目录
3.2.1:Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.h
3.2.2:Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.cpp
3.3.1:Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.h
1:非类型模板参数
- 模板参数分类类型形参与非类型形参。
- 类型形参即:出现在模板参数列表中,跟在class或者typename之类的参数类型名称。
- 非类型形参,就是用一个常量作为类(函数)模板的一个参数,在类(函数)模板中可将该参数当成常量来使用.
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace bit
{
// 定义一个模板类型的静态数组
template<class T, size_t N = 10>
class array
{
public:
T& operator[](size_t index)
{
return _array[index];
}
const T& operator[](size_t index)const
{
return _array[index];
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return 0 == _size;
}
private:
T _array[N];
size_t _size;
};
}
int main()
{
bit::array <int, 10> a1;
bit::array <int, 100> a2;
bit::array <int, 100> a3;
}

1.1:按需实例化
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
void Swap(T& e1, T& e2)
{
T temp = e1;
e1 = e2;
e2 = temp;
}
namespace bit
{
// 定义一个模板类型的静态数组
template<class T, size_t N = 10>
class array
{
public:
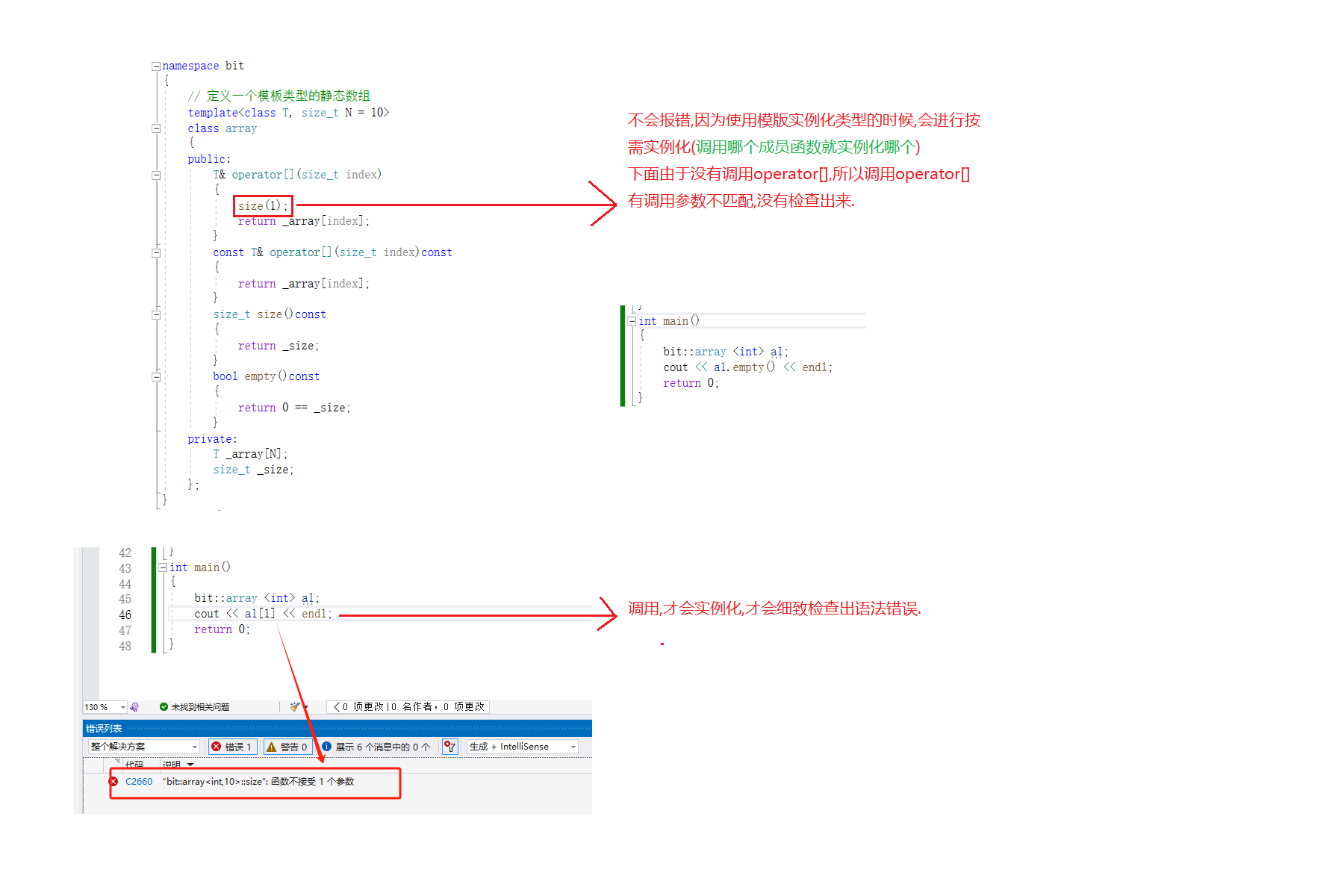
T& operator[](size_t index)
{
size(1);
return _array[index];
}
const T& operator[](size_t index)const
{
return _array[index];
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return 0 == _size;
}
private:
T _array[N];
size_t _size;
};
}
int main()
{
bit::array <int> a1;
cout << a1.empty() << endl;
cout << a1[1] << endl;
return 0;
}
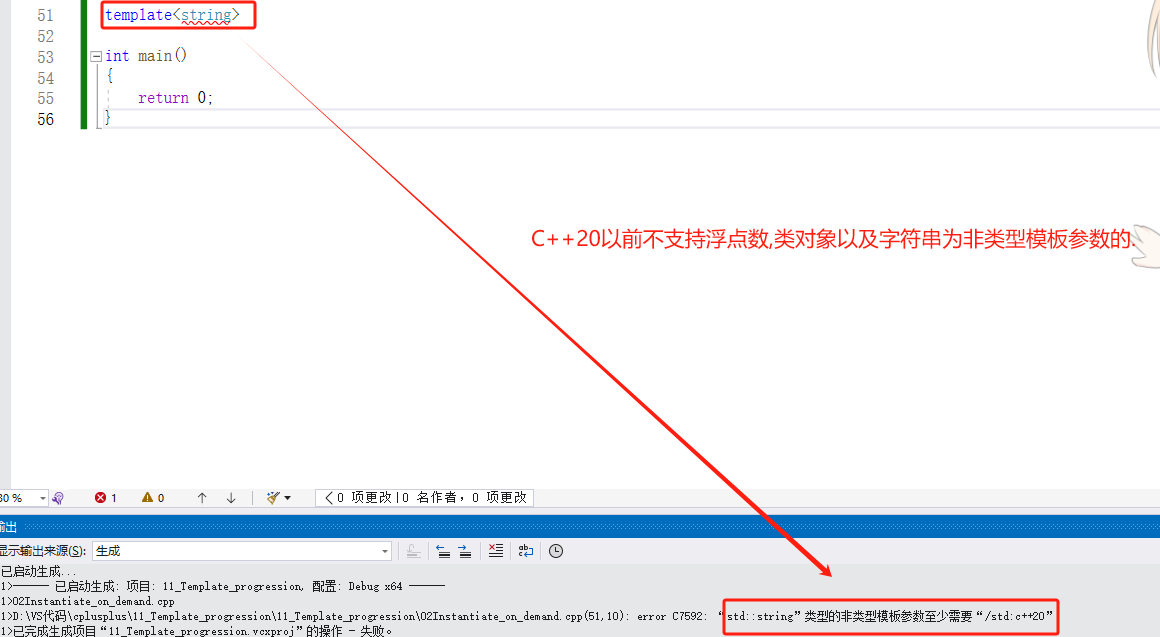
- 浮点数,类对象以及字符串时不能够作为非类型模板参数的.
- 非类型的模版参数在编译期间就能确认结果.
1.2:array
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <array>;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
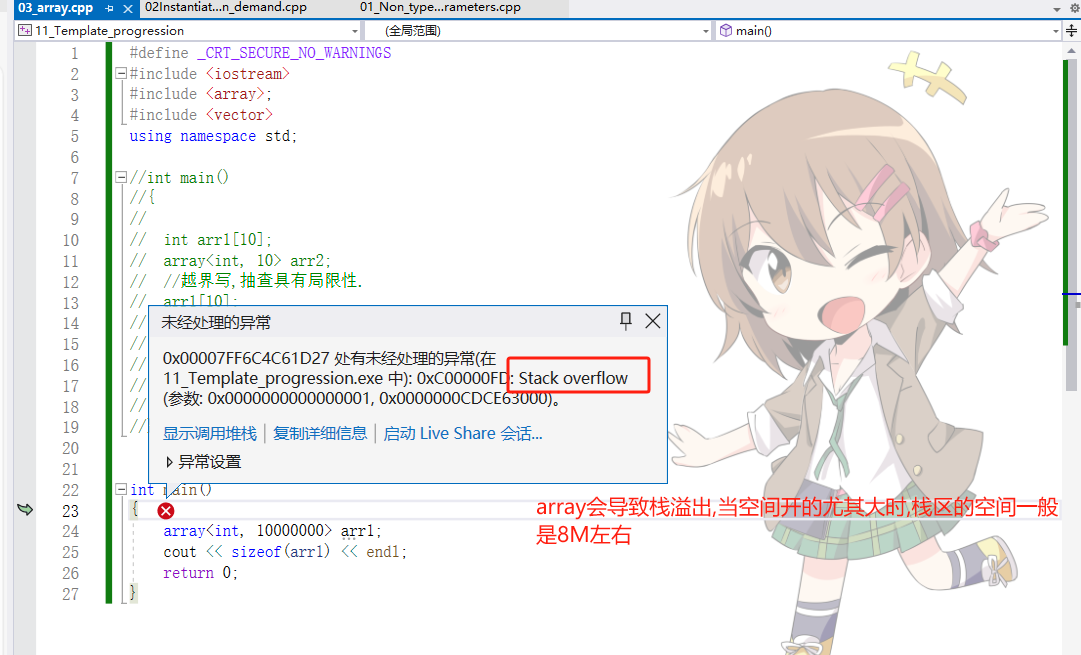
int arr1[10];
array<int, 10> arr2;
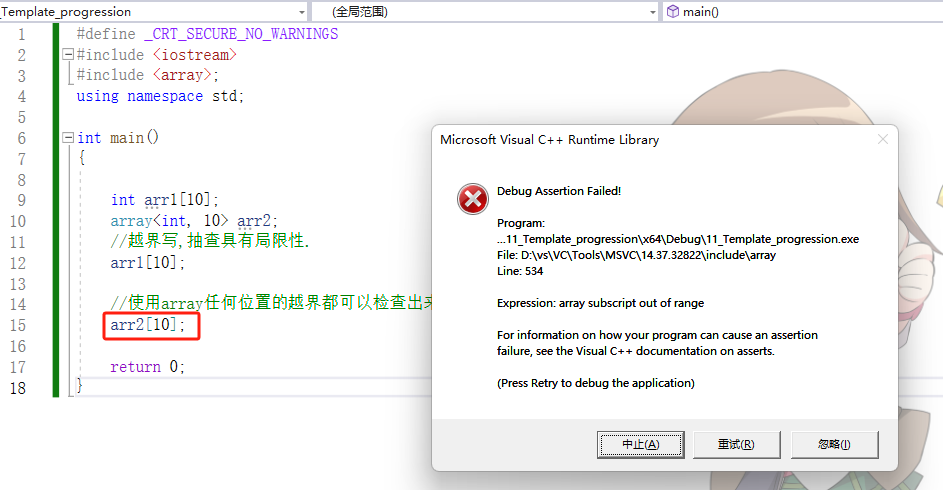
//越界写,抽查具有局限性.
