1 卷积神经网络CNN
1.1 简介与应用
卷积神经网络(CNN)是一种深受生物视觉皮层启发而设计的深度学习模型,特别适合处理图像、语音等网格状数据。CNN通过卷积层、池化层和全连接层等组件,能够自动从原始像素中学习层次化的特征表示,从而完成图像分类、目标检测等任务。其核心思想是局部感知 (每个神经元只响应局部区域)和权值共享(同一组权重在不同位置检测相同模式),这大幅减少了参数数量并增强了模型的泛化能力。
想象一下,我们要打造一位"AI神探",它的任务是从海量的监控视频中快速准确地找出嫌疑人。这位神探的破案过程分为三步:

-
现场勘察(卷积层):用不同的"特征放大镜"(卷积核)仔细查看每个局部区域,提取蛛丝马迹(如边缘、纹理、颜色等)。
-
线索整理(池化层):把勘察到的海量线索进行归纳摘要,去掉冗余细节,保留最核心的证据。
-
综合研判(全连接层):将所有关键线索汇总,进行综合推理判断,最终锁定嫌疑人。
这位AI神探的绝技在于:一次只看一小块(局部感知) ,并且用同一套标准审视全场(参数共享),这使得它既高效又准确。
环境配置
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
# 检查设备
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"AI神探将在 {device} 上展开调查!")1.2 核心组件
1.2.1 卷积层
卷积层是CNN的核心,由多个可学习的卷积核 构成。每个卷积核在输入数据上滑动,进行卷积运算 以提取特定特征。输出结果是多个特征图(Feature Map),每个图记录了原始输入中某种特征的强度和位置。
卷积层就像神探派出的多个专项勘察小组。每个小组配备一种独特的"特征放大镜"(卷积核):
-
小组A(竖线放大镜):专门探测门框、栅栏等竖直线条。
-
小组B(横线放大镜):专门探测地平线、桌面等水平线条。
-
小组C(斜线放大镜):专门探测屋顶、衣领等斜向特征。
每个小组用各自的放大镜扫描(滑动) 整个区域。扫描完成后,会生成一张"线索热力图"(特征图),图上亮度高的点,就代表该位置发现了其负责寻找的强烈特征。参数共享 意味着,整个区域都使用同一把放大镜,保证了检测标准的一致性。
python
class FeatureExtractor(nn.Module):
"""特征提取器 - AI神探的侦查小组"""
def __init__(self):
super(FeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
# 第一侦查小组:提取低级特征(边缘、纹理)
self.team1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 3通道RGB -> 16个特征图
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
# 第二侦查小组:提取中级特征(形状、部件)
self.team2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
# 第三侦查小组:提取高级特征(完整对象)
self.team3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
def forward(self, x):
print(f"\n侦查小组开始工作...")
# 第一小组勘察
clues1 = self.team1(x)
print(f" 第一小组报告: 发现 {clues1.size(1)} 种初级线索,线索图尺寸: {clues1.shape[2:]} (宽x高)")
# 第二小组深入勘察
clues2 = self.team2(clues1)
print(f" 第二小组报告: 发现 {clues2.size(1)} 种中级线索,线索图尺寸: {clues2.shape[2:]}")
# 第三小组高级勘察
clues3 = self.team3(clues2)
print(f" 第三小组报告: 发现 {clues3.size(1)} 种高级线索,线索图尺寸: {clues3.shape[2:]}")
return clues31.2.2 池化层
池化层(Pooling Layer)对特征图进行下采样(Downsampling),主要目的是:
减少数据量和计算复杂度。
保持特征的平移、旋转不变性。
突出最显著的特征响应。
最常见的是最大池化(Max Pooling),它在局部区域(如2x2)内只保留最大值。
池化层就是神探的情报分析科 。勘察小组送来的线索图太详细了,包含大量冗余信息。分析科的工作就是做摘要:
-
他们把线索图分成多个小区域(如2x2的格子)。
-
对于每个小区域,只记录最醒目、最确凿的那条线索(最大值),忽略其他次要信息。
-
例如,一个2x2区域内的线索强度为
[0.9, 0.2, 0.8, 0.1],分析科只记录0.9。
这样做的好处是:报告体积大大缩小,只留下精华,使得后续的研判部能更专注于关键证据,而不会因为嫌疑人换了个站姿或光线稍有变化就做出误判。
python
class CaseAnalyzer(nn.Module):
"""案件分析器 - AI神探的情报分析科"""
def __init__(self, input_features, hidden_size=128):
super(CaseAnalyzer, self).__init__()
# 展平线索:将所有线索整理成档案
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
# 分析团队:理解线索之间的关系
self.analyst_team = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_features, hidden_size),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.3),
nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size // 2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
def forward(self, x):
print(f"\n 情报分析科开始整理线索...")
