar: String?,
createdAt: Long
): User {
return User(
id = id.toInt(),
name = name,
email = email,
avatar = avatar
)
}
}4.5 实现缓存策略的Repository
kotlin
// commonMain/repository/CachedUserRepository.kt
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.Flow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.first
class CachedUserRepository(
private val userDao: UserDao,
private val apiClient: ApiClient
) {
// 观察本地缓存
fun observeUsers(): Flow<List<User>> {
return userDao.observeAll()
}
// 刷新数据(网络优先)
suspend fun refresh(): Result<Unit> = runCatching {
val result = apiClient.getUsers().getOrThrow()
userDao.deleteAll()
userDao.insertAll(result)
}
// 获取用户(缓存优先)
suspend fun getUser(id: Int, forceRefresh: Boolean = false): Result<User> {
if (!forceRefresh) {
val cached = userDao.getById(id)
if (cached != null) {
return Result.success(cached)
}
}
return runCatching {
val user = apiClient.getUserById(id).getOrThrow()
userDao.insert(user)
user
}
}
}五、平台互操作深度解析
5.1 Kotlin/Native与Swift互操作
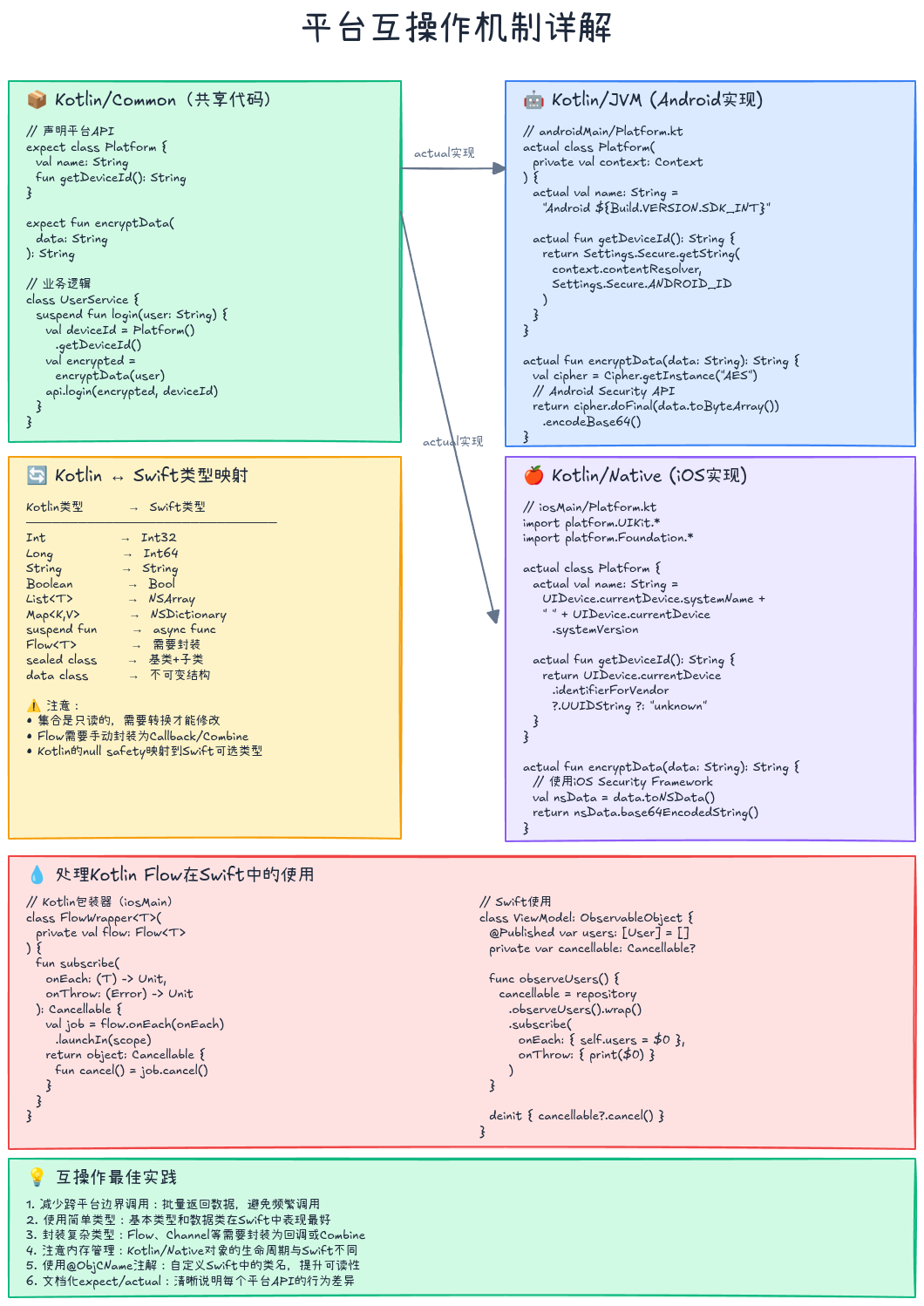
5.1.1 数据类型映射
| Kotlin类型 | Swift类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
Int |
Int32 |
32位整数 |
Long |
Int64 |
64位整数 |
Float |
Float |
32位浮点数 |
Double |
Double |
64位浮点数 |
Boolean |
Bool |
布尔值 |
String |
String |
字符串(自动桥接) |
List<T> |
NSArray |
列表(注意可变性) |
Map<K, V> |
NSDictionary |
字典 |
suspend fun |
async func |
异步函数 |
Flow<T> |
无直接映射 | 需要转换 |
5.1.2 处理Kotlin Flow在Swift中的使用
Kotlin的Flow在Swift中没有直接对应物,需要转换为Combine的Publisher或使用回调:
方案一:转换为Combine(推荐):
kotlin
// iosMain/util/FlowExtensions.kt
import kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.Dispatchers
import kotlinx.coroutines.Job
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.Flow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.launchIn
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.onEach
class FlowWrapper<T>(private val flow: Flow<T>) {
fun subscribe(
onEach: (T) -> Unit,
onComplete: () -> Unit,
onThrow: (Error) -> Unit
): Cancellable {