arr1[10];
//使用array任何位置的越界都可以检查出来.
arr2[10];
return 0;
}
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <array>;
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
array<int, 10000000> arr1;
cout << sizeof(arr1) << endl;
return 0;
}2:模板特化
2.1:概念
通常情况下,使用模板可以实现一些与类型无关的代码,但对于一些特殊类型的可能会得到一些错误的结果,需要特殊处理,比如:实现了一个专门用来进行小于比较的函数模板.
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
template<class T>
bool Less(const T& element1, const T& element2)
{
return element1 < element2;
}
int main()
{
//均可以比较
/*cout << Less(10, 20) << endl;
cout << Less(10.5, 20.5) << endl;
cout << Less(Date(2022, 6, 7), Date(2022, 6, 8)) << endl;*/
Date d1(2022, 6, 5);
Date d2(2022, 6, 6);
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl;
return 0;
}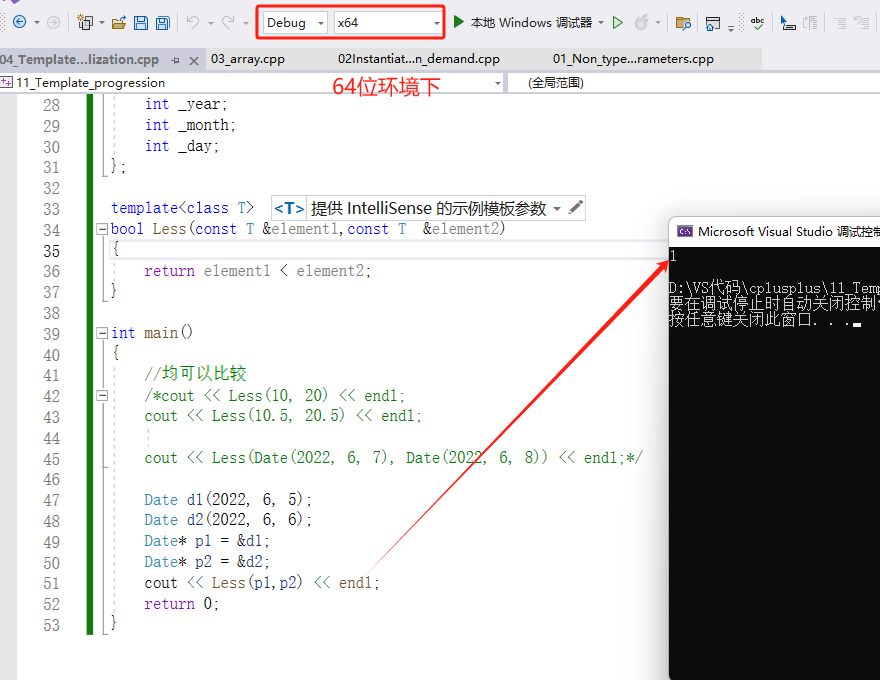
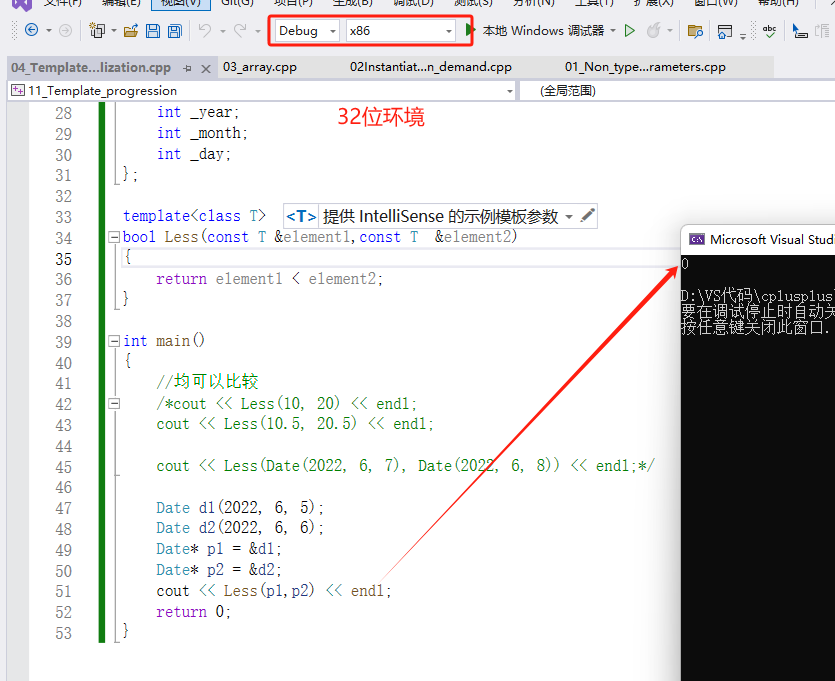
上述示例中,p1指向的d1显然小于p2指向的d2对象,但是Less内部并没有比较p1和p2指向的对象内容,而比较的是p1和p2指 针的地址,这就无法达到预期而错误。
此时,就需要对模板进行特化****。即: 在原模板类的基础上,针对特殊类型所进行特殊化的实现方式。模板特化中分为函数模板特化与类模板特化.
