panic的中文含义为"恐慌 惊慌".程序发生panic时会结束当前协程.进而触发整个程
序的崩溃.内置函数recover()可以接受panic并使程序回到正轨.
1.panic()函数:
panic是一个内置函数:
源码位置:src/builtin/builtin.go
Go
// The panic built-in function stops normal execution of the current
// goroutine. When a function F calls panic, normal execution of F stops
// immediately. Any functions whose execution was deferred by F are run in
// the usual way, and then F returns to its caller. To the caller G, the
// invocation of F then behaves like a call to panic, terminating G's
// execution and running any deferred functions. This continues until all
// functions in the executing goroutine have stopped, in reverse order. At
// that point, the program is terminated with a non-zero exit code. This
// termination sequence is called panicking and can be controlled by the
// built-in function recover.
//
// Starting in Go 1.21, calling panic with a nil interface value or an
// untyped nil causes a run-time error (a different panic).
// The GODEBUG setting panicnil=1 disables the run-time error.
func panic(v any)它接受一个任意类型的参数.参数将在程序崩溃时通过另一个内置函数print(args
...Type)打印出来.如果程序返回途中任意一个defer函数执行了recover().那么该参
数也是recover()的返回值.
panic可由程序员显示的通过内置函数触发.Go运行时遇到诸如内存越界之类的问题
也会触发.
2.工作流程:
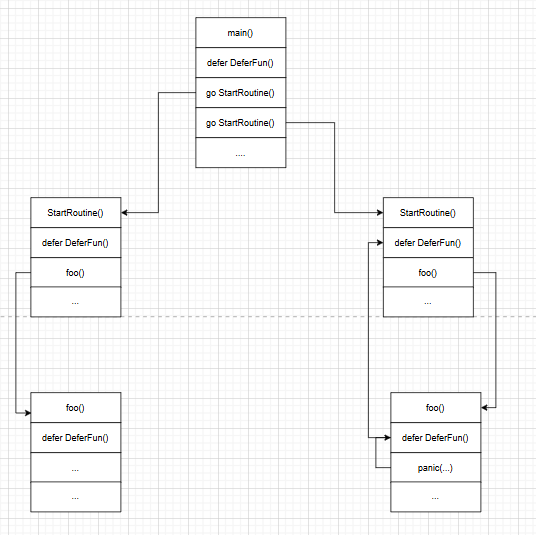
上面流程中.程序启动了两个协程.如果某个协程执行过程中产生了panic.那么程序将
立即转向执行defer函数.当前函数中的defer执行完毕后继续处理上层函数的defer.
当协程中所有defer处理完成以后.程序退出.
注:
panic会递归执行协程中所有的defer.与正常函数退出时一致.
panic不会处理其他协程中的defer.
当前协程中的defer处理完成后.触发程序退出.
