欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:推箱子游戏算法与关卡设计深度解析
文章目录
- [Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:推箱子游戏算法与关卡设计深度解析](#Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶:推箱子游戏算法与关卡设计深度解析)
-
- 摘要
- 一、推箱子算法基础
-
- [1.1 游戏状态表示](#1.1 游戏状态表示)
- [1.2 状态空间](#1.2 状态空间)
- 二、移动算法详解
-
- [2.1 基本移动逻辑](#2.1 基本移动逻辑)
- [2.2 推箱子逻辑](#2.2 推箱子逻辑)
- [2.3 碰撞检测流程](#2.3 碰撞检测流程)
- 三、自动求解算法
-
- [3.1 深度优先搜索(DFS)](#3.1 深度优先搜索(DFS))
- [3.2 广度优先搜索(BFS)](#3.2 广度优先搜索(BFS))
- [3.3 A*算法](#3.3 A*算法)
- 四、关卡设计原理
-
- [4.1 可解性判断](#4.1 可解性判断)
- [4.2 关卡生成算法](#4.2 关卡生成算法)
- [4.3 难度评估](#4.3 难度评估)
- 五、状态压缩与优化
-
- [5.1 状态哈希](#5.1 状态哈希)
- [5.2 双向BFS](#5.2 双向BFS)
- 六、算法复杂度分析
-
- [6.1 时间复杂度](#6.1 时间复杂度)
- [6.2 空间复杂度](#6.2 空间复杂度)
- 七、总结
摘要
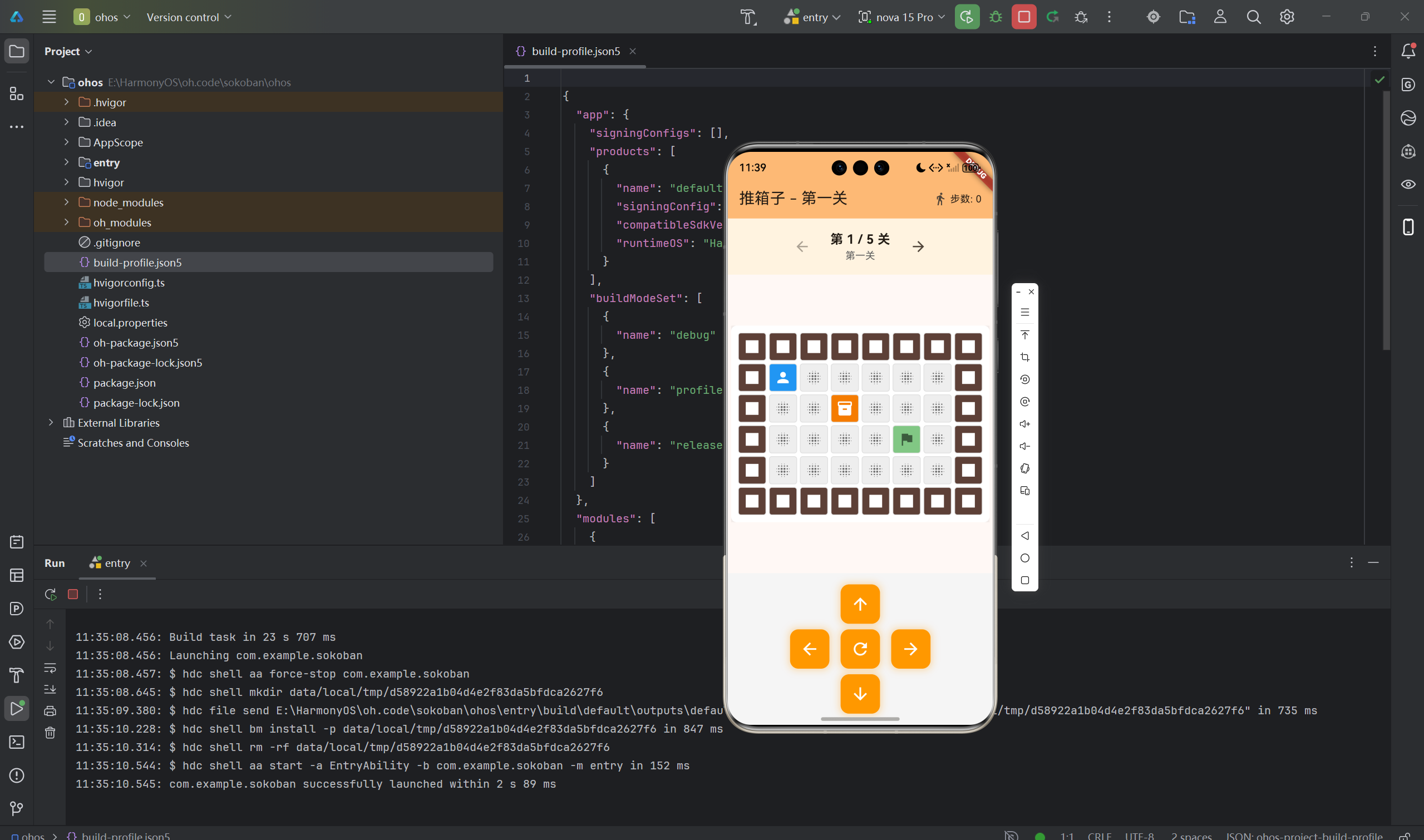
推箱子游戏不仅是有趣的益智游戏,更是理解算法和数据结构的绝佳案例。本文深入讲解推箱子游戏的核心算法实现、关卡设计原理、状态空间搜索、自动求解等高级技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握推箱子游戏的算法设计思路,了解如何使用递归回溯算法实现自动求解功能。
一、推箱子算法基础
1.1 游戏状态表示
推箱子游戏的状态可以用以下数据结构表示:
dart
class GameState {
final List<List<int>> map; // 地图
final Point player; // 玩家位置
final List<Point> boxes; // 箱子位置列表
GameState({
required this.map,
required this.player,
required this.boxes,
});
// 复制状态
GameState copy() {
return GameState(
map: map.map((row) => List<int>.from(row)).toList(),
player: Point(player.x, player.y),
boxes: boxes.map((p) => Point(p.x, p.y)).toList(),
);
}
}1.2 状态空间
推箱子游戏的状态空间包括:
- 玩家位置:地图上的任意空格
- 箱子位置:所有可能的组合
- 移动动作:上下左右四个方向
状态总数计算:
- 玩家位置:O(W×H)
- 箱子位置:O((W×H)^n),n为箱子数
- 总状态数:O(W×H×(W×H)^n)

二、移动算法详解
2.1 基本移动逻辑
dart
class MoveResult {
final bool success;
final GameState? newState;
final String? message;
MoveResult({required this.success, this.newState, this.message});
}
MoveResult tryMove(GameState state, int dx, int dy) {
final newX = state.player.x + dx;
final newY = state.player.y + dy;
// 边界检查
if (!_isValidPosition(newX, newY, state.map)) {
return MoveResult(success: false, message: '超出边界');
}
final targetCell = state.map[newY][newX];
// 碰到墙
if (targetCell == 1) {
return MoveResult(success: false, message: '碰到墙壁');
}
// 碰到箱子
if (targetCell == 2 || targetCell == 5) {