val scope = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main)
val job = flow.onEach { onEach(it) }
.launchIn(scope)
return object : Cancellable {
override fun cancel() {
job.cancel()
}
}
}
}
interface Cancellable {
fun cancel()
}
fun <T> Flow<T>.wrap(): FlowWrapper<T> = FlowWrapper(this)在Swift中使用:
swift
// iosApp/UserListViewModel.swift
import Combine
import shared
class UserListViewModel: ObservableObject {
@Published var users: [User] = []
private let repository: CachedUserRepository
private var cancellable: Cancellable?
init(repository: CachedUserRepository) {
self.repository = repository
observeUsers()
}
func observeUsers() {
cancellable = repository.observeUsers().wrap().subscribe(
onEach: { [weak self] users in
self?.users = users
},
onComplete: {},
onThrow: { error in
print("Error: \(error)")
}
)
}
func refresh() async {
do {
try await repository.refresh()
} catch {
print("Refresh failed: \(error)")
}
}
deinit {
cancellable?.cancel()
}
}方案二:使用回调:
kotlin
// commonMain/repository/UserRepositoryCallback.kt
class UserRepositoryCallback(private val repository: CachedUserRepository) {
private val scope = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main)
fun observeUsers(onChange: (List<User>) -> Unit): Cancellable {
val job = scope.launch {
repository.observeUsers().collect { users ->
onChange(users)
}
}
return object : Cancellable {
override fun cancel() = job.cancel()
}
}
}5.1.3 处理密封类(Sealed Class)
Kotlin的密封类在Swift中会生成一个基类和多个子类:
Kotlin定义:
kotlin
// commonMain/models/Resource.kt
sealed class Resource<out T> {
data class Success<T>(val data: T) : Resource<T>()
data class Error(val message: String, val code: Int) : Resource<Nothing>()
object Loading : Resource<Nothing>()
}Swift使用:
swift
func handleResource(resource: Resource<User>) {
switch resource {
case let success as Resource.Success<User>:
print("User: \(success.data)")
case let error as Resource.Error:
print("Error: \(error.message)")
case is Resource.Loading:
print("Loading...")