# 展平所有线索
flat_clues = self.flatten(x)
print(f" 线索档案长度: {flat_clues.size(1)} 个关键点")
# 分析线索
analyzed = self.analyst_team(flat_clues)
print(f" 分析完成,生成 {analyzed.size(1)} 条核心情报")
return analyzed1.2.3 全连接层
全连接层(Fully Connected Layer)通常位于网络末端。它将前面所有卷积和池化层提取的分布式局部特征"综合"起来,映射到最终的样本标记空间(如分类类别)。每个神经元都与前一层的所有神经元相连,通过学习到的权重来组合特征,完成最终的分类或回归任务。
全连接层就是专案指挥部 。当所有关键线索(经过卷积和池化后的高级特征)都汇总到这里后,指挥部的**专家团(神经元)** 开始工作:
-
线索汇总:首先,所有二维的线索图会被展平成一个长清单(Flatten操作)。
-
专家会商:每一位专家都会审视清单上的所有线索,并基于自己的专业知识(权重)给出一个综合判断分数。
-
民主决策:多位专家的意见通过加权组合,传递到最终决策层。
-
最终裁决:决策层(通常是Softmax函数)根据专家团的综合意见,计算出各种可能性(如"是嫌疑人A的概率为80%,是路人B的概率为15%..."),并做出最终裁决。
python
class VerdictCommittee(nn.Module):
"""判决委员会 - AI神探的专案指挥部"""
def __init__(self, input_size, num_classes):
super(VerdictCommittee, self).__init__()
# 专家团:综合所有情报做出判断
self.expert_panel = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_size, 64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(64, num_classes)
)
# 定义可能的嫌疑人类型
self.suspect_classes = [
"足球运动员",
"篮球运动员-乔丹",
"篮球运动员-詹姆斯",
"篮球运动员-科比",
"普通人",
"错误识别"
]
def forward(self, x):
print(f"\n 专案指挥部召开专家会议...")
# 专家讨论并投票
raw_verdict = self.expert_panel(x)
print(f" 专家团原始评分: {raw_verdict.tolist()}")
# 计算概率分布(使用Softmax)
probabilities = F.softmax(raw_verdict, dim=1)
print(f" 标准化概率分布: {probabilities.tolist()}")
# 做出最终判决
final_decision = torch.argmax(probabilities, dim=1)
return raw_verdict, probabilities, final_decision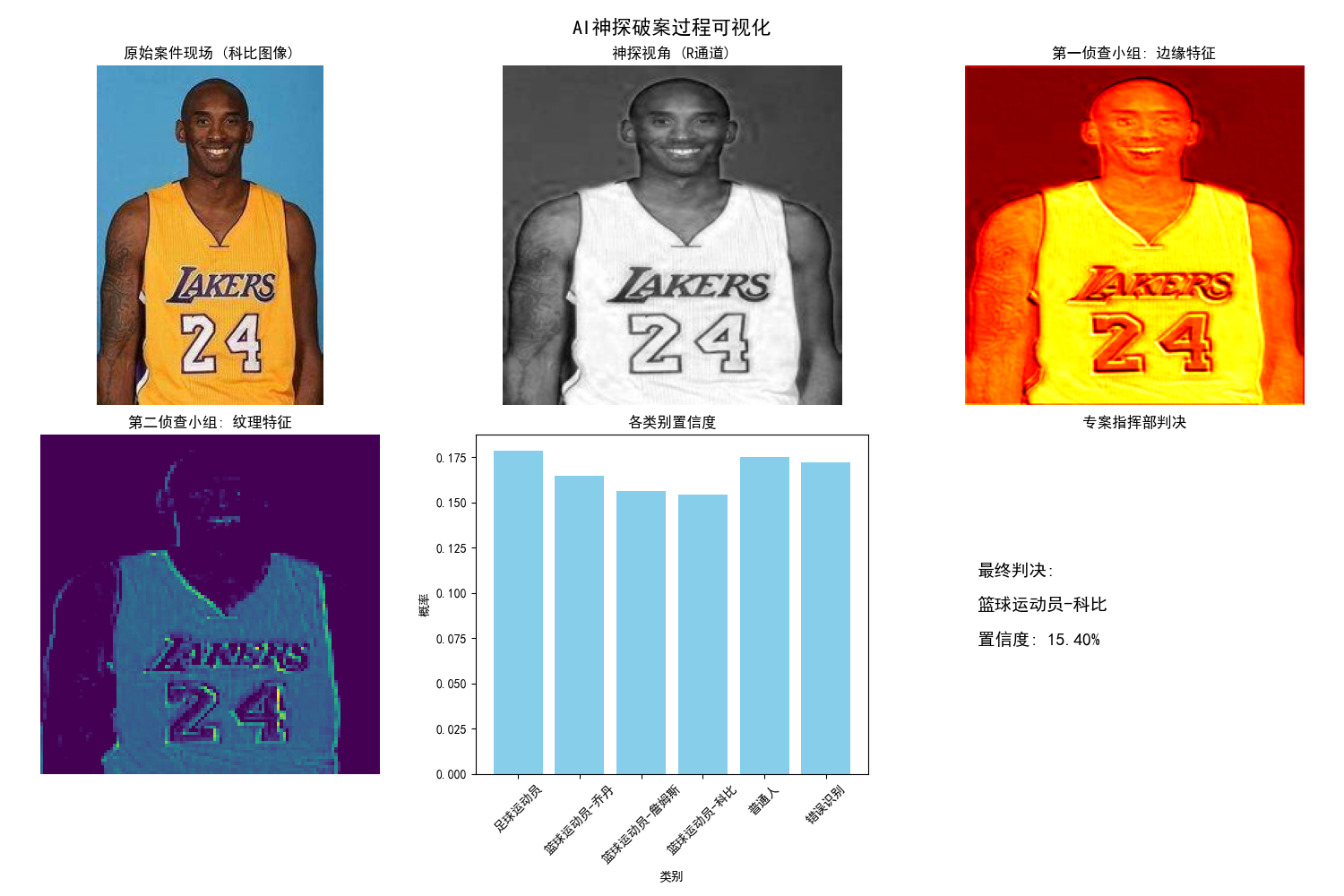
1.3 激活函数与训练
激活函数(Activation Function)为神经网络引入了非线性因素 。如果没有它,多层网络就等价于一个单层线性网络,无法学习复杂模式。**ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit)** 是CNN中最常用的激活函数,因其能有效缓解梯度消失问题且计算简单。
训练过程 就是让"AI神探"通过大量案例(带标签的数据)自我学习和优化的过程,使用反向传播算法 和梯度下降优化器 来调整网络中的所有参数(卷积核权重、全连接层权重等),目标是让网络的预测结果与真实标签之间的**损失(Loss)** 最小化。
-
激活函数是神探的"判断原则" :以ReLU为例,它的原则是"低于门槛的线索一律无视(输出0),高于门槛的才予以重视(原样输出)"。这个简单的原则让神探的判断非常高效。
-
训练是神探的"实习期":
-
给神探看一张已知答案的监控图片(训练样本)。
-
神探根据当前能力做出判断(前向传播)。
-
教练(优化算法)对比神探的判断和正确答案,计算出"失误程度"(损失函数)。
-
教练将失误原因反向传达给每一个勘察小组和指挥部专家,告诉他们应该如何调整各自的"放大镜"标准和"研判准则"(反向传播更新权重)。
-
经过成千上万张图片的反复练习,神探的破案能力(模型精度)越来越强。
-
python
def training(model):
# 切换到训练模式
model.train()
# 数据加载
batch_size = 4
data_load(simulated_images, simulated_labels)
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 训练周期
for epoch in range(3):
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清零梯度
# 前向传播
raw_scores, _, _ = model(simulated_images)
# 计算损失
loss = criterion(raw_scores, simulated_labels)
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 优化器更新参数
optimizer.step()
print(f" 训练周期 {epoch + 1}: 损失值 = {loss.item():.4f}")
print(" 训练完成!")
