系列文章目录
- 【3DV 进阶-4】VecSet 论文+代码对照理解
- 【3DV 进阶-5】3D生成中 Inductive Bias (归纳偏置)的技术路线图
- 【3DV 进阶-6】为什么3D点云是无序集合?而2D图片是有序的呢?
- 【3DV 进阶-7】Hunyuan3D2.1-ShapeVAE 整体流程
- 【3DV 进阶-10】Trellis 中的表示 SLat 理解
- 【3DV 进阶-11】Trellis.2 数据处理与训练流程图
- 【3DV 进阶-12】Trellis.2 数据处理脚本细节
- 【3D-AICG 系列-1】Trellis v1 和 Trellis v2 的区别和改进
- 【3D-AICG 系列-2】Trellis 2 的O-voxel (上) Shape: Flexible Dual Grid
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- [Volumetric Surface Attributes:PBR ↔ O-Voxel 材质转换详解](#Volumetric Surface Attributes:PBR ↔ O-Voxel 材质转换详解)
-
- 概述
-
- [支持的 PBR 属性](#支持的 PBR 属性)
- [Part 1: PBR → O-Voxel(编码)](#Part 1: PBR → O-Voxel(编码))
-
- 整体流程
- [Step 1: Voxel from FDG(从 Flexible Dual Grid 获取体素)](#Step 1: Voxel from FDG(从 Flexible Dual Grid 获取体素))
- [Step 2: Project to Surface(投影到表面)](#Step 2: Project to Surface(投影到表面))
- [Step 3: Sample Texture Map(采样纹理贴图)](#Step 3: Sample Texture Map(采样纹理贴图))
-
- [3.1 计算 UV 坐标](#3.1 计算 UV 坐标)
- [3.2 计算 Mipmap Level](#3.2 计算 Mipmap Level)
- [3.3 Mipmap 采样](#3.3 Mipmap 采样)
- [3.4 纹理包装模式](#3.4 纹理包装模式)
- [3.5 采样所有 PBR 属性](#3.5 采样所有 PBR 属性)
- [Step 4: 加权平均](#Step 4: 加权平均)
- [Part 2: O-Voxel → Material(解码)](#Part 2: O-Voxel → Material(解码))
-
- [Step 1: Query from Texel/Vertices](#Step 1: Query from Texel/Vertices)
- [Step 2: Trilinear Interpolation](#Step 2: Trilinear Interpolation)
- 完整数据流
- 关键技术点
-
- [1. Mipmap 构建](#1. Mipmap 构建)
- [2. 法向量变换](#2. 法向量变换)
- [3. Alpha 模式处理](#3. Alpha 模式处理)
- 代码索引
- [与 FDG 的关系](#与 FDG 的关系)
Trellis 2 中的 O-voxel 分为 Shape 和 Material 两个部分,本文聚焦于 Material: Volumetric Surface Attributes 这部分,关于 Shape 的介绍在上一篇文章。
Volumetric Surface Attributes:PBR ↔ O-Voxel 材质转换详解
基于 TRELLIS 2 源码 voxel/src/convert/volumetic_attr.cpp
的 PBR 材质体素化分析
概述
O-Voxel 不仅存储几何信息,还支持 Volumetric Surface Attributes(体积化表面属性),将 PBR 材质"烘焙"到稀疏体素中。
┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐
│ Textured Mesh │ ═══► 编码 (Encode) ═══► │ O-Voxel │
│ (PBR Materials) │ │ (Volumetric Attr)│
│ │ ◄═══ 解码 (Decode) ◄═══ │ │
└──────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘
支持的 PBR 属性
| 属性 | 通道数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Base Color | 3 | 基础颜色 (RGB) |
| Metallic | 1 | 金属度 |
| Roughness | 1 | 粗糙度 |
| Emissive | 3 | 自发光颜色 |
| Alpha | 1 | 透明度 |
| Normal | 3 | 法向量 |
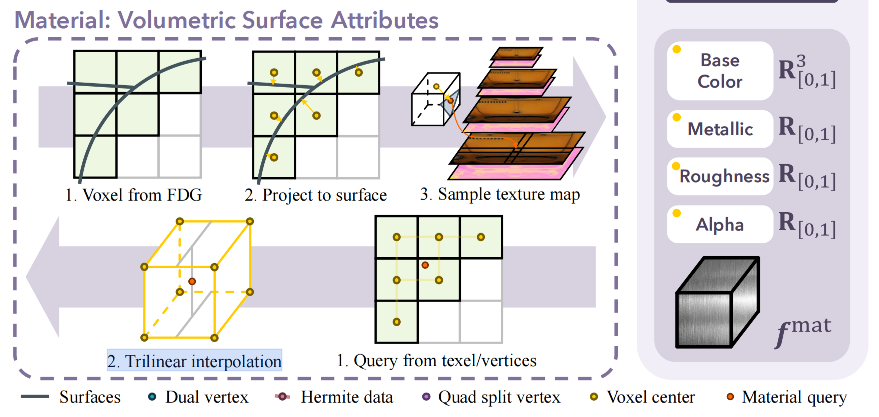
Part 1: PBR → O-Voxel(编码)
整体流程
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 1. Voxel from │ │ 2. Project to │ │ 3. Sample │
│ FDG │ ─► │ Surface │ ─► │ Texture │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘Step 1: Voxel from FDG(从 Flexible Dual Grid 获取体素)
目标:复用几何体素化的结果,确定哪些体素需要采样材质
算法 :与 flexible_dual_grid.cpp 相同的扫描线填充
cpp
// volumetic_attr.cpp: 第 421-485 行
// 找出与三角形相交的体素(复用 FDG 的扫描线算法)
std::unordered_set<VoxelCoord> intersected_voxels;
auto scan_line_fill = [&](const int ax2) {
// 从 x/y/z 三个方向扫描三角形
for (int y_idx = start; y_idx < end; ++y_idx) {
for (int x_idx = line_start; x_idx < line_end; ++x_idx) {
double z = lerp(...);