default:
break
}
}5.2 Kotlin/JVM与Android互操作
Android平台的互操作相对简单,因为Kotlin本身就是Android一等公民:
在Android中使用共享模块:
kotlin
// androidApp/di/AppModule.kt
@Module
@InstallIn(SingletonComponent::class)
object AppModule {
@Provides
@Singleton
fun provideDatabaseDriverFactory(
@ApplicationContext context: Context
): DatabaseDriverFactory {
return DatabaseDriverFactory(context)
}
@Provides
@Singleton
fun provideAppDatabase(
driverFactory: DatabaseDriverFactory
): AppDatabase {
return createDatabase(driverFactory)
}
@Provides
@Singleton
fun provideUserRepository(
database: AppDatabase
): CachedUserRepository {
return CachedUserRepository(
userDao = UserDao(database),
apiClient = ApiClient()
)
}
}注意事项:
- R8/ProGuard规则:确保不混淆共享模块的类
- 协程调度器 :使用
Dispatchers.Main.immediate避免不必要的调度 - 内存管理:注意避免内存泄漏,特别是在ViewModel中
六、KMP最佳实践
6.1 架构设计原则
1. 清晰的责任划分:
共享层职责:
✅ 业务逻辑
✅ 数据处理
✅ 网络请求
✅ 数据持久化
✅ 工具类
平台层职责:
✅ UI渲染
✅ 用户交互
✅ 平台特定API(如推送、支付)
✅ 性能敏感的UI动画2. 使用Repository模式隔离数据源:
kotlin
// 共享层只定义接口和业务逻辑
interface UserRepository {
suspend fun getUsers(): Result<List<User>>
}
// 平台层可以提供特定实现
class AndroidUserRepository(
private val sharedRepo: CachedUserRepository,
private val analytics: FirebaseAnalytics
) : UserRepository {
override suspend fun getUsers(): Result<List<User>> {
analytics.logEvent("fetch_users", null)
return sharedRepo.refresh()
.map { sharedRepo.observeUsers().first() }
}
}3. 避免在共享层使用平台特定类型:
kotlin
// ❌ 错误:Android特定类型泄漏到共享层
class ImageLoader(private val context: Context) { // Context是Android特定的
fun loadImage(url: String) { ... }
}
// ✅ 正确:使用expect/actual封装
expect class ImageLoader {
fun loadImage(url: String, callback: (ByteArray) -> Unit)
}6.2 性能优化建议
1. 减少跨平台边界调用:
kotlin
// ❌ 低效:频繁跨边界调用
fun processUsers(users: List<User>): List<String> {
return users.map { it.name } // 每次map都会跨边界
}
// ✅ 高效:批量返回
fun getUserNames(users: List<User>): List<String> {
return users.map { it.name } // 一次性返回整个列表
}2. 合理使用冻结(Freezing)机制(Kotlin/Native):
kotlin
// 在Kotlin/Native中,跨线程共享的对象必须冻结
class ThreadSafeCache<T : Any> {
private val cache = mutableMapOf<String, T>()
fun put(key: String, value: T) {
cache[key] = value.freeze() // 冻结对象
}
}注意:从Kotlin 1.7.20开始,新内存模型默认启用,大多数情况下不再需要手动冻结。
3. 使用协程优化异步操作:
kotlin
// 并发执行多个网络请求
suspend fun loadDashboardData(): DashboardData = coroutineScope {
val usersDeferred = async { apiClient.getUsers() }
val postsDeferred = async { apiClient.getPosts() }
val statsDeferred = async { apiClient.getStats() }
DashboardData(
users = usersDeferred.await().getOrThrow(),
posts = postsDeferred.await().getOrThrow(),
stats = statsDeferred.await().getOrThrow()
)
}6.3 测试策略
1. 共享代码的单元测试:
kotlin
// commonTest/repository/UserRepositoryTest.kt
class UserRepositoryTest {
private val mockApiClient = MockApiClient()
private val mockUserDao = MockUserDao()
private val repository = CachedUserRepository(mockUserDao, mockApiClient)
@Test
fun `refresh should update local cache`() = runTest {
// Given
val remoteUsers = listOf(
User(1, "Alice", "alice@example.com"),
User(2, "Bob", "bob@example.com")
)
mockApiClient.usersToReturn = remoteUsers
// When
val result = repository.refresh()
// Then
assertTrue(result.isSuccess)
assertEquals(remoteUsers, mockUserDao.storedUsers)
}
@Test
fun `getUser should return cached data when available`() = runTest {
// Given
