前言
MyBatis-plus与Spring Boot、Spring cloud等框架无缝集成,其在保持MyBatis性能的同时,提供了许多便捷的功能,极大地提高了开发效率。MyBatis-plus简化了MyBatis的开发,提供了基础的CURD操作的封装,无需编写XML配置文件,简化了数据库的操作。
前期工作
下载好数据库(mysql等)
一.搭建SpringBoot项目
二.引入mySQL依赖和MyBatis依赖
MyBatis-plus提供了由SpringBoot集成的starter启动器,在pom,xml中引入Mybatis-plus启动器,代码如下
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3.1</version>
</dependency>mysql驱动依赖,代码如下
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>三.创建数据库(表)和实体类
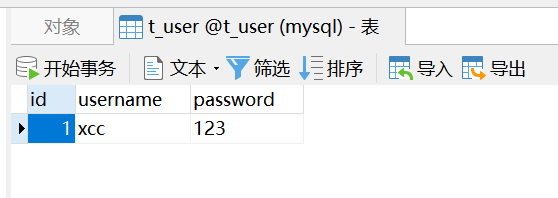
创建数据表t_user(演示案例)
创建实体类Tuser(演示案例)
package com.example.springbootmybatis.entity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Tuser {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
}四.创建DataSource数据源配置和MyBatis-plus配置
DataSource数据源配置,代码如下
#配置数据库的信息
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:///t_user #///代表省略了端口号和ip
username: root
password: rootMyBatis-plus配置(临时配置),代码如下
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
mapper-locations: classpath:/mappers/*.xml #在mappers路径下寻找xml文件
type-aliases-package: com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity #实体类所在包的路径,这样在xml文件里面不需要全限定类名
global-config: #全局配置
db-config:
id-type: auto
