Agent 经典范式构建之 ReAct (Reasoning and Acting): 一种将"思考"和"行动"紧密结合的范式,让智能体边想边做,动态调整
@[TOC](Agent 经典范式构建之 ReAct (Reasoning and Acting): 一种将"思考"和"行动"紧密结合的范式,让智能体边想边做,动态调整)
前言
11月份低,我开始尝试使用cursor帮我写一些苦力的业务的代码, 初始使用感觉AI编程已经基本啥都可以干,再加上企业的推广自家编码工具的流量特别大, 当时网络上一些主播跟着流量,导致整个网络满天飞AI可以取代程序员了,当时还是特别慌的了。当时随着我使用两个月, 我最近拿它做一下从0到1的开发两个技术性的项目最终都是以失败告终, 发现基本只是demo, 不能商业化使用而且发现项目代码基本最后你都能读懂,但是你就是不知道怎么改的情况。
第一次使用时候, 我是拿它写一些业务上的事情、项目上应急的和注释啥的, 感觉都可以胜任。 目前感觉写一些网页的画面可以使用它,其它一些还是自己写比较靠谱。
智能体(Agent)的经典范式之ReAct(思考和行动) 紧密结合的范式,让智能体边想边做的动态调整
最经典的一个智能体范式ReAct (Reason + Act)。ReAct由Shunyu Yao于2022年提出[1],其核心思想是模仿人类解决问题的方式,将推理 (Reasoning) 与行动 (Acting) 显式地结合起来,形成一个"思考-行动-观察"的循环。
一、ReAct 的工作流程
- Observation(观察)
- Thought / Reasoning(推理)
- Action(行动)
- Tool / Environment(工具/环境)
- Observation(反馈)
- 循环,直到 Final Answer
ReAct的巧妙之处在于,它认识到思考与行动是相辅相成的。思考指导行动,而行动的结果又反过来修正思考。为此,ReAct范式通过一种特殊的提示工程来引导模型,使其每一步的输出都遵循一个固定的轨迹:
- Thought (思考): 这是智能体的"内心独白"。它会分析当前情况、分解任务、制定下一步计划,或者反思上一步的结果。
- Action (行动): 这是智能体决定采取的具体动作,通常是调用一个外部工具,例如 Search['华为最新款手机']。
- Observation (观察): 这是执行Action后从外部工具返回的结果,例如搜索结果的摘要或API的返回值。
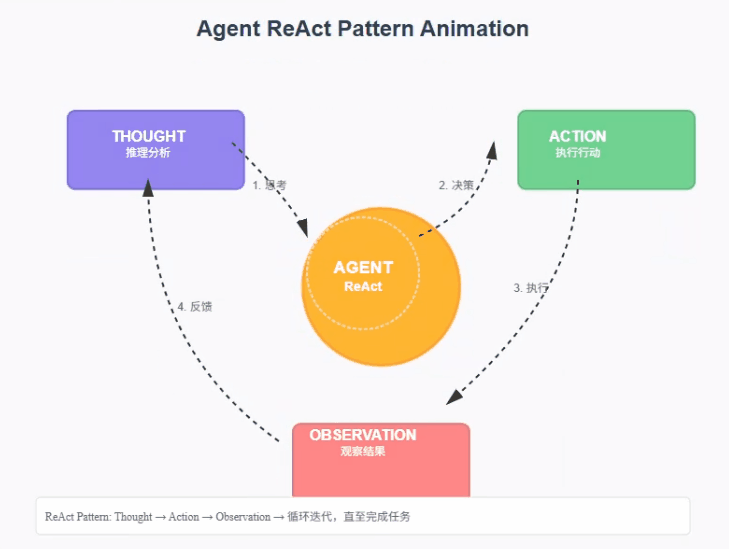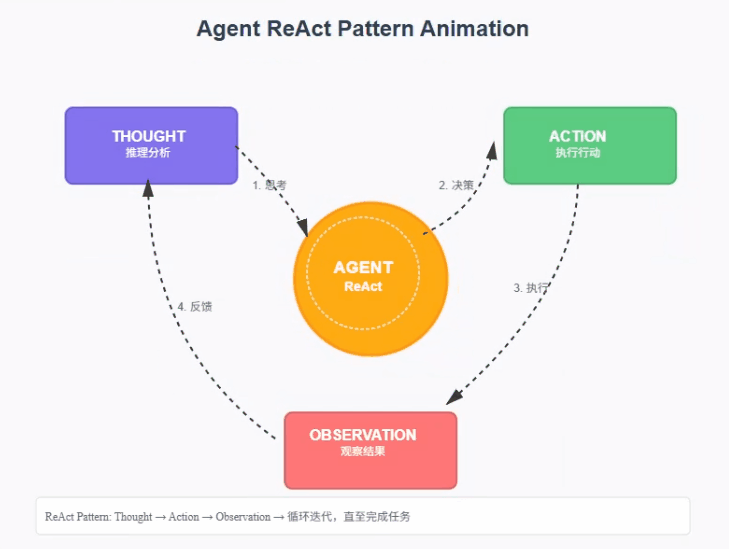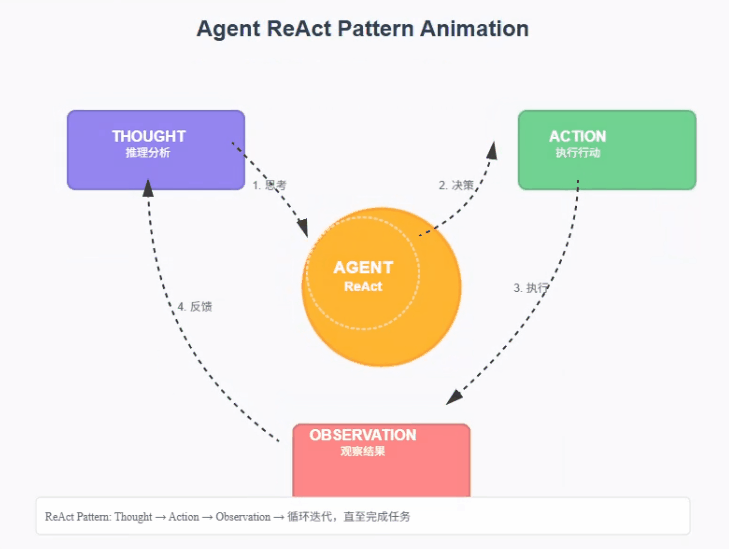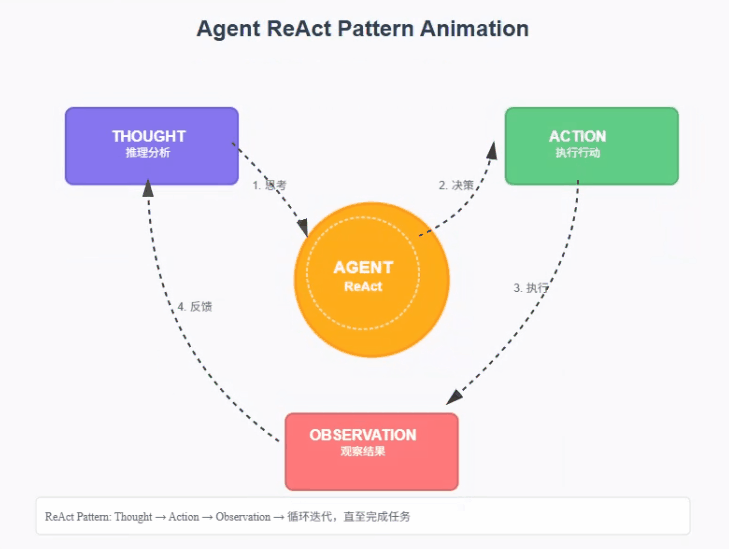
智能体将不断重复这个 Thought -> Action -> Observation 的循环,将新的观察结果追加到历史记录中,形成一个不断增长的上下文,直到它在Thought中认为已经找到了最终答案,然后输出结果。这个过程形成了一个强大的协同效应:推理使得行动更具目的性,而行动则为推理提供了事实依据。