2.2:函数模板特化
- 必须要有一个基础的函数模板.
- 关键字template后面接一对空的尖括号.
- 函数名后跟一对尖括号,尖括号中指定需要特化的类型.
- 函数形参表:必须要和模板函数的基础参数类型完全相同, 如果不同,编译器可能会发生报错.
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
//基础模板
template<class T>
bool Less(T left,T right)
{
return left < right;
}
//函数模板特化
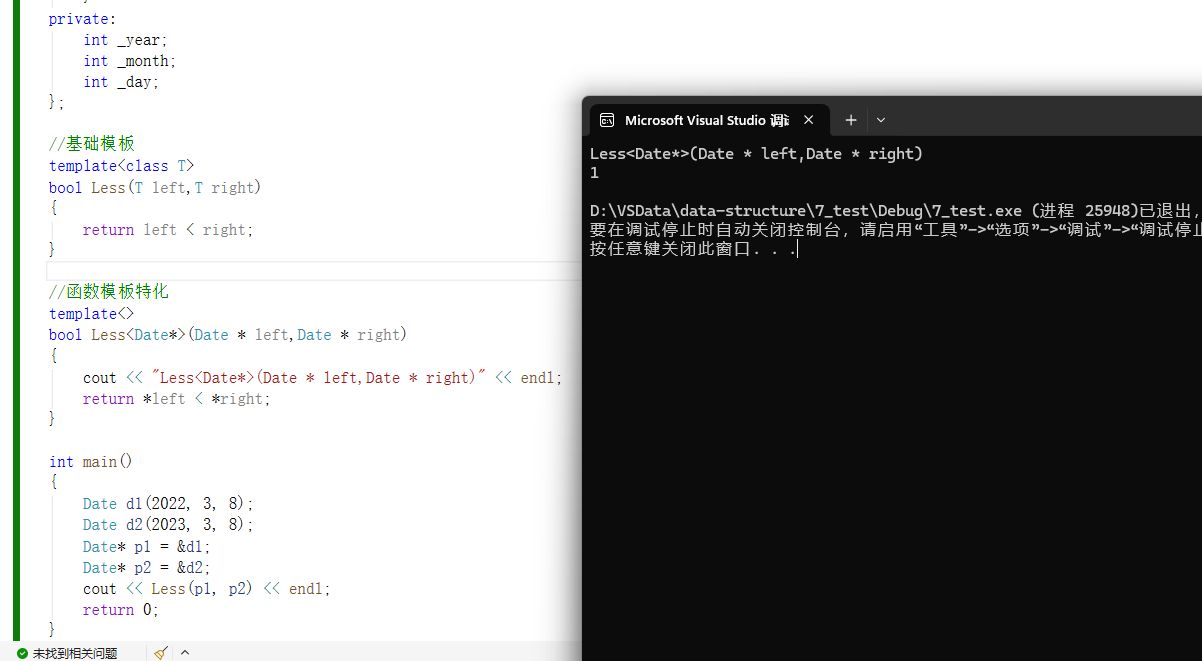
template<>
bool Less<Date*>(Date * left,Date * right)
{
cout << "Less<Date*>(Date * left,Date * right)" << endl;
return *left > *right;
}
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 3, 8);
Date d2(2023, 3, 8);
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl;
return 0;
}
PS:一般情况下如果函数模板遇到不能处理或者处理有误的类型,为了实现简单通常都是将该函数直接给出.
该种实现简单明了,代码的可读性高,容易书写,因为对于一些参数类型复杂的函数模板,特化时特别给出,因此函数模板不建议特化。
