文章目录
一、核心工具函数解析
首先,我们来看系统依赖的工具函数,这些函数为整个识别过程提供了基础支持:
python
import cv2
def sort_contours(cnts, method='left-to-right'):
"""
对轮廓进行排序
参数:
cnts: 轮廓列表
method: 排序方法,支持以下四种:
'left-to-right' - 从左到右(默认)
'right-to-left' - 从右到左
'top-to-bottom' - 从上到下
'bottom-to-top' - 从下到上
返回值:
cnts: 排序后的轮廓列表
boundingBoxes: 对应的边界框列表
"""
reverse = False
i = 0
# 根据排序方法设置参数
if method == 'right-to-left' or method == 'bottom-to-top':
reverse = True
if method == 'top-to-bottom' or method == 'bottom-to-top':
i = 1
# 计算每个轮廓的边界框
boundingBoxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in cnts]
# 根据边界框的x或y坐标进行排序
(cnts, boundingBoxes) = zip(*sorted(zip(cnts, boundingBoxes),
key=lambda b: b[1][i], reverse=reverse))
return cnts, boundingBoxes
def resize(image, width=None, height=None, inter=cv2.INTER_AREA):
"""
按比例调整图像大小
参数:
image: 输入图像
width: 目标宽度(可选)
height: 目标高度(可选)
inter: 插值方法,默认为cv2.INTER_AREA
返回值:
resized: 调整后的图像
"""
dim = None
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
# 如果未指定尺寸,直接返回原图
if width is None and height is None:
return image
# 根据指定的宽度或高度计算缩放比例
if width is None:
r = height / float(h)
dim = (int(w * r), height)
else:
r = width / float(w)
dim = (width, int(h * r))
# 执行缩放操作
resized = cv2.resize(image, dim, interpolation=inter)
return resized
def cv_show(name, img):
"""
显示图像窗口
参数:
name: 窗口名称
img: 要显示的图像
"""
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 枚举函数示例
for i, j in enumerate([5, 6, 7]):
print(i, j)
# 列表推导式示例
a = [i for i in range(5)]
print(a)
# 字符串连接示例
a = ''.join(['4', '0', '0', '0'])
print(a)关键函数解析:
-
sort_contours() :此函数的核心功能是依据轮廓的空间位置进行排序。在身份证号码识别中,我们需要确保数字按照正确的阅读顺序(从左到右)被处理。函数通过
cv2.boundingRect()获取每个轮廓的边界框,然后根据指定的排序方法对边界框的x或y坐标进行排序。 -
resize() :这是一个灵活的缩放函数,可以根据宽度或高度按比例调整图像大小,保持原始宽高比不变。
cv2.INTER_AREA插值方法特别适合缩小图像,能够减少锯齿效应。 -
cv_show() :简化了图像显示流程,调用
cv2.waitKey(0)使得窗口保持打开直到用户按键。
二、数字模板提取模块
模板匹配的前提是准备好标准的数字模板。以下是模板提取的完整实现:
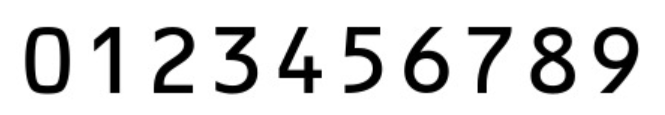
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
from myutils import sort_contours, cv_show
def process_template():
"""处理模板图像,提取数字模板"""
# 读取模板图像文件
img = cv2.imread("ID_Card_tem.png")
cv_show('Template Original', img)
# 将图像转换为灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 对灰度图进行二值化处理
ref = cv2.threshold(gray, 150, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)[1]
cv_show('Template Binary', ref)
# 查找二值图像中的所有轮廓
_, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(ref.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 绘制所有轮廓
img_copy = img.copy()
cv2.drawContours(img_copy, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv_show('Template Contours', img_copy)
# 对轮廓进行从左到右排序
refCnts = sort_contours(contours, method='left-to-right')[0]
# 创建字典存储数字模板
digits = {}
for i, c in enumerate(refCnts):
# 获取轮廓的边界矩形
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
# 裁剪数字区域并扩展边界
roi = ref[y - 2:y + h + 2, x - 2:x + w + 2]
# 调整到标准大小
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (57, 88))
# 黑白反转(使数字为白色,背景为黑色)
roi = cv2.bitwise_not(roi)
# 存储到字典
digits[i] = roi
print(f"Extracted {len(digits)} digit templates")
return digits模板提取关键步骤:
-
图像预处理 :首先将彩色模板转换为灰度图像,然后使用固定阈值(150)进行二值化。