- 需要外部知识的任务:如查询实时信息(天气、新闻、股价)、搜索专业领域的知识等。
- 需要精确计算的任务:将数学问题交给计算器工具,避免LLM的计算错误。
- 需要与API交互的任务:如操作数据库、调用某个服务的API来完成特定功能。
因此我们将构建一个具备使用外部工具能力的ReAct智能体,来回答一个大语言模型仅凭自身知识库无法直接回答的问题。例如:"华为最新的手机是哪一款?它的主要卖点是什么?" 这个问题需要智能体理解自己需要上网搜索,调用工具搜索结果并总结答案
二、ReAct系统提示词
python
REACT_PROMPT_TEMPLATE = """
请注意,你是一个有能力调用外部工具的智能助手。
可用工具如下:
{tools}
# 输出格式要求:
你的每次回复必须严格遵循以下格式,包含一对Thought和Action:
Thought: [你的思考过程和下一步计划]
Action: [你要执行的具体行动]
Action的格式必须是以下之一:
1. 调用工具:function_name(arg_name="arg_value")
2. 结束任务:Finish[最终答案]
# 重要提示:
- 每次只输出一对Thought-Action
- Action必须在同一行,不要换行
- 当收集到足够信息可以回答用户问题时,必须使用 Action: Finish[最终答案] 格式结束
现在,请开始解决以下问题:
Question: {question}
History: {history}
"""三、ReActAgent代码实现
python
class ReActAgent:
def __init__(self, llm_client: AgentsLLM, tool_executor: ToolExecutor, max_steps: int = 5):
self.llm_client = llm_client
self.tool_executor = tool_executor
self.max_steps = max_steps
self.history = []
def run(self, question: str):
self.history = []
current_step = 0
while current_step < self.max_steps:
current_step += 1
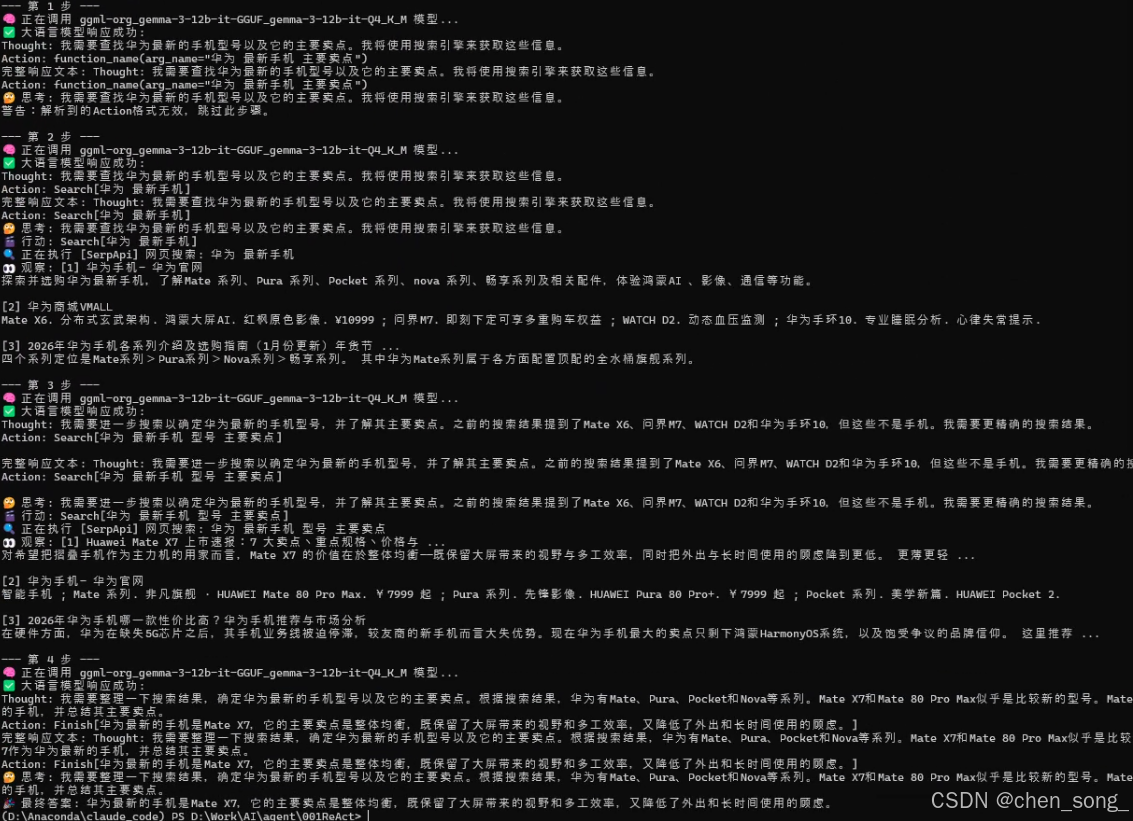
print(f"\n--- 第 {current_step} 步 ---")
tools_desc = self.tool_executor.getAvailableTools()
history_str = "\n".join(self.history)
prompt = REACT_PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(tools=tools_desc, question=question, history=history_str)