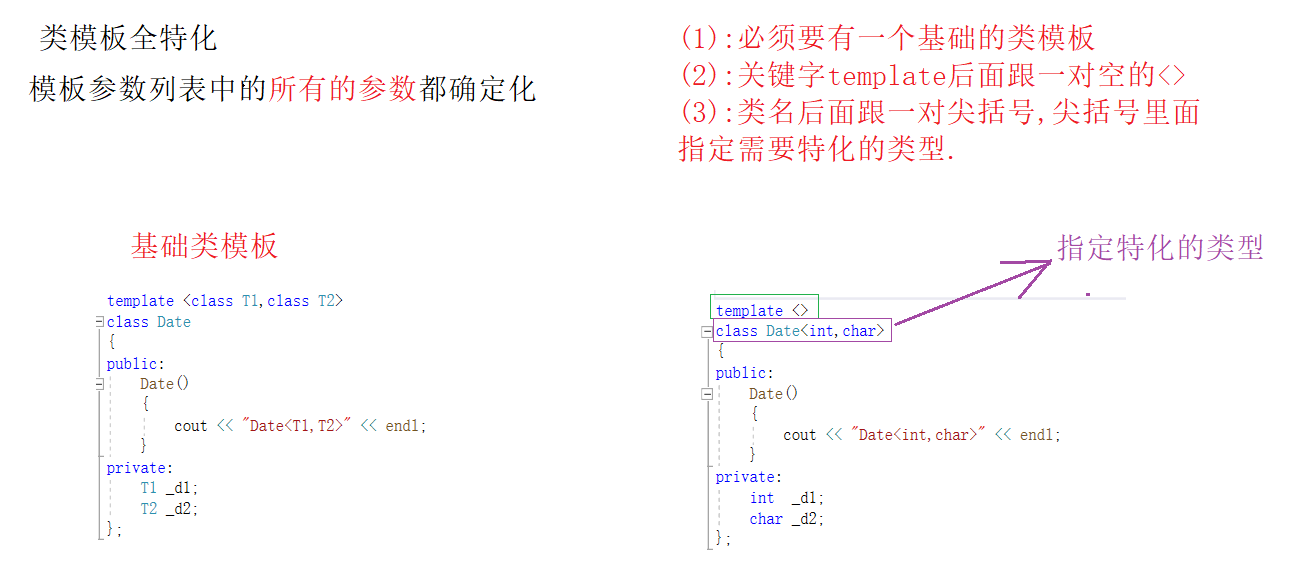
2.3:类模板特化
2.3.1:全特化
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T1, class T2>
class Date
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<T1,T2>" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
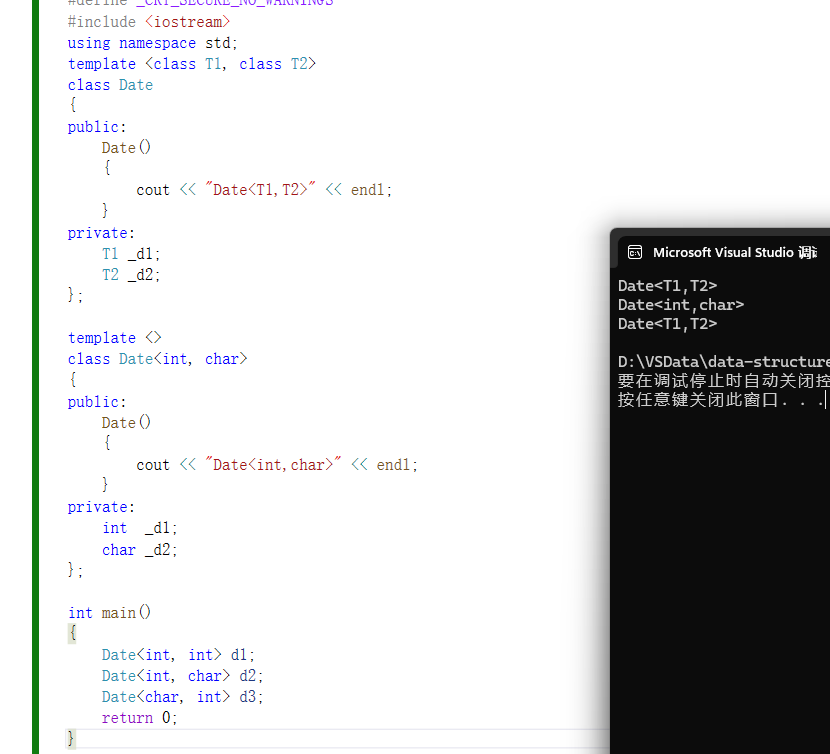
template <>
class Date<int, char>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<int,char>" << endl;
}
private:
int _d1;
char _d2;
};
int main()
{
Date<int, int> d1;
Date<int, char> d2;
Date<char, int> d3;
return 0;
}
2.3.2:部分特化
2.3.2.1:部分特化之参数特化
cpp
template <class T1,class T2>
class Date
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "template <class T1,class T2>" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
