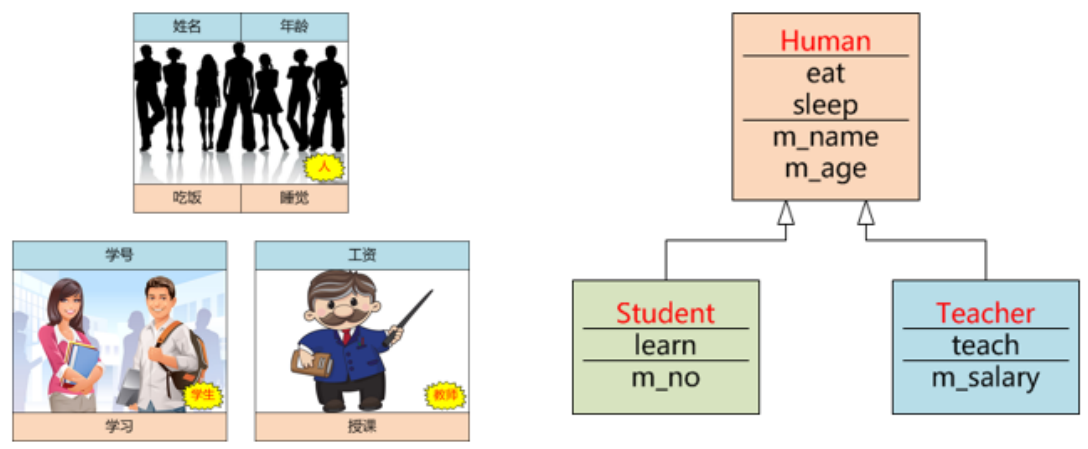
- 继承,基于一个已有类创建新类,使新类与已有类具有同样的功能,即新类具有已有类相同的数据成员和成员函数。
- 继承是代码重用的基本工 具。已有类称为基类(父类 /超类),新类称为派生类(子类)
- 注意:
- 基类的构造函数和析构函数不能继承
- 基类的友元函数不能继承
- 静态数据成员和静态成员函数不能继承
继承的方式
- C++的继承可以分为公有继承、保护继承和私有继承
- 不同继承方式会不同程度影响基类成员在派生类的访问权限
- 语法格式:
cpp
class 派生类名:继承方式 基类名{
派生类成员声明与定义
};| 访问控制限定符 | 访问控制属性 | 内部 | 子类 | 外部 | 友元 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| public | 公有成员 | ok | ok | ok | ok |
| protected | 保护成员 | ok | ok | no | ok |
| private | 私有成员 | ok | no | no | ok |
| 基类中的 | 在公有子类中变成 | 在保护子类中变成 | 在私有子类中变成 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 公有成员 | 公有成员 | 保护成员 | 私有成员 |
| 保护成员 | 保护成员 | 保护成员 | 私有成员 |
| 私有成员 | 私有成员 | 私有成员 | 私有成员 |
公有继承
- 继承方式为public的继承称为公有继承,在这种继承中,基类成员的访问权限在派生类中保持不变
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base{
private:
int m_a;
protected:
int m_b;
public:
int m_c;
Base(int a=1, int b=2, int c=3){
m_a = a;
m_b = b;
m_c = c;
}
int geta(){
return m_a;
}
};
class Derived: public Base{
public:
void print(){
//cout << m_a << endl; //error
cout << geta() << endl;
cout << m_b << endl;
cout << m_c << endl;
}
};
int main(void){
Derived test;
//cout << test.m_a << endl; // error private
//cout << test.m_b << endl; // error protected
cout << test.m_c << endl;
return 0;
}保护继承
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base{
private:
int m_a;
protected:
int m_b;
public:
int m_c;
Base(int a=1, int b=2, int c=3){
m_a = a;
m_b = b;
m_c = c;
}
int geta(){
return m_a;
}
};
class Derived: protected Base{
public:
void print(){
//cout << m_a << endl; //error
cout << geta() << endl;
cout << m_b << endl;
cout << m_c << endl;
}
};
int main(void){
Derived test;
//cout << test.m_a << endl; // error private
//cout << test.m_b << endl; // error protected
cout << test.m_c << endl; //protected继承 子类中该变量为protected error
return 0;
}私有继承
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base{
private:
int m_a;
protected:
int m_b;
public:
int m_c;
Base(int a=1, int b=2, int c=3){
m_a = a;
m_b = b;
m_c = c;
}
int geta(){
return m_a;
}
};
class Derived: private Base{
public:
void print(){
//cout << m_a << endl; //error
cout << geta() << endl;
cout << m_b << endl;
cout << m_c << endl;
}
};
int main(void){
Derived test;
//cout << test.m_a << endl; // error private
//cout << test.m_b << endl; // private继承 error private
//cout << test.m_c << endl; //private继承 子类中该变量为private error
return 0;
}