val cachedUser = User(1, "Alice", "alice@example.com")
mockUserDao.storedUsers = listOf(cachedUser)
// When
val result = repository.getUser(1, forceRefresh = false)
// Then
assertTrue(result.isSuccess)
assertEquals(cachedUser, result.getOrNull())
assertEquals(0, mockApiClient.callCount) // 未调用网络
}
}2. 平台特定测试:
kotlin
// androidTest/database/DatabaseDriverFactoryTest.kt
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class)
class DatabaseDriverFactoryTest {
@Test
fun testDatabaseCreation() {
val context = ApplicationProvider.getApplicationContext<Context>()
val driverFactory = DatabaseDriverFactory(context)
val driver = driverFactory.createDriver()
assertNotNull(driver)
driver.close()
}
}
swift
// iosAppTests/DatabaseDriverFactoryTests.swift
import XCTest
@testable import shared
class DatabaseDriverFactoryTests: XCTestCase {
func testDatabaseCreation() {
let driverFactory = DatabaseDriverFactory()
let driver = driverFactory.createDriver()
XCTAssertNotNil(driver)
}
}3. 集成测试:
kotlin
// commonTest/integration/UserFlowTest.kt
class UserFlowTest {
@Test
fun `complete user flow should work correctly`() = runTest {
val repository = createRealRepository()
// 1. 刷新数据
repository.refresh().getOrThrow()
// 2. 观察本地数据
val users = repository.observeUsers().first()
assertTrue(users.isNotEmpty())
// 3. 获取单个用户
val user = repository.getUser(users.first().id).getOrThrow()
assertEquals(users.first(), user)
}
}七、常见陷阱与解决方案
7.1 Kotlin/Native内存管理
陷阱1:尝试跨线程访问可变对象
kotlin
// ❌ 错误:在iOS上会崩溃
class DataManager {
private val cache = mutableListOf<User>()
fun addUser(user: User) {
cache.add(user) // 如果在不同线程调用会报错
}
}
// ✅ 解决方案:使用线程安全的集合或冻结
class DataManager {
private val cache = ConcurrentMutableList<User>()
fun addUser(user: User) {
cache.add(user)
}
}
// 或者使用协程+单一Dispatcher
class DataManager {
private val scope = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default)
private val cache = mutableListOf<User>()
fun addUser(user: User) {
scope.launch {
cache.add(user)
}
}
}陷阱2:Lambda捕获可变状态
kotlin
// ❌ 错误:Lambda捕获了可变变量
var counter = 0
val callback = { counter++ } // 可能导致内存问题
// ✅ 解决方案:使用原子类型
val counter = AtomicInt(0)
val callback = { counter.incrementAndGet() }7.2 expect/actual不匹配
陷阱3:签名不完全一致
kotlin
// ❌ 错误:参数名不一致
// commonMain
expect fun formatDate(timestamp: Long): String
// androidMain
actual fun formatDate(time: Long): String { ... } // 参数名不同
// ✅ 解决方案:确保参数名完全一致
// androidMain
actual fun formatDate(timestamp: Long): String { ... }7.3 依赖管理问题
陷阱4:使用了非KMP兼容的库
kotlin
// ❌ 错误:Gson只支持JVM
dependencies {
implementation("com.google.code.gson:gson:2.10.1")
}
// ✅ 解决方案:使用KMP兼容的库
dependencies {
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-serialization-json:1.6.2")
}陷阱5:平台特定依赖配置错误
kotlin
// ❌ 错误:在commonMain中添加平台特定依赖
val commonMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-android:2.3.7") // Android特定
}
}
// ✅ 正确:在对应平台源集中添加
val androidMain by getting {
dependencies {
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-android:2.3.7")
}
}7.4 序列化问题
陷阱6:使用了不支持序列化的类型
kotlin
// ❌ 错误:Date不支持kotlinx.serialization
@Serializable
data class Event(
val title: String,
val date: java.util.Date // 不支持
)
// ✅ 解决方案:使用kotlinx-datetime或Long
@Serializable
data class Event(
val title: String,
val timestamp: Long // 时间戳
)
// 或者使用自定义序列化器