template <class T1>
class Date<T1,int>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "class Date<T1,int>" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
int _d2;
};
int main()
{
Date<int,int> d1;
Date<char,int> d2;
cout << endl;
Date<int, double>d3;
}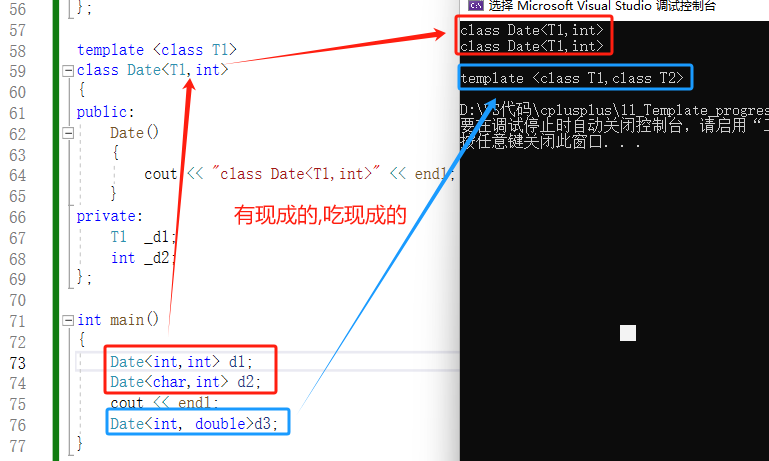
偏特化有以下两种表现形式
- 部分特化
将模板参数类表中的一部分参数特化
- 参数更进一步的限制
偏特化并不仅仅是指特化部分参数,而是针对模板参数更进一步的条件限制所设计出来的一个特化版本。
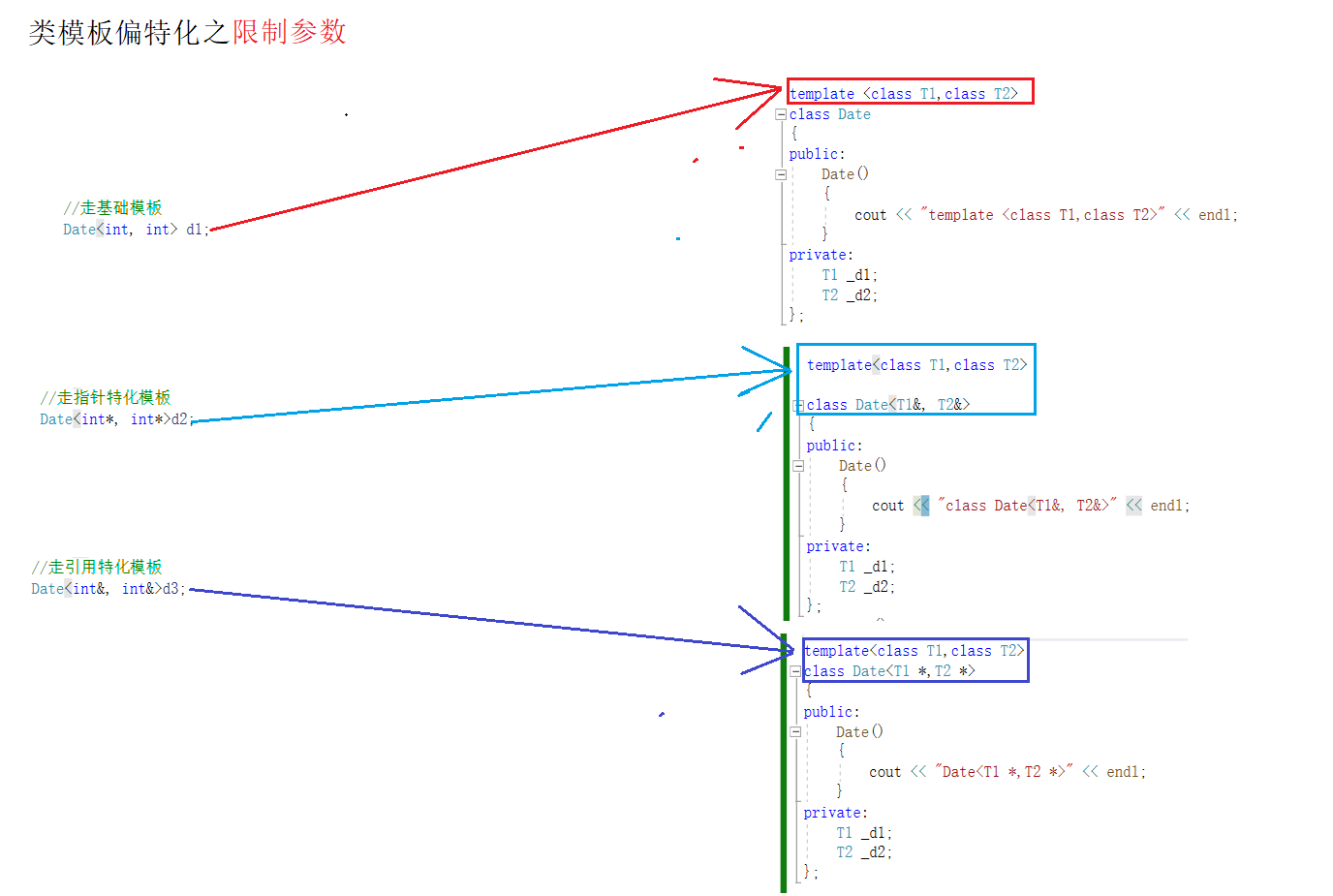
2.3.2.2:部分特化之限制参数
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T1, class T2>
class Date
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "template <class T1,class T2>" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
