一、曲率定义(PCA 法)
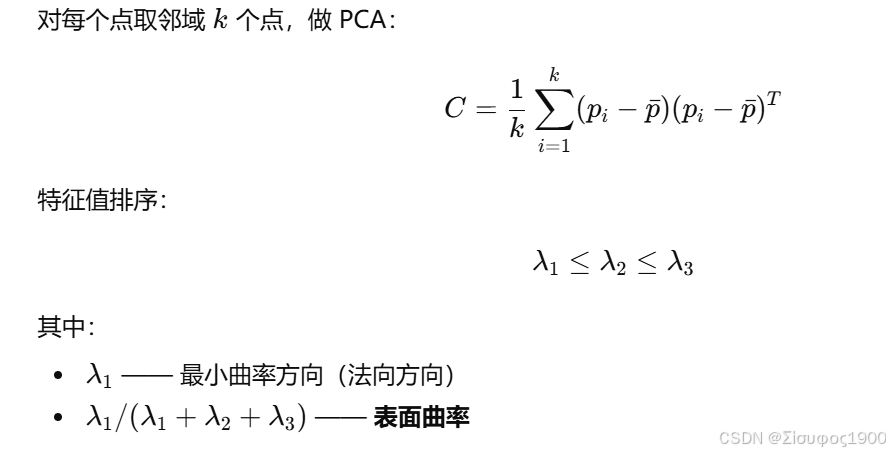
曲率的几何意义是单位弧长上曲线切线方向的变化率,它描述了曲线局部偏离直线的程度,并用密切圆的半径的倒数来量化。
二、MATLAB 完整代码
cpp
%% ----------------------------------------------------
% 点云 PCA 曲率计算 + 彩色可视化(可直接运行)
% ----------------------------------------------------
clear; clc; close all;
%% 1. 读取点云文件
filename = 'bun000.ply'; % 改成你的 dragon_vrip_res3.ply 也可以
ptCloud = pcread(filename);
pts = ptCloud.Location;
N = size(pts,1);
fprintf("Loaded %d points\n", N);
%% 2. 构建 KD 树
k = 50; % 真实点云建议 30~80
Mdl = KDTreeSearcher(pts);
%% 3. 准备输出
curvature = zeros(N,1);
%% 4. PCA 曲率计算
for i = 1:N
% 邻域
idx = knnsearch(Mdl, pts(i,:), 'K', k);
nbrs = pts(idx,:);
% 去均值
q = nbrs - mean(nbrs,1);
% 协方差
C = (q' * q) / k;
% 特征值
e = eig(C); % 升序
lambda = sort(e);
% 曲率公式
curvature(i) = lambda(1) / sum(lambda);
end
%% 5. 归一化用于 colormap
curvatureVis = curvature;
curvatureVis = curvatureVis / max(curvatureVis);
%% 6. 可视化 ------ 用曲率给点云上色
figure;
pcshow(pts, curvatureVis); % MATLAB 会自动使用 colormap
colormap(jet);
colorbar;
title('点云曲率可视化(PCA)');
axis equal;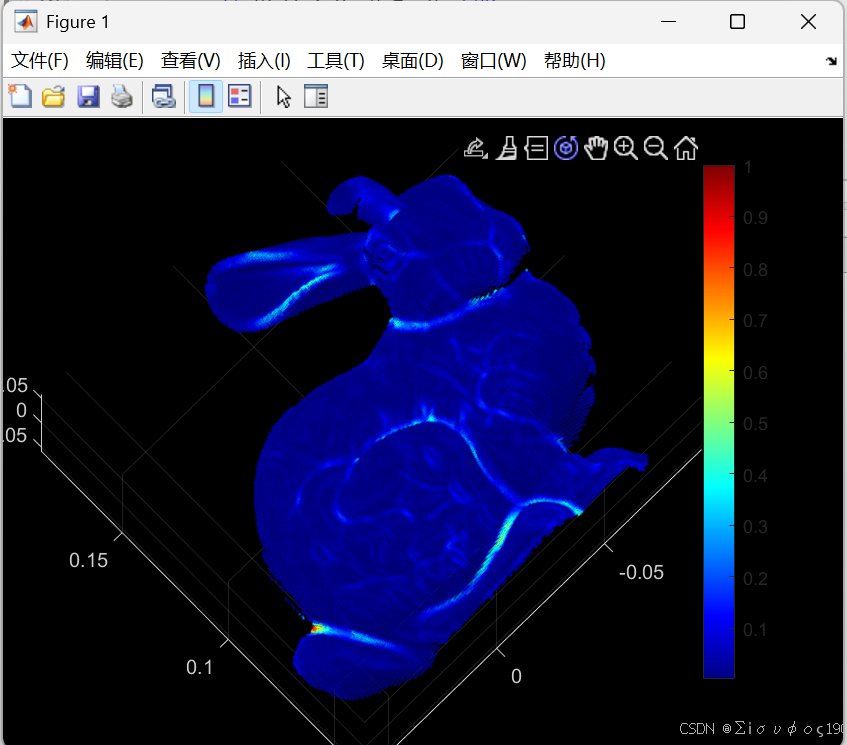
三、法向量的方向不唯一?
法向量方向不唯一,是因为法向在数学上是 ± 对称的,而 PCA/特征向量天生存在 ± 不确定性。因此实际工程中必须添加"方向一致性"步骤对法向进行统一。
原因
数学本质不唯一原因
法向量方向 不唯一 的原因来自数学本质、几何本质和物理意义