3.源码剖析:
示例:
Go
package Concurrent
func compile() {
panic("aa")
}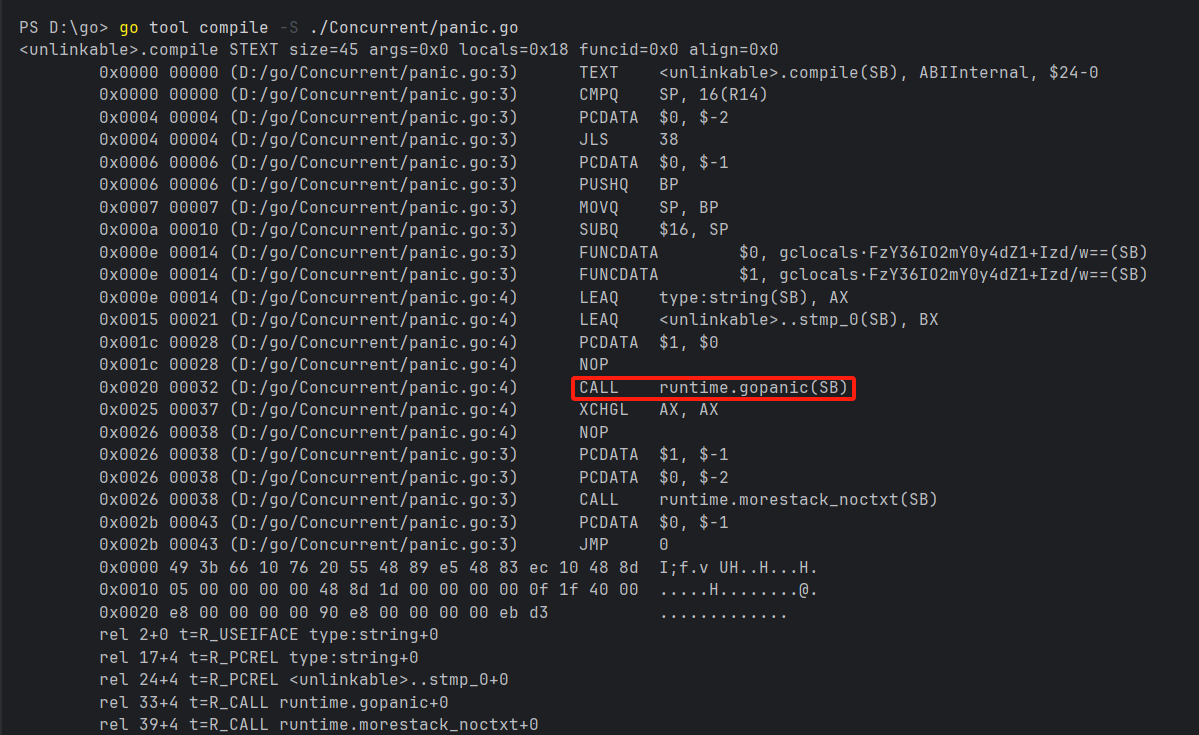
通过命令编译代码.可以看到panic语句被编译成 CALL runtime.gopanic(SB).也
就是panic()函数的真身是runtime.gopanic().源码位置为
src/runtime/panic.go.
4.数据结构:
源码位置:src/runtime/runtime2.go
Go
type _panic struct {
argp unsafe.Pointer // pointer to arguments of deferred call run during panic; cannot move - known to liblink
arg any // argument to panic
link *_panic // link to earlier panic
// startPC and startSP track where _panic.start was called.
startPC uintptr
startSP unsafe.Pointer
// The current stack frame that we're running deferred calls for.
sp unsafe.Pointer
lr uintptr
fp unsafe.Pointer
// retpc stores the PC where the panic should jump back to, if the
// function last returned by _panic.next() recovers the panic.
retpc uintptr
// Extra state for handling open-coded defers.
deferBitsPtr *uint8
slotsPtr unsafe.Pointer
recovered bool // whether this panic has been recovered
goexit bool
deferreturn bool
}argp:defer函数参数指针.
arg: panic 的触发参数.即 panic(x) 中的 x(如 panic("error") 中的字符串).
link: panic 链表指针.指向更早触发的 panic(支持嵌套 panic,如 defer 中再次
panic).
startPC: 调用 start 方法时的程序计数器 .
startSP: 调用 start 方法时的栈指针.
sp: 当前栈帧的栈指针(匹配 defer 注册时的 sp,确保执行当前函数的 defer).
lr: 链接寄存器(记录函数返回地址,用于栈帧回溯).
fp: 帧指针(指向当前栈帧底部,辅助定位局部变量).
retpc: 这是 recover 能让程序"恢复执行"的核心------修改执行流到 retpc 指向的位
置 .
deferBitsPtr: 指向开放编码 defer 的执行状态位(标记哪些 defer 已执行).
slotsPtr: 指向开放编码 defer 的函数槽(存储待执行的开放编码 defer 函数).
recovered: 该 panic 是否被 recover() 恢复(true 表示已恢复,终止 panic 流
程).
goexit: 是否是 runtime.Goexit() 触发的 panic(Goexit 本质是特殊 panic).
deferreturn: 是否是 deferreturn 触发的"伪 panic"(仅用于执行 defer,无实
际 panic).
