文章目录

一、项目介绍
使用SSM框架实现一个简单的博客系统
共5个页面
- 用户登录
- 博客发表页
- 博客编辑页
- 博客列表页
- 博客详情页
共9个功能
- 实现博客列表
- 实现博客详情
- 实现登录
- 实现强制要求登录
- 实现显示用户信息
- 实现用户退出
- 实现发布博客
- 实现删除/编辑博客
- 密码加密/加盐
功能描述:
用户登录成功后,可以查看所有人的博客。点击<<查看全文>>可以查看该博客的正文内容,如果该博客作者为当前登录用户,可以完成博客的修改和删除操作,以及发表新博客。
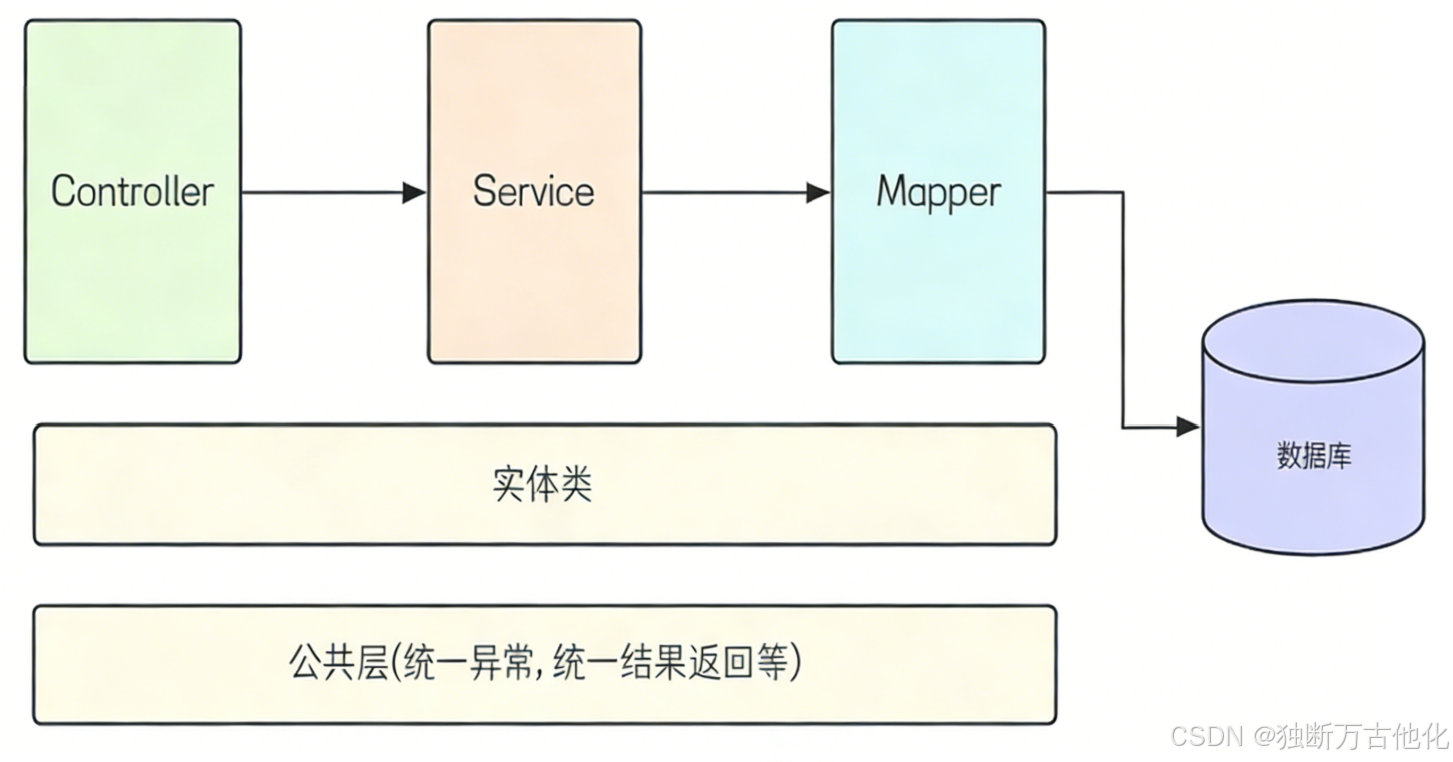
项目分层:项目分为控制层。服务层,持久层,各层级之间关系如下图。
二、项目准备
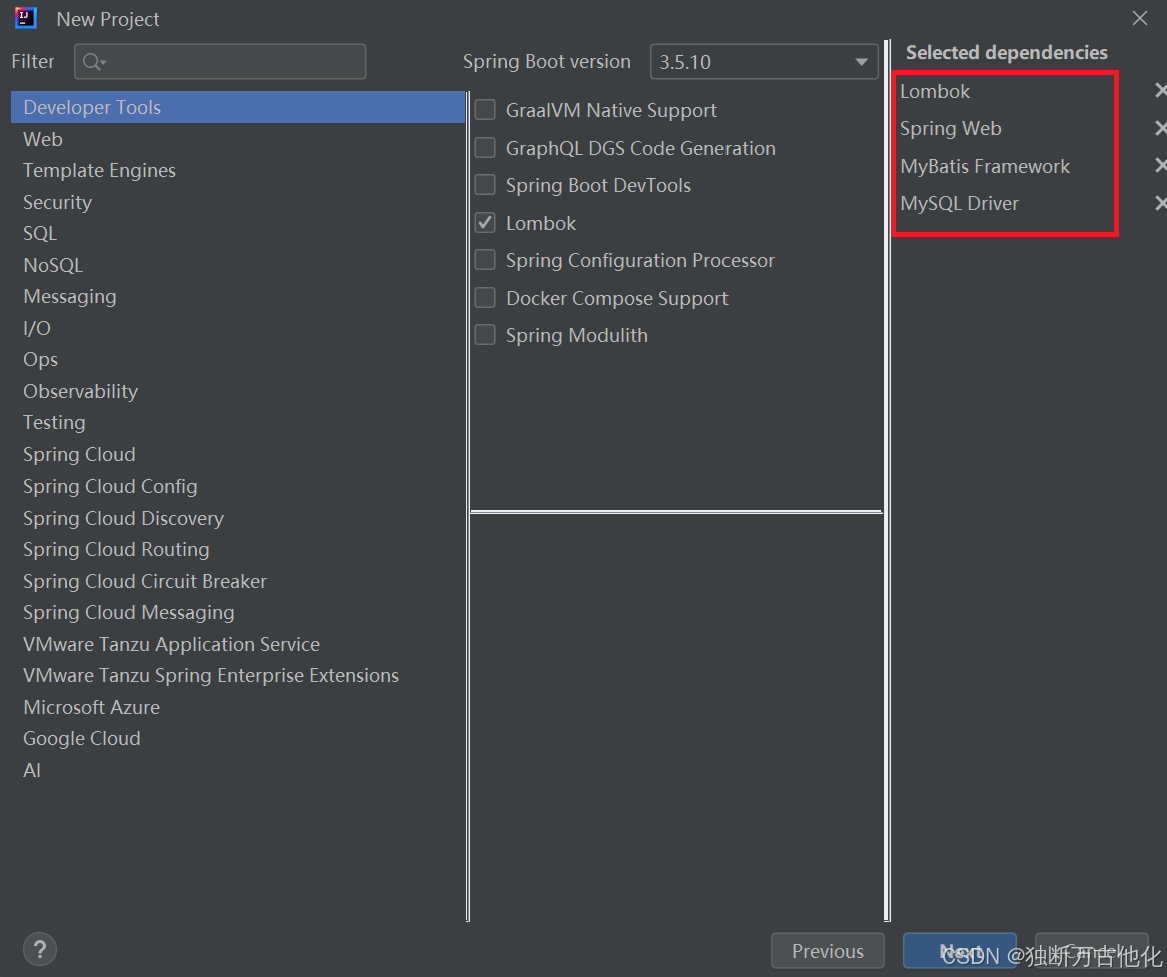
创建SpringBoot项目,并添加Spring MVC 和MyBatis的对应依赖。
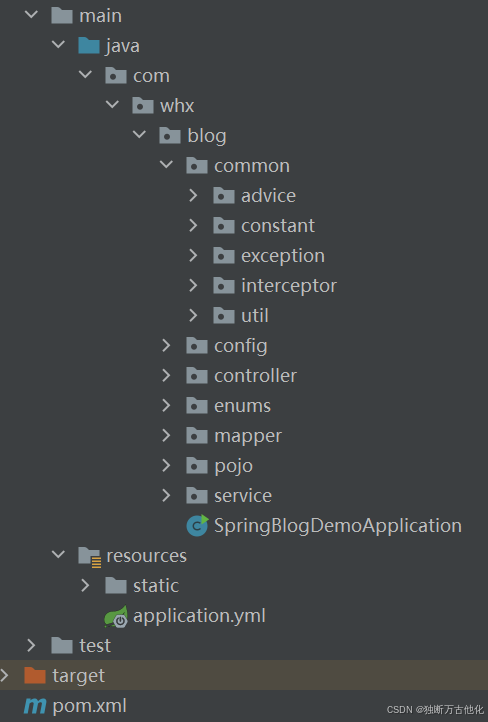
创建相应的目录
添加配置文件内容:
yaml
spring:
application:
name: spring-blog-demo
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/blog?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
logging:
file:
name: spring-blog.log三、项目公共模块
3.1 统一返回数据格式
首先定义统一返回结果的实体类:
- code:业务状态码
- errMsg:业务失败错误信息
- deta:业务返回数据
定义业务状态枚举:
java
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum ResultCodeEnum {
// -1 : 未登录 -2 : 后端出错 200 业务处理成功
SUCCESS(200),
ERROR(-2),
UNLOGIN(-1);
@Getter
private int code;
}业务实体类(如有其他返回形式可自行添加):
java
@Data
public class Result<T>{
private int code;
private String message;
private T data;
public static <T> Result<T> ok(T data){
Result<T> result = new Result<>();
result.setCode(ResultCodeEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
result.setData(data);
return result;
}
public static <T> Result<T> error(String errorMsg){
Result<T> result = new Result<>();
result.setCode(ResultCodeEnum.ERROR.getCode());
result.setMessage(errorMsg);
return result;