return _tryPushBox(state, newX, newY, dx, dy);
}
// 移动到空地
final newState = state.copy();
newState.player = Point(newX, newY);
return MoveResult(success: true, newState: newState);
}2.2 推箱子逻辑
dart
MoveResult _tryPushBox(GameState state, int boxX, int boxY, int dx, int dy) {
final boxNewX = boxX + dx;
final boxNewY = boxY + dy;
// 检查箱子新位置
if (!_isValidPosition(boxNewX, boxNewY, state.map)) {
return MoveResult(success: false, message: '箱子超出边界');
}
final boxTargetCell = state.map[boxNewY][boxNewX];
// 箱子后面是障碍
if (boxTargetCell == 1 || boxTargetCell == 2 || boxTargetCell == 5) {
return MoveResult(success: false, message: '箱子被阻挡');
}
// 创建新状态
final newState = state.copy();
// 更新箱子位置
final boxIndex = state.boxes.indexWhere((p) => p.x == boxX && p.y == boxY);
newState.boxes[boxIndex] = Point(boxNewX, boxNewY);
// 更新地图
if (state.map[boxY][boxX] == 5) {
newState.map[boxY][boxX] = 3; // 从目标点移开
} else {
newState.map[boxY][boxX] = 0; // 从空地移开
}
if (boxTargetCell == 3) {
newState.map[boxNewY][boxNewX] = 5; // 推到目标点
} else {
newState.map[boxNewY][boxNewX] = 2; // 推到空地
}
// 移动玩家
newState.player = Point(boxX, boxY);
return MoveResult(success: true, newState: newState);
}2.3 碰撞检测流程
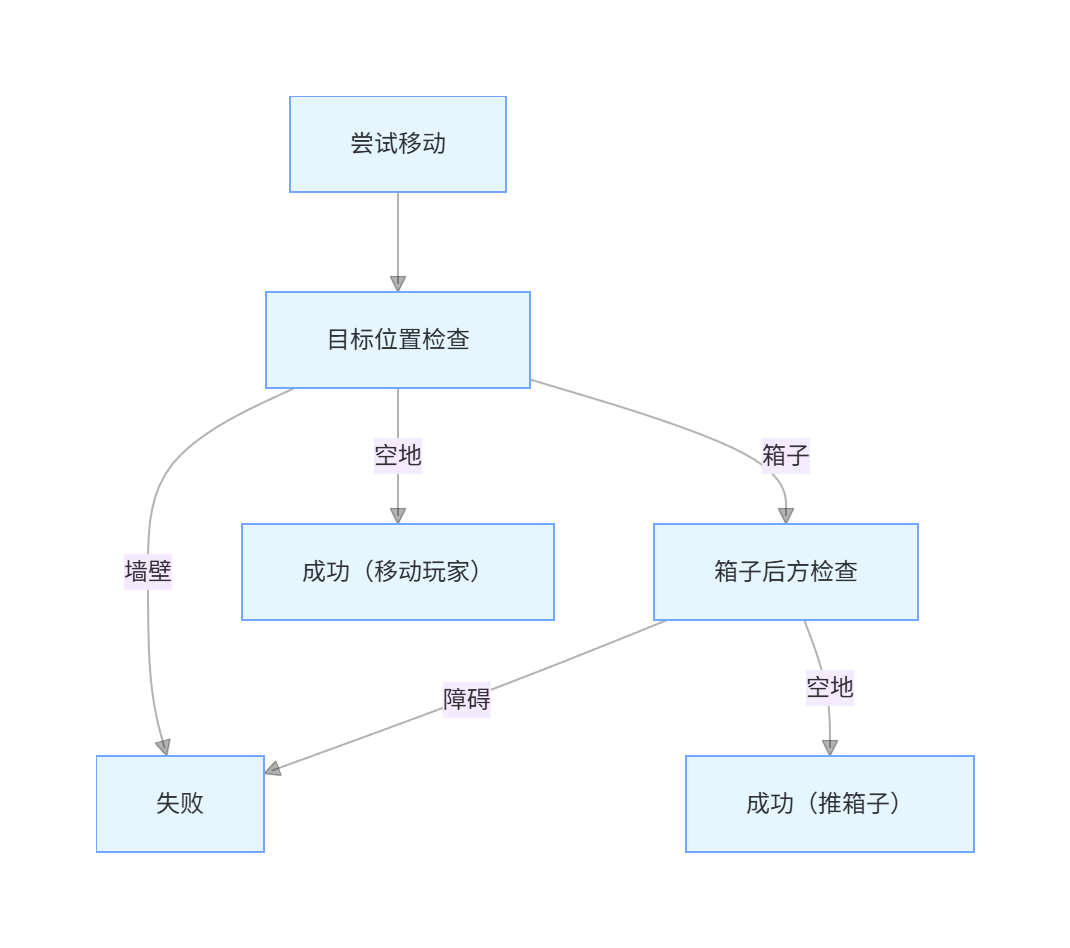
三、自动求解算法
3.1 深度优先搜索(DFS)
dart
class Solution {
final List<MoveDirection> moves;
final int steps;
Solution({required this.moves, required this.steps});
}
Solution? solveDFS(GameState initial, int maxDepth) {
final visited = <String>{};
final moves = <MoveDirection>[];
Solution? _dfs(GameState state, int depth) {
// 检查胜利
if (_isWin(state)) {
return Solution(moves: List.from(moves), steps: moves.length);
}
// 达到最大深度
if (depth >= maxDepth) {
return null;
}
// 记录访问状态
final stateKey = _getStateKey(state);
if (visited.contains(stateKey)) {
return null;
}
visited.add(stateKey);
// 尝试四个方向
for (final direction in MoveDirection.values) {
final result = _tryMove(state, direction);
if (result.success && result.newState != null) {
moves.add(direction);
final solution = _dfs(result.newState!, depth + 1);
if (solution != null) {
return solution;
}
moves.removeLast();
