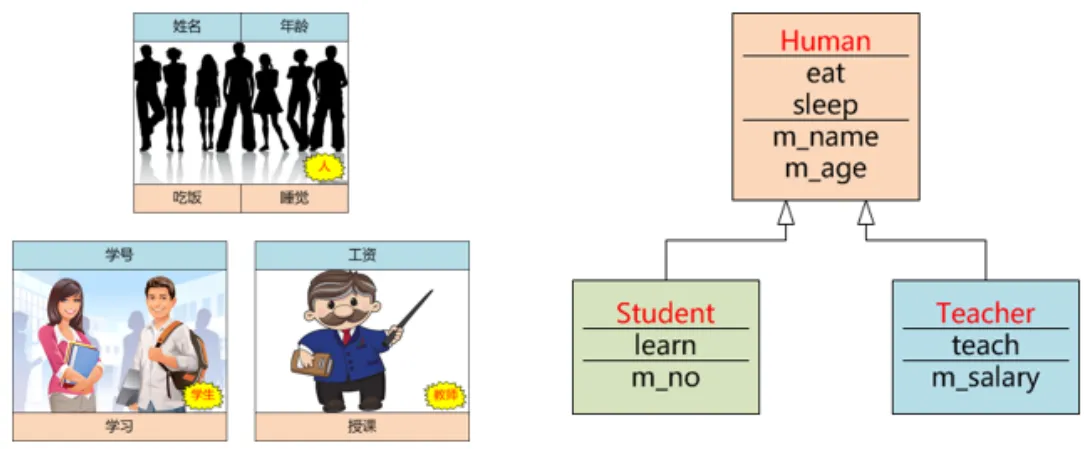
- 子类对象会继承基类的属性的行为,任何时候子类对象都可以被当做基类类型的对象,通过子类对象可以直接访问基类中的成员,如同是基类对象在访问它们一样
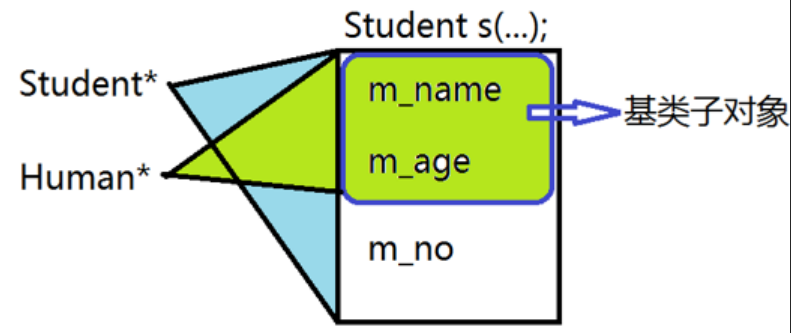
向上造型和向下造型
- 向上造型(upcast):将子类类型的指针或引用转换为基类类型的指针或引用;这种操作性缩小的类型转换,在编译器看来是安全的,可以隐式转换
- 向下造型(downcast):将基类类型的指针或引用转换为子类类型的指针或引用;这种操作性放大的类型转换,在编译器看来是危险的,不能隐式转化,但是可以显式转换
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Human{
private:
int m_private;
protected:
string m_name;
int m_age;
const int& get(void){
return m_private;
}
public:
Human(const string &name, int age){
m_name = name;
m_age = age;
m_private = 1234;
}
void eat(const string& food){
cout << "我在吃: " << food << endl;
}
void sleep(int hour){
cout << "我睡了" << hour << "小时" <<endl;
}
};
class Student: public Human{
private:
int m_no; //学号
public:
Student(const string& name, int age, int no):Human(name, age){
m_no = no;
}
void who(void){
cout << "我叫: " << m_name << ", 今年" <<m_age<<"岁,学号是: "<<m_no << endl;
//cout << m_private << endl; //error
cout << get() << endl;
}
void learn(const string& course){
cout << "我在学" << course << endl;
}
};
class Teacher: public Human{
private:
int m_salary;
public:
Teacher(const string& name, int age, int salary):Human(name, age),m_salary(salary){
}
void teach(const string& course){
cout << "我正在讲 " << course << endl;
}
void who(void){
cout << "我叫 "<<m_name << ",今年" << m_age << "岁, 工资是" << m_salary << endl;
}
};
int main(void){
Student s("张飞", 28, 100011);
cout << "sizeof(s) = "<<sizeof(s) << endl;
s.who();
s.eat("宫保鸡丁");
s.sleep(8);
s.learn("C++编程");
Teacher t("诸葛亮", 34, 200000);
t.who();
t.teach("嵌入式");
t.sleep(7);
t.eat("汉堡");
// Student * -----> Human *:向上造型
Human *ph = &s;
ph->eat("香蕉");
ph->sleep(10);
//ph->who(); //error
// Human * --------> Student *: 向下造型(合理)
Student *ps = static_cast<Student *>(ph);
ps->who();
Human h("赵云", 22);
//Human * -------> Student *: 向下造型 (不合理)
Student *ps2 = static_cast<Student *>(&h);
ps2->who();
return 0;
}成员函数的重定义(名字隐藏)
- 重定义: 简单的说就是子类中定义了和父类的同名函数,对父类的成员函数造成了隐藏
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base{
private:
int x;
public:
void set(int i){
x = i;
}
void print(){
cout << "Base class " << "x= " << x << endl;
}
};
class Derived: public Base{
private:
int m, n;
public:
void set(int p, int k){
m = p;
n = k;
}
void print(){
Base::print();
cout << "Derived class "<< "m = "<< m <<", n=" << n << endl;
}
};
int main(void){
Derived d;
d.set(10,20);
//d.set(100); // error 名字隐藏
d.Base::set(100);
d.print();
return 0;
}