}
}统一返回结果(具体返回格式可自行添加):
java
@ControllerAdvice
public class ResponseAdvice implements ResponseBodyAdvice {
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class converterType) {
return true;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public Object beforeBodyWrite(Object body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
// 逻辑可自行处理
}
}3.2 统一异常处理
- 自定义项目异常
java
@Getter
public class BlogException extends RuntimeException{
private int code;
private String message;
public BlogException(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public BlogException(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
}- 统一异常处理(若想处理其他异常可添加处理其他异常方法)
java
@ResponseBody
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler
public Result error(Exception e){
log.error("发生异常,e",e);
return Result.error(e.getMessage());
}
}四、项目业务层
4.1 持久层处理
使用 MybatisPlus 来完成持久层代码开发,创建mapper 实现BaseMapper 即可,BaseMapper 中已经定义了大多数基本的CRUD操作
java
@Mapper
public interface BlogInfoMapper extends BaseMapper<BlogInfo> {
}
@Mapper
public interface UserInfoMapper extends BaseMapper<UserInfo> {
}4.2 实现博客列表
首先要约定前后端接口,方便后端数据返回与接收数据请求
- 基本信息
- 接口路径 :
/blog/getList - 请求方式 :
GET - 接口描述:获取所有博客的列表数据,包含博客ID、标题、内容、作者ID及更新时间。
-
请求参数
该接口无需传入额外请求参数。
-
响应示例
json
{
"code": 200,
"message": null,
"data": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "第一篇博客",
"content": "我是博客正文我是博客正文我是博客正文",
"createTime": "2026-02-03 21:48:43"
}
]
