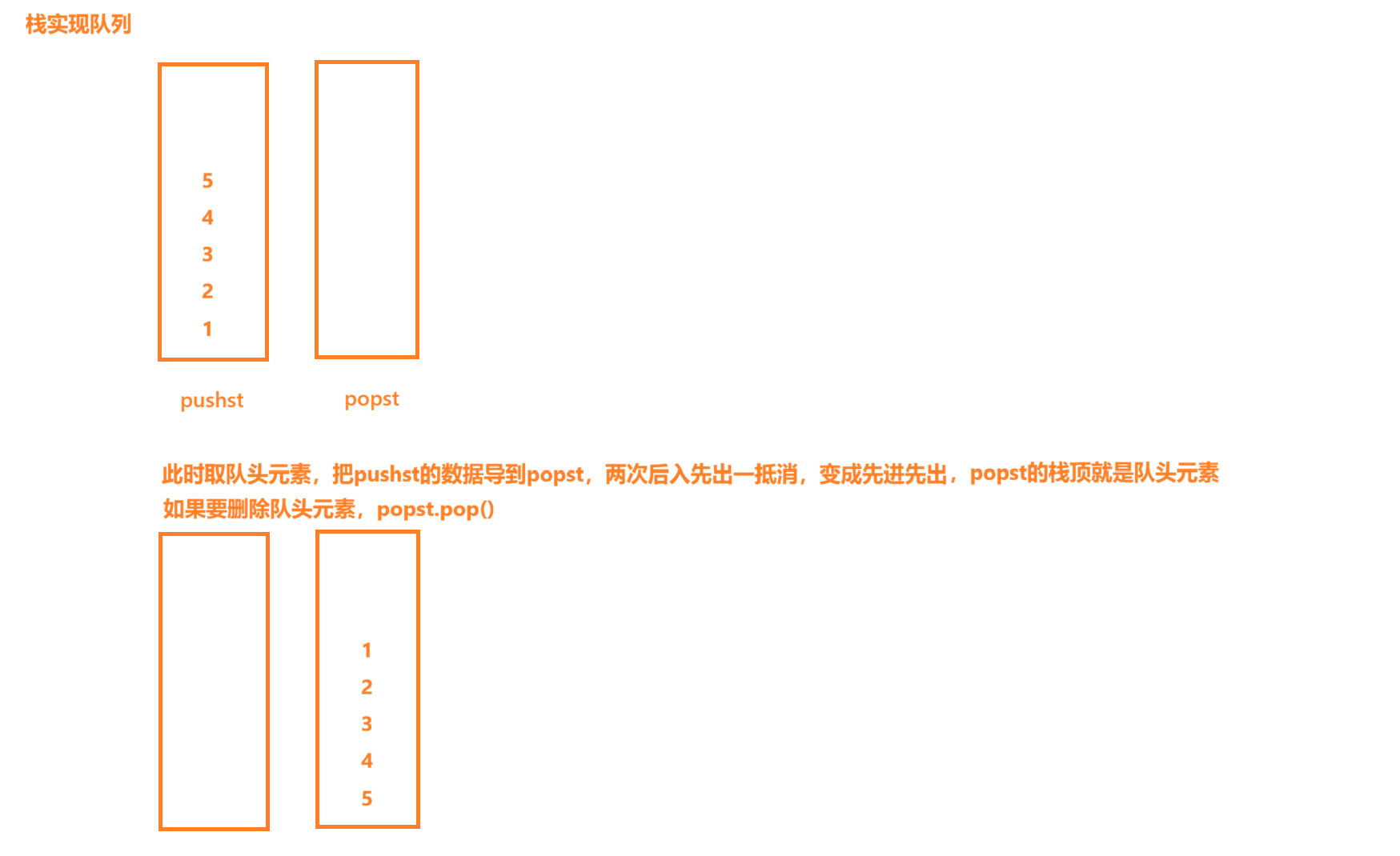
1. OJ题
cpp
class MyQueue {
public:
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
pushst.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(popst.empty()){
while(!pushst.empty()){
int x=pushst.top();
pushst.pop();
popst.push(x);
}
}
int x=popst.top();
popst.pop();
return x;
}
int peek() {
if(popst.empty()){
while(!pushst.empty()){
int x=pushst.top();
pushst.pop();
popst.push(x);
}
}
return popst.top();
}
bool empty() {
return popst.empty()&&pushst.empty();
}
private:
stack<int> pushst;
stack<int> popst;
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
cpp
class MyStack {
public:
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
pushq.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(pushq.empty()){
while(popq.size()>1){
int x=popq.front();
popq.pop();
pushq.push(x);
}
int x=popq.front();
popq.pop();
pushq.push(x);
}
while(pushq.size()>1){
int x=pushq.front();
pushq.pop();
popq.push(x);
}
int x=pushq.front();
pushq.pop();
return x;
}
int top() {
if(!pushq.empty())
return pushq.back();
return popq.back();
}
bool empty() {
return pushq.empty()&&popq.empty();
}
private:
queue<int> pushq;
queue<int> popq;
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
cpp
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pushV int整型vector
* @param popV int整型vector
* @return bool布尔型
*/
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int>& pushV, vector<int>& popV) {
stack<int> st;
int pushi=0,popi=0;
while(pushi<pushV.size()){
st.push(pushV[pushi++]);
while(!st.empty() && st.top()==popV[popi]){
st.pop();
popi++;
}
}
return popi==popV.size();
//return st.empty();
}
};
cpp
class MinStack {
public:
MinStack() {//因为成员变量都会走初始化列表,如果是内置类型不做处理,自定义类型走默认构造
}
//如果不写默认构造,系统自动生成,和上面逻辑一样
void push(int val) {
st.push(val);
if(minst.empty() || val<=minst.top())
minst.push(val);
}
void pop() {
if(st.top()==minst.top())