}
}
return null;
}
return _dfs(initial, 0);
}3.2 广度优先搜索(BFS)
dart
Solution? solveBFS(GameState initial) {
final queue = <_Node>[];
final visited = <String>{};
queue.add(_Node(initial, []));
visited.add(_getStateKey(initial));
while (queue.isNotEmpty) {
final current = queue.removeAt(0);
// 检查胜利
if (_isWin(current.state)) {
return Solution(moves: current.moves, steps: current.moves.length);
}
// 尝试四个方向
for (final direction in MoveDirection.values) {
final result = _tryMove(current.state, direction);
if (result.success && result.newState != null) {
final stateKey = _getStateKey(result.newState!);
if (!visited.contains(stateKey)) {
visited.add(stateKey);
queue.add(_Node(
result.newState!,
[...current.moves, direction],
));
}
}
}
}
return null; // 无解
}
class _Node {
final GameState state;
final List<MoveDirection> moves;
_Node(this.state, this.moves);
}3.3 A*算法
dart
Solution? solveAStar(GameState initial) {
final openSet = <_AStarNode>[];
final closedSet = <String>{};
final startNode = _AStarNode(
state: initial,
gScore: 0,
fScore: _heuristic(initial),
moves: [],
);
openSet.add(startNode);
while (openSet.isNotEmpty) {
// 找到fScore最小的节点
openSet.sort((a, b) => a.fScore.compareTo(b.fScore));
final current = openSet.removeAt(0);
// 检查胜利
if (_isWin(current.state)) {
return Solution(moves: current.moves, steps: current.moves.length);
}
final stateKey = _getStateKey(current.state);
if (closedSet.contains(stateKey)) {
continue;
}
closedSet.add(stateKey);
// 尝试四个方向
for (final direction in MoveDirection.values) {
final result = _tryMove(current.state, direction);
if (result.success && result.newState != null) {
final newKey = _getStateKey(result.newState!);
if (closedSet.contains(newKey)) continue;
final gScore = current.gScore + 1;
final hScore = _heuristic(result.newState!);
final fScore = gScore + hScore;
openSet.add(_AStarNode(
state: result.newState!,
gScore: gScore,
fScore: fScore,
moves: [...current.moves, direction],
));
}
}
}
return null;
}
class _AStarNode {
final GameState state;
final int gScore; // 从起点到当前的实际代价
final int fScore; // gScore + hScore