model.eval() # 切换回评估模式2*基于CNN花朵识别
我们通过上述简单了解了一下CNN的基本知识和内容,下面来完成一个比较复杂的案列进行学习。并将多个常用模型结合学习和使用。
2.1 任务目标
本项目的任务目标是:使用深度学习模型对花朵图像进行多分类。
| 项目 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 任务类型 | 图像分类(Image Classification) |
| 分类类别 | 默认 5 类:daisy(雏菊)、dandelion(蒲公英)、roses(玫瑰)、sunflowers(向日葵)、tulips(郁金香) |
| 输入 | 单张 RGB 图像(训练/推理时统一缩放到 224×224) |
| 输出 | 类别标签 + 各类别概率(推理时) |
| 模型来源 | 从 classic_models 中选择一种网络(如 AlexNet、VGG、ResNet 等),替换最后一层为 num_classes=5,在花朵数据上训练 |
完成本任务需要经历:
① 准备花朵数据集(按 train/val、每类一个文件夹组织)
② 选择模型并训练(得到最佳权重 .pth)
③ 使用训练好的权重对单张图片做推理,得到预测类别与概率
2.2 模型训练
模型训练指:在花朵数据集上训练所选网络,得到在验证集上表现最好的权重文件,供后续推理使用。
简单训练脚本实现
python
"""
train_sample.py ------ 最简训练脚本
本文件实现「花朵五分类」的完整训练流程:加载数据 → 构建模型 → 逐 epoch 训练与验证 → 保存验证集上
准确率最高的权重。没有命令行参数,所有路径和超参数在代码里写死,适合初学者先跑通再改。
使用前请修改 data_path 为你的花朵数据集根目录(其下需有 train/ 和 val/ 子目录,每类一个文件夹)。
运行方式:python train_sample.py
"""
import os
import sys
import json
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import torch.optim as optim
from tqdm import tqdm
from classic_models.alexnet import AlexNet
def main():
# 判断可用设备
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
data_path = '/dataload/flower'
assert os.path.exists(data_path), "{} path does not exist.".format(data_path)
# 数据预处理与增强
"""
ToTensor()能够把灰度范围从0-255变换到0-1之间的张量.
transform.Normalize()则把0-1变换到(-1,1). 具体地说, 对每个通道而言, Normalize执行以下操作: image=(image-mean)/std
其中mean和std分别通过(0.5,0.5,0.5)和(0.5,0.5,0.5)进行指定。原来的0-1最小值0则变成(0-0.5)/0.5=-1; 而最大值1则变成(1-0.5)/0.5=1.
