文档搜索引擎模块划分(第一篇)见系列文章:
索引模块程序见下文:
搜索模块程序见下文:
本文实现项目的多词检索结果的权重合并优化。
目录
[1. 实现检索结果计数](#1. 实现检索结果计数)
[2. 权重合并问题](#2. 权重合并问题)
修改点3:封装一个mergeResult方法进行具体的权重合并
1. 实现检索结果计数
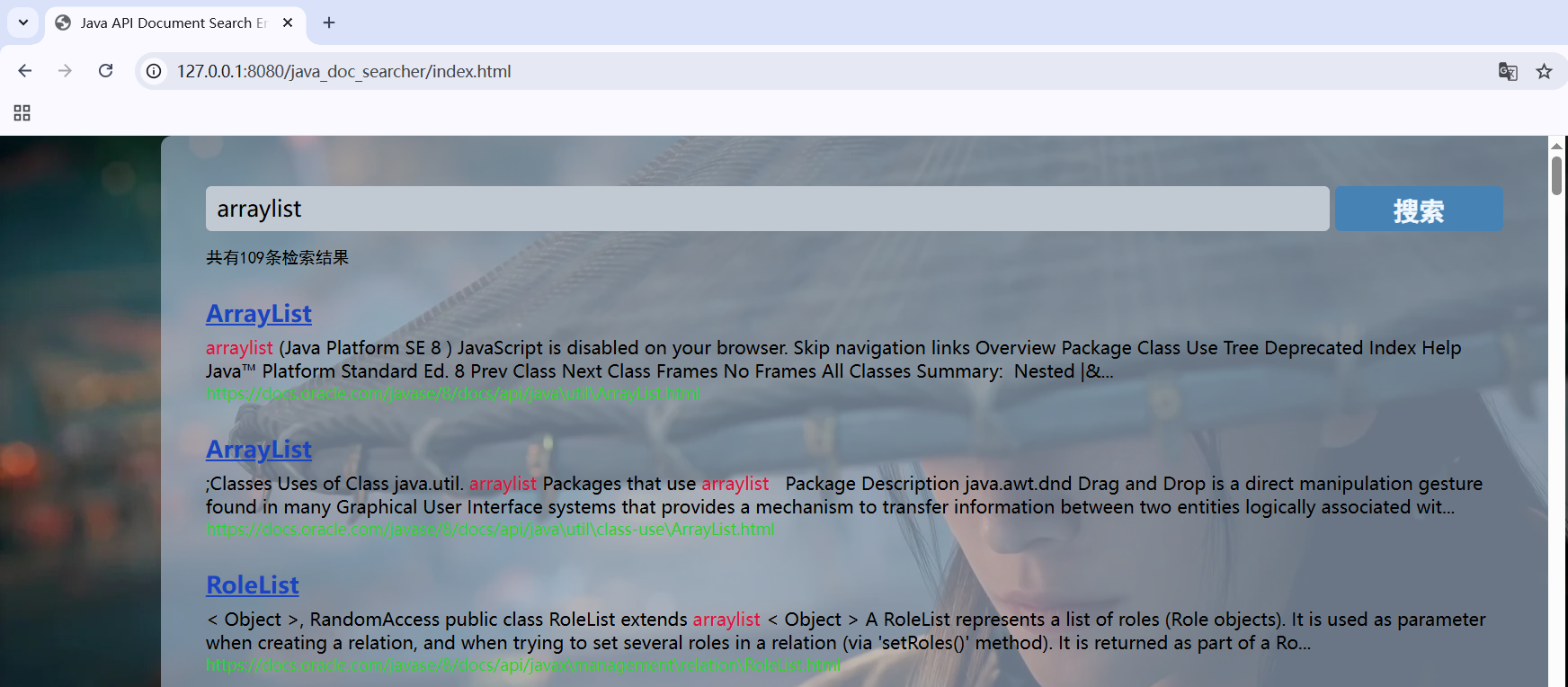
现在前端实现检索结果的计数。在构造所有检索结果前,即在buildResult函数中增加对检索结果条目数的计数:
javascript
// 展示查询结果的个数
let countDiv = document.createElement('div');
countDiv.innerHTML="共有"+data.length+"条检索结果";
result.appendChild(countDiv);
countDiv.className="count";定义其className为count后,增加选择器进行样式设计:
javascript
.result .count{
margin-top: 10px;
font-family: "黑体";
font-size: 15px;
}即可实现检索结果的计数,刷新浏览器进行测试,可在搜索结果顶端查看到检索结果数目:
2. 权重合并问题
测试搜索array list会发现:那些既包括array也包括list的文档会重复出现,如Collections,(可自行测试,两个结果具有一定距离,是由于一个结果是作为搜索array时计算array所占权重排序后的结果,另一个结果是作为搜索list时计算list所占权重排序后的结果)
这种现象存在有两个不合理之处:
(1)既包括array也包括list的文档不应该出现两次,应将多个结果合并;
(2)既包括array也包括list的文档应该是与两个搜索词均相关的结果,即相关性更高,应提高这些文档的权重,使其排序位置相对靠前。
接下来对DocSearcher类进行修改以解决多词查找导致的文档重复问题。
解决思路总体是:
把多个分词结果触发的文档按照docId进行去重,并采用权重相加的方式进行文档权重合并。
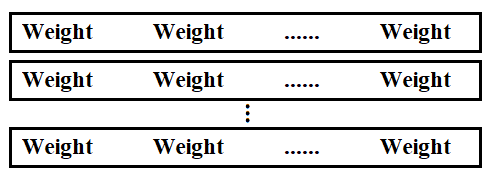
修改点1:使用二维数据结构存储分词检索结果
在之前的程序中,我们直接采用一个元素为Weight的List来存储结果,即List<Weight>。
故而对于多个词触发同一文档的问题无法进行去重。
现将存储检索结果的数据结构修改为List<List<Weight>>,每一行是一个分词结果触发的检索结果一维List:
java
List<List<Weight>> termResult = new ArrayList<>();修改点2:使用一个内部类Pos描述元素在二维数组中的位置
java
// 定义一个内部类Pos来描述一个元素在二维数组中的位置
static class Pos{
public int row;
public int column;
public Pos(int row, int column) {
this.row = row;
this.column = column;
}
}修改点3:封装一个mergeResult方法进行具体的权重合并
mergeResult方法的实现思路如下:
(1)首先,对每一行进行排序。此处按照docId进行升序排序;
(2)借助一个优先队列对若干行进行合并;
java
// 定义一个内部类Pos来描述一个元素在二维数组中的位置
static class Pos{
public int row;
public int column;
public Pos(int row, int column) {
this.row = row;
this.column = column;
}
}
private List<Weight> mergeResult(List<List<Weight>> source) {
// 1. 对每一行的Weight元素按照docId进行升序排序
for(List<Weight> curRow: source){
curRow.sort(new Comparator<Weight>() {
@Override
public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) {
return o1.getDocId()-o2.getDocId();
}
});
}