// 标记 4 个相邻体素
for (dx, dy in {0,1} × {0,1}) {
intersected_voxels.insert(coord);
}
}
}
};
scan_line_fill(0);
scan_line_fill(1);
scan_line_fill(2);关键点:几何和材质使用相同的体素集合,保证对齐。
Step 2: Project to Surface(投影到表面)
目标:将体素中心投影到三角形表面,获取重心坐标用于插值
cpp
// volumetic_attr.cpp: 第 125-151 行
static Eigen::Vector4f project_onto_triangle(
const Eigen::Vector3f& p, // 体素中心
const Eigen::Vector3f& a, // 三角形顶点
const Eigen::Vector3f& b,
const Eigen::Vector3f& c,
const Eigen::Vector3f& n // 面法向量
) {
// 1. 计算点到平面的距离
float d = (p - a).dot(n);
// 2. 投影到平面
Eigen::Vector3f p_proj = p - d * n;
// 3. 计算重心坐标 (u, v, w)
// 使用 Cramer 法则求解
float denom = d00 * d11 - d01 * d01;
float v = (d11 * d20 - d01 * d21) / denom;
float w = (d00 * d21 - d01 * d20) / denom;
float u = 1.0f - v - w;
return Eigen::Vector4f(u, v, w, d); // 返回重心坐标 + 距离
}图示:
体素中心 p
│
│ d (距离)
↓
────────●──────── 三角形平面
/│\
/ │ \
/ │ \
a───●───b 投影点 p_proj
\ 重心坐标 (u,v,w)
c用途:
- 重心坐标
(u, v, w)用于插值 UV 和法向量 - 距离
d用作权重(越近权重越大)
Step 3: Sample Texture Map(采样纹理贴图)
3.1 计算 UV 坐标
cpp
// 第 498-501 行
// 使用重心坐标插值 UV
Eigen::Vector2f uv = {
barycentric.x() * uv0.x() + barycentric.y() * uv1.x() + barycentric.z() * uv2.x(),
barycentric.x() * uv0.y() + barycentric.y() * uv1.y() + barycentric.z() * uv2.y()
};3.2 计算 Mipmap Level
问题:体素大小和纹理像素大小不匹配,直接采样会产生走样
解决:使用 Mipmap 采样,根据体素大小选择合适的 mip level
cpp
// 第 78-111 行: compute_TBN()
// 计算 TBN 矩阵和 mip_length
// Tangent 和 Bitangent 的长度反映了 UV → 3D 的缩放比例
Eigen::Vector3f t = (duv2.y() * e1 - duv1.y() * e2);
Eigen::Vector3f b = (duv1.x() * e2 - duv2.x() * e1);
Eigen::Vector2f mip_length(invDet * t.norm(), invDet * b.norm());
// 第 417 行
// mip_length = 体素大小 / UV梯度
float mip_length = delta_p.maxCoeff() / std::sqrt(v_mip_length.x() * v_mip_length.y());3.3 Mipmap 采样
cpp
// 第 250-288 行: sample_texture_mipmap()
static void sample_texture_mipmap(...) {
// 计算 mip level
float mip_level = log2(mip_length * H) + mipLevelOffset;
if (mip_level <= 0) {
// 使用原始纹理
sample_texture(texture, ...);
} else {
// 在两个 mip level 之间插值
int lower = floor(mip_level);
int upper = lower + 1;
float frac = mip_level - lower;
sample_texture(lower_mip, ...);
sample_texture(upper_mip, ...);
color = (1 - frac) * lower_sample + frac * upper_sample;
}
}3.4 纹理包装模式
cpp
// 第 154-167 行
static inline int wrap_texcoord(const int& x, const int& W, const int& filter) {
if (filter == 0) { // REPEAT
return (x % W + W) % W;
} else if (filter == 1) { // CLAMP_TO_EDGE
return std::max(0, std::min(x, W - 1));
} else if (filter == 2) { // MIRROR_REPEAT
int period = 2 * W;
int x_mod = (x % period + period) % period;
return (x_mod < W) ? x_mod : (period - x_mod - 1);
}
}3.5 采样所有 PBR 属性
cpp
// 第 509-606 行
// 对每个相交的体素:
// Base Color (RGB)
sample_texture_mipmap(baseColorTexture, uv, mip_length, ...);
baseColor *= baseColorFactor; // 乘以材质因子
// Metallic
sample_texture_mipmap(metallicTexture, uv, mip_length, ...);
metallic *= metallicFactor;
// Roughness
sample_texture_mipmap(roughnessTexture, uv, mip_length, ...);