template<class T1, class T2>
class Date<T1*, T2*>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<T1 *,T2 *>" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
template<class T1, class T2>
class Date<T1&, T2&>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "class Date<T1&, T2&>" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
int main()
{
//走基础模板
Date<int, int> d1;
//走指针特化模板
Date<int*, int*>d2;
cout << endl;
//走引用特化模板
Date<int&, int&>d3;
return 0;
}
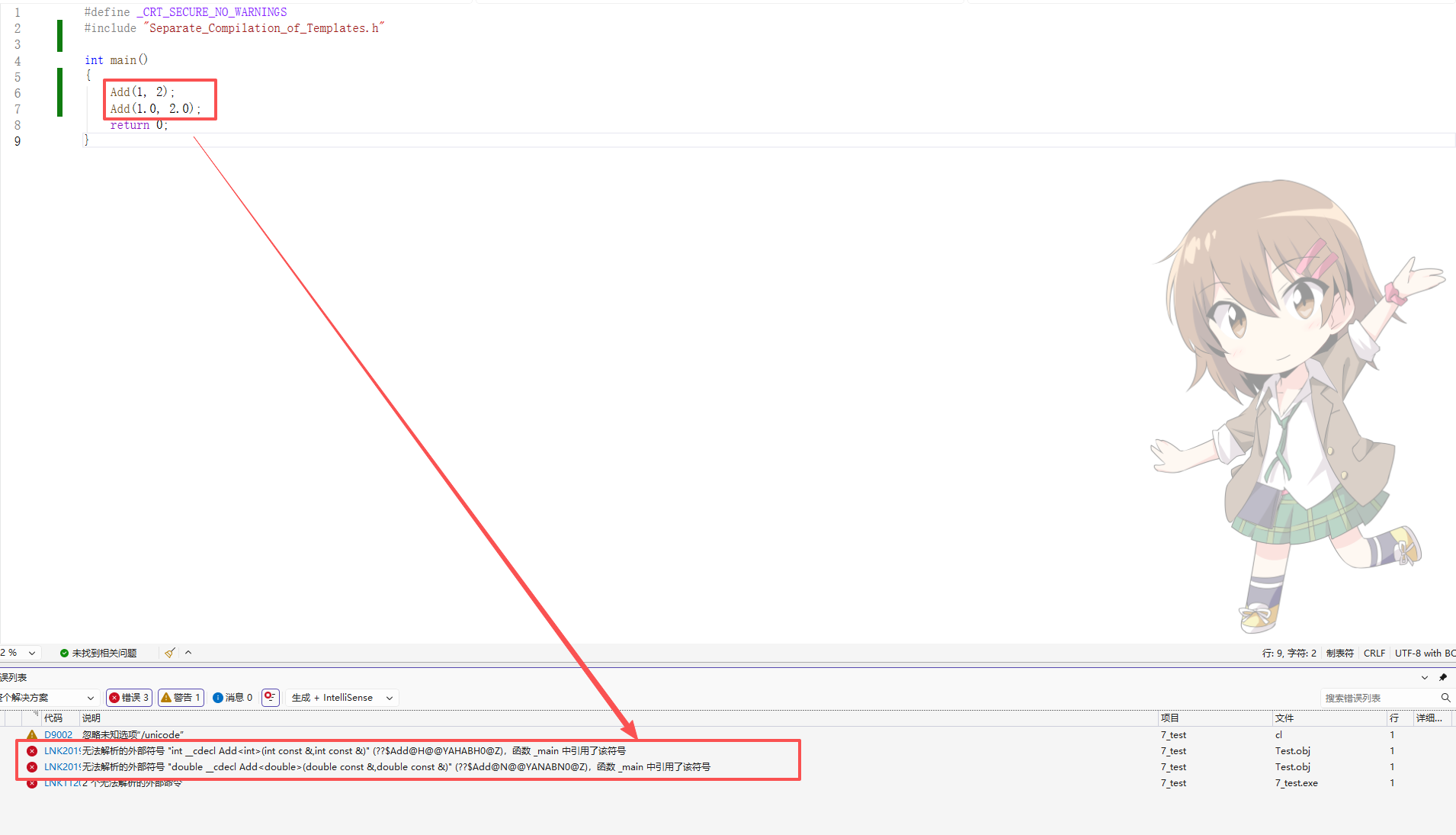
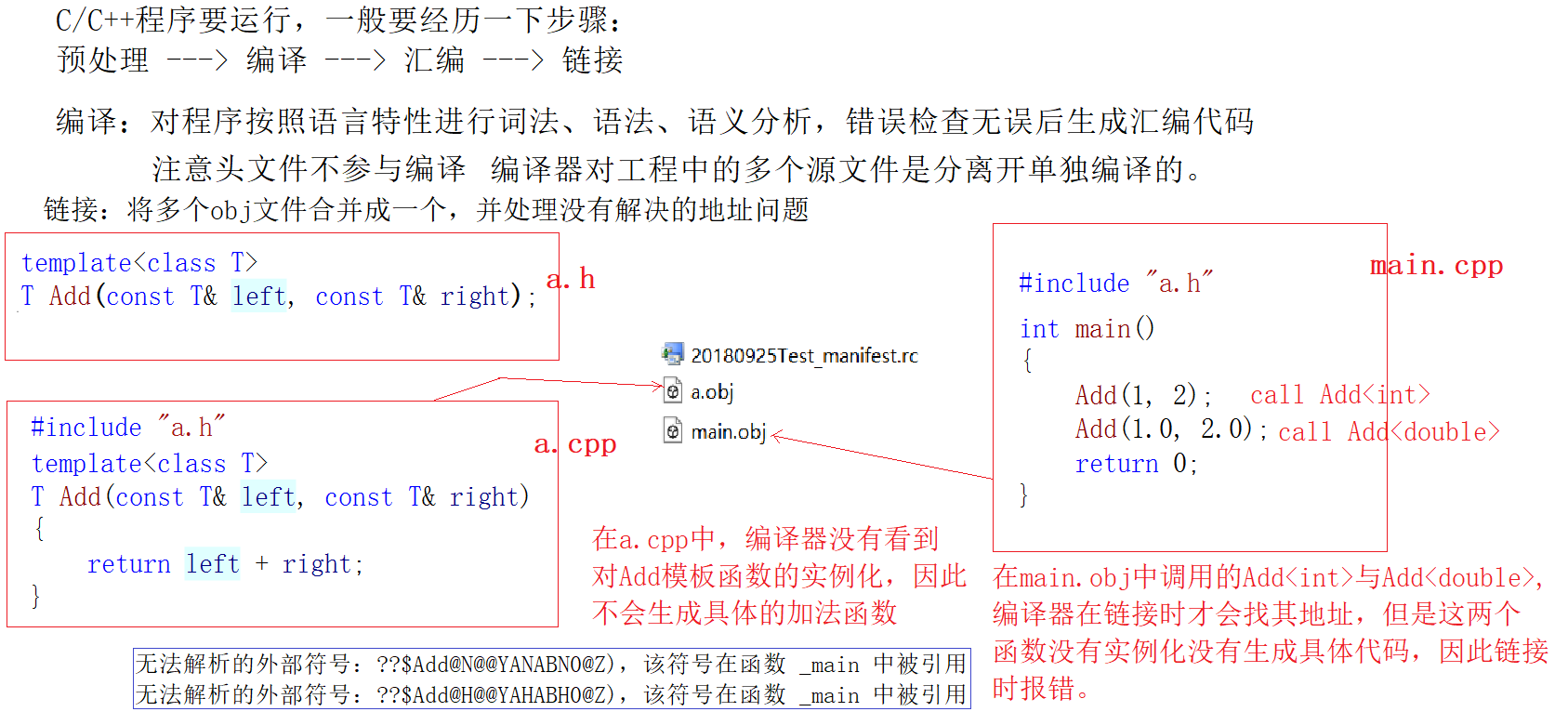
3:模板的分离编译
3.1:什么是分离编译
一个程序(项目)由若干个源文件共同实现,而每个源文件单独编译生成目标文件,最后将所有目标文件链接起来形成单一的可执行文件的过程称为分离编译模式。
3.2:模板的分离编译
假如有以下场景,模板的声明与定义分离开,在头文件中进行声明,源文件中完成定义.
