本期内容为自己总结归档,共分十一章,本人遇到过的面试问题会重点标记。
(若有任何疑问,可在评论区告诉我,看到就回复)
一、策略模式的核心概念
1.1 策略模式的定义
策略模式(Strategy Pattern)定义了一系列算法,将每一个算法封装起来,并让它们可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户端而变化。
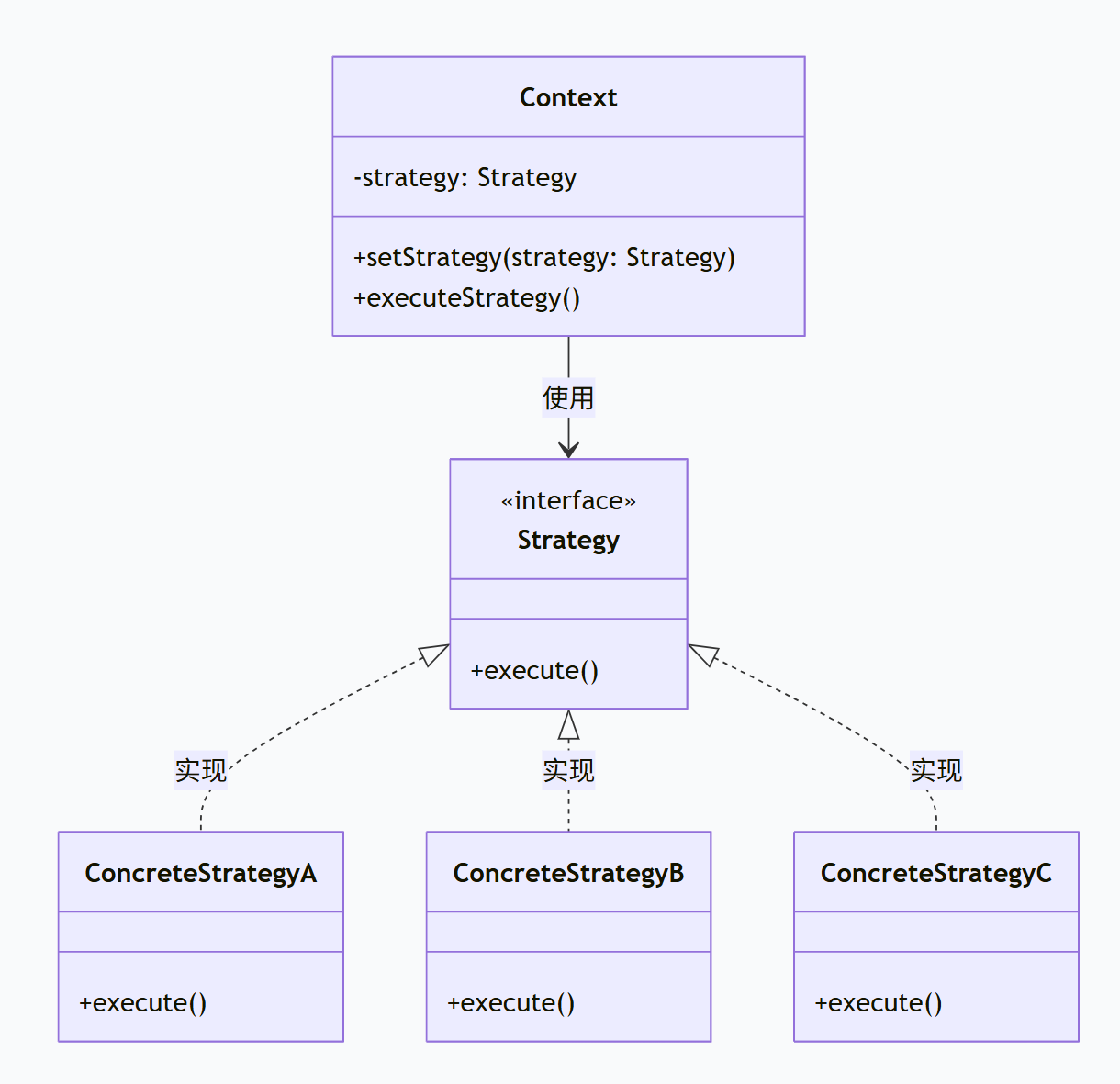
1.2 ⭐策略模式的结构
策略模式包含三个核心角色:
-
Context(上下文):维护一个策略对象的引用,可以动态设置策略
-
Strategy(策略接口):定义所有支持的算法的公共接口
-
ConcreteStrategy(具体策略):实现策略接口的具体算法
1.3 策略模式 vs 状态模式
策略模式和状态模式在结构上相似,但意图不同:
| 对比维度 | 策略模式 | 状态模式 |
|---|---|---|
| 目的 | 封装不同的算法 | 封装对象的不同状态 |
| 切换机制 | 客户端主动设置 | 状态类自动切换 |
| 独立性 | 策略之间通常独立 | 状态之间相互关联 |
| 关注点 | 如何执行任务 | 对象的行为如何随状态改变 |
二、策略模式的基础实现
2.1 电商价格计算策略示例
java
// 1. 策略接口
public interface PricingStrategy {
double calculatePrice(double originalPrice);
}
// 2. 具体策略:普通用户
public class RegularPricingStrategy implements PricingStrategy {
@Override
public double calculatePrice(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice;
}
}
// 3. 具体策略:VIP用户
public class VipPricingStrategy implements PricingStrategy {
private static final double DISCOUNT = 0.9;
@Override
public double calculatePrice(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice * DISCOUNT;
}
}
// 4. 具体策略:企业用户
public class EnterprisePricingStrategy implements PricingStrategy {
@Override
public double calculatePrice(double originalPrice) {
if (originalPrice > 10000) {
return originalPrice * 0.8;
} else if (originalPrice > 5000) {
return originalPrice * 0.85;
} else {
return originalPrice * 0.9;
}
}
}
// 5. 具体策略:新用户
public class NewUserPricingStrategy implements PricingStrategy {
private static final double DISCOUNT = 0.85;
@Override
public double calculatePrice(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice * DISCOUNT;
}
}
// 6. 上下文类
public class PriceCalculator {
private PricingStrategy strategy;
public PriceCalculator(PricingStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void setStrategy(PricingStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
return strategy.calculatePrice(originalPrice);
}
}
// 7. 客户端使用
public class StrategyPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double originalPrice = 1000.0;
// 普通用户
PriceCalculator calculator = new PriceCalculator(new RegularPricingStrategy());
System.out.println("普通用户价格: " + calculator.calculate(originalPrice));
// VIP用户
calculator.setStrategy(new VipPricingStrategy());
System.out.println("VIP用户价格: " + calculator.calculate(originalPrice));
// 企业用户
calculator.setStrategy(new EnterprisePricingStrategy());
System.out.println("企业用户价格: " + calculator.calculate(originalPrice));
// 新用户
calculator.setStrategy(new NewUserPricingStrategy());
System.out.println("新用户价格: " + calculator.calculate(originalPrice));
}
}2.2 策略模式的变体:带参数的策略
有时策略执行需要额外的参数:
java
// 带参数的策略接口
public interface ShippingStrategy {
double calculateShipping(double weight, String destination);
}
// 具体实现
public class StandardShippingStrategy implements ShippingStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateShipping(double weight, String destination) {
double basePrice = 10.0;
double pricePerKg = 5.0;
return basePrice + (weight * pricePerKg);
}
}
public class ExpressShippingStrategy implements ShippingStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateShipping(double weight, String destination) {