法向方程不区分方向,±n 都满足。
几何上法向是一条"穿过点的直线",不是带方向的射线
因此:
cpp
n=(a,b,c)
−n=(−a,−b,−c)它们都是合法法向。
这是"不唯一"的根本原因。
PCA 法向估计本身有 ± 反向不确定性
PCA 法向来自协方差矩阵特征分解:
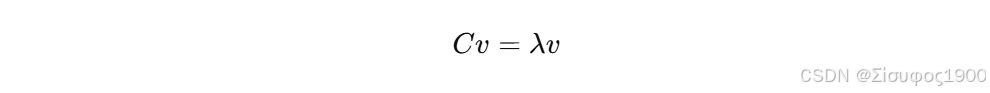
如果 v 是特征向量,那么:

也是特征向量,因为:
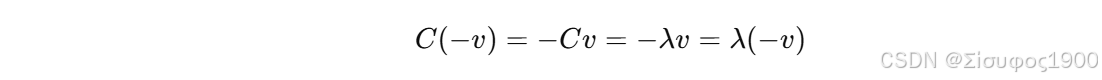
所以 特征分解无法告诉你:法向应该指向外,还是指向内。
换句话说:
PCA 得到的法向没有方向信息,只有方向"轴"信息
无邻域一致性:独立计算会造成方向随机翻转
如果你对每个点独立计算 PCA,得到法向:
-
点 A 得到方向 接近 (+0.2,+0.9,+0.3)
-
点 B 得到方向 接近 (−0.2,−0.9,−0.3)
这是完全正常的,因为二者都是同一个真正法向的 ± 两种可能 。
这就是为什么你看到:
-
法向箭头忽左忽右
-
点云显示很乱
-
法向图颜色跳变
工程解决方案:需要"法向一致性"步骤
方法 1:点云整体中心约束(常用)
若法向与点指向点云中心夹角 < 0:
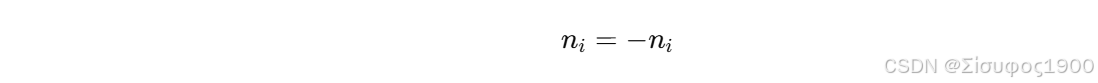
使法向朝外或朝内统一
方法 2:图(Graph)传播一致性(PCL 内部实现)
选一个参考点作为起点,用 BFS/DFS:
-
对邻域法向
-
如果 dot(n_i, n_ref) < 0
→ 反转
确保所有法向尽可能一致。

cpp
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 1. 读取点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (pcl::io::loadPLYFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("bun000.ply", *cloud) == -1)
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file\n");
return -1;
}
std::cout << "Loaded " << cloud->points.size() << " points." << std::endl;
// 2. 法向量估计
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;
ne.setInputCloud(cloud);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setKSearch(30);
ne.compute(*normals); // PCA 法向
// 3. 构建邻域图
std::vector<std::vector<int>> neighbor_indices(cloud->size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->size(); ++i)
{
std::vector<int> idx;
std::vector<float> dist;
tree->nearestKSearch(cloud->points[i], 10, idx, dist);
neighbor_indices[i] = idx;
}
// 4. 法向一致性传播(BFS)
std::vector<bool> visited(cloud->size(), false);
std::queue<int> q;
// 起点选择第0个点
q.push(0);
visited[0] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
int curr = q.front(); q.pop();
auto& n_curr = normals->points[curr];
// 遍历邻居
for (int nbr_idx : neighbor_indices[curr])
{
if (!visited[nbr_idx])
{
auto& n_nbr = normals->points[nbr_idx];
// dot < 0 → 翻转
float dot = n_curr.normal_x * n_nbr.normal_x +
n_curr.normal_y * n_nbr.normal_y +
n_curr.normal_z * n_nbr.normal_z;
if (dot < 0)
{
n_nbr.normal_x *= -1;
n_nbr.normal_y *= -1;
n_nbr.normal_z *= -1;
}
visited[nbr_idx] = true;
q.push(nbr_idx);
}
}
}
// 5. 保存法向一致化点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);
pcl::concatenateFields(*cloud, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);
pcl::io::savePLYFileBinary("bun000_normals_consistent.ply", *cloud_with_normals);
std::cout << "Saved consistent normals." << std::endl;
return 0;
}方法 3:基于模型先验方向固定
例如:
-
深度相机:法向 z 分量必须朝向相机
-
机械臂场景:法向 z 必须向上
| 步骤 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| PCA 法向估计 | NormalEstimation 计算 ± 法向 |
| 邻域图构建 | KNN 或 radius search,记录每个点邻域 |
| BFS / DFS | 从起点传播,保证每个点法向与已访问点一致 |
| dot < 0 翻转 | 保证法向方向一致 |
| 全局覆盖 | BFS / DFS 遍历所有点 |