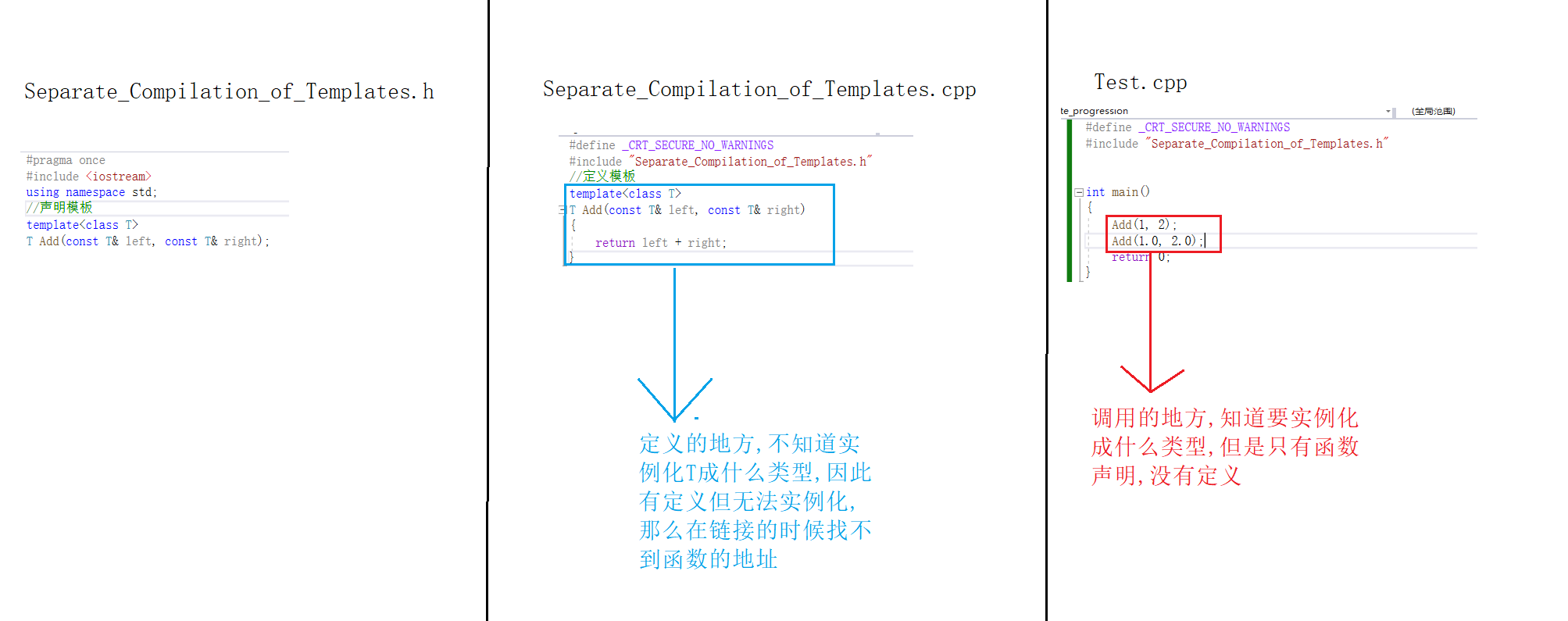
3.2.1:Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right);3.2.2:Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.cpp
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.h"
template <class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right)
{
return left + right;
}3.2.3:Test.cpp
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.h"
int main()
{
Add(1, 2);
Add(1.0, 2.0);
return 0;
}
3.3:解决办法
- 将声明和定义放到一个文件**"xxx.hpp"里面或者xxx.h****其实也是可以的**。推荐使用这种。
- 模板定义的位置显式实例化。这种方法不实用,不推荐使用。
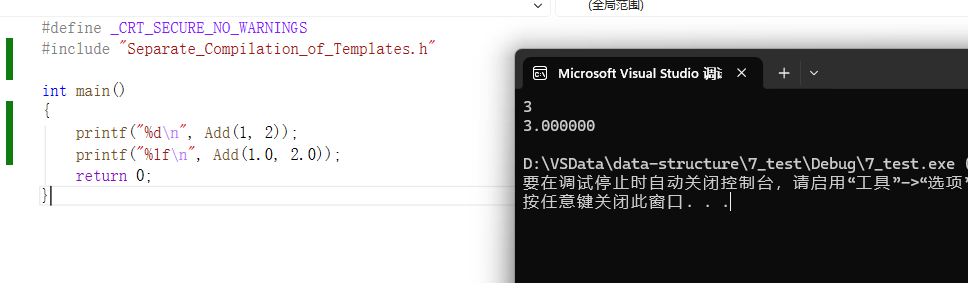
3.3.1:Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stdio.h>
template <class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right)
{
return left + right;
}3.3.2:Test.cpp
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Separate_Compilation_of_Templates.h"
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", Add(1, 2));
printf("%lf\n", Add(1.0, 2.0));
return 0;
}
4:模板总结
优点
- 模板复用了代码,节省资源,更快的迭代开发,C++的标准模板库(STL)因此而产生.
- 增强了代码的灵活性.
缺陷
- 模板会导致代码膨胀问题,也会导致编译时间变长.
- 出现模板编译错误时,错误信息会十分凌乱,不容易定位错误.