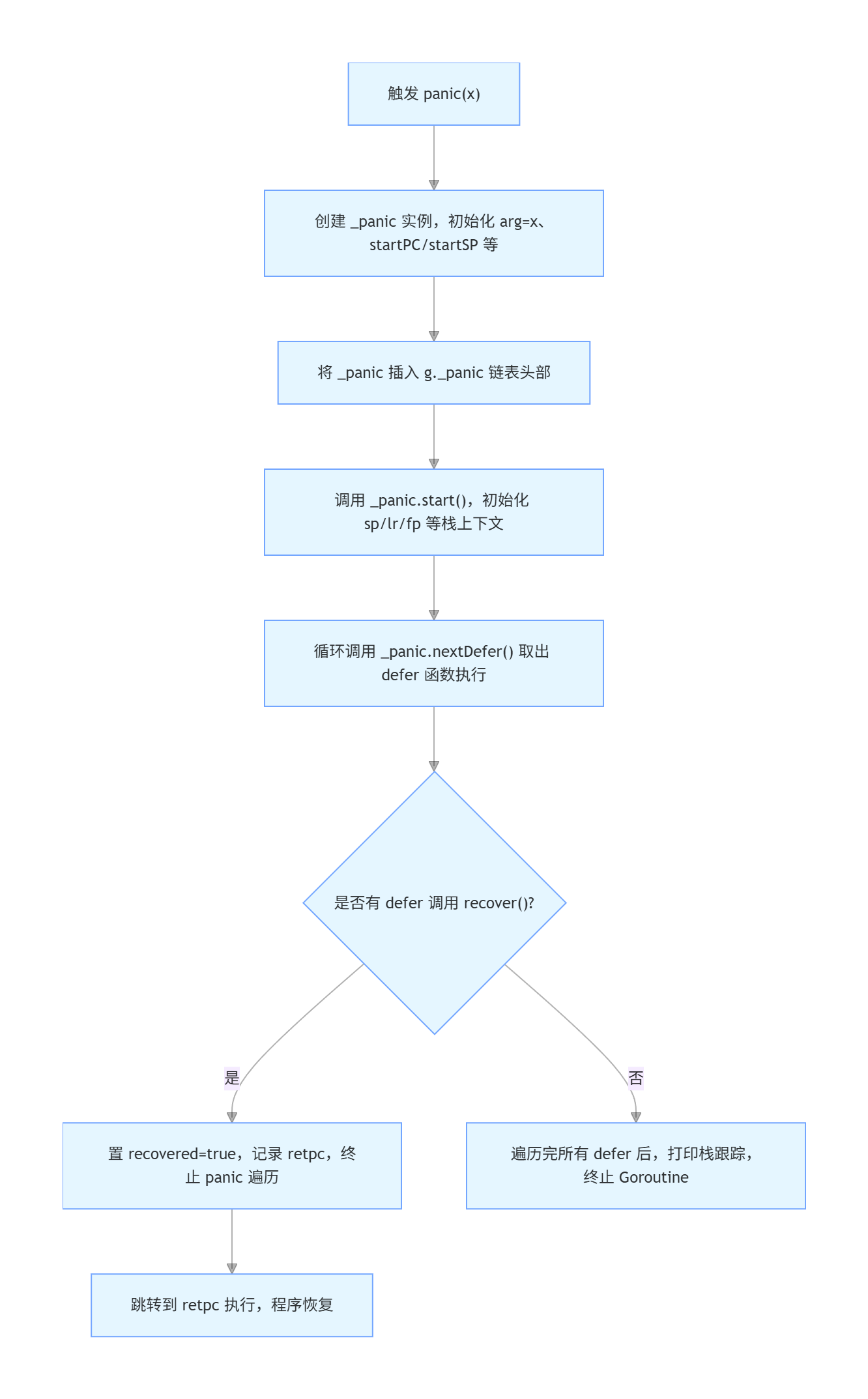
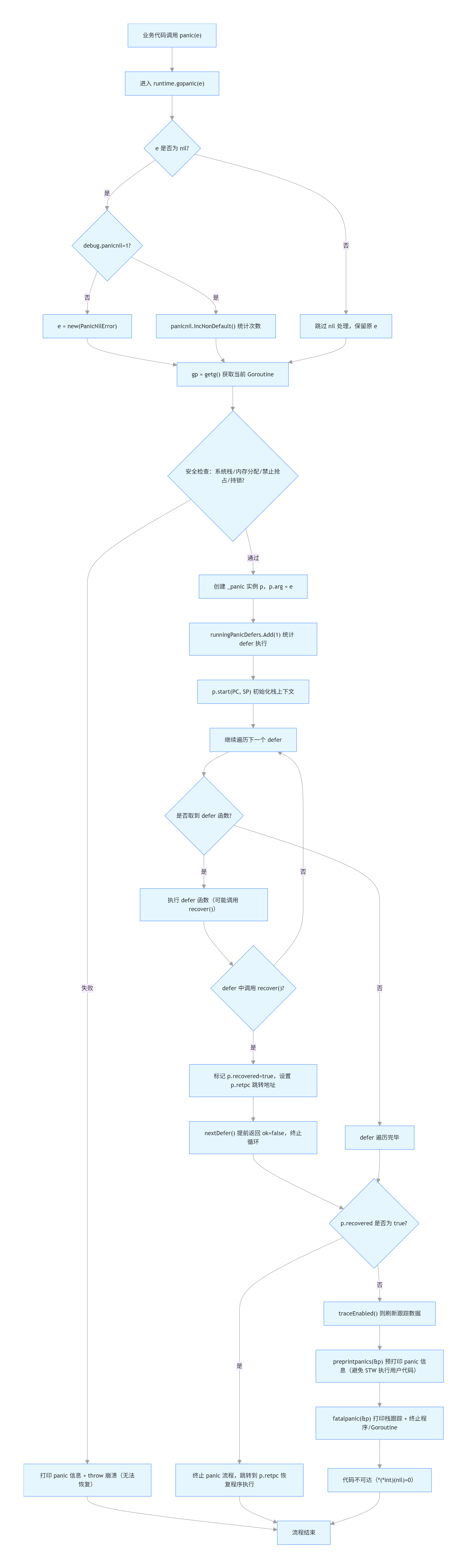
5.gopanic分析:
runtime.gopanic()函数的核心任务是消费协程中的defer链表.当所有的defer处
理完后再触发程序退出.由于defer函数中有可能触发新的panic.即产生新的
runtime.gopanic(),另外panic也有可能被recover()恢复.
源码位置:
src/runtime/panic.go
Go
func gopanic(e any) {
if e == nil {
if debug.panicnil.Load() != 1 {
e = new(PanicNilError)
} else {
panicnil.IncNonDefault()
}
}
gp := getg()
if gp.m.curg != gp {
print("panic: ")
printpanicval(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic on system stack")
}
if gp.m.mallocing != 0 {
print("panic: ")
printpanicval(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic during malloc")
}
if gp.m.preemptoff != "" {
print("panic: ")
printpanicval(e)
print("\n")
print("preempt off reason: ")
print(gp.m.preemptoff)
print("\n")
throw("panic during preemptoff")
}
if gp.m.locks != 0 {
print("panic: ")
printpanicval(e)
print("\n")
throw("panic holding locks")
}
var p _panic
p.arg = e
runningPanicDefers.Add(1)
p.start(sys.GetCallerPC(), unsafe.Pointer(sys.GetCallerSP()))
for {
fn, ok := p.nextDefer()
if !ok {
break
}
fn()
}
// If we're tracing, flush the current generation to make the trace more
// readable.
//
// TODO(aktau): Handle a panic from within traceAdvance more gracefully.