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
response_text = self.llm_client.think(messages=messages)
print(f"完整响应文本: {response_text}");
if not response_text:
print("错误:LLM未能返回有效响应。"); break
thought, action = self._parse_output(response_text)
if thought:
print(f"🤔 思考: {thought}")
if not action:
print("警告:未能解析出有效的Action,流程终止。");
break
if action.startswith("Finish"):
# 如果是Finish指令,提取最终答案并结束
final_answer = self._parse_action_input(action)
print(f"🎉 最终答案: {final_answer}")
return final_answer
tool_name, tool_input = self._parse_action(action)
if not tool_name or not tool_input:
self.history.append("Observation: 无效的Action格式,请检查。");
print("警告:解析到的Action格式无效,跳过此步骤。");
continue
print(f"🎬 行动: {tool_name}[{tool_input}]")
tool_function = self.tool_executor.getTool(tool_name)
observation = tool_function(tool_input) if tool_function else f"错误:未找到名为 '{tool_name}' 的工具。"
print(f"👀 观察: {observation}")
self.history.append(f"Action: {action}")
self.history.append(f"Observation: {observation}")
print("已达到最大步数,流程终止。")
return None
def _parse_output(self, text: str):
thought_match = re.search(r"Thought: (.*)", text)
action_match = re.search(r"Action: (.*)", text)
thought = thought_match.group(1).strip() if thought_match else None
