文章目录
成员变量
1._head指向头节点。
2._size统计有效节点个数。
cpp
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};创建节点
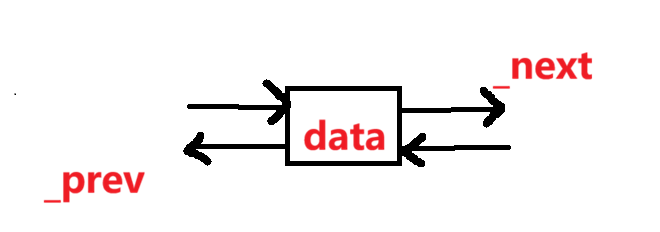
1.T是类型参数,使用模板可以存储任意类型的参数。
2._data存储数据。
3._next指向下一个节点的指针。
4._prev指向前一个节点的指针。
5.使用初始化列表进行初始化,const T& data = T(): 参数默认使用类型T的默认构造函数创建的对象。
cpp
template<class T>
struct list_node {
T _data;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
list_node(const T& data = T())
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
{
}
};
操作符重载
1.Ref是引用类型,可以是T&,const T&.
2.Ptr是指针类型,可以是T*,const T*.
3.Node节点类型。
4.Self迭代器的自身类型。
cpp
template<class T,class Ref, class Ptr>
struct list_iterator {
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*() {
return _node->_data;
}
//返回指向数据的指针
Ptr operator->() {
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self operator++() {
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int) {
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator--() {
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const {
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const {
return _node == s._node;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Self& it) {
out << it._node_data << endl;
return out;
}
};list主要函数操作实现
1.iterator定义普通迭代器操作。
2.const_iterator定义const迭代器操作。
3.begin()函数是哨兵位头节点指向的下一个位置。
4.end()函数指向哨兵位头节点。
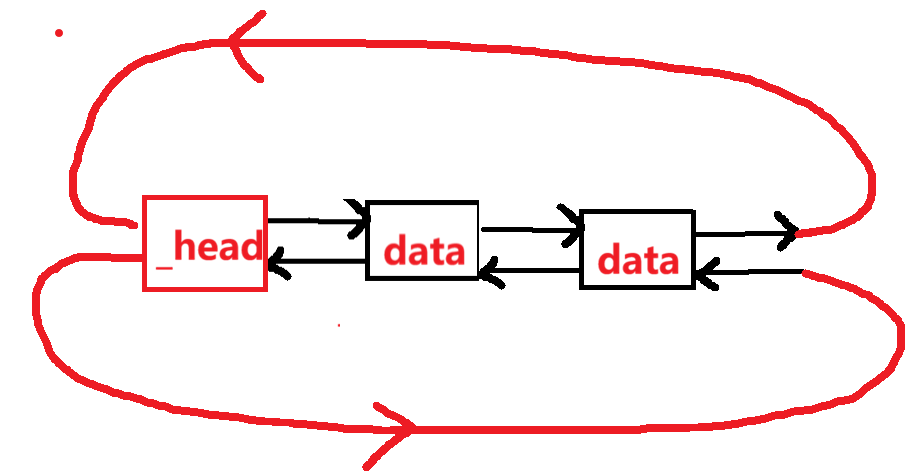
5.在默认构造函数list()中调用empty_init()初始化空列表。
6.初始化列表构造函数目的是为了支持 list mylist = {1, 2, 3, 4}; 语法。
7.拷贝构造函数,深拷贝,不会影响原始列表。
8.操作符重载,巧妙借助了swap函数交换当前变量和临时对象啊,临时对象在函数结束时自动销毁。
9.在析构函数中,先清除所有元素,在释放头节点。
10.push_back()函数进行尾插。
11.insert()在当前迭代器的位置插入新的数据,然后返回新的迭代器的位置,防止迭代器失效。
cpp
template<class T>
class list {
typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:
/*typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;
typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;*/
typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin() {
iterator it(_head->_next);
return it;
}
iterator end() {
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const {
return _head;
}
void empty_init() {
//传匿名对象
_head = new Node(T());
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list() {
empty_init();
}
list(initializer_list<T> il) {
empty_init();
for (auto& e : il) {
push_back(e);
}
}
//lt2(lt1)
list(const list<T>& lt) {
empty_init(); //初始化lt2的头节点
for (auto& e : lt) {
push_back(e);
}
}
//lt1 = lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt) {
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
~list() {
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void clear() {
auto it = begin();
while (it != end()) {
it = erase(it);
}
}
void swap(list<int>& lt) {
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
void push_back(const T& x) {
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//尾结点
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = tail;
_head->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_next = _head;
++_size;
}
void push_front(const T& x) {
insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_back() {
Node* cur = _head->_prev;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = _head;
prev->_next = next;
_size--;
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front() {
erase(begin());
_size--;
}
iterator insert(iterator it, const T& x) {
Node* cur = it._node;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
newnode->_next = cur;
newnode->_prev = cur->_prev;
cur->_prev->_next = newnode;
cur->_prev = newnode;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos) {
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* next = cur->_next;
cur->_prev->_next = cur->_next;
cur->_next->_prev = cur->_prev;
delete pos._node;
_size--;
return next;
}
size_t size() const {
return _size;
}
bool empty() const {
return _size==0;
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};Container容器
cpp
template<class Container>
void printf_container(const Container& con) {
//const iterator 迭代器本身不能修改
//const_iterator 迭代器指向的内容不能修改
typename Container::const_iterator it = con.begin();
while (it != con.end()) {
//这里使用了const_iterator迭代器,按理来说迭代器指向的内容不能修改
//会编译错误,但是这里没有报错
//进行了按需实例化,函数没有调用就没有检查细节
//
//*it += 10;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
觉得我回答有用的话,记得点个关注哟!谢谢支持!