1. 场景分析与缓存策略选择
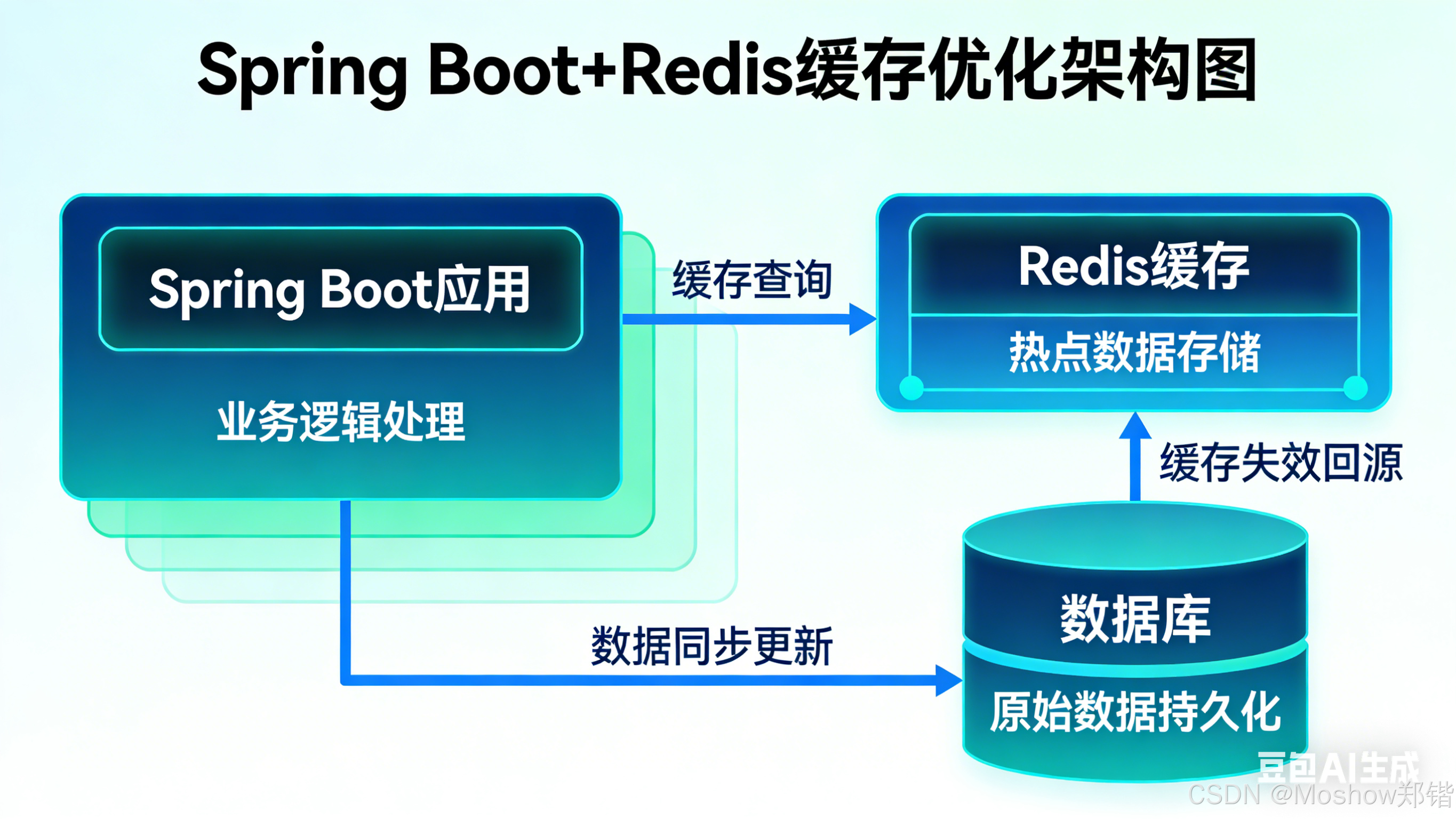
1.1 典型数据查询场景特性
-
KPI指标查询:实时性要求高,计算复杂,但数据更新频率中等
-
图表数据查询:聚合运算多,响应时间敏感,数据维度固定
-
表格数据查询:分页、排序、过滤复杂,数据量大但可缓存部分结果
1.2 缓存策略决策矩阵
| 场景类型 | 缓存时间 | 更新策略 | 缓存粒度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| KPI实时指标 | 30秒-5分钟 | 主动更新 + 失效 | 按指标+时间维度 |
| 历史图表 | 1-24小时 | 定时刷新 + 版本控制 | 按图表类型+参数 |
| 表格数据 | 5-30分钟 | 按需更新 + 条件失效 | 分页缓存 + 主键缓存 |
2. Spring Boot 集成 Redis 配置
2.1 依赖配置
XML
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Data Redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Redis连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 缓存支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 序列化支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.2 Redis 配置类
java
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory(
@Value("${spring.redis.host}") String host,
@Value("${spring.redis.port}") int port,
@Value("${spring.redis.password}") String password,
@Value("${spring.redis.database}") int database) {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration config = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
config.setHostName(host);
config.setPort(port);
config.setPassword(RedisPassword.of(password));
config.setDatabase(database);
LettuceClientConfiguration clientConfig = LettuceClientConfiguration.builder()
.commandTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.build();
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(config, clientConfig);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
// 使用Jackson序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> serializer =
new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
serializer.setObjectMapper(mapper);
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(getDefaultCacheConfig())
.withInitialCacheConfigurations(getCacheConfigurations())
.transactionAware()
.build();
}
private RedisCacheConfiguration getDefaultCacheConfig() {
return RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()))
.disableCachingNullValues();
}
private Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> getCacheConfigurations() {
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> configs = new HashMap<>();
// KPI缓存配置:短时间,高频率
configs.put("kpi", getDefaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(5))
.computePrefixWith(cacheName -> "cache:kpi:" + cacheName + ":"));
// 图表缓存配置:中等时间
configs.put("chart", getDefaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1))
.computePrefixWith(cacheName -> "cache:chart:" + cacheName + ":"));
// 表格缓存配置:按查询条件缓存
configs.put("table", getDefaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(15))
.computePrefixWith(cacheName -> "cache:table:" + cacheName + ":"));
return configs;
}
}3. 数据层缓存实现策略
3.1 KPI指标查询缓存