action = action_match.group(1).strip() if action_match else None
return thought, action
def _parse_action(self, action_text: str):
match = re.match(r"(\w+)\[(.*)\]", action_text)
return (match.group(1), match.group(2)) if match else (None, None)
def _parse_action_input(self, action_text: str):
match = re.match(r"\w+\[(.*)\]", action_text)
return match.group(1) if match else ""
if __name__ == '__main__':
llm = AgentsLLM()
tool_executor = ToolExecutor()
search_desc = "一个网页搜索引擎。当你需要回答关于时事、事实以及在你的知识库中找不到的信息时,应使用此工具。"
tool_executor.registerTool("Search", search_desc, search)
agent = ReActAgent(llm_client=llm, tool_executor=tool_executor, max_steps=10)
question = "华为最新的手机是哪一款?它的主要卖点是什么?"
agent.run(question)四、工具执行实现
python
class ToolExecutor:
"""
一个工具执行器,负责管理和执行工具。
"""
def __init__(self):
self.tools: Dict[str, Dict[str, Any]] = {}
def registerTool(self, name: str, description: str, func: callable):
"""
向工具箱中注册一个新工具。
"""
if name in self.tools:
print(f"警告:工具 '{name}' 已存在,将被覆盖。")
self.tools[name] = {"description": description, "func": func}
print(f"工具 '{name}' 已注册。")
def getTool(self, name: str) -> callable:
"""
根据名称获取一个工具的执行函数。
"""
return self.tools.get(name, {}).get("func")
def getAvailableTools(self) -> str:
"""
获取所有可用工具的格式化描述字符串。
"""
return "\n".join([
f"- {name}: {info['description']}"
for name, info in self.tools.items()
])运行效果图