// Currently it would hang. Not handled now because it is very unlikely, and
// already unrecoverable.
if traceEnabled() {
traceAdvance(false)
}
// ran out of deferred calls - old-school panic now
// Because it is unsafe to call arbitrary user code after freezing
// the world, we call preprintpanics to invoke all necessary Error
// and String methods to prepare the panic strings before startpanic.
preprintpanics(&p)
fatalpanic(&p) // should not return
*(*int)(nil) = 0 // not reached
}1).panic(nil)特殊场景:

2).gp:=getg()获取当前goroutine.
3). 安全检查1:禁止在系统栈上触发 panic.
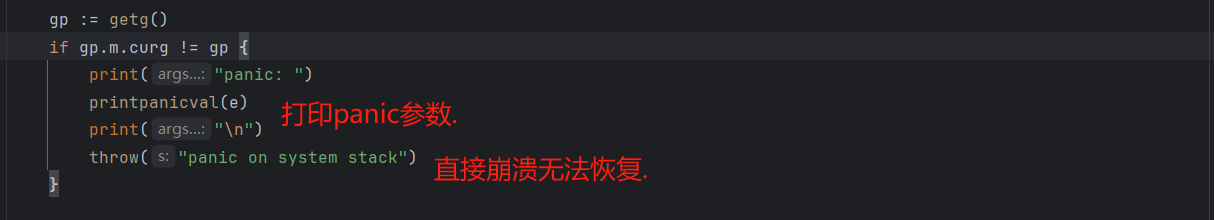
4). 安全检查2:禁止在内存分配期间 panic(mallocing 标记为 1 表示正在分配内存).
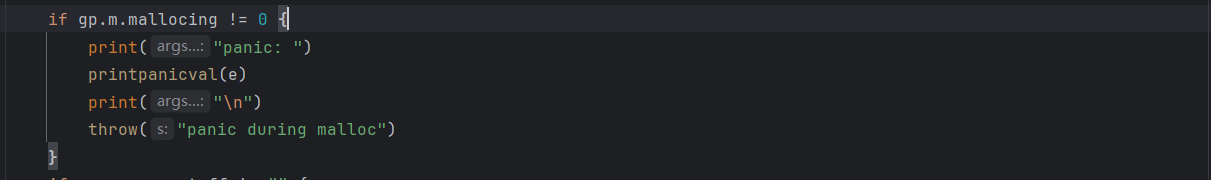
5). 安全检查3:禁止在"禁止抢占"期间 panic(preemptoff 非空表示禁止抢占).
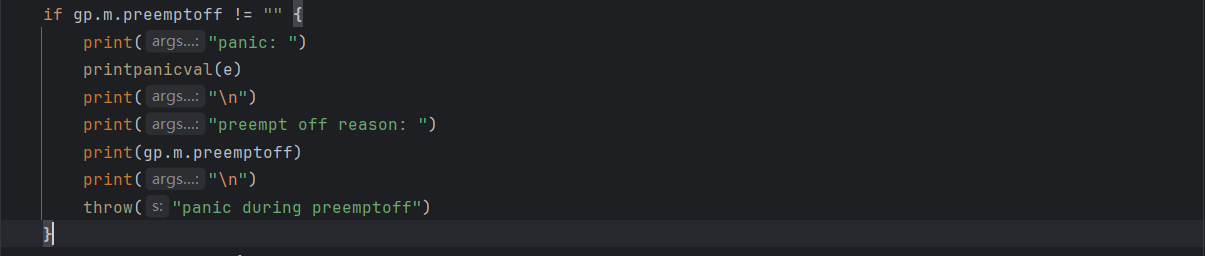
6). 安全检查4:禁止在持有运行时锁期间 panic(locks 非 0 表示持有锁).
7). 创建 _panic 实例,初始化核心字段.

8). 统计 panic 期间执行 defer 的计数器(监控/调试用).
runningPanicDefers.Add(1).