也就是一个均值为0, 方差为1的正态分布. 这样的数据输入格式可以使神经网络更快收敛。
"""
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(224),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)), # val不需要任何数据增强
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
# 使用ImageFlolder加载数据集中的图像,并使用指定的预处理操作来处理图像, ImageFlolder会同时返回图像和对应的标签。 (image path, class_index) tuples
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(data_path, "train"), transform=data_transform["train"])
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(data_path, "val"), transform=data_transform["val"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
# 使用class_to_idx给类别一个index,作为训练时的标签: {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
# 创建一个字典,存储index和类别的对应关系,在模型推理阶段会用到。
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# 将字典写成一个json文件
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open( os.path.join(data_path, 'class_indices.json') , 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
# batch_size大小,是超参,可调,如果模型跑不起来,尝试调小batch_size
batch_size = 64
# 使用 DataLoader 将 ImageFloder 加载的数据集处理成批量(batch)加载模式
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True )
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=False ) # 注意,验证集不需要shuffle
print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(train_num, val_num))
# 实例化模型,并送进设备
net = AlexNet(num_classes=5 )
net.to(device)
# 指定损失函数用于计算损失;指定优化器用于更新模型参数;指定训练迭代的轮数,训练权重的存储地址
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # MSE
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0002)
epochs = 70
save_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), './results/weights/alexnet'))
if not os.path.exists(save_path):
os.makedirs(save_path)
# 初始化验证集上最好的准确率,以便后面用该指标筛选模型最优参数。
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(epochs):
net.train()
acc_num = torch.zeros(1).to(device) # 初始化,用于计算训练过程中预测正确的数量
sample_num = 0 # 初始化,用于记录当前迭代中,已经计算了多少个样本
# tqdm是一个进度条显示器,可以在终端打印出现在的训练进度
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout, ncols=100)
for data in train_bar :
images, labels = data
sample_num += images.shape[0] #[64, 3, 224, 224]
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(images.to(device)) # output_shape: [batch_size, num_classes]
pred_class = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1] # torch.max 返回值是一个tuple,第一个元素是max值,第二个元素是max值的索引。
acc_num += torch.eq(pred_class, labels.to(device)).sum()
loss = loss_function(outputs, labels.to(device)) # 求损失
loss.backward() # 自动求导
optimizer.step() # 梯度下降
# print statistics
train_acc = acc_num.item() / sample_num
# .desc是进度条tqdm中的成员变量,作用是描述信息
train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1, epochs, loss)
# validate
net.eval()
acc_num = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number per epoch
with torch.no_grad():
for val_data in validate_loader:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device))
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc_num += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_accurate = acc_num / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f train_acc: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' % (epoch + 1, loss, train_acc, val_accurate))
# 判断当前验证集的准确率是否是最大的,如果是,则更新之前保存的权重
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), os.path.join(save_path, "AlexNet.pth") )
# 每次迭代后清空这些指标,重新计算
train_acc = 0.0
val_accurate = 0.0
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()AlexNet
python
"""
【文件说明】alexnet.py ------ AlexNet 模型定义
经典 CNN 结构:5 层卷积 + 3 层全连接,输入 224×224 RGB,输出 num_classes 维 logits。
提供类 AlexNet 与工厂函数 alexnet(num_classes),供训练/推理使用。
"""
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
"""AlexNet:卷积特征提取 + 全连接分类头。"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False):
"""
传参:
num_classes (int, 可选): 分类数,默认 1000(ImageNet)。
init_weights (bool, 可选): 是否用 Kaiming/Normal 初始化权重,默认 False。
返回值:
无(构造器)。
"""
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2), # input[3, 224, 224] output[96, 55, 55]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[96, 27, 27]
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), # output[256, 27, 27]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[256, 13, 13]
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[384, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[384, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[256, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[256, 6, 6]
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
"""
传参:
x (torch.Tensor): 输入图像,形状 (N, 3, 224, 224)。
返回值:
torch.Tensor: logits,形状 (N, num_classes)。
"""
x = self.features(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def alexnet(num_classes):
"""
工厂函数:构造 AlexNet 模型。
传参:
num_classes (int): 分类类别数。
返回值:
AlexNet: 已实例化的模型。
"""
model = AlexNet(num_classes=num_classes)
return model优化训练实现
python
############################################################################################################
# 相较于简单版本的训练脚本 train_sample 增添了以下功能:
# 1. 使用argparse类实现可以在训练的启动命令中指定超参数
# 2. 可以通过在启动命令中指定 --seed 来固定网络的初始化方式,以达到结果可复现的效果
# 3. 使用了更高级的学习策略 cosine warm up:在训练的第一轮使用一个较小的lr(warm_up),从第二个epoch开始,随训练轮数逐渐减小lr。
# 4. 可以通过在启动命令中指定 --model 来选择使用的模型
# 5. 使用amp包实现半精度训练,在保证准确率的同时尽可能的减小训练成本
# 6. 实现了数据加载类的自定义实现
# 7. 可以通过在启动命令中指定 --tensorboard 来进行tensorboard可视化, 默认不启用。
# 注意,使用tensorboad之前需要使用命令 "tensorboard --logdir= log_path"来启动,结果通过网页 http://localhost:6006/'查看可视化结果
############################################################################################################
import os
import argparse
import math
import random
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import transforms
import torch.optim.lr_scheduler as lr_scheduler
import classic_models
from utils.lr_methods import warmup
from dataload.dataload_five_flower import Five_Flowers_Load
from utils.train_engin import train_one_epoch, evaluate
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--num_classes', type=int, default=5, help='the number of classes')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=50, help='the number of training epoch')
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=64, help='batch_size for training')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.0002, help='star learning rate')
parser.add_argument('--lrf', type=float, default=0.0001, help='end learning rate')
parser.add_argument('--seed', default=False, action='store_true', help='fix the initialization of parameters')
parser.add_argument('--use_amp', default=False, action='store_true', help=' training with mixed precision')
parser.add_argument('--data_path', type=str, default="/mnt/d/Datasets/flower")
parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default="vgg", help=' select a model for training')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)')
opt = parser.parse_args()
if opt.seed:
def seed_torch(seed=7):
random.seed(seed) # Python random module.
os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = str(seed) # 为了禁止hash随机化,使得实验可复现
np.random.seed(seed) # Numpy module.
torch.manual_seed(seed) # 为CPU设置随机种子
torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) # 为当前GPU设置随机种子
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) # if you are using multi-GPU.