field-strategy: ignored
column-like: true五.创建持久层mapper接口文件
在mapper包下创建一个用于数据库t_user数据库的操作接口MyUserDao,代码如下:
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface MyUserDao extends BaseMapper<Tuser> {
// 这里不需要编写任何方法,继承了 BaseMapper 接口后,已经包含了常用的数据库操作方法
}由上图,MyUserDao接口里面暂时不用写通用的增删查改方法,MyUserDao接口继承了BaseMapper<Tuser>, BaseMapper<T >接口又是MyBatis-plus提供的基础Mapper接口,它继承了MyBatis的mapper接口,并增加了大量通用的CURD方法。
所有实体mapper接口(MyUserDao)都可以继承这个接口,从而获得默认的通用方法。
BaseMapper接口默认的基本通用方法,表格如下:
|-------------------------------------------------------|----------------------|
| 基本方法 | 描述 |
| int insert(T entity) | 插入一条记录,返回的是影响的行数 |
| int deleteById(Serializable id) | 根据ID删除一条记录,返回的是影响的行数 |
| T updateById(T entity) | 根据ID更新一条记录 |
| T selectById(Serializable id) | 根据ID查询一条记录 |
| List<T> selectBatchIds(Collect< Interage> idList) | 根据id集合查询多条记录 |
| List<T> selectByMap(Map<String,Object> map) | 根据map条件查询多条记录 |
| List<T> selectList(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) | 根据条件查询多条记录 |
六.创建服务层接口文件
在service包下创建一个用于mapper接口文件的业务层操作接口MyUserService,代码如下:
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
public interface MyUserService extends IService<Tuser> {
}MyUserService接口继承了Iservice接口,Iservice是MyBatis-plus提供的通用的接口,它定义了一些常用的业务方法,可以在业务层中直接使用,Iservice接口提供的常用方法,如下图
Iservice提供的常用方法
|------------------------------------------------|--------------|
| 基本方法 | 描述 |
| boolean save(T entity) | 保存一条记录 |
| boolean saveBatch(Collection<T > entityList) | 批量保存记录 |
| boolean removeById(Serializable id) | 根据Id删除一条记录 |
| boolean removeByMap(Map<String ,Object> map) | 根据map条件删除记录 |
| boolean updateById(T entity) | 根据id跟新一条记录 |
| T getById(Serializable id) | 根据id查询一条记录 |
| List<T> list | 查询所有记录 |
| List<T> listByIds(Collection<T> idList) | 根据id集合查询多条记录 |
七.创建服务层接口实现类
在service包下创建一个实现业务接口的MyUserServiceImpl实现类,代码如下:
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper.MyUserDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyUserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<MyUserDao, Tuser> implements MyUserService {
}上述MyUserServiceImpl类继承了ServiceImpl类并实现了MyUserService接口。ServiceImpl类是MyBatis-plus提供的通用Service实现类,它实现了IService接口,并提供了一些默认的 实现方法
八.创建控制器层(去测试数据库的操作)
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Wrappers;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service.MyUserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/Tuser")
public class TuserController {
@Autowired
private MyUserService myUserService;
//查询所有
@GetMapping("/testSelectUser")
public void testSelectUser(){
List<Tuser> list=myUserService.list();
System.out.println(list);
}
//根据ID查询某条记录
@GetMapping("/testOneSelectUserById")
public void testOneSelectUserById(){
Tuser tuser=myUserService.getById("1");
System.out.println(tuser);
}
//根据username查询某条记录
@GetMapping("/testOneSelectUserByUsername")
public void testOneSelectUserByUsername(){
// LambdaQueryWrapper<Tuser> wrapper= Wrappers.lambdaQuery(); //条件选择器
LambdaQueryWrapper<Tuser> wrapper= new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); //条件选择器
/
// wrapper.nq() 不等于 wrapper.gt() 大于 wrapper.lt() 小于 wrapper.ge() 大等于 wrapper.le()小等于
// wrapper.eq(Tuser::getUsername,"xc"); //等于xc的username
wrapper.like(Tuser::getUsername,"xcc"); // //选出%xcc%左右模糊匹配
// wrapper.likeLeft(Tuser::getUsername,"%xcc"); //选出%xcc 左模糊匹配
// wrapper.likeRight(Tuser::getUsername,"xcc%"); //选出xcc% 右模糊匹配
Tuser tuser=myUserService.getOne(wrapper);
System.out.println(tuser);
}
//增加一条记录
@GetMapping("/testInsertUser")