minst.pop();
st.pop();
}
int top() {
return st.top();
}
int getMin() {
return minst.top();
}
private:
stack<int> st;
stack<int> minst;
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(val);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->getMin();
*/
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
vector<int> v;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
size_t levelsize=0;
if(root){
q.push(root);
levelsize=1;
}
while(!q.empty()){
for(size_t i=0;i<levelsize;i++){
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
q.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
q.push(front->right);
}
vv.push_back(v);
v.clear();
levelsize=q.size();
}
return vv;
}
};
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
vector<int> v;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
size_t levelsize=0;
if(root){
q.push(root);
levelsize=1;
}
while(!q.empty()){
for(size_t i=0;i<levelsize;i++){
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
q.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
q.push(front->right);
}
vv.push_back(v);
v.clear();
levelsize=q.size();
}
reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end());//调用vector库里的swap对两个vector进行交换,本质是交换二者的三个指针,开销不大
return vv;
}
};
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {//传参传的是string对象数组,因为像+-*/都是一个字符,但-3,一个字符就存不下,就需要放在字符串中,所以就都放在了字符串中,tokens存的是一个又一个常量字符串;如果直接存在一个字符串,操作符和操作数需要我们进行拆分,很麻烦
stack<int> st;
for(auto& str: tokens){
if(str=="+"||str=="-"||str=="*"||str=="/"){//这个地方要进行字符串的比较,如果只比较第一个字符,就可能把负数的符号判成减号
int right=st.top();
st.pop();
int left=st.top();
st.pop();
switch(str[0]){
case '+':
st.push(left+right);
break;
case '-':
st.push(left-right);
break;
case '*':
st.push(left*right);
break;
case '/':
st.push(left/right);
break;
}
}
else{
st.push(stoi(str));
}
}
return st.top();
}
};逆波兰表达式也就是后缀表达式,

那么后缀表达式如何运算呢?我们在
2. 模拟实现
cpp
#pragma once