# 设置cuDNN:cudnn中对卷积操作进行了优化,牺牲了精度来换取计算效率。如果需要保证可重复性,可以使用如下设置:
# torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
# torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
# 实际上这个设置对精度影响不大,仅仅是小数点后几位的差别。所以如果不是对精度要求极高,其实不太建议修改,因为会使计算效率降低。
print('random seed has been fixed')
seed_torch()
def main(args):
"""
主函数:根据命令行参数完成训练(数据加载、模型构建、train_one_epoch + evaluate、保存最佳权重)。
传参:
args: 解析后的命令行参数对象。常用属性:num_classes, epochs, batch_size, lr, lrf, data_path,
model, device, use_amp, seed 等。
返回值:
无。最佳权重保存到 results/weights/<args.model>/AlexNet.pth,日志追加到同目录 AlexNet_log.txt。
"""
device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(args)
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])}
# 对标pytorch封装好的ImageFlolder,我们自己实现了一个数据加载类 Five_Flowers_Load,并使用指定的预处理操作来处理图像,结果会同时返回图像和对应的标签。
train_dataset = Five_Flowers_Load(os.path.join(args.data_path , 'train'), transform=data_transform["train"])
val_dataset = Five_Flowers_Load(os.path.join(args.data_path , 'val'), transform=data_transform["val"])
if args.num_classes != train_dataset.num_class:
raise ValueError("dataset have {} classes, but input {}".format(train_dataset.num_class, args.num_classes))
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), args.batch_size if args.batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
# 使用 DataLoader 将加载的数据集处理成批量(batch)加载模式
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, pin_memory=True, num_workers=nw, collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False, pin_memory=True, num_workers=nw, collate_fn=val_dataset.collate_fn)
# create model
model = classic_models.find_model_using_name(opt.model, num_classes=opt.num_classes).to(device)
pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = optim.Adam(pg, lr=args.lr)
# Scheduler https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.01187.pdf
lf = lambda x: ((1 + math.cos(x * math.pi / args.epochs)) / 2) * (1 - args.lrf) + args.lrf # cosine
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lf)
best_acc = 0.
# save parameters path
save_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'results/weights', args.model)
if os.path.exists(save_path) is False:
os.makedirs(save_path)
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
# train
mean_loss, train_acc = train_one_epoch(model=model, optimizer=optimizer, data_loader=train_loader, device=device, epoch=epoch, use_amp=args.use_amp, lr_method= warmup)
scheduler.step()
# validate
val_acc = evaluate(model=model, data_loader=val_loader, device=device)
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f train_acc: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' % (epoch + 1, mean_loss, train_acc, val_acc))
with open(os.path.join(save_path, "AlexNet_log.txt"), 'a') as f:
f.writelines('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f train_acc: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' % (epoch + 1, mean_loss, train_acc, val_acc) + '\n')
# 判断当前验证集的准确率是否是最大的,如果是,则更新之前保存的权重
if val_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = val_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(save_path, "AlexNet.pth"))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(opt)输出分析
2.3 模型推理
python
"""
【文件说明】test.py ------ 推理脚本(用训练好的模型预测单张图片)
本文件实现:加载一张图片 → 做与训练时一致的预处理 → 加载模型权重 → 前向推理得到各类别概率 →
在窗口显示原图并打印类别与概率。运行前需在代码中修改:图片路径 img_path、类别索引文件 json_path、
权重路径 weights_path。
运行方式:python test.py
"""
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from classic_models.alexnet import AlexNet
def main():
"""
主函数:加载一张图片和训练好的模型,输出预测类别与概率,并弹窗显示图片和标题。
传参:
无。需在函数内修改 img_path、json_path、weights_path 为你的路径。
返回值:
无。会打印各类别概率,并调用 plt.show() 显示带预测结果的图片。
"""
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# load image
img_path = "/data/haowen_yu/code/dataset/flowers/val/daisy/3640845041_80a92c4205_n.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = '/data/haowen_yu/code/dataset/flowers/class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = AlexNet(num_classes=5).to(device)
# load model weights
weights_path = "/data/haowen_yu/code/results/weights/alexnet/AlexNet.pth"
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(weights_path)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path))
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)],
predict[i].numpy()))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2.4 模型介绍
2.4.1 DLA
python
"""
【文件说明】dla.py ------ DLA (Deep Layer Aggregation) 模型
支持层级聚合的骨干网络。对外接口:dla34(num_classes, **kwargs)。
"""
import math
import torch
from torch import nn
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1 ):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False )
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x, residual=None):
if residual is None:
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Root(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, residual):
super(Root, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d( in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, bias=False, padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.residual = residual
def forward(self, *x):
children = x
x = self.conv(torch.cat(x, 1))
x = self.bn(x)
if self.residual:
x += children[0]
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class Tree(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, levels, block, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1,
level_root=False, root_dim=0, root_kernel_size=1, root_residual=False):
super(Tree, self).__init__()
self.level_root = level_root
self.levels = levels
self.root_dim = root_dim
self.downsample = None
self.project = None
if root_dim == 0:
root_dim = 2 * out_channels
if level_root:
root_dim += in_channels
if levels == 1:
self.tree1 = block(in_channels, out_channels, stride)
self.tree2 = block(out_channels, out_channels, stride=1)
self.root = Root(root_dim, out_channels, root_kernel_size, root_residual)
else:
self.tree1 = Tree(levels - 1, block, in_channels, out_channels, stride,
root_dim=0,
root_kernel_size=root_kernel_size,
root_residual=root_residual)
self.tree2 = Tree(levels - 1, block, out_channels, out_channels,
root_dim=root_dim + out_channels,
root_kernel_size=root_kernel_size,
root_residual=root_residual)
if stride > 1:
self.downsample = nn.MaxPool2d(stride, stride=stride)
if in_channels != out_channels:
self.project = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
def forward(self, x, residual=None, children=None):
children = [] if children is None else children
