卷积操作是一种线性滤波技术,通过在图像上滑动一个卷积核(滤波器)来提取图像特征。每个输出像素是卷积核与对应图像区域像素的加权和。
卷积操作步骤:
-
滑动卷积核:在图像上逐像素移动卷积核
-
对应相乘:卷积核权重与图像对应像素值相乘
-
求和:将所有乘积相加得到输出像素值
-
边缘处理:通常需要对图像边缘进行填充(如补0)
-
见卷积核类型:
-
边缘检测:Sobel, Laplacian, Prewitt
-
模糊/平滑:平均模糊,高斯模糊
-
锐化:增强边缘对比度
-
浮雕:创建3D效果
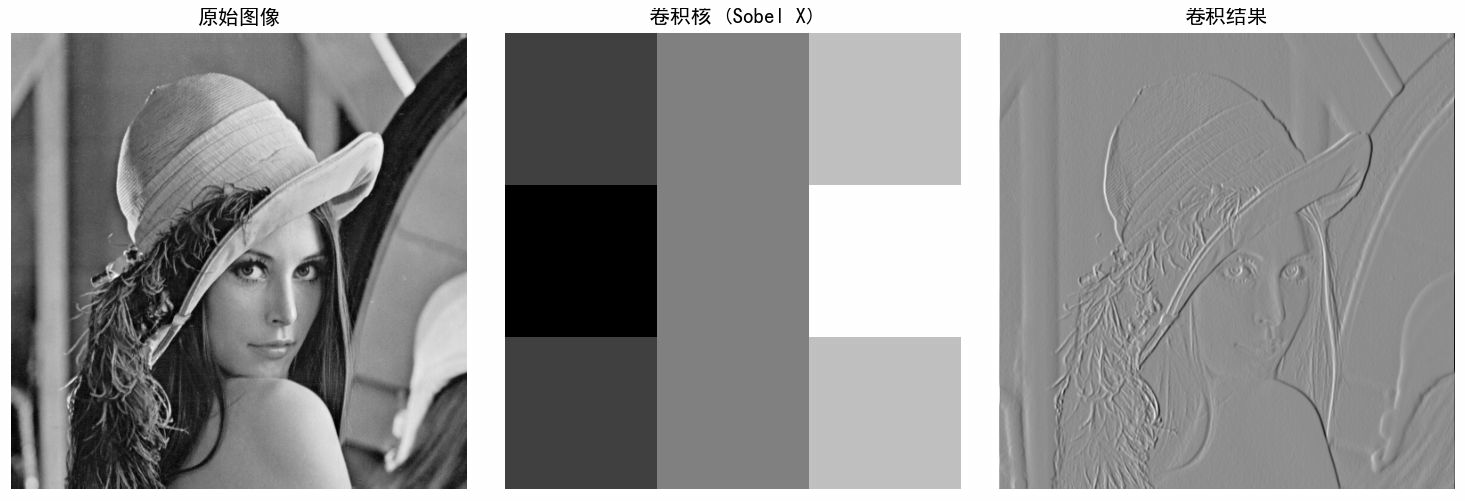
python# ==================== # 1. 基础卷积实现 # ==================== def conv2d(image, kernel, padding=0, stride=1): """ 2D卷积实现 :param image: 输入图像(2D数组) :param kernel: 卷积核(2D数组) :param padding: 边缘填充大小 :param stride: 步长 :return: 卷积结果 """ # 添加padding if padding > 0: image = np.pad(image, padding, mode='constant') # 获取尺寸 img_h, img_w = image.shape kernel_h, kernel_w = kernel.shape # 计算输出尺寸 output_h = (img_h - kernel_h) // stride + 1 output_w = (img_w - kernel_w) // stride + 1 # 初始化输出 output = np.zeros((output_h, output_w)) # 卷积计算 for y in range(0, output_h): for x in range(0, output_w): # 计算当前区域 y_start = y * stride y_end = y_start + kernel_h x_start = x * stride x_end = x_start + kernel_w # 提取图像区域 region = image[y_start:y_end, x_start:x_end] # 卷积计算 output[y, x] = np.sum(region * kernel) return output # ==================== # 2. 常见卷积核示例 # ==================== # 定义常用卷积核 kernels = { # 边缘检测 'sobel_x': np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-2, 0, 2], [-1, 0, 1]]), 'sobel_y': np.array([[-1, -2, -1], [0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 1]]), 'laplacian': np.array([[0, 1, 0], [1, -4, 1], [0, 1, 0]]), # 模糊/平滑 'box_blur': np.ones((3, 3)) / 9, 'gaussian_blur': np.array([[1, 2, 1], [2, 4, 2], [1, 2, 1]]) / 16, # 锐化 'sharpen': np.array([[0, -1, 0], [-1, 5, -1], [0, -1, 0]]) } # ==================== # 6. 多通道图像卷积 # ==================== def conv2d_multi_channel(image, kernel): """ 多通道图像卷积(简化版) image: (H, W, C) 或 (C, H, W) kernel: (C_out, C_in, H, W) 或单个2D卷积核应用于所有通道 """ if len(image.shape) == 2: return conv2d(image, kernel) if len(image.shape) == 3: # 假设是 (H, W, C) h, w, c = image.shape output = np.zeros((h - 2, w - 2, c)) for channel in range(c): output[:, :, channel] = conv2d(image[:, :, channel], kernel) return output def visualize_convolution(): """ 可视化卷积过程 """ try: # 创建示例图像 # 读取图像 image = cv2.imread('D:\\photo\\lena.tif',0) # rgb_image = cv2.imread('D:\\photo\\lena.tif') # print(image) # image = np.zeros((10, 10)) # image[2:8, 2:8] = 1 # 白色方块 # 创建卷积核 # kernel = np.array([[1, 0, -1], # [2, 0, -2], # [1, 0, -1]]) kernel = kernels['sharpen'] # 对每个通道应用相同卷积核 # result = conv2d_multi_channel(rgb_image, kernels['gaussian_blur']) print(kernel) # 卷积计算 result = conv2d(image, kernel, padding=1) # print(result) # 可视化 fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(12, 4)) axes[0].imshow(image, cmap='gray') axes[0].set_title('原始图像') axes[0].axis('off') axes[1].imshow(kernel, cmap='gray', interpolation='nearest') axes[1].set_title('卷积核 (Sobel X)') axes[1].axis('off') axes[2].imshow(result, cmap='gray') axes[2].set_title('卷积结果') axes[2].axis('off') plt.tight_layout() plt.show() except Exception as e: print(f"可视化需要matplotlib库: {e}") if __name__ == "__main__": # 可以选择运行可视化 visualize_convolution()运行其中一个边缘滤波器结果如下: