Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:手势识别与碰撞检测算法深度解析
文章目录
- [Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:手势识别与碰撞检测算法深度解析](#Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:手势识别与碰撞检测算法深度解析)
-
- 摘要
- 一、手势识别系统概述
-
- [1.1 Flutter手势体系](#1.1 Flutter手势体系)
- [1.2 常用手势类型](#1.2 常用手势类型)
- 二、GestureDetector详解
-
- [2.1 GestureDetector基础](#2.1 GestureDetector基础)
- [2.2 垂直拖动手势](#2.2 垂直拖动手势)
- [2.3 Pan手势处理](#2.3 Pan手势处理)
- [2.4 华容道中的手势实现](#2.4 华容道中的手势实现)
- 三、键盘事件处理
-
- [3.1 KeyboardListener基础](#3.1 KeyboardListener基础)
- [3.2 KeyEvent类型](#3.2 KeyEvent类型)
- [3.3 方向键处理](#3.3 方向键处理)
- [3.4 KeyEventResult](#3.4 KeyEventResult)
- 四、焦点事件机制
-
- [4.1 FocusNode基础](#4.1 FocusNode基础)
- [4.2 焦点状态监听](#4.2 焦点状态监听)
- [4.3 华容道中的焦点管理](#4.3 华容道中的焦点管理)
- [4.4 焦点视觉反馈](#4.4 焦点视觉反馈)
- 五、碰撞检测算法
-
- [5.1 矩形碰撞检测](#5.1 矩形碰撞检测)
- [5.2 多格子碰撞检测](#5.2 多格子碰撞检测)
- [5.3 矩形相交检测](#5.3 矩形相交检测)
- 六、移动验证逻辑
-
- [6.1 移动验证流程](#6.1 移动验证流程)
- [6.2 边界检测](#6.2 边界检测)
- [6.3 完整移动验证](#6.3 完整移动验证)
- [6.4 移动动画](#6.4 移动动画)
- 七、高级功能扩展
-
- [7.1 撤销功能](#7.1 撤销功能)
- [7.2 关卡系统](#7.2 关卡系统)
- [7.3 计时功能](#7.3 计时功能)
- [7.4 自动求解提示](#7.4 自动求解提示)
- 八、性能优化策略
-
- [8.1 减少不必要的setState](#8.1 减少不必要的setState)
- [8.2 优化碰撞检测](#8.2 优化碰撞检测)
- [8.3 使用const构造函数](#8.3 使用const构造函数)
- 九、总结
摘要
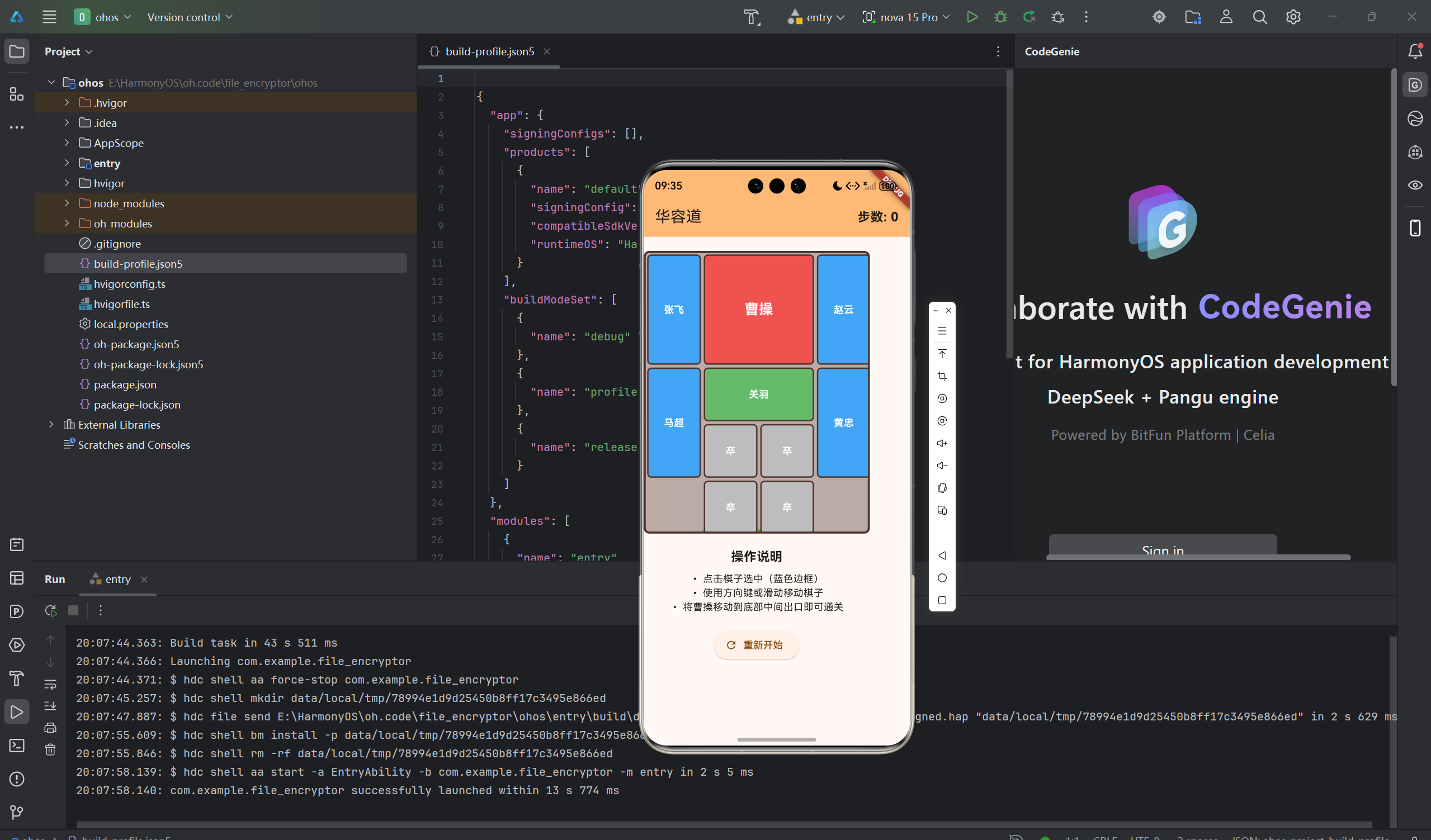
手势识别和碰撞检测是华容道游戏的核心交互技术。本文深入讲解Flutter中的手势识别系统,详细分析GestureDetector、KeyboardListener、焦点事件机制、碰撞检测算法等高级技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握Flutter在鸿蒙平台上的交互处理技巧,了解如何构建流畅、准确的游戏控制系统。
一、手势识别系统概述
1.1 Flutter手势体系
Flutter的手势系统是一个竞技场(Arena)模型:
- 多个手势识别器可以同时监听
- 通过竞技机制决定谁获胜
- 支持手势冲突解决
1.2 常用手势类型
| 手势 | 描述 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 点击 | Tap | 按钮点击、选择 |
| 双击 | DoubleTap | 快速操作 |
| 长按 | LongPress | 上下文菜单 |
| 滑动 | Pan/Drag | 拖拽、移动 |
| 缩放 | Scale | 图片缩放 |
| 旋转 | Rotation | 旋转操作 |
二、GestureDetector详解
2.1 GestureDetector基础
GestureDetector是Flutter中最常用的手势识别组件:
dart
GestureDetector(
onTap: () {
print('点击');
},
onDoubleTap: () {
print('双击');
},
onLongPress: () {
print('长按');
},
child: Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.blue,
),
)2.2 垂直拖动手势
dart
GestureDetector(
onVerticalDragStart: (details) {
print('开始拖动: ${details.globalPosition}');
},
onVerticalDragUpdate: (details) {
print('拖动中: ${details.delta.dy}');
},
onVerticalDragEnd: (details) {
print('拖动结束: ${details.velocity.pixelsPerSecond}');
},
child: Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.green,
),
)2.3 Pan手势处理
dart
GestureDetector(
onPanStart: (details) {
// 开始拖动
_startPosition = details.globalPosition;
},
onPanUpdate: (details) {
// 拖动中
final delta = details.delta;
// 根据delta更新位置
},
onPanEnd: (details) {
// 拖动结束
final velocity = details.velocity.pixelsPerSecond;
},
child: Widget,
)2.4 华容道中的手势实现
使用onPanEnd检测滑动方向:
dart
onPanEnd: (details) {
final dx = details.localPosition.dx;
final dy = details.localPosition.dy;
if (dx.abs() > dy.abs()) {
// 水平移动
if (dx > 10) {
_movePiece(piece, 1, 0); // 向右
} else if (dx < -10) {
_movePiece(piece, -1, 0); // 向左
}
} else {
// 垂直移动
if (dy > 10) {
_movePiece(piece, 0, 1); // 向下
} else if (dy < -10) {
_movePiece(piece, 0, -1); // 向上
}
}
}算法要点
- 比较dx和dy的绝对值判断主方向
- 使用阈值(10像素)避免误触
- 根据正负方向确定移动方向
三、键盘事件处理
3.1 KeyboardListener基础
KeyboardListener用于监听键盘事件:
dart
KeyboardListener(
focusNode: _focusNode,
onKeyEvent: (KeyEvent event) {
if (event is KeyDownEvent) {
print('按键按下: ${event.logicalKey}');
} else if (event is KeyUpEvent) {
print('按键释放: ${event.logicalKey}');
}
return KeyEventResult.handled;
},
child: Widget,
)3.2 KeyEvent类型
dart
// KeyDownEvent:按键按下
// KeyUpEvent:按键释放
// KeyRepeatEvent:按键重复
KeyEventResult _handleKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
if (event is KeyDownEvent) {
// 处理按键按下
return KeyEventResult.handled;
}
return KeyEventResult.ignored;
}3.3 方向键处理
dart
KeyEventResult _handleKeyEvent(FocusNode node, KeyEvent event) {
if (event is! KeyDownEvent) return KeyEventResult.ignored;
switch (event.logicalKey) {
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowUp:
_movePiece(focusedPiece, 0, -1);
return KeyEventResult.handled;
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowDown:
_movePiece(focusedPiece, 0, 1);
return KeyEventResult.handled;
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowLeft:
_movePiece(focusedPiece, -1, 0);
return KeyEventResult.handled;
case LogicalKeyboardKey.arrowRight:
_movePiece(focusedPiece, 1, 0);
return KeyEventResult.handled;
default:
return KeyEventResult.ignored;
}
}3.4 KeyEventResult
dart
enum KeyEventResult {
handled, // 已处理,停止传播
ignored, // 忽略,继续传播
skipRemaining siblings, // 跳过兄弟节点
}四、焦点事件机制
4.1 FocusNode基础
dart
class _WidgetState extends State<Widget> {
final FocusNode _focusNode = FocusNode();
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_focusNode.requestFocus(); // 请求焦点
}
@override
void dispose() {
_focusNode.dispose(); // 释放资源
super.dispose();
}
}4.2 焦点状态监听
dart
_focusNode.addListener(() {
if (_focusNode.hasFocus) {
print('获得焦点');
} else {
print('失去焦点');
}
});4.3 华容道中的焦点管理
dart
// 点击棋子设置焦点
onTap: () {
setState(() {
// 清除其他棋子的焦点
for (var p in _pieces) {
p.hasFocus = false;
}
// 设置当前棋子焦点
piece.hasFocus = true;
});
}
// 获取当前焦点棋子
Piece? getFocusedPiece() {
try {
return _pieces.firstWhere((p) => p.hasFocus);
} catch (e) {
return null;
}
}4.4 焦点视觉反馈
dart
Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: piece.hasFocus ? Colors.blue : piece.color,
border: Border.all(
color: piece.hasFocus ? Colors.blue.shade700 : Colors.grey,
width: piece.hasFocus ? 3 : 1,
),
),
)五、碰撞检测算法
5.1 矩形碰撞检测
华容道使用矩形碰撞检测(AABB算法):
dart
bool _isPositionOccupied(int x, int y, Piece? excludePiece) {
for (var piece in _pieces) {
if (piece == excludePiece) continue;
// 检查点(x, y)是否在piece内
if (x >= piece.x && x < piece.x + piece.width &&
y >= piece.y && y < piece.y + piece.height) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}算法原理
- 检查点是否在矩形内
- 使用>=和<实现边界判断
- excludePiece参数排除自身
5.2 多格子碰撞检测
对于大尺寸棋子(如曹操2x2),需要检查所有占用的格子:
dart
bool _canMoveTo(Piece piece, int newX, int newY) {
// 检查边界
if (newX < 0 || newX + piece.width > boardColumns) return false;
if (newY < 0 || newY + piece.height > boardRows) return false;
// 检查所有占用格子的碰撞
for (int dx = 0; dx < piece.width; dx++) {
for (int dy = 0; dy < piece.height; dy++) {
if (_isPositionOccupied(newX + dx, newY + dy, piece)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}算法流程
- 遍历棋子占用的所有格子
- 对每个格子检查碰撞
- 任何一个格子碰撞则返回false
- 全部通过才返回true
5.3 矩形相交检测
检测两个矩形是否相交:
dart
bool _rectsIntersect(
int x1, int y1, int w1, int h1,
int x2, int y2, int w2, int h2,
) {
return x1 < x2 + w2 && x1 + w1 > x2 &&
y1 < y2 + h2 && y1 + h1 > y2;
}
// 使用
if (_rectsIntersect(
piece.x, piece.y, piece.width, piece.height,
other.x, other.y, other.width, other.height,
)) {
// 发生碰撞
}六、移动验证逻辑
6.1 移动验证流程
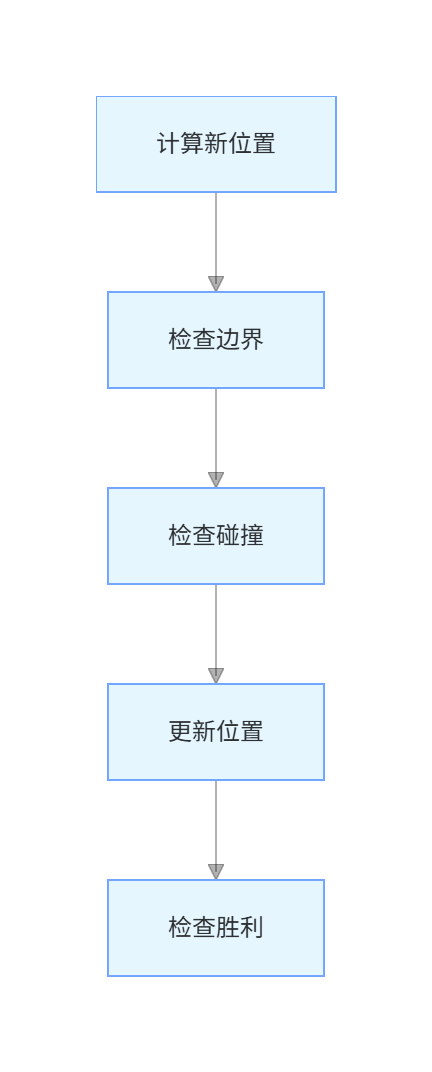
6.2 边界检测
dart
bool _isWithinBounds(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
// 左边界
if (x < 0) return false;
// 右边界
if (x + width > boardColumns) return false;
// 上边界
if (y < 0) return false;
// 下边界
if (y + height > boardRows) return false;
return true;
}6.3 完整移动验证
dart
void _movePiece(Piece piece, int dx, int dy) {
int newX = piece.x + dx;
int newY = piece.y + dy;
// 验证移动
if (_canMoveTo(piece, newX, newY)) {
setState(() {
piece.x = newX;
piece.y = newY;
_moveCount++;
});
_checkWin();
} else {
// 移动失败反馈
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text('无法移动到该位置')),
);
}
}6.4 移动动画
添加平滑的移动动画:
dart
void _movePieceWithAnimation(Piece piece, int targetX, int targetY) {
final tween = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 1);
final animationController = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 200),
vsync: this,
);
animationController.addListener(() {
setState(() {
double progress = animationController.value;
piece.x = (piece.x + (targetX - piece.x) * progress).round();
piece.y = (piece.y + (targetY - piece.y) * progress).round();
});
});
animationController.addListener(() {
if (animationController.isCompleted) {
piece.x = targetX;
piece.y = targetY;
_checkWin();
animationController.dispose();
}
});
animationController.forward();
}七、高级功能扩展
7.1 撤销功能
dart
class _KlotskiGamePageState extends State<KlotskiGamePage> {
final List<List<Piece>> _history = [];
void _saveState() {
_history.add(_pieces.map((p) => Piece(
name: p.name,
type: p.type,
x: p.x,
y: p.y,
width: p.width,
height: p.height,
hasFocus: p.hasFocus,
)).toList());
// 限制历史记录数量
if (_history.length > 100) {
_history.removeAt(0);
}
}
void _undo() {
if (_history.isEmpty) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text('没有可撤销的步骤')),
);
return;
}
setState(() {
_pieces.clear();
_pieces.addAll(_history.removeLast());
_moveCount--;
});
}
void _movePiece(Piece piece, int dx, int dy) {
if (_canMoveTo(piece, piece.x + dx, piece.y + dy)) {
_saveState(); // 保存状态
// ... 执行移动
}
}
}7.2 关卡系统
dart
class Level {
final String name;
final String description;
final List<Piece> pieces;
Level({
required this.name,
required this.description,
required this.pieces,
});
}
class _KlotskiGamePageState extends State<KlotskiGamePage> {
int _currentLevel = 0;
late List<Level> _levels;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_levels = _loadLevels();
_loadLevel(_currentLevel);
}
List<Level> _loadLevels() {
return [
Level(
name: '横刀立马',
description: '经典布局',
pieces: [
Piece(name: '曹操', type: PieceType.caocao, x: 1, y: 0, width: 2, height: 2),
// ... 其他棋子
],
),
Level(
name: '指挥若定',
description: '第二关',
pieces: [...],
),
// ... 更多关卡
];
}
void _loadLevel(int index) {
final level = _levels[index];
setState(() {
_pieces.clear();
_pieces.addAll(level.pieces);
_moveCount = 0;
});
}
void _nextLevel() {
if (_currentLevel < _levels.length - 1) {
_loadLevel(++_currentLevel);
}
}
}7.3 计时功能
dart
class _KlotskiGamePageState extends State<KlotskiGamePage> {
Timer? _timer;
int _elapsedSeconds = 0;
void _startTimer() {
_stopTimer();
_timer = Timer.periodic(const Duration(seconds: 1), (timer) {
setState(() {
_elapsedSeconds++;
});
});
}
void _stopTimer() {
_timer?.cancel();
_timer = null;
}
String _formatTime(int seconds) {
final minutes = seconds ~/ 60;
final secs = seconds % 60;
return '${minutes.toString().padLeft(2, '0')}:${secs.toString().padLeft(2, '0')}';
}
}7.4 自动求解提示
dart
class _KlotskiGamePageState extends State<KlotskiGamePage> {
void _showHint() {
// 简单的提示:找出可以移动的棋子
List<Map<String, dynamic>> movablePieces = [];
for (var piece in _pieces) {
List<String> directions = [];
if (_canMoveTo(piece, piece.x, piece.y - 1)) directions.add('上');
if (_canMoveTo(piece, piece.x, piece.y + 1)) directions.add('下');
if (_canMoveTo(piece, piece.x - 1, piece.y)) directions.add('左');
if (_canMoveTo(piece, piece.x + 1, piece.y)) directions.add('右');
if (directions.isNotEmpty) {
movablePieces.add({
'piece': piece.name,
'directions': directions,
});
}
}
if (movablePieces.isEmpty) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text('没有可移动的棋子')),
);
} else {
showDialog(
context: context,
builder: (context) => AlertDialog(
title: const Text('可移动的棋子'),
content: Column(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: movablePieces.map((item) {
return ListTile(
title: Text(item['piece']),
subtitle: Text(item['directions'].join('、')),
);
}).toList(),
),
),
);
}
}
}八、性能优化策略
8.1 减少不必要的setState
dart
// 不推荐:每次移动都触发重绘
void _movePiece(Piece piece, int dx, int dy) {
setState(() {
piece.x += dx;
piece.y += dy;
});
}
// 推荐:只在位置实际改变时更新
void _movePiece(Piece piece, int dx, int dy) {
int newX = piece.x + dx;
int newY = piece.y + dy;
if (newX != piece.x || newY != piece.y) {
if (_canMoveTo(piece, newX, newY)) {
setState(() {
piece.x = newX;
piece.y = newY;
});
}
}
}8.2 优化碰撞检测
dart
// 不推荐:每次都检查所有棋子
bool _canMoveTo(Piece piece, int newX, int newY) {
for (var p in _pieces) {
if (_isColliding(piece, p)) return false;
}
return true;
}
// 推荐:只检查附近的棋子
bool _canMoveTo(Piece piece, int newX, int newY) {
// 只检查附近的棋子(+1范围)
for (var p in _pieces) {
if (p == piece) continue;
if ((p.x - newX).abs() <= piece.width + 1 &&
(p.y - newY).abs() <= piece.height + 1) {
if (_isColliding(piece, p)) return false;
}
}
return true;
}8.3 使用const构造函数
dart
// 推荐:使用const减少重建
const Positioned(
left: 0,
top: 0,
child: Text('曹操'),
)九、总结
本文深入讲解了华容道游戏中的手势识别和碰撞检测技术,主要内容包括:
- 手势识别:GestureDetector、Pan手势、方向检测
- 键盘事件:KeyboardListener、KeyEvent处理
- 焦点管理:FocusNode、焦点状态、视觉反馈
- 碰撞检测:AABB算法、矩形相交检测、多格子检测
- 移动验证:边界检查、碰撞检查、位置更新
- 功能扩展:撤销、关卡、计时、提示
- 性能优化:减少setState、优化碰撞检测
掌握这些技术可以让你开发出交互流畅、逻辑严谨的游戏应用。在实际项目中,还需要考虑用户体验、性能优化、错误处理等方面,确保应用的稳定性和可玩性。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区 : 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区