// 2. 借助一个优先队列进行合并
List<Weight> target = new ArrayList<>();
// (1) 创建优先级队列,并指定比较规则为按照Weight的docId取小者优先
PriorityQueue<Pos> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Pos>() {
@Override
public int compare(Pos o1, Pos o2) {
// 先根据Pos值找到对应的Weight对象
Weight w1 = source.get(o1.row).get(o1.column);
Weight w2 = source.get(o2.row).get(o2.column);
// 再根据Weight的docId排序
return w1.getDocId()- w2.getDocId();
}
});
// (2) 初始化队列:把每一行第一个元素放到队列中
for(int row=0; row<source.size(); row++){
queue.offer(new Pos(row, 0));
}
// (3) 循环取队首元素
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Pos minPos = queue.poll();
Weight curWeight = source.get(minPos.row).get(minPos.column); // 当前取出的元素
// 若target非空
if(target.size()>0){
Weight lastWeight = target.get(target.size()-1); // 上一次取出的元素
// 若文档的docId相同(即是相同文档),对旧Weight相加权重,无需再插入新Weight
if(lastWeight.getDocId() == curWeight.getDocId()){
lastWeight.setWeight(lastWeight.getWeight() + curWeight.getWeight());
}else{
// 若文档的dicId不同(即是不同文档),直接插入新Weight
target.add(curWeight);
}
}else{
// 若target为空,则直接插入当前元素
target.add(curWeight);
}
// (4) 处理完当前元素后,把对应这个元素的光标向后移动去取这一行的下一个元素
Pos newPos = new Pos(minPos.row, minPos.column+1);
if(newPos.column >= source.get(newPos.row).size()){
// 若移动光标后超出列数,则说明本行处理完毕
continue;
}
queue.offer(newPos);
}
return target;
}注:source表示未处理前的二维Weight表,target表示合并处理后的一维Weight List;
修改点4:调用mergeResult进行权重合并
java
// 2. 针对分词结果查倒排索引
/*
* 新版:进行权重合并
* */
List<List<Weight>> termResult = new ArrayList<>();
for(Term term: terms){
String word = term.getName();
List<Weight> invertedList = index.getInverted(word);
// 词在文档中不存在,则跳过本次循环
if(invertedList == null)
continue;
termResult.add(invertedList);
}
// 3. 对多个分词结果触发出的相同文档进行权重合并
List<Weight> allTermResult = mergeResult(termResult);
// 4. 针对触发结果按照权重降序排序
allTermResult.sort(new Comparator<Weight>() {
@Override
public int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) {
return o2.getWeight()-o1.getWeight(); // 降序
// 若为升序,则返回o1.getWeight()-o2.getWeight()
}
});