一、多智能体系统工作流的核心理解
1.1 基本概念界定
多智能体工作流 是指由多个具有自主决策能力的AI智能体通过结构化协作,完成复杂任务的系统性过程。这不是简单的任务队列,而是动态、自适应、可恢复的协作网络。
1.2 与传统工作流的区别
| 维度 | 传统工作流 | 多智能体工作流 |
|---|---|---|
| 执行单元 | 固定程序/脚本 | 自主决策的智能体 |
| 协作方式 | 预定义接口调用 | 动态协商与协调 |
| 容错性 | 硬编码异常处理 | 自适应恢复策略 |
| 学习能力 | 无 | 持续优化协作模式 |
| 灵活性 | 低 | 高,可根据情境调整 |
二、多智能体工作流的典型模式
2.1 层级协调模式
XML
首席智能体 (Chief Agent)
├── 规划智能体 (Planning Agent)
├── 执行智能体组 (Execution Agents)
│ ├── 数据收集智能体
│ ├── 分析智能体
│ └── 验证智能体
└── 监控智能体 (Monitoring Agent)适用场景:复杂项目管理、产品研发流程
2.2 市场协商模式
XML
智能体A (需求发布) → 任务市场 →
├── 智能体B (竞标) → 执行 → 交付
├── 智能体C (竞标) → 执行 → 交付
└── 智能体D (竞标) → 执行 → 交付
仲裁智能体:评估交付质量,分配报酬适用场景:众包式任务处理、资源优化分配
2.3 管道流水线模式
XML
输入 → 智能体1(预处理) → 智能体2(分析) →
智能体3(决策) → 智能体4(执行) → 输出
缓冲队列:管理智能体间的数据流
监控器:检测管道性能瓶颈适用场景:数据处理流水线、内容生成流程
2.4 黑板协作模式
XML
共享工作区 (Blackboard)
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
智能体A 智能体B 智能体C 智能体D
(读取/写入) (读取/写入) (读取/写入) (读取/写入)
协调器:管理访问权限,解决冲突适用场景:协同设计、科研发现、诊断系统
2.5 分布式自治模式
XML
智能体A ↔ 智能体B ↔ 智能体C
↓ ↓ ↓
智能体D ↔ 智能体E ↔ 智能体F
每个智能体:自主决策,局部协调
共识机制:确保全局目标一致性适用场景:去中心化组织、分布式控制系统
三、多智能体工作流设计框架
3.1 设计流程
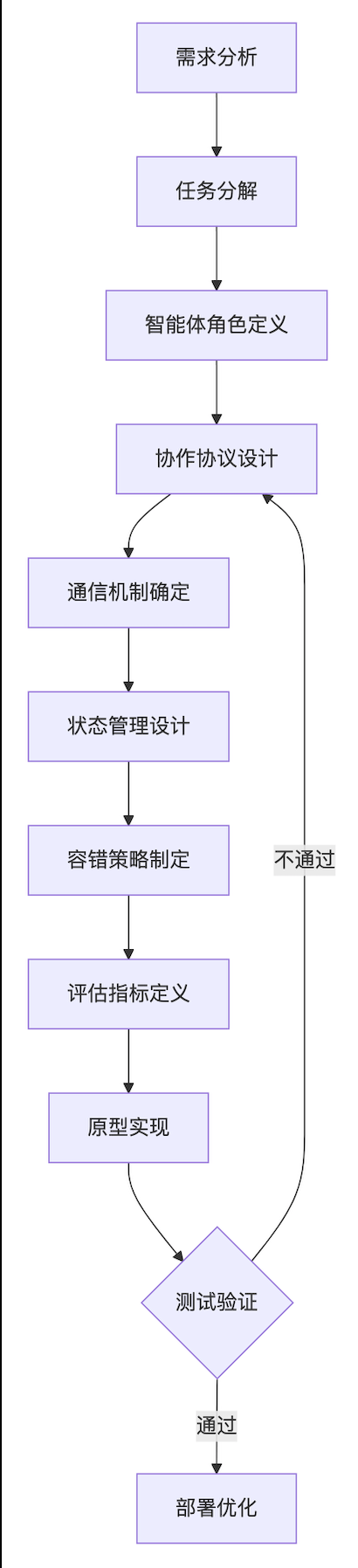
3.2 关键设计决策点
3.2.1 智能体粒度决策
python
# 决策矩阵:何时使用细粒度vs粗粒度智能体
def determine_agent_granularity(requirements):
factors = {
"任务复杂度": requirements.get("complexity"),
"协作频率": requirements.get("collaboration_frequency"),
"资源限制": requirements.get("resource_constraints"),
"性能需求": requirements.get("performance_needs")
}
if factors["任务复杂度"] == "高" and factors["协作频率"] == "高":
return "细粒度智能体" # 更灵活的协作
elif factors["资源限制"] == "严格" and factors["性能需求"] == "高":
return "粗粒度智能体" # 减少通信开销
else:
return "混合粒度" # 平衡方案3.2.2 通信协议选择
| 协议类型 | 适用场景 | 优势 | 挑战 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCP | 工具集成、跨平台协作 | 标准化、易于集成 | 新兴标准,工具链不成熟 |
| A2A | 智能体间直接协作 | 高效、灵活 | 缺乏标准化 |
| REST/HTTP | 企业系统集成 | 成熟、广泛支持 | 不适合实时协作 |
| gRPC | 高性能内部通信 | 高效、强类型 | 跨语言复杂性 |
| 消息队列 | 异步、松耦合协作 | 可靠、解耦 | 延迟较高 |
四、实战:设计一个内容创作多智能体工作流
4.1 场景需求
目标:创建自动化的内容创作流水线,从主题确定到发布的全流程。
4.2 工作流设计
python
class ContentCreationWorkflow:
"""
内容创作多智能体工作流示例
模式:混合模式(层级协调 + 管道流水线)
"""
def __init__(self):
self.agents = self.initialize_agents()
self.orchestrator = WorkflowOrchestrator()
self.blackboard = SharedBlackboard() # 共享工作区
def initialize_agents(self):
"""初始化各角色智能体"""
return {
"topic_strategist": TopicStrategyAgent(),
"research_agent": ResearchAgent(),
"outline_creator": OutlineCreationAgent(),
"content_writer": ContentWritingAgent(),
"seo_optimizer": SEOOptimizationAgent(),
"fact_checker": FactCheckingAgent(),
"editor": EditingAgent(),
"multimedia_creator": MultimediaCreationAgent(),