final List<MoveDirection> moves;
_AStarNode({
required this.state,
required this.gScore,
required this.fScore,
required this.moves,
});
}
// 启发函数:估算到目标的距离
int _heuristic(GameState state) {
int totalDistance = 0;
for (final box in state.boxes) {
// 找到最近的目标点
int minDist = double.maxFinite.toInt();
for (int y = 0; y < state.map.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < state.map[y].length; x++) {
if (state.map[y][x] == 3) {
final dist = (box.x - x).abs() + (box.y - y).abs();
if (dist < minDist) {
minDist = dist;
}
}
}
}
totalDistance += minDist;
}
return totalDistance;
}四、关卡设计原理
4.1 可解性判断
一个关卡是可解的必要条件:
dart
bool isSolvable(GameState state) {
// 1. 检查是否所有箱子都能到达目标点
if (!_allBoxesReachable(state)) {
return false;
}
// 2. 检查是否有箱子被卡在角落
if (_hasStuckBox(state)) {
return false;
}
// 3. 检查玩家是否能到达所有必要位置
if (!_playerCanReachAll(state)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool _allBoxesReachable(GameState state) {
for (final box in state.boxes) {
bool canReachTarget = false;
for (int y = 0; y < state.map.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < state.map[y].length; x++) {
if (state.map[y][x] == 3) {
if (_canReach(state, box, Point(x, y))) {
canReachTarget = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (canReachTarget) break;
}
if (!canReachTarget) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool _hasStuckBox(GameState state) {
for (final box in state.boxes) {
// 检查是否在目标点上
if (state.map[box.y][box.x] == 3) continue;
// 检查是否在角落(两边是墙)
final leftIsWall = _isWall(state, box.x - 1, box.y);
final rightIsWall = _isWall(state, box.x + 1, box.y);
final topIsWall = _isWall(state, box.x, box.y - 1);
final bottomIsWall = _isWall(state, box.x, box.y + 1);
if ((leftIsWall && topIsWall) ||
(leftIsWall && bottomIsWall) ||
(rightIsWall && topIsWall) ||
(rightIsWall && bottomIsWall)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}4.2 关卡生成算法
dart
class LevelGenerator {
final int width;
final int height;
final int boxCount;
final Random _random = Random();
LevelGenerator({
required this.width,
required this.height,
required this.boxCount,
});
