哈希(散列)方法:通过某种函数hashFunc使元素的储存位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,从而快速查找元素。这种方法构造出来的转换函数称为哈希函数,散列函数,构造出来的结构称为哈希表
一.哈希函数
引入:
- 我们知道数组的优势在于快速查找某个元素,拿到数组的下标(索引)就直接可以定位到元素的位置
- 如果想知道一组元素出现的个数,可以创建一个范围足够大的数组,数组内每一个元素值代表相应元素出现的次数,如果插入元素i,就执行A[i]++,删除元素执行A[i]--,搜索元素时检查A[i]是否为0,这种做法用空间换时间
- 缺点:浪费空间,当遇到字符串时的编码问题
- 于是需要一种映射函数将大数映射成小数(散列函数),例如:hash[key] = key % size
- 问题:不同的元素被映射到相同的位置,产生哈希冲突
- 解决:线性探测,二次探测,开链...
常见哈希函数
- 直接定址法:hash[key] = A*key + B,需要事先知道关键字的分布
- 除留余数法:hash[key] = key % p,将关键码转换成哈希地址
- 平方取中法:对key平方取中间三位,例如:1234平方,取1522756中间3位,227
- 数学分析法:取一组数重复次数最少,得到几位数字,将其反转,右环位移,左环位移。例如电话号码取后四位,得到2345,反转后5432,右换位移5234
二.哈希冲突的解决
闭散列:
闭散列(开放定址法),当出现哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未填满,可以把key存放到冲突位置的下一个空位置
寻找方法
- 线性探测:从冲突位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻到下一个空位置
- 删除:采用闭散列处理哈希冲突,不能随便删除哈希表已有元素,若直接删除元素会影响其他元素的搜索(索引改变),所以线性探测采用标记的伪删除来删除元素
- 一旦发生哈希冲突,所有冲突连在一起,容易产生产生数据堆积
- 标记:EXIST,EMPTY,DELETE
- 二次探测:H = H+ i^2
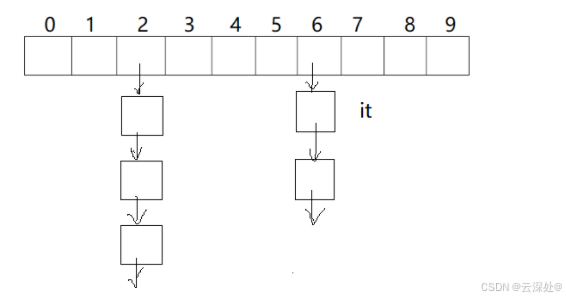
- 开散列:利用哈希桶(数组里面存的链表的地址)
三.哈希表的实现
线性探测:
cpp
enum STATE
{
EXIST,
EMPTY,
DELETE
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
STATE _state = EMPTY;
};
template<class K>
struct DefaultFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key; //转成无符号整型
}
};
template<> //类模板的全特化
struct DefaultFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : str)
{
hash *= 131;
hash += ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class K, class V, class HashFunc = DefaultFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
//构造函数
HashTable()
{
_table.resize(10);
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
static HashFunc hf;
//最低扩容标准
if (_n * 10 / _table.size() >= 7)
{
size_t nsize = _table.size() * 2;
//遍历旧表,重新映射新表
HashTable<K, V> newtable;
newtable._table.resize(nsize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_table[i]._state == EXIST)
{
newtable.Insert(_table[i]._kv);
}
}
_table.swap(newtable._table);
}
//线性探测
size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();
while (_table[hashi]._state == EXIST)
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _table.size();
}
_table[hashi]._kv = kv;
_table[hashi]._state = EXIST;
_n++;
return true;
}
HashData<const K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _table.size();
while (_table[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_table[hashi]._state == EXIST && _table[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return (HashData<const K, V>) & _table[hashi];
}
hashi++;
return nullptr;
}
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashData<const K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
_n--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
void Print()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_table[i]._state == EXIST)
{
cout << "键" << ":" << _table[i]._kv.first << "值:" << _table[i]._kv.second << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
vector<HashData<K, V>> _table; //编译器对内置类型不做处理,自定义类型调用析构
size_t _n = 0;
};开散列:
cpp
namespace hash_bucket
{
template<class K>
struct DefaultFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
template<>
struct DefaultFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& kv)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : kv)
{
hash *= 131; //哈希算法,处理字符串
hash += ch;
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv) :_kv(kv), _next(nullptr) {}
};
template<class K, class V, class HashFunc = DefaultFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
HashTable()
{
_table.resize(10, nullptr);
}
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
}
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
static HashFunc hf;
if (_n == _table.size())
{
size_t newSize = _table.size() * 2;
vector<Node*> newTable(newSize, nullptr);
//遍历新链表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hf(cur->_kv.first) % newSize;
cur->_next = newTable[hashi];
newTable[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
_table.swap(newTable);
}
size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_next = _table[hashi]; //头插
_table[hashi] = newnode;
_n++;
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_table[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
_n--;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
void Print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
printf("[%d]->", i);
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
cout << cur->_kv.first << ":" << cur->_kv.second << "->";
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _table; //指针数组,vector被delete后,Node*指向的空间还未删除,需要析构
size_t _n = 0;
};
}