"publisher": PublishingAgent()
}
def execute_workflow(self, initial_topic):
"""执行完整工作流"""
# 阶段1:策略与规划(层级协调)
strategy_results = self.strategic_phase(initial_topic)
# 阶段2:内容创建(管道流水线)
content_results = self.creation_phase(strategy_results)
# 阶段3:优化与发布(市场协商)
final_results = self.optimization_phase(content_results)
return final_results
def strategic_phase(self, initial_topic):
"""策略阶段:确定内容方向"""
# 首席智能体协调
strategy_brief = self.orchestrator.create_strategy_brief(initial_topic)
# 并行执行市场分析和主题研究
market_analysis = self.agents["topic_strategist"].analyze_market(strategy_brief)
topic_research = self.agents["research_agent"].conduct_research(strategy_brief)
# 综合结果,确定最终主题
final_topic = self.orchestrator.synthesize_strategy(
market_analysis, topic_research
)
# 写入共享工作区
self.blackboard.update("final_topic", final_topic)
return {
"final_topic": final_topic,
"market_insights": market_analysis,
"research_data": topic_research
}
def creation_phase(self, strategy_data):
"""创建阶段:管道式内容生产"""
# 步骤1:大纲创建
outline = self.agents["outline_creator"].create_outline(
strategy_data["final_topic"],
strategy_data["research_data"]
)
# 步骤2:并行内容创作(多智能体协作)
content_sections = []
section_tasks = outline.get("sections", [])
# 使用任务分发器分配章节
for section in section_tasks:
# 根据章节类型选择最合适的写作智能体
writer = self.select_best_writer(section["type"])
content = writer.write_section(section)
content_sections.append(content)
# 步骤3:内容整合
draft = self.agents["content_writer"].assemble_draft(
outline, content_sections
)
# 更新共享工作区
self.blackboard.update("current_draft", draft)
return {
"outline": outline,
"draft": draft,
"section_authors": self.get_authors_info(content_sections)
}
def optimization_phase(self, content_data):
"""优化阶段:质量保证与增强"""
# 并行执行多个优化任务
optimization_tasks = [
("seo", self.agents["seo_optimizer"], content_data["draft"]),
("fact_check", self.agents["fact_checker"], content_data["draft"]),
("editing", self.agents["editor"], content_data["draft"]),
("multimedia", self.agents["multimedia_creator"], content_data)
]
# 市场协商模式:智能体竞标优化任务
optimization_results = {}
for task_name, agent, input_data in optimization_tasks:
# 智能体评估自己处理此任务的能力
confidence = agent.evaluate_task(input_data)
# 任务分配器基于置信度分配任务
if confidence > self.orchestrator.get_threshold(task_name):
result = agent.execute_task(input_data)
optimization_results[task_name] = result
# 综合优化结果
final_content = self.orchestrator.integrate_optimizations(
content_data["draft"], optimization_results
)
# 发布
publication_result = self.agents["publisher"].publish(final_content)
return {