double basePrice = 30.0;
double pricePerKg = 8.0;
// 偏远地区加收费用
if (isRemoteArea(destination)) {
basePrice += 20.0;
}
return basePrice + (weight * pricePerKg);
}
private boolean isRemoteArea(String destination) {
return destination.contains("新疆") || destination.contains("西藏");
}
}三、策略模式的高级应用
3.1 策略模式与Lambda表达式
java
// 使用函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface DiscountStrategy {
double applyDiscount(double price);
}
public class LambdaStrategyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用Lambda表达式定义策略
DiscountStrategy vipStrategy = price -> price * 0.9;
DiscountStrategy newUserStrategy = price -> price * 0.85;
DiscountStrategy bulkStrategy = price -> price > 1000 ? price * 0.8 : price;
// 策略上下文
double price = 1500.0;
System.out.println("VIP价格: " + vipStrategy.applyDiscount(price));
System.out.println("新用户价格: " + newUserStrategy.applyDiscount(price));
System.out.println("大客户价格: " + bulkStrategy.applyDiscount(price));
}
}3.2 策略模式与枚举
对于固定的策略集合,可以使用枚举实现:
java
public enum PricingStrategyEnum {
REGULAR {
@Override
public double calculate(double price) {
return price;
}
},
VIP {
@Override
public double calculate(double price) {
return price * 0.9;
}
},
NEW_USER {
@Override
public double calculate(double price) {
return price * 0.85;
}
};
public abstract double calculate(double price);
}
// 使用示例
public class EnumStrategyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double price = 1000.0;
System.out.println("VIP价格: " + PricingStrategyEnum.VIP.calculate(price));
System.out.println("新用户价格: " + PricingStrategyEnum.NEW_USER.calculate(price));
}
}3.3 策略模式工厂
结合工厂模式创建策略对象:
java
public class StrategyFactory {
private static final Map<String, PricingStrategy> strategies = new HashMap<>();
static {
strategies.put("REGULAR", new RegularPricingStrategy());
strategies.put("VIP", new VipPricingStrategy());
strategies.put("ENTERPRISE", new EnterprisePricingStrategy());
strategies.put("NEW_USER", new NewUserPricingStrategy());
}
public static PricingStrategy getStrategy(String type) {
PricingStrategy strategy = strategies.get(type);
if (strategy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的策略类型: " + type);
}
return strategy;
}
public static void registerStrategy(String type, PricingStrategy strategy) {
strategies.put(type, strategy);
}
}
// 使用示例
public class StrategyFactoryDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriceCalculator calculator = new PriceCalculator(
StrategyFactory.getStrategy("VIP")
);
double price = 1000.0;
System.out.println("计算价格: " + calculator.calculate(price));
// 动态注册新策略
StrategyFactory.registerStrategy("SPECIAL", price -> price * 0.7);
calculator.setStrategy(StrategyFactory.getStrategy("SPECIAL"));
System.out.println("特殊价格: " + calculator.calculate(price));
}
}四、策略模式在Java标准库中的应用
4.1 Collections.sort()中的策略模式
java
public class Student {
private String name;
private int score;
private int age;
// 构造方法、getter、setter省略
}
public class SortingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("Alice", 85, 20));
students.add(new Student("Bob", 75, 22));
students.add(new Student("Charlie", 95, 19));
// 策略1:按分数排序
students.sort((s1, s2) -> Integer.compare(s1.getScore(), s2.getScore()));