public void testInsertUser(){
Tuser tuser=new Tuser();
tuser.setUsername("wangwu");
tuser.setPassword("123");
boolean b=myUserService.save(tuser);
System.out.println(b);
}
//修改一条记录
@GetMapping("/testUpdateUser")
public void testUpdateUser(){
Tuser tuser=new Tuser();
tuser.setId(3);
tuser.setUsername("wangwu");
tuser.setPassword("123");
boolean b=myUserService.updateById(tuser);
System.out.println(b);
}
//删除一条记录
@GetMapping("/testDeleteUser")
public void testDeleteUser(){
LambdaQueryWrapper<Tuser> wrapper=new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
// wrapper.like(Tuser::getUsername,"xc"); //等同于%xc%左右模糊匹配
wrapper.eq(Tuser::getUsername,"xc"); //等于xc的username
boolean b=myUserService.remove(wrapper);
System.out.println(b);
}
}九.运行测试
浏览器输入:
http://localhost:8080/Tuser/testSelectUser进阶用法
自定义SQL语句
假设我们有一个实体类Tuser 和对应的 Mapper 接口
(案例)我们希望添加一个查询功能,自定义一个方法根据username去查询记录。
方式一:使用注解自定义SQL方法
在mapper目录下创建一个MyUserDao接口
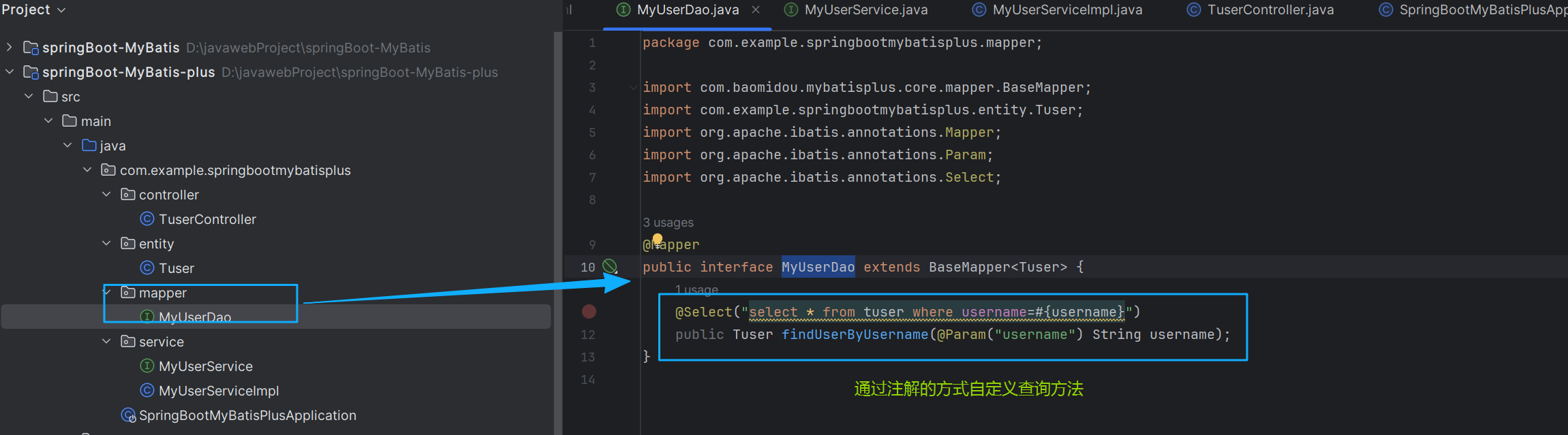
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface MyUserDao extends BaseMapper<Tuser> {
@Select("select * from tuser where username=#{username}")