}根据接口描述,客服端给服务端发送一个/blog/getlist 的请求,服务端给客户端返回JSON格式的数据。
因为接口返回实体和数据库表对应定义的实体类不一致,因此可以额外创建一个接口实体类用来返回。也就是客户端需要什么,就返回什么,而不是讲数据库中内容全部返回。
实现 Controller 层:
java
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("blog")
public class BlogController {
@Resource(name = "blogService")
private BlogService blogService;
@GetMapping("/getList")
public List<BlogInfoResponse> getList(){
log.info("查询博客列表");
return blogService.getList();
}
}实现 Service 层:
Service 的采用接口对外提供服务,实现类使用Impl的后缀和接口进行区别。
java
public interface BlogService {
List<BlogInfoResponse> getList();
}
java
@Service("blogService")
public class BlogServiceImpl implements BlogService {
@Resource(name = "blogInfoMapper")
private BlogInfoMapper blogInfoMapper;
@Override
public List<BlogInfoResponse> getList() {
List<BlogInfo> blogInfos = blogInfoMapper.selectList(
new LambdaQueryWrapper<BlogInfo>().eq(BlogInfo::getDeleteFlag, Constants.NOT_DELETE)
.orderByDesc(BlogInfo::getUpdateTime));
return blogInfos.stream().map(blogInfo -> BeanTransUtils.trans(blogInfo))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}因为从数据库中查询到数据和需要返回的实体不一样,所以做一个数据的转换。数据格式转换可以单独抽取出来放入公共模块处理:代码如下:
抽取数据转换:
java
public static BlogInfoResponse trans(BlogInfo blogInfo){
BlogInfoResponse response = new BlogInfoResponse();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(blogInfo,response);
return response;
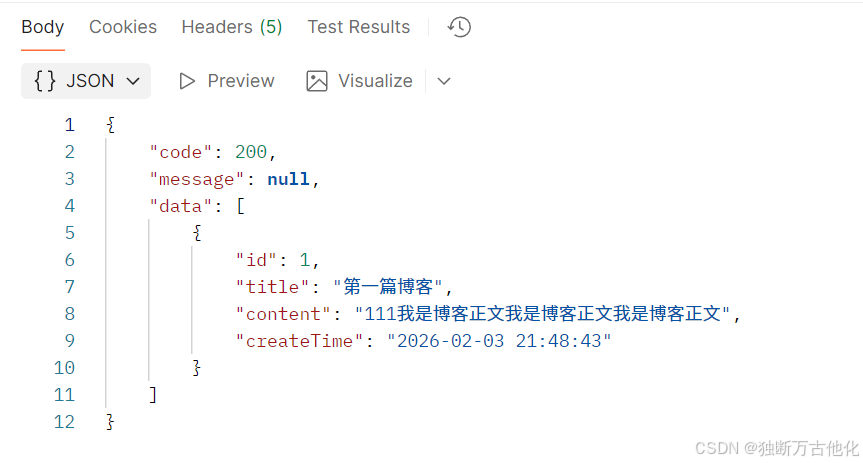
}验证接口发现成功查询到博客列表信息:
3.3 实现博客详情
功能:根据当前的博客Id从服务器动态获取博客内容
约定前后端交互接口:
- 基本信息
- 接口路径 :
/blog/getBlogDetail - 请求方式 :
GET - 接口描述:根据博客ID获取单篇博客的详细信息。
- 请求参数
| 参数名 | 类型 | 是否必填 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
blogId |
Integer |
是 | 博客唯一ID,如:1 |
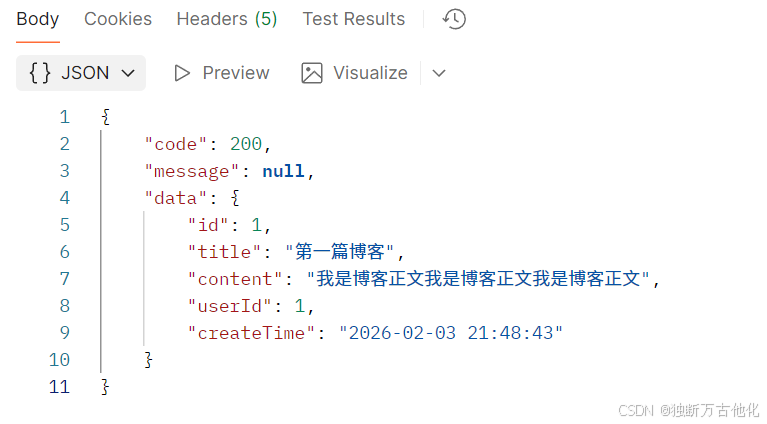
- 响应示例
json
{
"code": 200,
"message": null,
"data": {
"id": 1,
"title": "第一篇博客",
"content": "我是博客正文我是博客正文我是博客正文",
"userId": 1,
"createTime": "2026-02-03 21:48:43"
}
}实现 Controller 层:
java
@GetMapping("/getBlogDetail")
public BlogInfoGetDetailResponse getBlogDetail(@NotNull(message = "blogId 不能为null") Integer blogId){
log.info("查询博客详情,blogId:{}",blogId);
return blogService.getBlogDetail(blogId);
}实现 Service 层:
java
@Override
public BlogInfoGetDetailResponse getBlogDetail(Integer blogId) {
return BeanTransUtils.transDetail(getBlogInfo(blogId));
}因为接口返回实体与上面一样,因此需要进行数据转换处理,代码如上个接口类似。
3.3.1 参数校验:jakarta.validation
在这个接口中,blogId 的值不能为null,可以借助jakarta.validation来进行参数的校验,避免自己繁琐的处理。
- javax.validation 是 Java Bean Validation API 的包名,这个 API 允许开发者通过注解(如
@NotNull、@NotBlank、@Null等)来声明对象的验证规则,然后在运行时自动验证这些对象。
常见注解
| 注解 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @NotBlank | CharSequence子类型 | 验证注解的元素值不为空(不为null、去除首位空格后长度为0) |
| @NotEmpty | CharSequence子类型、Collection、Map、数组 | 验证注解的元素值不为null且不为空(字符串长度不为0、集合大小不为0) |
| @NotNull | 任意类型 | 验证注解的元素值不是null |
在 Spring Boot 项目中使用时,添加以下依赖即可:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>测试接口发现后端数据正确返回:
该篇文章介绍项目的前置工作和博客列表的实现以及博客详情展示工作,其余功能将在后续不断完善。