System.out.println("按分数排序: " + students);
// 策略2:按年龄排序
students.sort((s1, s2) -> Integer.compare(s1.getAge(), s2.getAge()));
System.out.println("按年龄排序: " + students);
// 策略3:先按分数再按年龄排序
students.sort(Comparator
.comparingInt(Student::getScore)
.thenComparingInt(Student::getAge));
System.out.println("先分数后年龄排序: " + students);
}
}4.2 ThreadPoolExecutor中的拒绝策略
Java线程池的拒绝策略案例
java
public class RejectionPolicyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 策略1:直接抛出异常
ThreadPoolExecutor executor1 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, 4, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 拒绝策略
);
// 策略2:由调用者线程执行
ThreadPoolExecutor executor2 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, 4, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
);
// 策略3:丢弃最老的任务
ThreadPoolExecutor executor3 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, 4, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()
);
// 策略4:静默丢弃新任务
ThreadPoolExecutor executor4 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, 4, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy()
);
}
}五、策略模式在Spring框架中的应用
5.1 Spring事务管理策略
Spring的事务管理使用策略模式支持不同的事务管理器:
java
// 策略接口:事务管理器
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition);
void commit(TransactionStatus status);
void rollback(TransactionStatus status);
}
// 具体策略实现
public class DataSourceTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager {
// 基于DataSource的事务管理
@Override
public TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) {
// 实现略
return null;
}
@Override
public void commit(TransactionStatus status) {
// 实现略
}
@Override
public void rollback(TransactionStatus status) {
// 实现略
}
}
public class JpaTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager {
// 基于JPA的事务管理
// 实现略
}
public class JtaTransactionManager implements PlatformTransactionManager {
// 基于JTA的分布式事务管理
// 实现略
}
// 配置示例
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class TransactionConfig {
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
// 根据需求选择不同的事务策略
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
// 或者 return new JpaTransactionManager();
// 或者 return new JtaTransactionManager();
}
}5.2 Spring缓存策略
Spring的缓存抽象也使用了策略模式:
java
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
// 策略选择:使用哪种缓存实现
return new ConcurrentMapCacheManager(); // 内存缓存
// return new RedisCacheManager(); // Redis缓存
// return new EhCacheCacheManager(); // EhCache缓存
}
}
// 使用示例
@Service
public class UserService {
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#id")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
// 数据库查询
return userRepository.findById(id);
}
@CacheEvict(value = "users", key = "#user.id")
public void updateUser(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
}
}六、总结
6.1 何时使用策略模式
使用策略模式的典型场景:
-
多种算法实现:系统需要在多种算法中选择一种
-
避免条件判断:需要消除大量的条件判断语句
-
算法需要独立变化:算法可能经常变化或扩展
-
客户端不需要知道算法细节:客户端只需要知道如何使用算法
6.2 优缺点
策略模式的优点:
-
算法(规则)可自由地切换。
-
避免 使用多重条件判断。
-
方便拓展和增加新的算法(规则)。
策略模式的缺点:所有策略类都需要对外暴露。
6.3 核心要点
设计原则体现:
开闭原则:新增策略无需修改现有代码
单一职责:每个策略类只负责一个算法
依赖倒置:客户端依赖于抽象策略接口
实现关键:
定义清晰的策略接口
实现具体策略类
上下文类通过组合使用策略
在Java和Spring中的应用:
Java集合框架的Comparator
线程池的拒绝策略
Spring的事务管理、缓存、视图解析等