namespace diy {
//栈
template<class T,class Container = vector<T>>
class stack {
public:
T& top() {
return _con.back();
}
void pop() {
_con.pop_back();
}
void push(const T& x) {
_con.push_back(x);
}
size_t size() {
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() {
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test() {
//stack<int, vector<int>> st;
stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);//栈的插入和删除是尾插尾删
while (!st.empty()) {
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
stack<int,list<int>> st1;
st1.push(1);
st1.push(2);
st1.push(3);
st1.push(4);
while (!st1.empty()) {
cout << st1.top() << " ";
st1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
cpp
#pragma once
namespace diy {
//队列
template<class T, class Container>
class queue {
public:
T& front() {
return _con.front();
}
T& back() {
return _con.back();
}
void pop() {
_con.pop_front();
//_con.erase(_con.begin()); 一般是链式队列,vector头删效率低,如果是vector作为容器,vector没有提供pop_front,要用迭代器
}
void push(const T& x) {
_con.push_back(x);
}
size_t size() {
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() {
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test1() {
queue<int, list<int>> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
cpp
//测试代码
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#include "stack.h"
#include "queue.h"
//测试std下的栈
void test_stack_queue() {
stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);//栈的插入和删除是尾插尾删
while (!st.empty()) {
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
//测试std下的队列
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
////测试std下的双端队列
deque<int> dq;
dq.push_back(1);
dq.push_back(2);
dq.push_back(3);
dq.push_back(4);
dq.push_back(5);
dq.push_back(6);
for (size_t i = 0; i < dq.size(); i++) {
cout << dq[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//测试双端队列的sort效率,和vector对比
void test_op() {