9). 初始化 panic 上下文:传入调用 gopanic 时的 PC/SP,关联当前栈帧 . 让 _panic 定位到当前函数的 defer 链表,准备遍历执行 .
10). 核心循环:遍历并执行所有 defer 函数 .
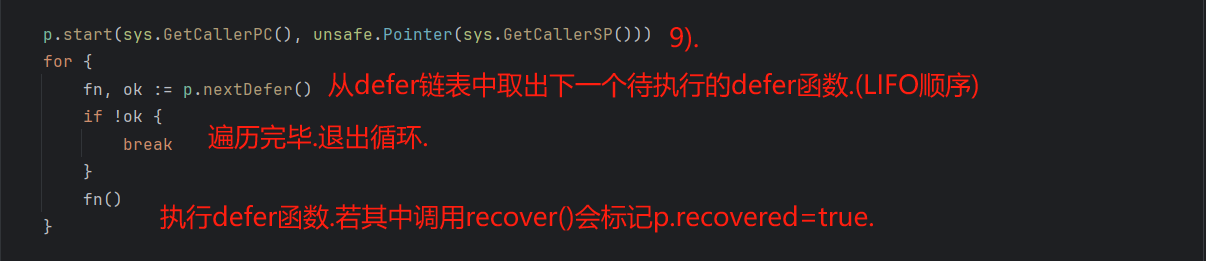
11). 跟踪(trace)相关:若开启了执行跟踪,刷新当前跟踪数据(提升 panic 日志可读性).
12). 所有 defer 执行完毕且未 recover → 触发致命 panic .
13). 致命 panic:打印栈跟踪、终止 Goroutine/程序(不会返回).
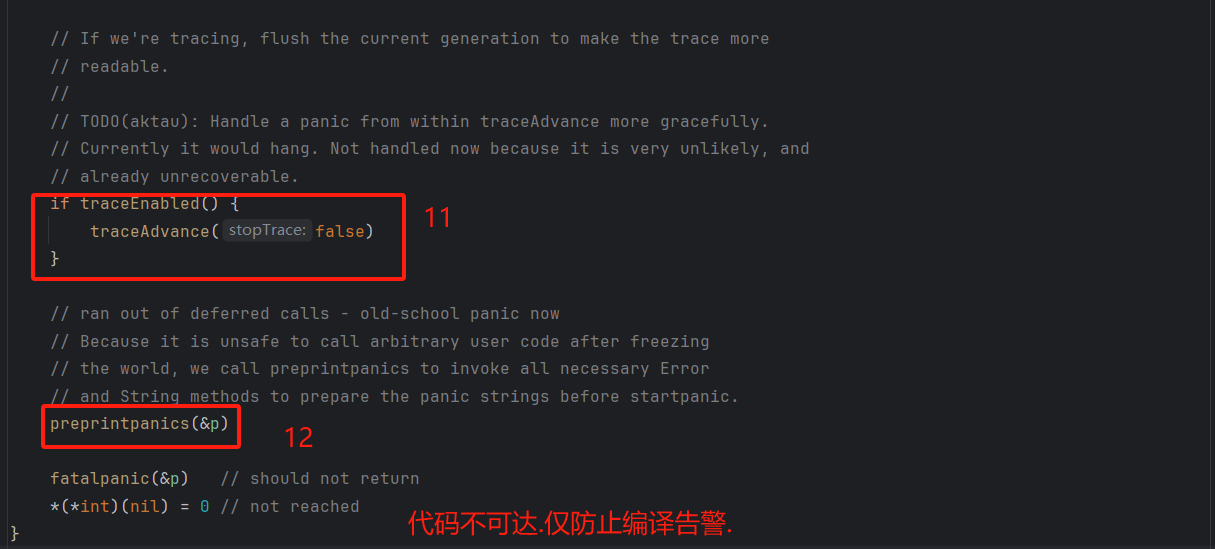
6.流程图:
++春风若有怜花意.可否许我再少年.++
++如果大家喜欢我的分享的话.可以关注我的微信公众号++
++念何架构之路++