"final_content": final_content,
"optimization_results": optimization_results,
"publication_status": publication_result,
"performance_metrics": self.collect_metrics()
}
def select_best_writer(self, section_type):
"""基于类型选择最合适的写作智能体"""
# 可扩展为更复杂的匹配算法
writer_specialties = {
"technical": self.agents["content_writer"].technical_writer,
"creative": self.agents["content_writer"].creative_writer,
"data_driven": self.agents["content_writer"].data_writer,
"persuasive": self.agents["content_writer"].persuasive_writer
}
return writer_specialties.get(section_type, self.agents["content_writer"])4.3 关键组件详细设计
4.3.1 工作流协调器
python
class WorkflowOrchestrator:
"""工作流协调器:管理智能体间的协作"""
def __init__(self):
self.workflow_state = {}
self.agent_registry = {}
self.mcp_client = MCPClient() # MCP协议客户端
def create_strategy_brief(self, initial_input):
"""创建策略简报"""
brief = {
"raw_input": initial_input,
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"context": self.gather_context(),
"constraints": self.identify_constraints(initial_input)
}
return brief
def synthesize_strategy(self, *inputs):
"""综合多个智能体的输入,制定策略"""
# 使用共识算法或加权决策
synthesis_method = self.select_synthesis_method(inputs)
return synthesis_method.combine(inputs)
def integrate_optimizations(self, base_content, optimizations):
"""整合多个优化结果"""
integrated = base_content.copy()
# 解决优化冲突(如SEO建议与编辑建议冲突)
for opt_name, opt_result in optimizations.items():
if not self.has_conflict(integrated, opt_result):
integrated = self.apply_optimization(integrated, opt_result)
else:
# 冲突解决策略
resolution = self.resolve_conflict(integrated, opt_result)
integrated = resolution
return integrated
def monitor_workflow(self):
"""监控工作流执行"""
metrics = {
"agent_performance": self.collect_agent_metrics(),
"communication_overhead": self.calculate_communication_cost(),
"bottlenecks": self.identify_bottlenecks(),
"error_rates": self.calculate_error_rates()
}
# 动态调整工作流
if metrics["bottlenecks"]:
self.reconfigure_workflow(metrics)
return metrics4.3.2 共享工作区实现
python
class SharedBlackboard:
"""共享工作区:智能体间的信息交换中心"""
def __init__(self):
self.data = {}
self.version_history = {}
self.access_control = {}
self.lock_manager = LockManager()
def update(self, key, value, agent_id=None):
"""更新共享数据"""
with self.lock_manager.get_lock(key):
# 版本控制
if key in self.data:
old_value = self.data[key]
self.version_history.setdefault(key, []).append({
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"old_value": old_value,
"new_value": value,
"agent": agent_id
})
self.data[key] = value
# 通知相关智能体
self.notify_subscribers(key, value)