public Tuser findUserByUsername(@Param("username") String username);
}在service目录下创建 MyUserServiceImpl类
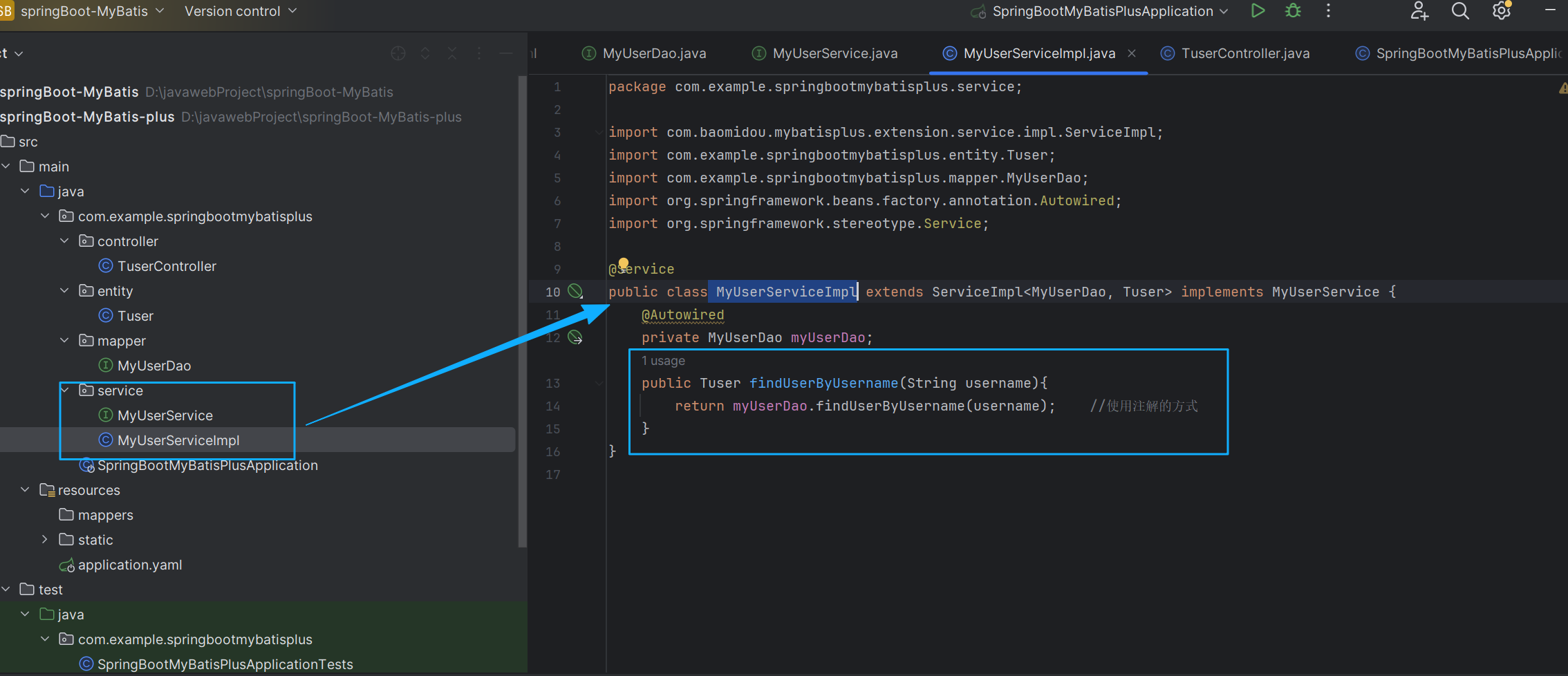
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper.MyUserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyUserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<MyUserDao, Tuser> implements MyUserService {
@Autowired
private MyUserDao myUserDao;
public Tuser findUserByUsername(String username){
return myUserDao.findUserByUsername(username); //使用注解的方式
}
}在controller目录下创建TuserController类(用来测试案例)
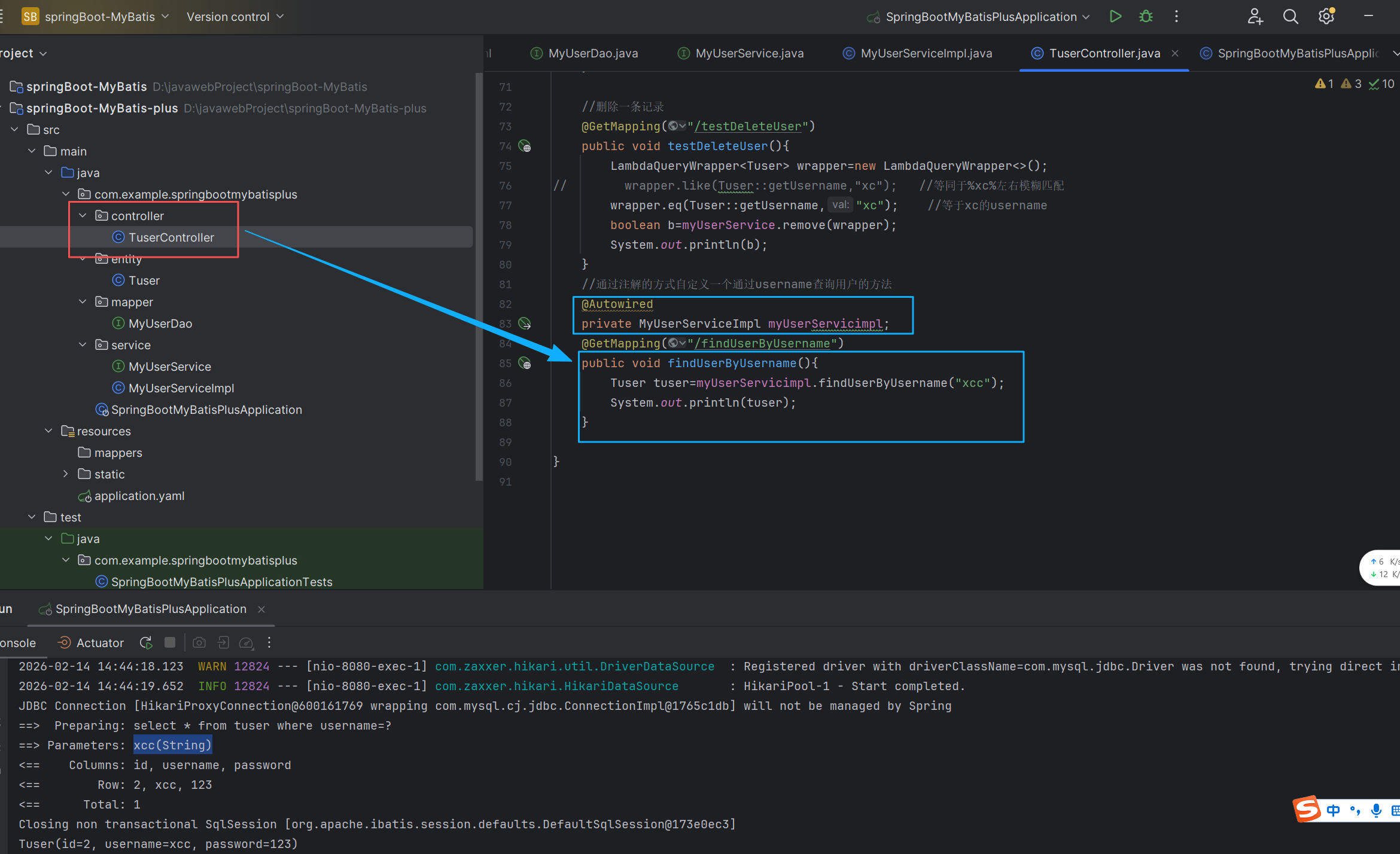
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Wrappers;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service.MyUserService;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service.MyUserServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/Tuser")
public class TuserController {
@Autowired
private MyUserService myUserService;
//通过注解的方式自定义一个通过username查询用户的方法
@Autowired
private MyUserServiceImpl myUserServicimpl;
@GetMapping("/findUserByUsername")
public void findUserByUsername(){
Tuser tuser=myUserServicimpl.findUserByUsername("xcc");