roughness *= roughnessFactor;
// Emissive
sample_texture_mipmap(emissiveTexture, uv, mip_length, ...);
emissive *= emissiveFactor;
// Alpha (with mode handling)
if (alphaMode != 0) {
sample_texture_mipmap(alphaTexture, uv, mip_length, ...);
alpha *= alphaFactor;
if (alphaMode == 1) { // MASK mode
alpha = alpha < alphaCutoff ? 0.0f : 1.0f;
}
}
// Normal (需要 TBN 变换)
sample_texture_mipmap(normalTexture, uv, mip_length, ...);
normal = normal * 2 - 1; // [0,1] → [-1,1]
normal = (normal[0] * t + normal[1] * b + normal[2] * n).normalized();Step 4: 加权平均
问题:一个体素可能与多个三角形相交,如何融合?
解决:使用距离作为权重进行加权平均
cpp
// 第 507 行
float weight = 1 - barycentric.w(); // weight = 1 - 距离(越近权重越大)
// 第 608-631 行: 累加
if (体素是新的) {
buf_weights.push_back(weight);
buf_baseColors.push_back(baseColor * weight);
// ...
} else {
buf_weights[i] += weight;
buf_baseColors[i] += baseColor * weight;
// ...
}
// 第 637-662 行: 归一化
for (int i = 0; i < coords.size(); i++) {
out_baseColor[i] = buf_baseColors[i] / buf_weights[i];
out_metallic[i] = buf_metallics[i] / buf_weights[i];
// ...
}图示:
Triangle A Triangle B
│ │
weight_A weight_B
│ │
└───────► Voxel ◄───────┘
│
▼
final = (A × w_A + B × w_B) / (w_A + w_B)Part 2: O-Voxel → Material(解码)
解码在 Python 层实现(flexible_dual_grid.py),主要步骤:
Step 1: Query from Texel/Vertices
从 O-Voxel 查询给定位置的材质属性:
python
# 伪代码
def query_attr(position, coords, attrs):
# 找到包含 position 的体素
voxel_idx = find_containing_voxel(position, coords)
# 返回该体素的属性
return attrs[voxel_idx]Step 2: Trilinear Interpolation
对于任意位置,使用三线性插值:
python
# 伪代码
def trilinear_interp(position, coords, attrs):
# 找到 8 个相邻体素
neighbors = find_8_neighbors(position, coords)
# 计算插值权重
fx, fy, fz = position - floor(position)
# 8 个角的权重
weights = [
(1-fx)*(1-fy)*(1-fz), # (0,0,0)
fx*(1-fy)*(1-fz), # (1,0,0)
(1-fx)*fy*(1-fz), # (0,1,0)
fx*fy*(1-fz), # (1,1,0)
(1-fx)*(1-fy)*fz, # (0,0,1)
fx*(1-fy)*fz, # (1,0,1)
(1-fx)*fy*fz, # (0,1,1)
fx*fy*fz, # (1,1,1)
]
# 加权平均
result = sum(w * attrs[n] for w, n in zip(weights, neighbors))
return result图示:
三线性插值示意图:
(0,1,1)────────(1,1,1)
/│ /│
/ │ / │
(0,0,1)────────(1,0,1)
│ │ │ │
│(0,1,0)─────│─(1,1,0)
│ / │ /
│/ │/
(0,0,0)────────(1,0,0)
任意点 P 的属性 = Σ (8个角的属性 × 对应权重)完整数据流
╔═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ PBR Textured Mesh → O-Voxel ║
╠═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╣
║ ║
║ 输入: ║
║ ├── vertices, normals, uvs (几何) ║
║ ├── baseColorTexture, metallicTexture, ... (纹理) ║
║ └── baseColorFactor, metallicFactor, ... (材质参数) ║
║ ║
║ Step 1: Voxel from FDG ║
║ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ ║
║ │ scan_line_fill() → intersected_voxels │ ║
║ │ (复用 FDG 的体素化结果) │ ║
║ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ ║
║ │ ║
║ ▼ ║
║ Step 2: Project to Surface ║
║ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ ║
║ │ project_onto_triangle() → (u, v, w, distance) │ ║
║ │ 重心坐标用于插值,距离用于权重 │ ║
║ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ ║