def subscribe(self, agent_id, key_pattern, callback):
"""智能体订阅数据变化"""
# 实现发布-订阅模式
pass
def resolve_conflicts(self, key, proposed_values):
"""解决数据冲突(多个智能体同时修改)"""
# 冲突解决策略:
# 1. 时间戳优先(最新修改)
# 2. 智能体优先级
# 3. 投票机制
# 4. 人工干预
pass五、高级模式:自适应工作流
5.1 基于反馈的优化
python
class AdaptiveWorkflowEngine:
"""自适应工作流引擎:根据执行反馈优化工作流"""
def __init__(self, base_workflow):
self.base_workflow = base_workflow
self.performance_log = []
self.adaptation_rules = self.load_adaptation_rules()
self.llm_advisor = LLMAdvisor() # LLM驱动的优化建议
def execute_and_adapt(self, input_data):
"""执行工作流并根据结果自适应优化"""
# 执行当前工作流
result = self.base_workflow.execute(input_data)
# 收集性能数据
performance = self.analyze_execution(result)
self.performance_log.append(performance)
# 检查是否需要优化
if self.needs_optimization(performance):
# 生成优化建议
optimization_suggestions = self.generate_optimizations(performance)
# 选择最佳优化方案
best_optimization = self.select_best_optimization(
optimization_suggestions
)
# 应用优化
self.apply_optimization(best_optimization)
return result
def generate_optimizations(self, performance_data):
"""生成工作流优化建议"""
optimizations = []
# 规则驱动的优化
for rule in self.adaptation_rules:
if rule.condition_matches(performance_data):
optimizations.append(rule.suggested_change)
# LLM驱动的创新优化
llm_suggestions = self.llm_advisor.suggest_optimizations(
self.base_workflow,
performance_data
)
optimizations.extend(llm_suggestions)
return optimizations5.2 工作流组合与复用
python
class WorkflowComposer:
"""工作流组合器:通过组合现有工作流创建新工作流"""
def compose_workflow(self, requirements):
"""根据需求组合工作流"""
# 1. 需求分析
decomposed = self.decompose_requirements(requirements)
# 2. 查找匹配的子工作流
candidate_workflows = self.find_candidate_workflows(decomposed)
# 3. 组合验证
valid_combinations = self.validate_combinations(
candidate_workflows, decomposed
)
# 4. 选择最优组合
best_combination = self.select_best_combination(valid_combinations)
# 5. 生成接口适配器
adapters = self.create_adapters(best_combination)
return ComposedWorkflow(best_combination, adapters)六、评估与监控框架
6.1 评估指标体系
python
class WorkflowEvaluationFramework:
"""工作流评估框架"""
METRICS = {
# 效率指标
"execution_time": "工作流总执行时间",
"throughput": "单位时间处理的任务数",
"resource_utilization": "资源使用效率",
# 质量指标
"output_quality": "输出结果质量评分",
"error_rate": "错误发生率",
"consistency": "输出一致性",
# 协作指标
"communication_efficiency": "通信效率",
"coordination_overhead": "协调开销",
"conflict_resolution_rate": "冲突解决成功率",
# 经济指标
"cost_per_task": "单任务成本",
"roi": "投资回报率",
"scalability": "扩展性指标"
}
def evaluate_workflow(self, workflow, test_cases):
"""全面评估工作流性能"""
results = {}