bottom = self.downsample(x) if self.downsample else x
residual = self.project(bottom) if self.project else bottom
if self.level_root:
children.append(bottom)
x1 = self.tree1(x, residual)
if self.levels == 1:
x2 = self.tree2(x1)
out = self.root(x2, x1, *children)
else:
children.append(x1)
out = self.tree2(x1, children=children)
return out
class DLA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layers, channels, num_classes=1000, block=BasicBlock, residual_root=False, pool_size=7 ):
super().__init__()
self.channels = channels
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.patchfy_stem = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, channels[0], kernel_size=7, stride=1, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channels[0]),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.stage_0 = self._make_conv_level(channels[0], channels[0], layers[0])
self.stage_1 = self._make_conv_level(channels[0], channels[1], layers[1], stride=2)
self.stage_2 = Tree(layers[2], block, channels[1], channels[2], stride=2,
level_root=False, root_residual=residual_root)
self.stage_3 = Tree(layers[3], block, channels[2], channels[3], stride=2,
level_root=True, root_residual=residual_root)
self.stage_4 = Tree(layers[4], block, channels[3], channels[4], stride=2,
level_root=True, root_residual=residual_root)
self.stage_5 = Tree(layers[5], block, channels[4], channels[5], stride=2,
level_root=True, root_residual=residual_root)
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(pool_size)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], num_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def _make_conv_level(self, inplanes, planes, num_layers, stride=1 ):
modules = []
for i in range(num_layers):
modules.extend([
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride if i == 0 else 1,
padding=1, bias=False ),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)])
inplanes = planes
return nn.Sequential(*modules)
def forward(self, x):
stages_features_list = []
x = self.patchfy_stem(x)
for i in range(6):
x = getattr(self, 'stage_{}'.format(i))(x)
stages_features_list.append(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = self.fc(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
return x
def dla34(num_classes, **kwargs):
"""传参: num_classes (int), **kwargs 可选。返回值: DLA 模型实例。"""
model = DLA(layers=[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1],
channels=[16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512],
block=BasicBlock, num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs)
return model
# net = dla34(5)
# summary(net.to('cuda'), (3, 224,224))2.4.2 RESNET
python
"""
【文件说明】resnet.py ------ ResNet / ResNeXt 系列模型
包含 BasicBlock、Bottleneck、ResNet 及工厂函数:resnet34、resnet50、resnet101、
resnext50_32x4d、resnext101_32x8d。输入 224×224,输出 num_classes 维 logits。
"""
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
"""
注意:原论文中,在虚线残差结构的主分支上,第一个1x1卷积层的步距是2,第二个3x3卷积层步距是1。
但在pytorch官方实现过程中是第一个1x1卷积层的步距是1,第二个3x3卷积层步距是2,
这么做的好处是能够在top1上提升大概0.5%的准确率。
可参考Resnet v1.5 https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch
"""
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None,
groups=1, width_per_group=64):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(out_channel * (width_per_group / 64.)) * groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=width, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=width, groups=groups, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block,
blocks_num,
num_classes=1000,
include_top=True,
groups=1,
width_per_group=64):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.groups = groups
self.width_per_group = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
downsample=downsample,
stride=stride,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# # resnet34 pre-train parameters https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
# def resnet_samll(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
# # resnet50 pre-train parameters https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
# def resnet(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
# # resnet101 pre-train parameters https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
# def resnet_big(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
# # resneXt pre-train parameters https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth
# def resnext(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# groups = 32
# width_per_group = 4
# return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
# num_classes=num_classes,
# include_top=include_top,
# groups=groups,
# width_per_group=width_per_group)
# # resneXt_big pre-train parameters https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth
# def resnext_big(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# groups = 32
# width_per_group = 8
# return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
# num_classes=num_classes,
# include_top=include_top,
# groups=groups,
# width_per_group=width_per_group)
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
"""传参: num_classes (int), include_top (bool)。返回值: ResNet 模型实例。"""
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
"""传参: num_classes (int), include_top (bool)。返回值: ResNet 模型实例。"""
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
"""传参: num_classes (int), include_top (bool)。返回值: ResNet 模型实例。"""
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnext50_32x4d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
"""传参: num_classes (int), include_top (bool)。返回值: ResNet 模型实例。"""
groups = 32
width_per_group = 4
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
def resnext101_32x8d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
"""传参: num_classes (int), include_top (bool)。返回值: ResNet 模型实例。"""
groups = 32
width_per_group = 8
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)2.4.3 VAN
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from functools import partial
from timm.models.layers import DropPath, to_2tuple, trunc_normal_
import math
class DWConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim=768):
super(DWConv, self).__init__()
self.dwconv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1, bias=True, groups=dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.dwconv(x)
return x
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(in_features, hidden_features, 1)