GameState generate() {
while (true) {
final level = _generateLevel();
if (level != null && isSolvable(level)) {
return level;
}
}
}
GameState? _generateLevel() {
// 创建空地图
final map = List.generate(
height,
(y) => List.generate(width, (x) => 0),
);
// 添加边界墙
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
map[0][x] = 1;
map[height - 1][x] = 1;
}
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
map[y][0] = 1;
map[y][width - 1] = 1;
}
// 随机放置一些内部墙壁
final wallCount = (width * height * 0.1).toInt();
for (int i = 0; i < wallCount; i++) {
final x = _random.nextInt(width - 2) + 1;
final y = _random.nextInt(height - 2) + 1;
map[y][x] = 1;
}
// 放置玩家
final player = _findEmptyPosition(map);
if (player == null) return null;
// 放置目标点和箱子
final targets = <Point>[];
final boxes = <Point>[];
for (int i = 0; i < boxCount; i++) {
final target = _findEmptyPosition(map);
if (target == null) return null;
map[target.y][target.x] = 3;
targets.add(target);
final box = _findEmptyPosition(map);
if (box == null) return null;
map[box.y][box.x] = 2;
boxes.add(box);
}
return GameState(
map: map,
player: player,
boxes: boxes,
);
}
Point? _findEmptyPosition(List<List<int>> map) {
final empty = <Point>[];
for (int y = 1; y < height - 1; y++) {
for (int x = 1; x < width - 1; x++) {
if (map[y][x] == 0) {
empty.add(Point(x, y));
}
}
}
if (empty.isEmpty) return null;
return empty[_random.nextInt(empty.length)];
}
}4.3 难度评估
dart
class DifficultyEvaluator {
int evaluate(GameState state) {
int score = 0;
// 1. 箱子数量
score += state.boxes.length * 10;
// 2. 箱子到目标点的总距离
int totalDistance = 0;
for (final box in state.boxes) {
int minDist = double.maxFinite.toInt();
for (int y = 0; y < state.map.length; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < state.map[y].length; x++) {
if (state.map[y][x] == 3) {
final dist = (box.x - x).abs() + (box.y - y).abs();
if (dist < minDist) {
minDist = dist;
}
}
}
}
totalDistance += minDist;
}
score += totalDistance * 2;
// 3. 障碍物密度
int obstacleCount = 0;
for (final row in state.map) {
for (final cell in row) {
if (cell == 1) obstacleCount++;
}
}