java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class KPIService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
private static final String KPI_CACHE_PREFIX = "kpi:indicators:";
/**
* 获取实时KPI指标 - 带缓存
*/
@Cacheable(value = "kpi", key = "#indicatorType + ':' + #timeRange + ':' + #dimension")
public KPIResult getKPIWithCache(String indicatorType, TimeRange timeRange, String dimension) {
log.info("查询数据库获取KPI数据: {}-{}-{}", indicatorType, timeRange, dimension);
return calculateKPI(indicatorType, timeRange, dimension);
}
/**
* 批量获取KPI - 使用Pipeline优化
*/
public Map<String, KPIResult> batchGetKPI(List<KPIQuery> queries) {
Map<String, KPIResult> results = new HashMap<>();
List<Object> cacheResults = redisTemplate.executePipelined(
(RedisCallback<Object>) connection -> {
StringRedisConnection stringRedisConn = (StringRedisConnection) connection;
for (KPIQuery query : queries) {
String key = buildKPIKey(query);
stringRedisConn.get(key);
}
return null;
});
// 处理缓存命中与未命中
for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) {
KPIQuery query = queries.get(i);
String cached = (String) cacheResults.get(i);
if (cached != null) {
results.put(query.getId(), deserializeKPI(cached));
} else {
KPIResult result = calculateKPI(query);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
buildKPIKey(query),
serializeKPI(result),
Duration.ofMinutes(5)
);
results.put(query.getId(), result);
}
}
return results;
}
/**
* 主动更新KPI缓存
*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 300000) // 每5分钟更新一次
@CacheEvict(value = "kpi", allEntries = true)
public void refreshKPICache() {
log.info("刷新KPI缓存");
}
private String buildKPIKey(KPIQuery query) {
return KPI_CACHE_PREFIX + query.getType() + ":" +
query.getTimeRange() + ":" + query.getDimension();
}
}3.2 图表数据缓存策略
java
@Service
public class ChartDataService {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
/**
* 获取图表数据 - 带多级缓存
*/
public ChartData getChartData(ChartRequest request) {
String cacheKey = buildChartCacheKey(request);
// 1. 尝试从Redis获取
String cachedData = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);
if (cachedData != null) {
return parseChartData(cachedData);
}
// 2. 尝试从本地缓存获取(Guava Cache作为二级缓存)
ChartData localCached = localChartCache.getIfPresent(cacheKey);
if (localCached != null) {
// 异步刷新Redis缓存
refreshRedisCacheAsync(cacheKey, localCached);
return localCached;
}
// 3. 查询数据库
ChartData data = fetchFromDatabase(request);
// 4. 更新缓存
updateChartCache(cacheKey, data, getChartTTL(request.getChartType()));
return data;
}
/**
* 图表缓存键生成策略
*/
private String buildChartCacheKey(ChartRequest request) {
// 包含图表类型、时间范围、过滤条件等维度
return String.format("chart:%s:%s:%s:%s",
request.getChartType(),
request.getTimeRange().getCode(),
request.getFilters().hashCode(),