System.out.println(tuser);
}
}方式二:使用XML文件自定义SQL方法
在mapper目录下创建一个MyUserDao接口,在此接口创建findUserXMLByUsername(String username)方法
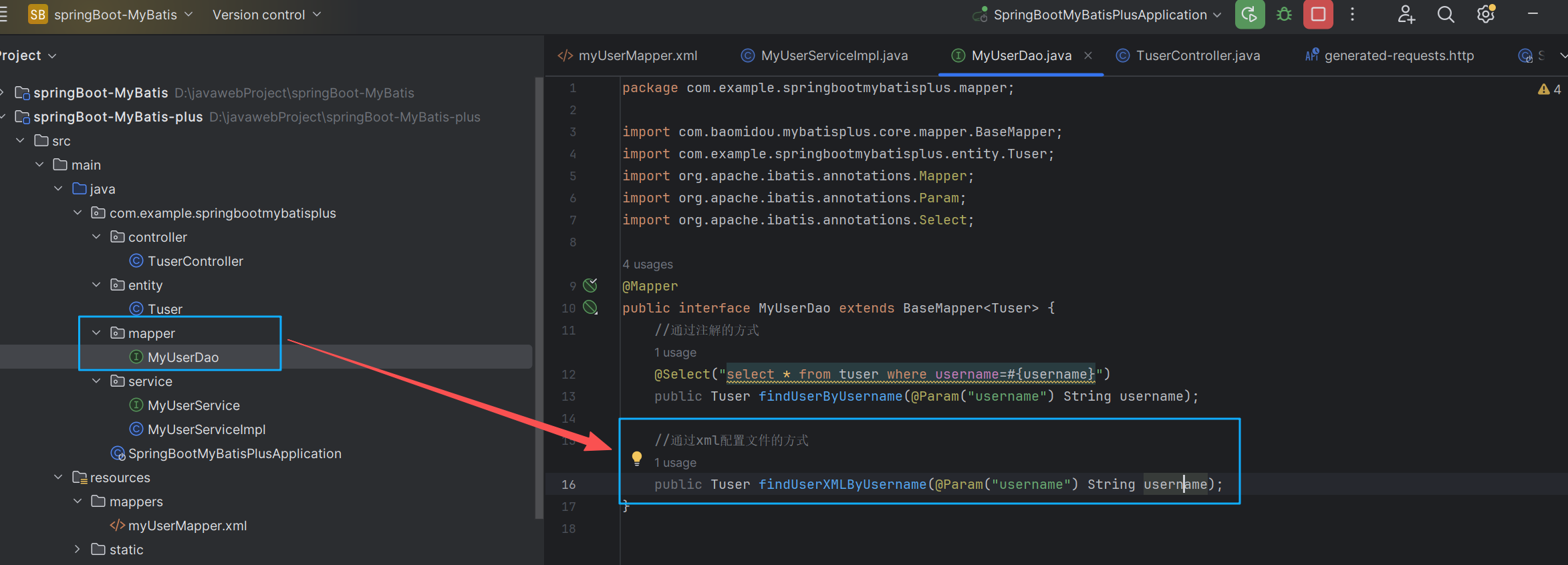
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface MyUserDao extends BaseMapper<Tuser> {
//通过xml配置文件的方式
public Tuser findUserXMLByUsername(@Param("username") String username);
}在 resources目录下创建mappers目录,并在mappers目录下创建一个名为 myUserMapper.xml的文件。这个文件与 com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper.MyUserDao接口绑定。
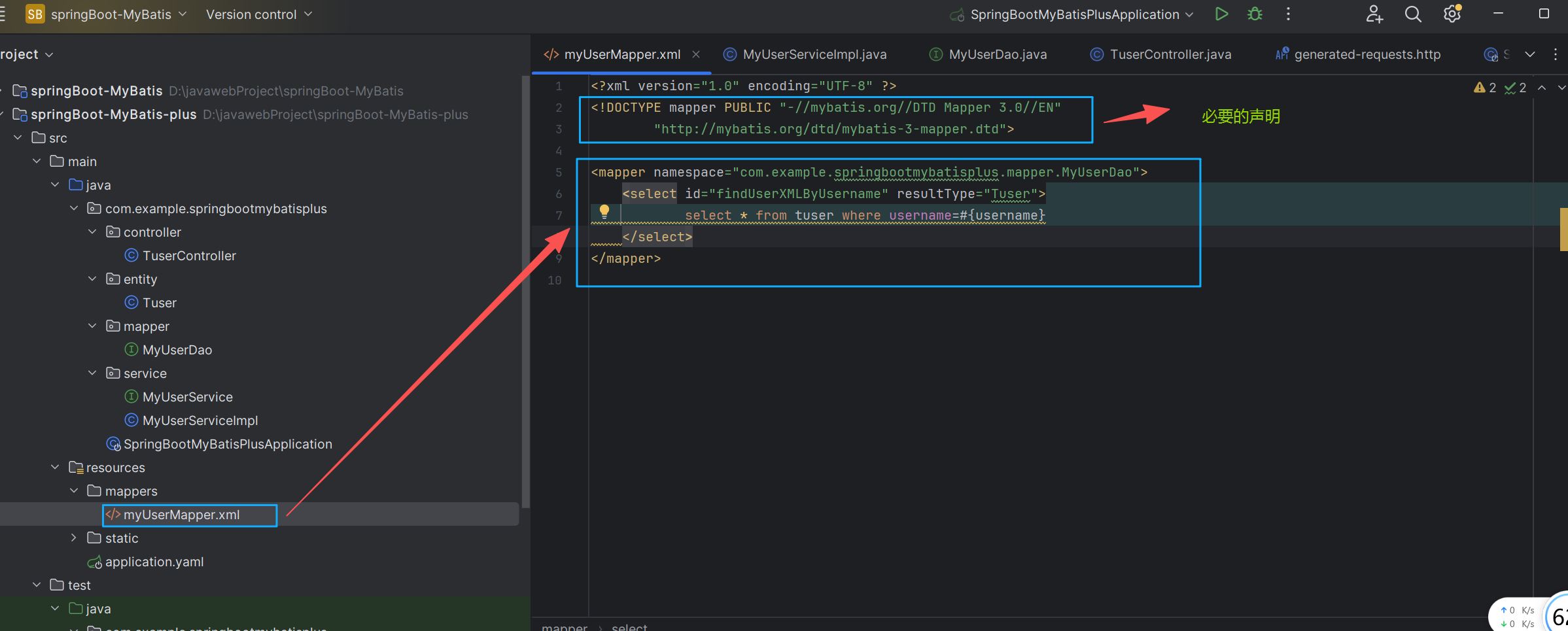
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper.MyUserDao">
<select id="findUserXMLByUsername" resultType="Tuser">
select * from tuser where username=#{username}
</select>
</mapper>在service目录下创建 MyUserServiceImpl类
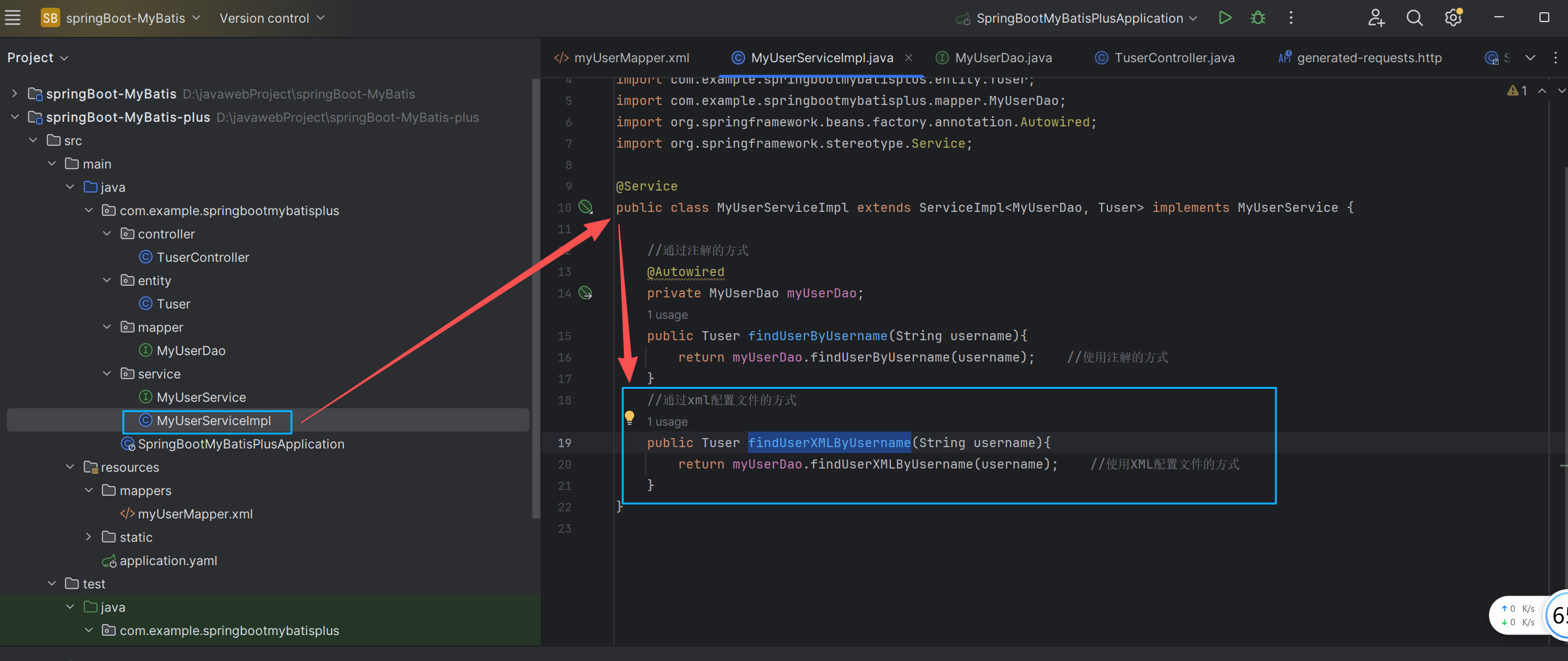
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.mapper.MyUserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyUserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<MyUserDao, Tuser> implements MyUserService {
//通过xml配置文件的方式
public Tuser findUserXMLByUsername(String username){
return myUserDao.findUserXMLByUsername(username); //使用XML配置文件的方式
}