srand(time(0));
deque<int> dq1, dq2;
vector<int> v;
int N = 10000000;
v.reserve(N);
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) {
auto e = rand();
dq1.push_back(e);
dq2.push_back(e);
}
size_t begin1 = clock();
for (auto& e : dq1) {
v.push_back(e);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
size_t i = 0;
for (auto& e : dq1) {
e = v[i++];
}
size_t end1 = clock();
size_t begin2 = clock();
sort(dq2.begin(), dq2.end());
size_t end2 = clock();
cout << "vector copy sort: " << end1 - begin1 << endl;
cout << "deque sort: " << end2 - begin2 << endl;
}
int main() {
//test_stack_queue();
//test_op();
diy::test1();
return 0;
}3. 双端队列
栈和队列都是运用已有的容器来适配自己的需求,栈和队列的默认适配容器都是deque双端队列;
我们先来回顾一下,链表和vector

好似二者的优劣天生不能共容,但还真有一个可以共容的,双端队列,允许头插头删尾插尾删,重载[ ]运算符
我们来简单看一下,
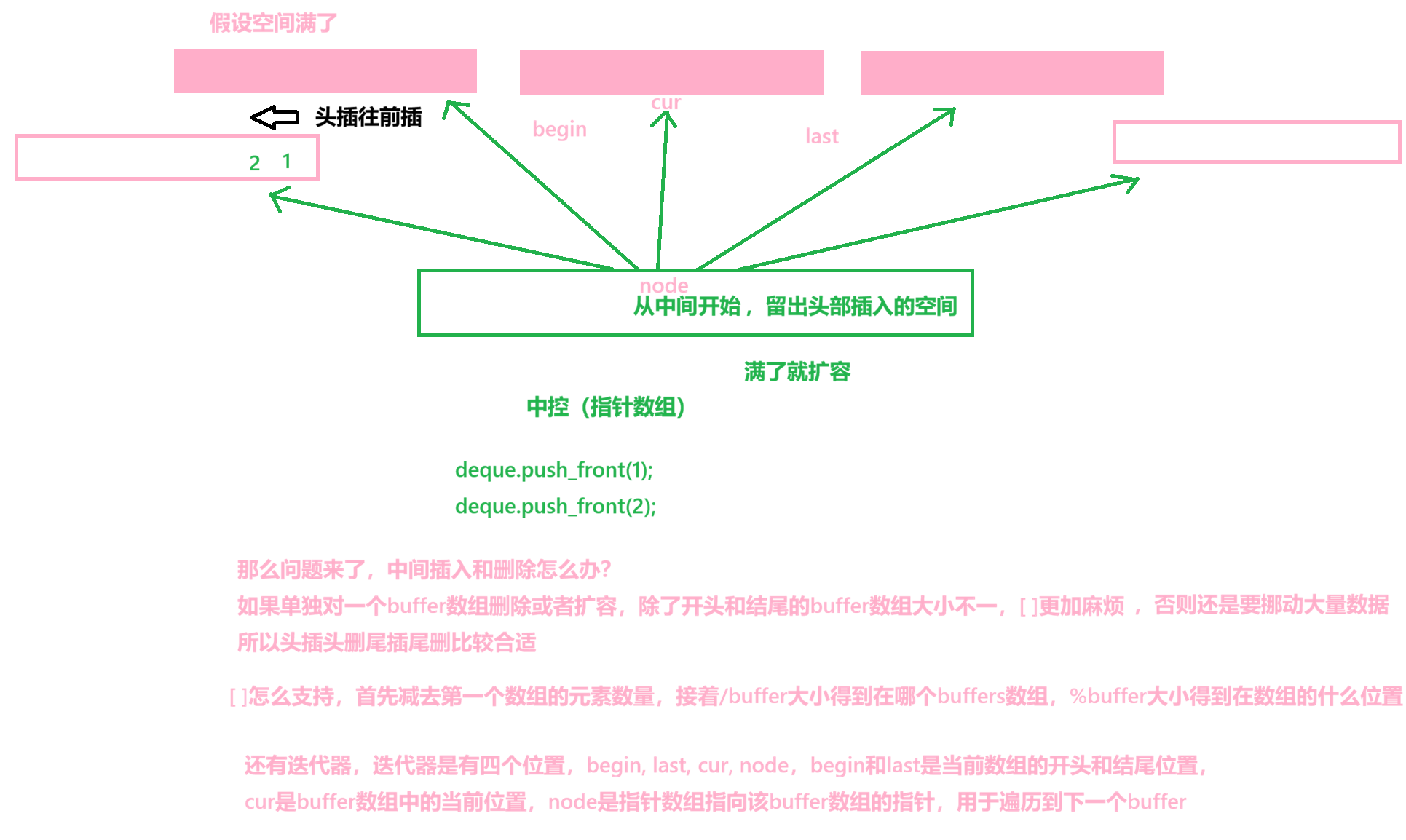
双端队列和vector相比,[ ]不够极致,极大缓解头插头删以及扩容效率问题,和list相比CPU高速缓存效率不错,支持随机访问
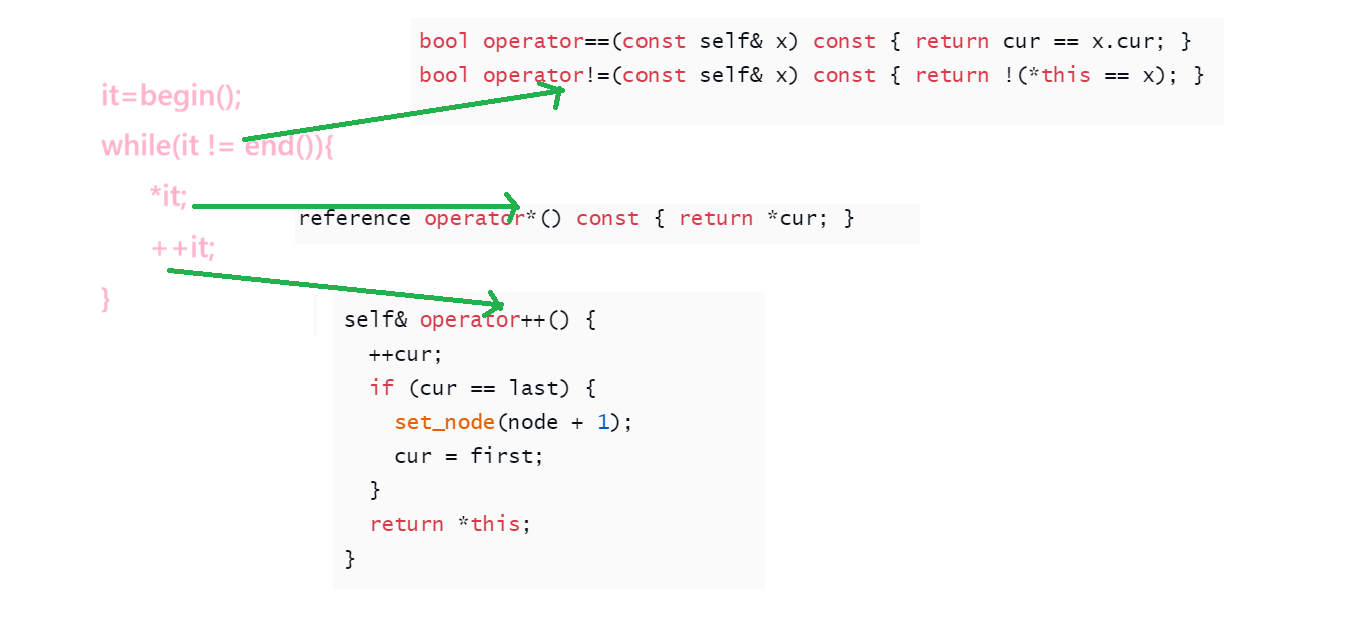
牛刀小试
- 一个栈的输入顺序是a,b,c,d,e则下列序列中不可能是出栈顺序是( )
A.e,d,a,c,b
B.a,e,d,c,b
C.b,c,d,a,e
D.b,c,a,d,e
A
- 下列代码的运行结果是( )
A.gstrin
B.grtnsg
C.srting
D.stirng
cpp
void main(){
queue<char> Q;
char x,y;
x='n';y='g';
Q.push(x);Q.push('i');Q.push(y);
Q.pop();Q.push('r');Q.push('t');Q.push(x);
Q.pop();Q.push('s');
while(!Q.empty()){
x = Q.front();
Q.pop();
cout<<x;
};
cout<<y;
}B
- 下列代码的运行结果是( )
A.gstrin
B.string
C.srting
D.stirng
cpp
void main(){
stack<char> S;
char x,y;
x='n';y='g';
S.push(x);S.push('i');S.push(y);
S.pop();S.push('r');S.push('t');S.push(x);
S.pop();S.push('s');
while(!S.empty()){
x = S.top();
S.pop();
cout<<x;
};
cout<<y;
}B
- 以下是一个二叉树的遍历算法,queue是FIFO队列,请参考下面的二叉树,根节点是root,正确的输出是( )
A.1376254
B.1245367
C.1234567
D.1327654
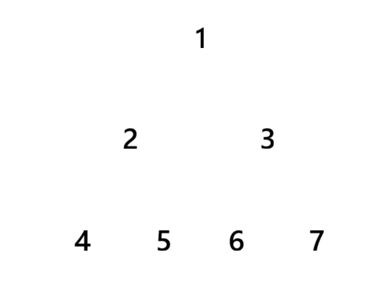
cpp
queue.push(root);
while(!queue.empty())
{
node = queue.top();
queue.pop();
output(node->value) //输出节点对应数字
if(node->left)
queue.push(node->left);
if(node->right)
queue.push(node->right);
}C