self.dwconv = DWConv(hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_features, out_features, 1)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
fan_out = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
fan_out //= m.groups
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2.0 / fan_out))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.dwconv(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class LKA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
self.conv0 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 5, padding=2, groups=dim)
self.conv_spatial = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 7, stride=1, padding=9, groups=dim, dilation=3)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
u = x.clone()
attn = self.conv0(x)
attn = self.conv_spatial(attn)
attn = self.conv1(attn)
return u * attn
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model):
super().__init__()
self.proj_1 = nn.Conv2d(d_model, d_model, 1)
self.activation = nn.GELU()
self.spatial_gating_unit = LKA(d_model)
self.proj_2 = nn.Conv2d(d_model, d_model, 1)
def forward(self, x):
shorcut = x.clone()
x = self.proj_1(x)
x = self.activation(x)
x = self.spatial_gating_unit(x)
x = self.proj_2(x)
x = x + shorcut
return x
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, mlp_ratio=4., drop=0.,drop_path=0., act_layer=nn.GELU):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(dim)
self.attn = Attention(dim)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
layer_scale_init_value = 1e-2
self.layer_scale_1 = nn.Parameter(
layer_scale_init_value * torch.ones((dim)), requires_grad=True)
self.layer_scale_2 = nn.Parameter(
layer_scale_init_value * torch.ones((dim)), requires_grad=True)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
fan_out = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
fan_out //= m.groups
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2.0 / fan_out))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.layer_scale_1.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) * self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.layer_scale_2.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) * self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
class OverlapPatchEmbed(nn.Module):
""" Image to Patch Embedding
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=7, stride=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=768):
super().__init__()
patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=stride,
padding=(patch_size[0] // 2, patch_size[1] // 2))
self.norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(embed_dim)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
fan_out = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
fan_out //= m.groups
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2.0 / fan_out))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.proj(x)
_, _, H, W = x.shape
x = self.norm(x)
return x, H, W
class VAN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=224, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000, embed_dims=[64, 128, 256, 512],
mlp_ratios=[4, 4, 4, 4], drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
depths=[3, 4, 6, 3], num_stages=4, flag=False):
super().__init__()
if flag == False:
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.depths = depths
self.num_stages = num_stages
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule
cur = 0
for i in range(num_stages):
patch_embed = OverlapPatchEmbed(img_size=img_size if i == 0 else img_size // (2 ** (i + 1)),
patch_size=7 if i == 0 else 3,
stride=4 if i == 0 else 2,
in_chans=in_chans if i == 0 else embed_dims[i - 1],
embed_dim=embed_dims[i])
block = nn.ModuleList([Block(
dim=embed_dims[i], mlp_ratio=mlp_ratios[i], drop=drop_rate, drop_path=dpr[cur + j])
for j in range(depths[i])])
norm = norm_layer(embed_dims[i])
cur += depths[i]
setattr(self, f"patch_embed{i + 1}", patch_embed)
setattr(self, f"block{i + 1}", block)
setattr(self, f"norm{i + 1}", norm)
# classification head
self.head = nn.Linear(embed_dims[3], num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
fan_out = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
fan_out //= m.groups
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2.0 / fan_out))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward_features(self, x):
B = x.shape[0]
for i in range(self.num_stages):
patch_embed = getattr(self, f"patch_embed{i + 1}")
block = getattr(self, f"block{i + 1}")
norm = getattr(self, f"norm{i + 1}")
x, H, W = patch_embed(x)
for blk in block:
x = blk(x)
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = norm(x)
if i != self.num_stages - 1:
x = x.reshape(B, H, W, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
return x.mean(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x2.4.4 VGG
python
"""
【文件说明】vggnet.py ------ VGG 系列模型(VGG11/13/16/19)
通过 make_features(cfg) 与 VGG 分类头组成网络,输入 224×224,输出 num_classes 维 logits。
对外接口:vgg11(num_classes)、vgg13(num_classes)、vgg16(num_classes)、vgg19(num_classes)。
"""
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# official pretrain weights
model_urls = {
'vgg11': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg11-bbd30ac9.pth',
'vgg13': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg13-c768596a.pth',
'vgg16': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg16-397923af.pth',
'vgg19': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth'
}
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512*7*7, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes)
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 224 x 224
x = self.features(x)
# N x 512 x 7 x 7
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
# N x 512*7*7
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
# nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
# nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def make_features(cfg: list):
layers = []
in_channels = 3
for v in cfg:
if v == "M":
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(True)]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# vgg_tiny(VGG11), vgg_small(VGG13), vgg(VGG16), vgg_big(VGG19)
cfgs = {
'vgg11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
}
def vgg11(num_classes):
"""传参: num_classes (int)。返回值: VGG 模型实例。"""
cfg = cfgs["vgg11"]
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vgg13(num_classes):
"""传参: num_classes (int)。返回值: VGG 模型实例。"""
cfg = cfgs["vgg13"]
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vgg16(num_classes):