}在controller目录下创建TuserController类(用来测试案例)
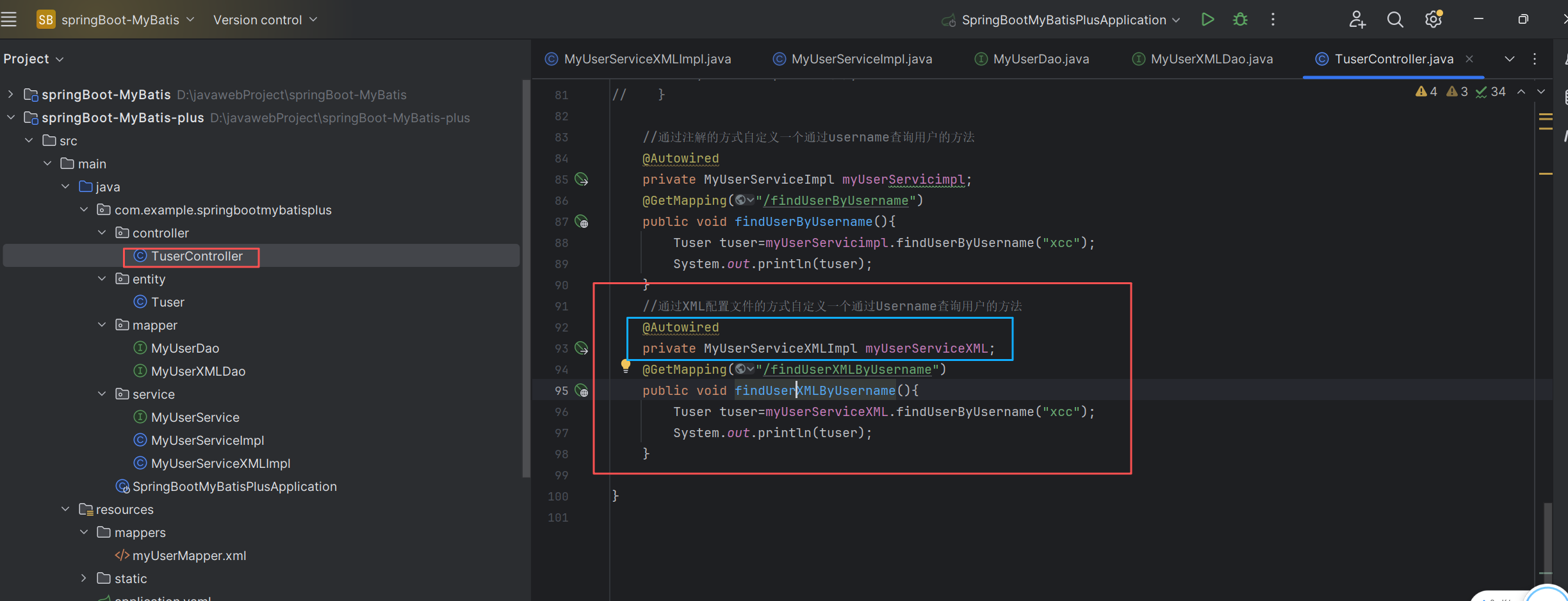
package com.example.springbootmybatisplus.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Wrappers;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.entity.Tuser;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service.MyUserService;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service.MyUserServiceImpl;
import com.example.springbootmybatisplus.service.MyUserServiceXMLImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/Tuser")
public class TuserController {
//通过XML配置文件的方式自定义一个通过Username查询用户的方法
@Autowired
private MyUserServiceXMLImpl myUserServiceXML;
@GetMapping("/findUserXMLByUsername")
public void findUserXMLByUsername(){
Tuser tuser=myUserServiceXML.findUserByUsername("xcc");
System.out.println(tuser);
}
}注解方式和XML比较:
- 注解
优点:简单、清晰,适合处理较为简单的 SQL 查询。
缺点:对于复杂查询,SQL 语句难以维护,可读性较差。 - XML
优点:适合复杂查询,SQL 语句与 Java 代码分离,易于维护和调试。
缺点:需要额外的 XML 文件,配置稍微麻烦一些
学习参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/Gavin_915/article/details/142886400
(36 封私信 / 6 条消息) 理解并学会mybatis-plus,BaseMapper运用,常见注解,条件构造器,自定义SQL,Service接口,代码生成,静态工具,分页插件 - 知乎