request.getAggregationLevel());
}
/**
* 按图表类型设置不同的TTL
*/
private Duration getChartTTL(ChartType type) {
switch (type) {
case REAL_TIME:
return Duration.ofMinutes(5);
case DAILY_REPORT:
return Duration.ofHours(1);
case HISTORICAL_TREND:
return Duration.ofDays(1);
default:
return Duration.ofHours(6);
}
}
/**
* 使用Bloom Filter防止缓存穿透
*/
public ChartData getChartDataWithBloomFilter(ChartRequest request) {
String cacheKey = buildChartCacheKey(request);
// 检查Bloom Filter
if (!bloomFilter.mightContain(cacheKey)) {
return null; // 或返回默认空数据
}
return getChartData(request);
}
}3.3 表格数据查询优化
java
@Repository
public class TableDataRepository {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 分页查询表格数据 - 缓存优化
*/
public PageResult<TableRow> getTableData(TableQuery query, Pageable pageable) {
String cacheKey = buildTableCacheKey(query, pageable);
// 尝试获取缓存
PageResult<TableRow> cached = (PageResult<TableRow>)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
// 查询数据库
List<TableRow> data = queryDatabase(query, pageable);
int total = getTotalCount(query);
PageResult<TableRow> result = new PageResult<>(data, pageable, total);
// 缓存结果
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(
cacheKey,
result,
getTableCacheTTL(query),
TimeUnit.MINUTES
);
// 缓存记录ID列表,用于数据更新时失效缓存
cacheRecordIds(query, data);
return result;
}
/**
* 智能缓存键生成:只缓存热点查询
*/
private String buildTableCacheKey(TableQuery query, Pageable pageable) {
// 只缓存前5页数据,后面的查询不缓存
if (pageable.getPageNumber() > 5) {
return null;
}
return String.format("table:data:%s:page%d:size%d:%s",
query.getTableName(),
pageable.getPageNumber(),
pageable.getPageSize(),
query.getConditionHash());
}
/**
* 数据更新时失效相关缓存
*/
@Transactional
public void updateTableData(TableRow row) {
// 更新数据库
updateDatabase(row);
// 失效相关缓存
String pattern = String.format("table:*%s*", row.getTableName());
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
if (keys != null && !keys.isEmpty()) {
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
}
// 更新Bloom Filter
updateBloomFilter(row);
}
}4. 高级缓存模式
4.1 缓存预热与预加载
java
@Component
public class CacheWarmUpService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private KPIService kpiService;
@Autowired
private ChartDataService chartDataService;
@PostConstruct
@EventListener(ContextRefreshedEvent.class)
public void warmUpCache() {
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
log.info("开始缓存预热...");
// 预热高频KPI查询
warmUpKPICache();
// 预热常用图表
warmUpChartCache();
// 预热热点表格数据
warmUpTableCache();
log.info("缓存预热完成");
});
}
private void warmUpKPICache() {
List<KPIQuery> hotQueries = getHotKPIQueries();
for (KPIQuery query : hotQueries) {
try {
kpiService.getKPIWithCache(query.getType(),