"""传参: num_classes (int)。返回值: VGG 模型实例。"""
cfg = cfgs["vgg16"]
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vgg19(num_classes):
"""传参: num_classes (int)。返回值: VGG 模型实例。"""
cfg = cfgs['vgg19']
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), num_classes=num_classes)
return model2.5 *完整代码资源
数据加载模块
python
"""
【文件说明】dataload_five_flower.py ------ 五类花朵数据集(PyTorch Dataset)
本文件定义 Five_Flowers_Load,按「每个类别一个子文件夹」的目录结构读取图片,支持自定义
transform,可与 DataLoader 配合使用。要求目录下为若干子文件夹,文件夹名为类别名,其内为 .jpg/.png 等图片。
使用示例:
dataset = Five_Flowers_Load("/path/to/flower/train", transform=my_transform)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True, collate_fn=Five_Flowers_Load.collate_fn)
"""
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib.cbook import ls_mapper
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import random
import os
class Five_Flowers_Load(Dataset):
"""
五类花朵数据集。按子文件夹名作为类别,收集所有支持后缀的图片路径与标签。
"""
def __init__(self, data_path: str, transform=None):
"""
初始化:扫描 data_path 下每个子文件夹,记录每张图片路径与类别索引。
传参:
data_path (str): 数据集根目录,其下每个子文件夹名为一类(如 daisy, dandelion)。
transform (callable, 可选): 对 PIL 图像做的变换,如 transforms.Compose([...]);为 None 时 __getitem__ 会报错要求必须预处理。
返回值:
无。实例属性包括:data_path, transform, num_class, images_path, images_label, images_num。
"""
self.data_path = data_path
self.transform = transform
random.seed(0) # 保证随机结果可复现
assert os.path.exists(data_path), "dataset root: {} does not exist.".format(data_path)
# 遍历文件夹,一个文件夹对应一个类别
flower_class = [cla for cla in os.listdir(os.path.join(data_path))]
self.num_class = len(flower_class)
# 排序,保证顺序一致
flower_class.sort()
# 生成类别名称以及对应的数字索引 {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
class_indices = dict((cla, idx) for idx, cla in enumerate(flower_class))
self.images_path = [] # 存储训练集的所有图片路径
self.images_label = [] # 存储训练集图片对应索引信息
self.images_num = [] # 存储每个类别的样本总数
supported = [".jpg", ".JPG", ".png", ".PNG"] # 支持的文件后缀类型
# 遍历每个文件夹下的文件
for cla in flower_class:
cla_path = os.path.join(data_path, cla)
# 遍历获取supported支持的所有文件路径
images = [os.path.join(data_path, cla, i) for i in os.listdir(cla_path) if os.path.splitext(i)[-1] in supported]
# 获取该类别对应的索引
image_class = class_indices[cla]
# 记录该类别的样本数量
self.images_num.append(len(images))
# 写入列表
for img_path in images:
self.images_path.append(img_path)
self.images_label.append(image_class)
print("{} images were found in the dataset.".format(sum(self.images_num)))
def __len__(self):
"""
返回数据集中样本总数。
传参: 无(使用 self)。
返回值: int,即 sum(self.images_num)。
"""
return sum(self.images_num)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
"""
返回第 idx 个样本的(图像张量, 标签)。
传参:
idx (int): 样本索引,范围 [0, len(self)-1]。
返回值:
tuple: (img, label)。img 为经 self.transform 处理后的张量;label 为 int,类别索引。
"""
img = Image.open(self.images_path[idx])
label = self.images_label[idx]
if img.mode != 'RGB':
raise ValueError("image: {} isn't RGB mode.".format(self.images_path[idx]))
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img)
else:
raise ValueError('Image is not preprocessed')
return img, label
# 非必须实现,torch里有默认实现;该函数的作用是: 决定一个batch的数据以什么形式来返回数据和标签
# 官方实现的default_collate可以参考
# https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/67b7e751e6b5931a9f45274653f4f653a4e6cdf6/torch/utils/data/_utils/collate.py
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
"""
将 DataLoader 采样的一个 batch 的 list[(img, label)] 整理成 (images, labels) 张量。
传参:
batch (list of tuple): 每个元素为 (img_tensor, label),长度为 batch_size。
返回值:
tuple: (images, labels)。images 形状 (B, C, H, W);labels 形状 (B,) 的 LongTensor。
"""
images, labels = tuple(zip(*batch))
images = torch.stack(images, dim=0)
labels = torch.as_tensor(labels)
return images, labels
学习率调节
python
"""
【文件说明】lr_methods.py ------ 学习率调度方法
提供 warmup:在训练前若干 step 内,学习率从 base_lr * warm_up_factor 线性增加到 base_lr,
之后保持 1 倍。返回的调度器需在每 step 或每 epoch 调用 .step()。
"""
import torch
def warmup(optimizer, warm_up_iters, warm_up_factor):
"""
构造一个 warmup 学习率调度器:前 warm_up_iters 步内 lr 倍率从 warm_up_factor 线性增至 1。
传参:
optimizer (Optimizer): 优化器,其 param_groups[0]['lr'] 为 base 学习率。
warm_up_iters (int): warmup 步数,超过后倍率为 1。
warm_up_factor (float): 起始倍率,通常取较小值如 1/1000。
返回值:
LambdaLR: 调度器,每调用 .step() 一次即一步;实际 lr = base_lr * lr_lambda(step)。
"""
def f(x):
"""根据 step 数 x 返回学习率倍率因子。"""
if x >= warm_up_iters:
return 1
alpha = float(x) / warm_up_iters
return warm_up_factor * (1 - alpha) + alpha
return torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=f)特征图绘制
python
"""
【文件说明】visualization.py ------ 特征图可视化示例
本文件内含一个「可输出中间特征图」的 AlexNet 变体(仅 features 部分前若干层输出 list),以及
使用示例:加载权重、读图、前向得到特征图并画图保存。与 classic_models/alexnet 中的 AlexNet 不同,
此处用于可视化而非训练/推理。直接运行本脚本会执行示例代码。
"""
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
"""
用于可视化的 AlexNet:forward 返回指定层的特征图 list,便于画图。
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=5, init_weights=False):
"""
传参: num_classes (int),init_weights (bool)。此处 classifier 仍存在但示例中未用到完整分类。
返回值: 无。
"""
super().__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2), # input[3, 224, 224] output[96, 55, 55]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[96, 27, 27]
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), # output[256, 27, 27]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[256, 13, 13]
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[384, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[384, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[256, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[256, 6, 6]
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
"""
传参: x (torch.Tensor),形状 (N, 3, H, W)。
返回值: list of Tensor,仅包含指定层(如 "0")的特征图,用于可视化。
"""
outputs = []
for name, module in self.features.named_children():
x = module(x)
if name in ["0"]:
outputs.append(x)
return outputs
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# create model
model = AlexNet(num_classes=5)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "../results/weights/alexnet/AlexNet.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path))
print(model)
# load image
img = Image.open("./sunflower.jpg")
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# forward
out_put = model(img)
for feature_map in out_put:
# [N, C, H, W] -> [C, H, W]
im = np.squeeze(feature_map.detach().numpy())
# [C, H, W] -> [H, W, C]
im = np.transpose(im, [1, 2, 0])
# show top 12 feature maps
plt.figure()
for i in range(12):
ax = plt.subplot(3, 4, i+1)
# [H, W, C]
plt.imshow(im[:, :, i], cmap='gray')
plt.show()
plt.savefig("./AelxNet_vis.jpg")2026.02.08