for metric_name, metric_desc in self.METRICS.items():
metric_value = self.calculate_metric(
metric_name, workflow, test_cases
)
results[metric_name] = {
"value": metric_value,
"description": metric_desc,
"benchmark": self.get_benchmark(metric_name)
}
# 综合评分
results["overall_score"] = self.compute_overall_score(results)
return results
def compare_workflows(self, workflow_a, workflow_b, test_cases):
"""比较两个工作流设计"""
eval_a = self.evaluate_workflow(workflow_a, test_cases)
eval_b = self.evaluate_workflow(workflow_b, test_cases)
comparison = {}
for metric in self.METRICS.keys():
comparison[metric] = {
"workflow_a": eval_a[metric]["value"],
"workflow_b": eval_b[metric]["value"],
"difference": eval_b[metric]["value"] - eval_a[metric]["value"],
"percent_change": self.calculate_percent_change(
eval_a[metric]["value"], eval_b[metric]["value"]
)
}
return comparison6.2 实时监控面板
python
class WorkflowDashboard:
"""工作流实时监控面板"""
def __init__(self, workflow_system):
self.workflow_system = workflow_system
self.metrics_collector = MetricsCollector()
self.alert_manager = AlertManager()
def display_realtime_view(self):
"""显示实时监控视图"""
current_state = {
"active_workflows": self.get_active_workflows(),
"agent_status": self.get_agent_status(),
"performance_metrics": self.get_current_metrics(),
"bottlenecks": self.detect_bottlenecks(),
"recent_errors": self.get_recent_errors()
}
return self.render_dashboard(current_state)
def setup_alerts(self, threshold_config):
"""设置监控告警"""
self.alert_manager.configure({
"execution_time": {"threshold": threshold_config.get("max_time")},
"error_rate": {"threshold": threshold_config.get("max_error_rate")},
"resource_usage": {"threshold": threshold_config.get("max_resource")}
})七、实施路线图
阶段1:基础建设(1-3个月)
-
技术栈选择
-
选择MCP等协议实现
-
确定智能体框架(LangChain、AutoGen等)
-
建立基础通信基础设施
-
-
试点项目
-
选择低风险、高价值场景
-
设计简单工作流(2-3个智能体)
-
建立基础监控
-
阶段2:扩展与优化(4-9个月)
-
模式库建设
-
收集和标准化工作流模式
-
建立智能体角色库
-
开发共享组件
-
-
高级功能
-
实现自适应工作流
-
建立评估体系
-
开发可视化工具
-
阶段3:规模化(10-18个月)
-
企业级部署
-
跨部门工作流集成
-
大规模智能体管理
-
安全与合规加固
-
-
创新应用
-
探索新型工作流模式
-
AI驱动的流程优化
-
生态系统建设
-
八、风险与缓解策略
| 风险类别 | 具体风险 | 缓解策略 |
|---|---|---|
| 技术风险 | 智能体间通信故障 | 实现冗余通信通道,设置超时重试机制 |
| 协调风险 | 智能体目标冲突 | 建立冲突检测与解决框架,设置优先级规则 |
| 性能风险 | 工作流执行缓慢 | 实施性能监控,动态调整智能体分配 |
| 安全风险 | 数据泄露或滥用 | 实施严格的数据访问控制,加密通信 |
| 管理风险 | 工作流难以维护 | 建立文档标准,实施版本控制,模块化设计 |
结语
多智能体系统工作流设计是一场从机械自动化 到智能协作 的范式转变。成功的核心不是技术的堆砌,而是对协作模式的深刻理解和精心设计。
关键成功因素:
-
始于清晰的价值主张:每个工作流都应解决明确的业务问题
-
拥抱渐进式演进:从简单到复杂,从确定到不确定
-
投资于可观测性:无法监控的系统无法优化
-
培养系统思维:关注智能体间的互动,而非单个智能体的能力
-
建立反馈循环:让工作流能够从执行中学习并改进
2026年的组织竞争优势,将很大程度上取决于其设计和运营多智能体工作流的能力。现在开始探索和实践,正是时候。