query.getTimeRange(), query.getDimension());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("预热KPI缓存失败: {}", query, e);
}
}
}
}4.2 分布式锁避免缓存击穿
java
@Service
public class CacheBreakdownPreventionService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 使用Redis分布式锁防止缓存击穿
*/
public Object getDataWithLock(String key, Supplier<Object> dataLoader,
Duration lockTimeout, Duration cacheTTL) {
// 1. 尝试从缓存获取
Object cached = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
// 2. 尝试获取分布式锁
String lockKey = "lock:" + key;
Boolean locked = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(
lockKey, "locked", lockTimeout);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(locked)) {
try {
// 3. 再次检查缓存(双检锁)
cached = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
// 4. 加载数据
Object data = dataLoader.get();
// 5. 写入缓存
if (data != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, data, cacheTTL);
}
return data;
} finally {
// 释放锁
redisTemplate.delete(lockKey);
}
} else {
// 等待并重试
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
return getDataWithLock(key, dataLoader, lockTimeout, cacheTTL);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return dataLoader.get();
}
}
}
}5. 监控与优化
5.1 缓存监控配置
java
@Configuration
public class CacheMetricsConfig {
@Bean
public MeterRegistryCustomizer<MeterRegistry> cacheMetrics() {
return registry -> {
// 监控缓存命中率
registry.gauge("cache.hit.rate",
Tags.of("type", "kpi"),
this,
ctx -> calculateHitRate("kpi"));
// 监控缓存大小
registry.gauge("cache.size",
Tags.of("type", "chart"),
this,
ctx -> estimateCacheSize("chart"));
};
}
/**
* 缓存健康检查
*/
@Component
public class CacheHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Autowired
private RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory;
@Override
public Health health() {
try {
RedisConnection connection = connectionFactory.getConnection();
String result = connection.ping();
connection.close();
if ("PONG".equals(result)) {
return Health.up()
.withDetail("message", "Redis缓存服务正常")
.build();
} else {
return Health.down()
.withDetail("message", "Redis响应异常")
.build();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return Health.down()
.withDetail("message", "Redis连接失败")
.withException(e)
.build();
}
}
}
}5.2 性能优化建议
-
序列化优化:使用Protobuf或Msgpack替代JSON
-
内存优化:配置Redis最大内存和淘汰策略
-
连接优化:使用连接池,合理配置连接参数
-
数据压缩:对大value进行压缩存储
-
批量操作:使用Pipeline减少网络往返
6. 最佳实践总结
6.1 缓存设计原则
-
按需缓存:只缓存热点数据
-
合理过期:根据业务场景设置TTL
-
及时失效:数据更新时清除相关缓存
-
分级缓存:本地缓存+Redis多级缓存
-
监控告警:实时监控缓存命中率和性能
6.2 业务场景适配表
| 场景 | 推荐策略 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|
| 实时KPI | 短时间缓存 + 主动刷新 | 注意数据一致性 |
| 历史报表 | 长时间缓存 + 版本控制 | 注意内存占用 |
| 复杂查询 | 结果集缓存 + 条件索引 | 注意缓存键设计 |
| 频繁更新 | 只缓存只读数据 | 及时失效缓存 |
6.3 故障处理预案
-
缓存雪崩:设置随机过期时间,使用熔断降级
-
缓存穿透:使用Bloom Filter,缓存空值
-
缓存击穿:使用分布式锁,热点数据永不过期
-
缓存一致:采用双删策略,消息队列同步