score += (obstacleCount / (state.map.length * state.map[0].length) * 50).toInt();
return score;
}
String getDifficultyLabel(int score) {
if (score < 30) return '简单';
if (score < 60) return '中等';
if (score < 100) return '困难';
return '专家';
}
}五、状态压缩与优化
5.1 状态哈希
dart
String _getStateKey(GameState state) {
// 压缩状态为字符串
final buffer = StringBuffer();
// 玩家位置
buffer.write('${state.player.x},${state.player.y};');
// 箱子位置(排序后)
final sortedBoxes = List<Point>.from(state.boxes);
sortedBoxes.sort((a, b) => a.y != b.y ? a.y.compareTo(b.y) : a.x.compareTo(b.x));
for (final box in sortedBoxes) {
buffer.write('${box.x},${box.y};');
}
return buffer.toString();
}5.2 双向BFS
dart
Solution? solveBidirectionalBFS(GameState initial) {
final forwardQueue = <_Node>[];
final backwardQueue = <_Node>[];
final forwardVisited = <String, _Node>{};
final backwardVisited = <String, _Node>{};
final startNode = _Node(initial, []);
forwardQueue.add(startNode);
forwardVisited[_getStateKey(initial)] = startNode;
// 从目标状态开始
final goal = _createGoalState(initial);
final goalNode = _Node(goal, []);
backwardQueue.add(goalNode);
backwardVisited[_getStateKey(goal)] = goalNode;
while (forwardQueue.isNotEmpty && backwardQueue.isNotEmpty) {
// 正向搜索一步
if (_stepBFS(forwardQueue, forwardVisited, backwardVisited) case Solution solution) {
return solution;
}
// 反向搜索一步
if (_stepBFS(backwardQueue, backwardVisited, forwardVisited) case Solution solution) {
return _reverseSolution(solution);
}
}
return null;
}六、算法复杂度分析
6.1 时间复杂度
| 算法 | 时间复杂度 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| DFS | O(b^d) | b为分支数(4),d为最大深度 |
| BFS | O(b^d) | 最坏情况遍历整个状态空间 |
| A* | O(b^d) | 实际通常优于BFS |
6.2 空间复杂度
| 算法 | 空间复杂度 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| DFS | O(d) | 递归栈深度 |
| BFS | O(b^d) | 需要存储所有状态 |
| A* | O(b^d) | 需要存储openSet和closedSet |
七、总结
本文深入讲解了推箱子游戏的算法实现,主要内容包括:
- 游戏状态:状态表示、状态空间
- 移动算法:碰撞检测、推箱子逻辑
- 自动求解:DFS、BFS、A*算法
- 关卡设计:可解性判断、随机生成
- 难度评估:多因素综合评分
- 优化技术:状态压缩、双向搜索
掌握这些算法可以让你设计出更有挑战性和趣味性的推箱子关卡。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区 : 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区