THRESH_BINARY_INV参数表示反色二值化,使数字区域变为白色,背景变为黑色。 -
轮廓检测 :
cv2.findContours()函数检测所有外部轮廓。RETR_EXTERNAL只检测最外层轮廓,CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE使用简单的轮廓近似,减少点的数量。 -
轮廓排序 :使用自定义的
sort_contours()函数确保数字按正确顺序排列。这对于建立索引(0对应数字0,1对应数字1等)至关重要。 -
模板标准化:将每个数字裁剪出来,统一缩放到57×88像素,并进行黑白反转,为后续的模板匹配做准备。
三、身份证号码识别模块
有了数字模板后,就可以识别实际身份证图像中的号码:

python
def recognize_id_card(digits):
"""识别身份证图像中的号码"""
# 读取身份证图像
img = cv2.imread("ID_Card.jpg")
original_img = img.copy()
cv_show('ID Card Original', img)
# 灰度化处理
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv_show('ID Card Gray', gray)
# 二值化处理
binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 120, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)[1]
cv_show('ID Card Binary', binary)
# 查找所有轮廓
_, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 绘制所有轮廓
img_with_contours = img.copy()
cv2.drawContours(img_with_contours, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv_show('All Contours', img_with_contours)
# 筛选身份证号码区域
locs = []
for i, c in enumerate(contours):
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
# 根据位置筛选(需要根据实际图像调整参数)
if (y > 330 and y < 360) and x > 220:
locs.append((x, y, w, h))
# 按x坐标排序
locs = sorted(locs, key=lambda x: x[0])
# 如果没有找到数字区域,输出调试信息
if len(locs) == 0:
print("Error: No ID number region found")
for i, c in enumerate(contours):
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
print(f"Contour{i}: x={x}, y={y}, w={w}, h={h}")
return
print(f"Found {len(locs)} digit regions")
# 识别每个数字区域
output = []
for i, (gX, gY, gW, gH) in enumerate(locs):
# 裁剪数字区域
group = gray[gY - 2:gY + gH + 2, gX - 2:gX + gW + 2]
# 使用OTSU方法进行自适应二值化
group = cv2.threshold(group, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# 调整到模板大小
roi = cv2.resize(group, (57, 88))
# 模板匹配
scores = []
for digit, digitROI in digits.items():
result = cv2.matchTemplate(roi, digitROI, cv2.TM_CCOEFF)
_, score, _, _ = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
scores.append(score)
# 选择最佳匹配
digit_index = np.argmax(scores)
groupOutput = str(digit_index)
output.append(groupOutput)
# 在图像上绘制结果
cv2.rectangle(original_img, (gX - 5, gY - 5),
(gX + gW + 5, gY + gH + 5), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(original_img, groupOutput, (gX, gY - 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.8, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 组合识别结果
id_number = "".join(output)
print(f"识别到的身份证号码: {id_number}")
# 显示最终结果
cv2.putText(original_img, "".join(groupOutput), (gX, gY - 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.65, (0, 0, 255), 2)
output.extend(groupOutput)
cv_show('Recognition Result', original_img)
return id_number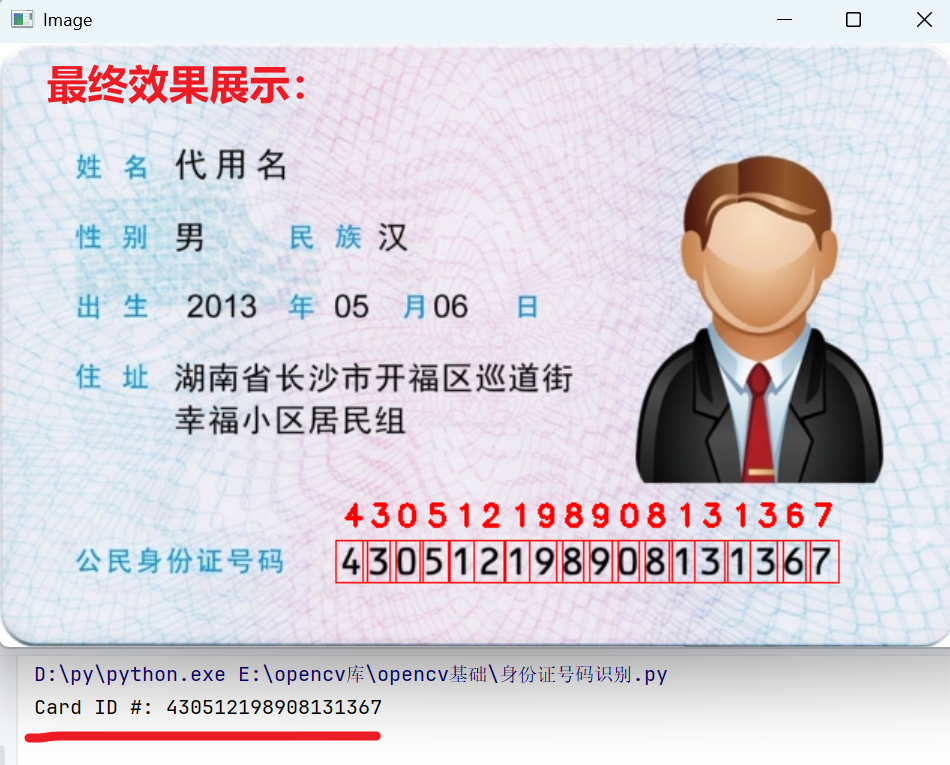
识别过程核心环节:
-
预处理与轮廓检测:与模板处理类似,但对身份证图像使用较低的阈值(120)进行二值化,以适应实际图像中可能存在的亮度变化。
-
区域筛选 :这是识别成功的关键。代码通过位置条件
(y > 330 and y < 360) and x > 220筛选出身份证号码区域。实际应用中,这些参数需要根据具体图像进行调整。 -
自适应二值化 :对于裁剪出的每个数字区域,使用
THRESH_OTSU方法进行自适应阈值处理。OTSU算法能自动计算最佳阈值,特别适合光照不均的图像。 -
模板匹配 :使用
cv2.matchTemplate()函数将当前数字区域与所有模板进行比较。TM_CCOEFF(相关系数匹配)方法计算模板与图像区域的相关系数,值越大表示匹配度越高。 -
结果可视化:识别过程中,在原始图像上用红色矩形框标出每个数字区域,并在上方显示识别结果,提供直观的反馈。