@Serializable
data class Event(
val title: String,
@Serializable(with = DateSerializer::class)
val date: Instant
)八、KMP生态系统与工具链
8.1 常用KMP库
| 库名 | 功能 | 支持平台 |
|---|---|---|
| Ktor Client | HTTP客户端 | Android, iOS, JVM, JS, Native |
| SQLDelight | 类型安全的SQL数据库 | Android, iOS, JVM, JS, Native |
| kotlinx.serialization | 序列化/反序列化 | 全平台 |
| kotlinx.coroutines | 协程 | 全平台 |
| kotlinx.datetime | 日期时间API | 全平台 |
| Koin | 依赖注入 | Android, iOS, JVM |
| Napier | 日志库 | 全平台 |
| Multiplatform Settings | 键值存储 | Android, iOS, JVM, JS |
| KStore | 数据流存储 | Android, iOS, JVM |
8.2 开发工具
1. Android Studio / Fleet:
- KMP插件:提供模板和代码导航
- Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile插件:iOS模拟器集成
2. Xcode:
- 通过CocoaPods或SPM集成Kotlin框架
- 调试Kotlin代码需要LLDB支持
3. KDoctor :
检查KMP开发环境配置
bash
brew install kdoctor
kdoctor4. Gradle相关插件:
kotlin
plugins {
kotlin("multiplatform") version "1.9.22"
kotlin("plugin.serialization") version "1.9.22"
id("com.android.library")
id("app.cash.sqldelight") version "2.0.1"
}8.3 CI/CD配置
GitHub Actions示例:
yaml
name: KMP CI
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: macos-latest # 需要macOS才能编译iOS
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up JDK 17
uses: actions/setup-java@v3
with:
java-version: '17'
distribution: 'temurin'
- name: Cache Gradle
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: |
~/.gradle/caches
~/.gradle/wrapper
key: ${{ runner.os }}-gradle-${{ hashFiles('**/*.gradle*') }}
- name: Build Shared Module
run: ./gradlew :shared:build
- name: Run Tests
run: ./gradlew :shared:allTests
- name: Build Android App
run: ./gradlew :androidApp:assembleDebug
- name: Build iOS Framework
run: ./gradlew :shared:linkDebugFrameworkIosX64
- name: Upload Test Results
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
if: always()
with:
name: test-results
path: '**/build/test-results/**/*.xml'九、总结与学习路径
核心要点回顾
- KMP是务实的跨平台方案:不强制"一次编写到处运行",而是让你自由选择共享粒度
- expect/actual是核心机制:连接共享代码与平台实现的桥梁
- 选择合适的共享边界:业务逻辑、网络、数据库适合共享,UI保持平台原生
- 重视平台互操作:理解Kotlin/Native的内存模型和Swift互操作细节
- 生态逐渐成熟:主流库(Ktor、SQLDelight、Koin等)已支持KMP
学习资源
官方文档:
- Kotlin Multiplatform官方文档:https://kotlinlang.org/docs/multiplatform.html
开源项目参考:
- Jetpack Compose Multiplatform:https://github.com/JetBrains/compose-multiplatform
- Touchlab KaMPKit:https://github.com/touchlab/KaMPKit
社区:
- Kotlin Slack的#multiplatform频道
- Reddit: r/Kotlin_Multiplatform
- Stack Overflow标签:kotlin-multiplatform
进阶方向
- Compose Multiplatform:学习使用Jetpack Compose构建跨平台UI
- Kotlin/Wasm:关注WebAssembly目标平台的发展
- 自定义Gradle插件:为KMP项目定制构建流程
- 性能优化:深入理解编译器优化和运行时性能
实践建议
- 从小做起:先共享数据模型和API层,逐步扩大共享范围
- 保持团队沟通:iOS和Android开发者需要紧密协作
- 自动化测试:共享代码必须有完善的测试覆盖
- 监控性能指标:跟踪应用大小和运行时性能
- 持续学习:KMP生态快速发展,保持技术敏感度
Kotlin Multiplatform不是银弹,但它为跨平台开发提供了一个实用、渐进式的解决方案。通过合理的架构设计和对平台特性的尊重,你可以在保证应用质量的同时显著提升开发效率。现在,开始你的KMP之旅吧!
参考资料:
- Kotlin Multiplatform官方文档 - https://kotlinlang.org/docs/multiplatform.html
- SQLDelight官方文档 - https://cashapp.github.io/sqldelight/
- Ktor Client文档 - https://ktor.io/docs/client.html
- Google's Guide to Kotlin Multiplatform - https://developer.android.com/kotlin/multiplatform
系列文章导航:
- 👉 上一篇: 编译器插件与注解处理器开发:在编译期操控Kotlin
- 👉 下一篇: 性能优化:内联、内存与字节码分析
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、分享!有任何问题或建议,欢迎在评论区留言讨论。让我们一起学习,一起成长!
也欢迎访问我的个人主页发现更多宝藏资源