║ │ ║
║ ▼ ║
║ Step 3: Sample Texture ║
║ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ ║
║ │ compute_TBN() → mip_length │ ║
║ │ sample_texture_mipmap() → baseColor, metallic, roughness, ... │ ║
║ │ 加权累加 + 归一化 │ ║
║ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ ║
║ ║
║ 输出 O-Voxel: ║
║ ├── coords (体素坐标) ║
║ ├── baseColor (N, 3) ║
║ ├── metallic (N,) ║
║ ├── roughness (N,) ║
║ ├── emissive (N, 3) ║
║ ├── alpha (N,) ║
║ └── normal (N, 3) ║
║ ║
╚═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝
╔═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ O-Voxel → Material Query ║
╠═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╣
║ ║
║ Step 1: Query from Texel/Vertices ║
║ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ ║
║ │ 给定位置 → 找到对应体素 → 返回属性 │ ║
║ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ ║
║ │ ║
║ ▼ ║
║ Step 2: Trilinear Interpolation ║
║ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ ║
║ │ 找到 8 个相邻体素 │ ║
║ │ 计算插值权重 │ ║
║ │ 加权平均得到最终属性 │ ║
║ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ ║
║ ║
╚═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝关键技术点
1. Mipmap 构建
cpp
// 第 170-207 行
static std::vector<std::vector<uint8_t>> build_mipmaps(...) {
// 要求纹理是 2 的幂次且正方形
while (next_H > 0 && next_W > 0) {
// 每个 mip level 是上一级的 1/4 大小
// 4 个像素平均得到 1 个像素
for (int y = 0; y < next_H; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < next_W; x++) {
sum = pixel[2x,2y] + pixel[2x+1,2y]
+ pixel[2x,2y+1] + pixel[2x+1,2y+1];
next_map[x,y] = sum / 4;
}
}
}
}2. 法向量变换
法向量纹理存储的是切线空间的法向量,需要用 TBN 矩阵变换到世界空间:
cpp
// 第 599-606 行
normal[0] = normal[0] * 2 - 1; // [0,1] → [-1,1]
normal[1] = normal[1] * 2 - 1;
normal[2] = normal[2] * 2 - 1;
// TBN 变换: 切线空间 → 世界空间
// n_world = normal.x * T + normal.y * B + normal.z * N
Eigen::Vector3f _n = (normal[0] * t + normal[1] * b + normal[2] * int_n).normalized();3. Alpha 模式处理
cpp
// 第 569-586 行
if (alphaMode[mid] == 0) {
// OPAQUE: 忽略 alpha
alpha = 1.0f;
} else if (alphaMode[mid] == 1) {
// MASK: 二值化
alpha = alpha < alphaCutoff ? 0.0f : 1.0f;
} else {
// BLEND: 保持原始 alpha
}代码索引
| 功能 | 函数 | 位置 |
|---|---|---|
| TBN 计算 | compute_TBN() |
第 78-111 行 |
| 投影到三角形 | project_onto_triangle() |
第 125-151 行 |
| 纹理坐标包装 | wrap_texcoord() |
第 154-167 行 |
| Mipmap 构建 | build_mipmaps() |
第 170-207 行 |
| 纹理采样 | sample_texture() |
第 210-247 行 |
| Mipmap 采样 | sample_texture_mipmap() |
第 250-288 行 |
| 主体素化函数 | voxelize_trimesh_pbr_impl() |
第 291-675 行 |
| Python 接口 | textured_mesh_to_volumetric_attr_cpu() |
第 678-871 行 |
与 FDG 的关系
| 方面 | Flexible Dual Grid (几何) | Volumetric Attributes (材质) |
|---|---|---|
| 文件 | flexible_dual_grid.cpp |
volumetic_attr.cpp |
| 输入 | vertices, faces | vertices, normals, uvs, textures |
| 输出 | coords, dual_vertices, intersected | coords, baseColor, metallic, ... |
| 体素化 | 扫描线 + QEF 优化 | 扫描线 + 纹理采样 |
| 核心算法 | QEF 最小化 | Mipmap 采样 + 加权平均 |
体素集合对齐:两者使用相同的扫描线算法,确保几何体素和材质体素完全对应。